The global industrial laser cleaning machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precise, and efficient surface treatment solutions across manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and defense sectors. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 386.4 million in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.6% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by advancements in laser technology, rising adoption of automation in industrial maintenance, and stringent environmental regulations that favor non-abrasive cleaning methods over traditional techniques involving chemicals or sandblasting. Mordor Intelligence also highlights a similar upward trajectory, noting accelerating investments in Industry 4.0 infrastructure and the growing preference for low-maintenance, high-precision equipment. As market demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront, pioneering innovation in laser cleaning performance, system integration, and application versatility. Below are the top 10 industrial laser cleaning machine manufacturers shaping the future of surface decontamination.
Top 10 Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: PULSAR Laser is a manufacturer of professional laser cleaning machines, developed and engineered for industrial maintenance, manufacturing, restoration and ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Our laser cleaning machines are complete solutions with fume extraction, laser safety, performance optimization, and more. They are ready for robot lines, ……
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#5 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics offers continuous wave (CW) laser systems for industrial cleaning applications. These units are designed for heavy duty, speedy surface ……
#6 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#7 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, fiber laser…
#8 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
#9 Laser Cleaning
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is used across a variety of industries to remove unwanted surface materials like coatings, paints, rust, oil, and for surface preparation for ……
#10 Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: wattsan.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning uses powerful laser beams to remove contaminants such as rust, paint, dirt or oxidation from a variety of surfaces….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines
The global market for industrial laser cleaning machines is poised for significant transformation and expansion by 2026, driven by technological innovation, regulatory pressures, and rising demand across key industries. As environmental sustainability becomes a top priority and automation accelerates, laser cleaning is emerging as a preferred alternative to traditional abrasive and chemical cleaning methods. The following analysis outlines the dominant market trends expected to shape the industrial laser cleaning landscape by 2026.
1. Accelerated Adoption in Manufacturing and Automotive Sectors
By 2026, the automotive and general manufacturing industries are expected to be leading adopters of laser cleaning technology. With the need for precision surface preparation in welding, coating, and maintenance operations, manufacturers are shifting toward non-contact, residue-free cleaning solutions. Laser systems offer repeatable, high-precision cleaning that supports quality control—especially critical in electric vehicle (EV) production, where battery and motor components require contamination-free surfaces.
2. Growth Driven by Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Stringent environmental regulations—particularly in North America and Europe—are pushing industries to phase out sandblasting and chemical solvents due to their hazardous waste output and health risks. Laser cleaning, being a dry, chemical-free process with minimal secondary waste, aligns with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. By 2026, compliance mandates are expected to be a primary growth catalyst, especially in aerospace, shipbuilding, and heritage restoration sectors.
3. Advancements in Portable and Handheld Systems
The market will see a surge in demand for portable and handheld laser cleaning devices by 2026. These systems enhance flexibility for on-site maintenance and field applications, such as pipeline cleaning, mold remediation, and historical monument restoration. Continued improvements in fiber laser efficiency, cooling systems, and ergonomic design are making these units more accessible and user-friendly, expanding their adoption beyond large industrial facilities.
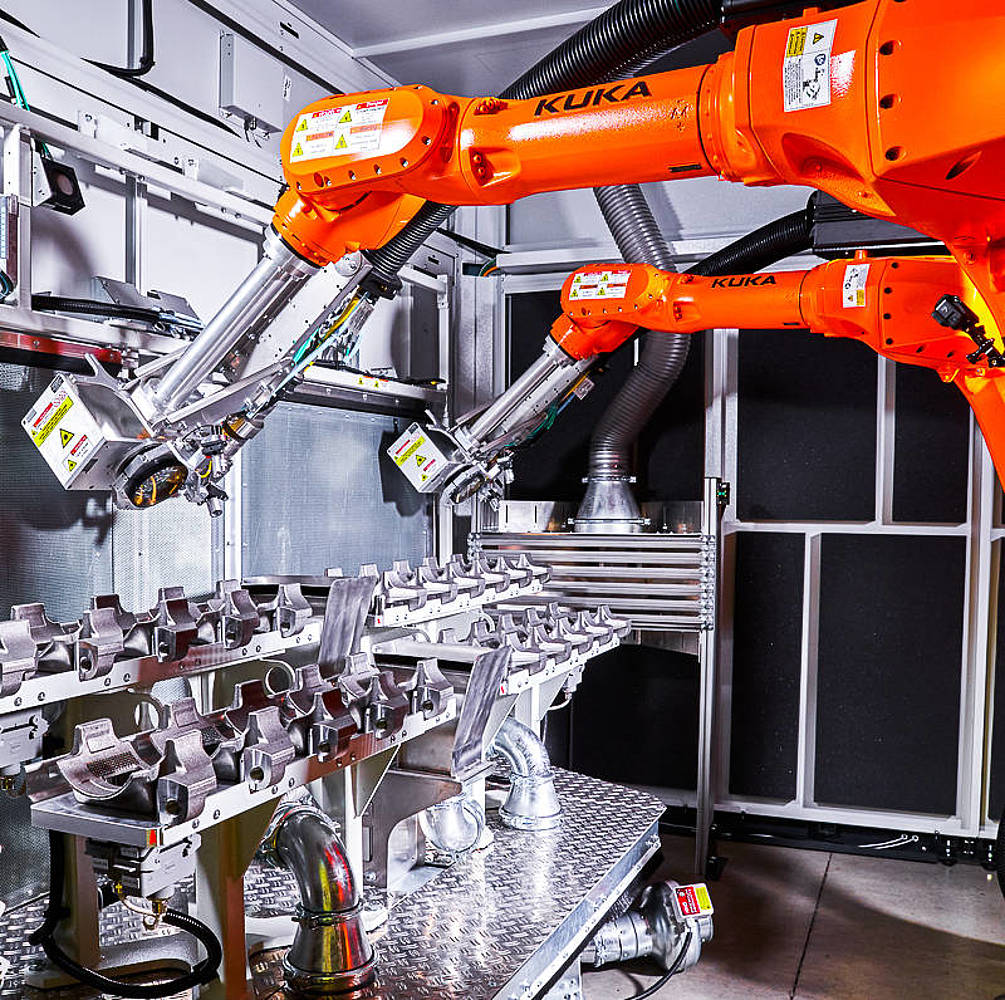
4. Integration with Robotics and Smart Manufacturing
