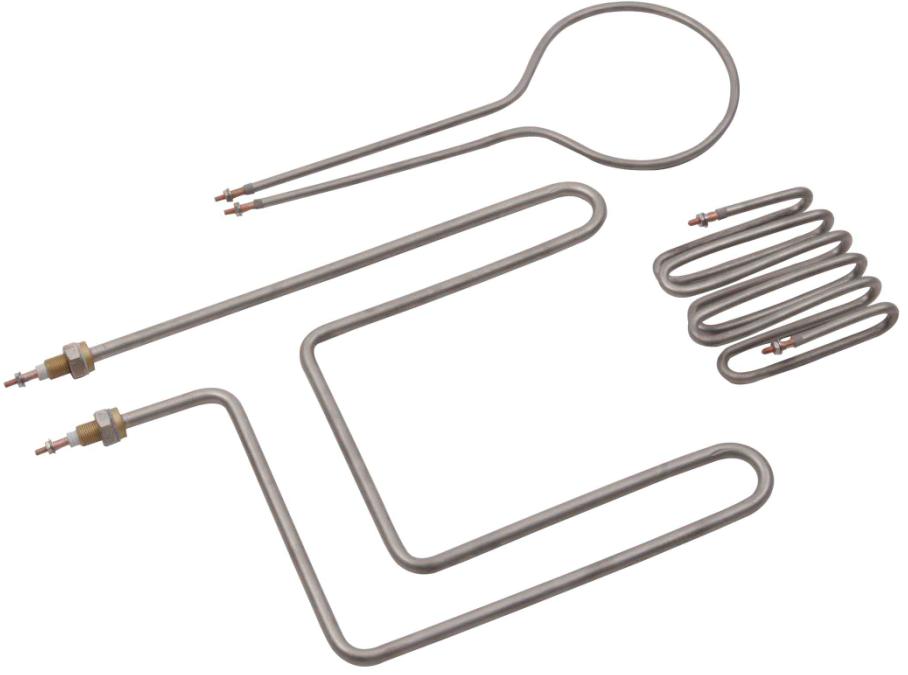
The global industrial heating elements market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across sectors such as petrochemicals, automotive, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 5.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in energy-efficient heating technologies and the increasing adoption of automation in industrial processes. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a similar trajectory, citing expanding industrialization in emerging economies and stricter energy efficiency regulations as key drivers. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and reliability in heating element solutions—setting the benchmark for performance across high-temperature and precision-critical applications.
Top 10 Industrial Heating Elements Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kanthal®
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kanthal.com
Key Highlights: Kanthal® is a world-leading brand for products and services in the area of industrial heating technology and resistance materials….
#2 hotset
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1973
Website: hotset.com
Key Highlights: Starting with heating elements over thermo sensor technology up to process control – hotset has been developing smart product and system solutions since 1973….
#3 Wattco
Domain Est. 1999
Website: wattco.com
Key Highlights: Wattco manufactures a complete line of flange heaters, circulation heaters, tubular heaters, and immersion heaters. Browse our product catalogue….
#4 Heaters
Domain Est. 1995
Website: watlow.com
Key Highlights: Watlow is a leader in the industrial heater industry manufacturing high quality cartridge heaters, immersion heaters, advanced ceramic heaters and other ……
#5 Accutherm
Domain Est. 1996
Website: accutherm.com
Key Highlights: Products · Heaters · Air Duct Heaters · Circulation Heaters · Immersion Heaters · Extrusion Press · Die Casting · Urn Heaters · Tubular Heating Elements….
#6 Industrial Electric Heating Elements
Domain Est. 1998
Website: nationalelement.com
Key Highlights: American quality electrical heating elements, designed by experienced and tested engineers with a commitment to long term service for all types of ovens, kilns ……
#7 Heating Element Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: heating-elements.com
Key Highlights: Hotwatt manufactures a complete line of heating elements for a wide range of uses. We offer a broad product line from electric to cartridge and countless other ……
#8 Chromalox
Domain Est. 1997
Website: chromalox.com
Key Highlights: Providing advanced electric thermal solutions worldwide. We engineer technologies that deliver superior performance and support the drive to decarbonize….
#9 Electrified Heating Solutions
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tutco.com
Key Highlights: TUTCO is one of the worlds largest suppliers of electric resistive heating elements and holds 80% of the US patents in open coil heating products….
#10 Vulcanic
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1973
Website: vulcanic.com
Key Highlights: VULCANIC GROUP has been designing and manufacturing electric heating and cooling solutions for industry since 1973….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Industrial Heating Elements

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Industrial Heating Elements
The global industrial heating elements market is poised for substantial transformation and growth by 2026, driven by technological innovation, energy efficiency demands, and expanding industrial automation. As industries across manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, food processing, and chemical sectors continue to modernize, the demand for reliable, high-performance heating solutions intensifies. This analysis explores key trends shaping the industrial heating elements market through 2026 under the H2 framework—highlighting Hydrogen Integration, High-Efficiency Technologies, and Hybrid Heating Systems.