Industrial laser cleaning systems are increasingly being integrated into automated production lines and robotic cells. By 2026, the convergence with Industry 4.0 technologies—including IoT-enabled monitoring, AI-based process optimization, and real-time diagnostics—will enhance cleaning efficiency and enable predictive maintenance. Fully automated laser cleaning cells are expected to become standard in high-volume production environments.
5. Regional Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific
While Europe and North America currently lead in adoption, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to register the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) by 2026. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in advanced manufacturing and green technologies. Government incentives and growing awareness of laser cleaning benefits are accelerating market penetration in electronics, precision engineering, and heavy industries.
6. Cost Reduction and Broader Accessibility
Although laser cleaning systems have historically carried high upfront costs, ongoing advancements in diode-pumped fiber lasers and mass production are driving prices downward. By 2026, reduced equipment costs and lower total cost of ownership—due to minimal consumables and maintenance—will make laser cleaning more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), further broadening market reach.
7. Emergence of New Applications and Niche Markets
Beyond traditional uses, new applications are emerging, such as nuclear decontamination, medical device sterilization, and semiconductor manufacturing. By 2026, specialized laser cleaning solutions tailored for these high-value sectors are expected to create lucrative niche markets, supported by R&D investments from both private and public institutions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the industrial laser cleaning machine market will be characterized by robust growth, technological sophistication, and broader industrial integration. As sustainability, automation, and precision remain key drivers, companies that innovate in system efficiency, portability, and smart integration will be best positioned to capture market share. The transition from conventional to laser-based cleaning methods is no longer a trend—it is becoming an industrial imperative.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing industrial laser cleaning machines presents significant opportunities for improving manufacturing and maintenance processes. However, buyers often encounter critical challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) that can lead to operational failures, financial losses, and legal risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for making a sound investment.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many suppliers, particularly in competitive or emerging markets, cut costs by using substandard materials and low-grade components. This can include inferior optical lenses, underpowered or unstable laser sources, and weak mechanical structures. Such compromises result in reduced cleaning efficiency, shorter service life, frequent breakdowns, and inconsistent performance—especially in demanding industrial environments.
Inaccurate or Inflated Performance Specifications
Some manufacturers exaggerate key performance metrics such as laser power output, cleaning speed, or effective working distance. For example, a machine advertised as 1000W might deliver significantly less actual average power due to poor thermal management or duty cycle limitations. Buyers may discover too late that the machine cannot meet production requirements, leading to costly downtime and reevaluation.
Lack of Robust Safety Features and Compliance
Industrial laser systems must comply with international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825). However, some machines lack adequate safety interlocks, proper beam enclosures, or certified laser protective housings. Sourcing equipment without proper safety certifications not only endangers personnel but may also result in non-compliance with workplace regulations, exposing the buyer to liability.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Technical Expertise
A common issue with lower-cost suppliers is the absence of reliable technical support, training, and spare parts availability. When machines fail or require optimization, delayed responses or unqualified support staff can halt production. Additionally, unclear documentation and language barriers further complicate troubleshooting and integration.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Purchasing from unverified suppliers may expose buyers to IP violations. Some manufacturers clone designs or use proprietary laser control software without licensing. If the equipment incorporates stolen technology, the end-user could face legal scrutiny, especially in regions with strict IP enforcement. This risk is heightened when suppliers cannot provide proof of original design, patents, or software licensing.