Hydrogen Integration
One of the most prominent trends by 2026 is the integration of hydrogen as a clean energy vector in industrial heating processes. With global decarbonization targets accelerating, industries are exploring hydrogen combustion and hydrogen-ready heating systems to replace fossil fuel-based furnaces and ovens.
- Hydrogen-Compatible Heating Elements: Manufacturers are developing heating elements capable of operating in hydrogen-rich environments, resistant to embrittlement and high-temperature oxidation. These elements are crucial for steel, glass, and cement industries transitioning to green hydrogen.
- Regulatory Push: Governments in the EU, North America, and parts of Asia are incentivizing low-carbon industrial processes. By 2026, compliance with emissions standards is expected to mandate retrofitting or replacing conventional heating systems with hydrogen-adaptable solutions.
- Pilot Projects Scaling Up: Several industrial clusters are launching hydrogen-powered heating demonstrations. Successful pilots are expected to drive adoption, increasing demand for robust heating elements designed for variable flame temperatures and thermal cycles.
High-Efficiency Technologies
Energy efficiency remains a core driver in the evolution of industrial heating elements. By 2026, advanced materials and smart controls are enabling significant improvements in thermal performance and operational savings.
- Advanced Materials: Adoption of ceramic fiber, silicon carbide (SiC), and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements is rising due to their higher operating temperatures (up to 1,800°C), longer lifespans, and improved energy transfer efficiency.
- Smart Heating Elements: Integration of IoT sensors and AI-driven control systems allows real-time monitoring of temperature, power consumption, and wear. Predictive maintenance and adaptive power modulation reduce energy waste and downtime.
- Induction and Infrared Heating: These contactless heating methods are gaining traction due to their precision and efficiency. Induction heating, in particular, is expanding in metal processing and automotive assembly due to rapid, localized heating capabilities.
Hybrid Heating Systems
By 2026, hybrid systems combining multiple heating technologies are becoming standard in complex industrial applications, offering flexibility, reliability, and optimized energy use.
- Electric + Gas Hybrid Solutions: In applications where full electrification is not yet feasible, hybrid systems blend electric heating elements with gas burners. This enables load balancing, peak shaving, and smoother transitions toward full electrification.
- Modular and Scalable Designs: Heating systems are being designed with plug-and-play modules that allow factories to scale capacity based on production needs. This trend supports Industry 4.0 and agile manufacturing models.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Hybrid systems increasingly interface with on-site solar or wind power, storing excess energy or adjusting operations based on renewable availability—enhancing sustainability credentials.
Conclusion
By 2026, the industrial heating elements market will be shaped by the convergence of sustainability, digitalization, and energy transition. The H2 trends—Hydrogen Integration, High-Efficiency Technologies, and Hybrid Heating Systems—are not only redefining product design but also transforming industrial operations. Companies that embrace these trends will gain competitive advantages through reduced emissions, lower operating costs, and improved process control, positioning themselves at the forefront of the next-generation industrial landscape.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Industrial Heating Elements (Quality & IP)
Sourcing industrial heating elements involves significant technical and commercial risks. Overlooking key factors can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, production downtime, and intellectual property (IP) exposure. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Long-Term Performance
Choosing the lowest-cost supplier often leads to compromised materials, poor craftsmanship, and inadequate testing. Substandard heating elements may fail prematurely due to overheating, insulation breakdown, or corrosion, resulting in costly maintenance, unplanned downtime, and safety risks. A focus on total cost of ownership—factoring in lifespan, energy efficiency, and reliability—is essential.
2. Inadequate Specification of Operating Conditions
Failing to clearly define operational parameters (e.g., temperature range, watt density, ambient conditions, cycling frequency, and media compatibility) can result in mismatched components. Heating elements exposed to conditions beyond their design limits degrade rapidly. Always provide comprehensive technical specifications, including electrical requirements, mechanical constraints, and environmental exposure.
3. Overlooking Material Compatibility
Using incorrect sheath or terminal materials (e.g., stainless steel, Incoloy, copper) for corrosive or high-temperature environments leads to premature failure. For example, standard 304 stainless steel may corrode in chlorinated environments, while high-temperature applications may require Incoloy 800/840. Ensure material selection aligns with the chemical and thermal environment.
4. Insufficient Quality Assurance and Testing
Suppliers without robust quality control processes may deliver inconsistent products. Avoid vendors who do not perform standardized tests such as high-potential (hi-pot) testing, insulation resistance checks, leak testing (for tubular heaters), and dimensional verification. Request test reports and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) to validate quality systems.