Hidden Software Limitations and Lack of Transparency
Proprietary control software may contain undisclosed limitations, such as locked features, remote deactivation clauses, or data collection practices. Some systems require ongoing subscription fees for full functionality or updates. Buyers may also find it impossible to integrate the machine into existing automation systems due to closed or undocumented APIs.
Absence of Third-Party Verification and Testing
Reputable suppliers provide independent test reports, certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, RoHS), and allow on-site or third-party inspections. Sourcing without such verification increases the risk of receiving non-compliant or underperforming equipment. Always demand verifiable test data under real-world conditions before finalizing procurement.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: request references, verify certifications, perform on-site demonstrations, and consult legal experts on IP concerns. Prioritize suppliers with transparent operations, strong warranties, and a proven track record in industrial applications.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the import, export, transport, and operation of industrial laser cleaning machines. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, legal compliance, and smooth operations across international and domestic borders.
Regulatory Classification & Documentation
Proper classification and documentation are critical for customs clearance and regulatory compliance. Industrial laser cleaning machines are typically classified under specific HS (Harmonized System) codes, often falling within 8515 (Electro-thermic appliances, laser-based), though exact codes vary by country and machine specifications. Key documentation includes commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and technical specifications. A detailed product description highlighting laser type, power output, and intended industrial use must accompany shipments to avoid delays or misclassification.
Laser Safety & International Standards
Industrial laser cleaning machines must comply with international laser safety standards such as IEC 60825-1 (Safety of laser products) and ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers). These standards classify lasers by hazard level (typically Class 4 for industrial cleaning systems) and mandate engineering controls, labeling, and operational safeguards. Machines must be equipped with appropriate safety interlocks, emergency stop functions, and warning labels in the local language(s) of the destination country. Compliance with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and regional equivalents (e.g., CE in Europe, FCC in the USA) is required for market access.
Import/Export Controls & Permits
Due to their high-power laser components, industrial laser cleaning machines may be subject to export controls under regimes such as the Wassenaar Arrangement, which monitors dual-use technologies. Exporters must determine if an export license is required based on destination country, end-user, and technical specifications (e.g., laser power exceeding certain thresholds). Similarly, importers may need to obtain import permits or notify national authorities (e.g., FDA in the U.S. for radiation-emitting devices). Always consult with national trade compliance agencies before shipping.
Transportation & Handling Requirements
Laser cleaning systems are sensitive equipment requiring secure and climate-controlled transport. Use shock-absorbing packaging and secure crating to prevent damage during transit. Clearly label crates with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and laser hazard symbols. Due to potential battery components (e.g., in portable units), compliance with IATA/IMDG regulations for hazardous materials may be necessary. Coordinate with freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial machinery and laser equipment.
Electrical & Environmental Compliance
Ensure the machine meets electrical safety standards of the destination country, such as CE (Europe), UKCA (United Kingdom), or UL (United States). Voltage, frequency, and plug type must match local infrastructure. Additionally, verify compliance with environmental directives like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) where applicable. Proper disposal procedures for laser components and optics must be documented and followed.
On-Site Installation & Operational Compliance
Upon delivery, installation must be performed by trained personnel following manufacturer guidelines. The operational site must comply with local occupational safety regulations, including laser-controlled areas, personal protective equipment (PPE), and ventilation systems to manage fumes and particulates generated during cleaning. Employers must conduct risk assessments and provide laser safety training to operators per OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent national workplace safety standards.
Maintenance & Regulatory Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records of maintenance, safety inspections, operator training, and any incidents. Regulatory bodies may require documentation to demonstrate ongoing compliance. Regular calibration and safety checks ensure continued adherence to laser safety standards. Keep copies of all compliance certificates, user manuals, and regulatory approvals on file for audit purposes.
Conclusion on Sourcing an Industrial Laser Cleaning Machine
Sourcing an industrial laser cleaning machine is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance manufacturing efficiency, improve product quality, and support sustainable production practices. As industries increasingly prioritize precision, automation, and eco-friendly processes, laser cleaning emerges as a superior alternative to traditional methods such as sandblasting, chemical cleaning, or mechanical brushing.
Key factors to consider when sourcing include laser power, wavelength, pulse duration, portability, safety features, automation compatibility, and after-sales support. It is crucial to select a supplier that offers reliable technology, industry-specific expertise, comprehensive training, and strong service support. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—factoring in energy efficiency, minimal consumables, and low maintenance—highlights the long-term economic advantages.
In conclusion, investing in a high-quality industrial laser cleaning system not only improves operational performance but also aligns with environmental and safety standards. By carefully assessing technical requirements and vendor credibility, organizations can make an informed sourcing decision that delivers lasting value and a competitive edge in modern industrial applications.