5. Ignoring IP Protection and Reverse Engineering Risks
Custom-designed heating elements represent proprietary technology. Sourcing from suppliers in jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement or without proper legal safeguards (e.g., NDAs, IP assignment clauses in contracts) risks design theft and unauthorized replication. Ensure contracts explicitly define IP ownership and include confidentiality agreements.
6. Poor Supplier Qualification and Due Diligence
Engaging suppliers without verifying technical capability, manufacturing capacity, and track record can lead to delivery delays and non-conforming products. Conduct audits or request references, especially for mission-critical applications. Evaluate their R&D capability and ability to support modifications or troubleshooting.
7. Underestimating Lead Times and Supply Chain Reliability
Extended lead times or inconsistent supply disrupt production schedules. Relying on single-source suppliers or those with opaque supply chains increases vulnerability. Diversify sourcing where possible and confirm component availability for raw materials (e.g., specialty alloys, magnesium oxide).
8. Neglecting Certification and Compliance Requirements
Industrial heating elements may require certifications such as UL, CSA, CE, ATEX, or RoHS compliance, depending on the region and application. Sourcing non-certified elements for regulated environments can result in safety violations, failed inspections, or legal liabilities.
9. Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Poor documentation—including drawings, material certifications, and test data—complicates maintenance, regulatory audits, and failure analysis. Ensure suppliers provide full traceability (e.g., batch/lot numbers, material test reports) and updated technical documentation.
10. Failing to Consider After-Sales Support
Limited technical support or spare parts availability from the supplier hampers troubleshooting and maintenance. Choose partners offering engineering support, failure analysis, and long-term product availability to ensure operational continuity.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires a strategic sourcing approach focused on technical fit, quality assurance, IP protection, and supplier reliability—ensuring safe, efficient, and sustainable operation of industrial heating systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Industrial Heating Elements
Shipping and Transportation
Industrial heating elements require careful handling during shipping due to their fragility, weight, and potential exposure to environmental factors. Use secure, custom-fitted packaging with shock-absorbing materials to prevent damage. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators. Choose freight carriers experienced in handling industrial equipment and ensure proper crating for long-distance or international shipments. Temperature-sensitive elements (e.g., those with ceramic insulation) must be transported within recommended thermal ranges to avoid material degradation.
Storage Conditions
Store heating elements in a clean, dry, climate-controlled environment with temperatures between 10°C and 35°C and relative humidity below 60%. Avoid direct sunlight and exposure to corrosive atmospheres (e.g., salt spray, chemicals). Keep elements on elevated pallets to prevent floor moisture absorption and ensure adequate ventilation. Store vertically when recommended by the manufacturer to prevent warping or internal stress. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize long-term storage risks.
Import and Export Regulations
Compliance with international trade regulations is essential when shipping heating elements across borders. Verify Harmonized System (HS) codes—commonly 8516.79 for electrical heating resistors. Obtain necessary export licenses if components are subject to dual-use or strategic trade controls (e.g., under EAR or ITAR). Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Be aware of import restrictions in destination countries, especially for high-wattage or specialized heating systems used in critical infrastructure.
Product Certification and Standards
Industrial heating elements must comply with regional and international safety and performance standards. Key certifications include:
– CE Marking (EU): Complies with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
– UL/CSA (North America): Certified to UL 1479 (through-feed fire tests) and CSA C22.2 for electrical safety.
– RoHS & REACH (EU): Restricts hazardous substances and ensures chemical safety.
– IEC 60079 (Global): Required for heating elements used in explosive atmospheres (ATEX/IECEx compliance).
Maintain up-to-date technical documentation and test reports for audit readiness.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations regarding manufacturing waste, packaging materials, and end-of-life disposal. Heating elements containing hazardous materials (e.g., certain insulating ceramics or coatings) must be labeled and handled per local environmental codes (e.g., EPA in the U.S., WEEE in the EU). Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for components requiring special handling. Ensure workplace logistics (e.g., warehouse movement, loading) follow OSHA or equivalent safety guidelines to prevent injury.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain comprehensive records for full traceability, including batch numbers, material certifications (e.g., mill test reports for sheath alloys), calibration data, and inspection reports. Use serialized labeling for high-reliability applications (e.g., aerospace, nuclear). Digital tracking systems (e.g., ERP or SCM platforms) enhance compliance and recall readiness. Customer-facing documentation should include installation manuals, compliance statements, and warranty information.
Conclusion: Sourcing Industrial Heating Elements
Sourcing the right industrial heating elements is a critical decision that directly impacts the efficiency, reliability, and safety of industrial processes. A thorough evaluation of factors such as operating temperature, material compatibility, watt density, and environmental conditions is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. When selecting a supplier, it is equally important to consider their technical expertise, manufacturing standards, customization capabilities, and after-sales support.
Investing time in identifying reputable suppliers who adhere to international quality certifications and offer scalable, innovative solutions can lead to reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and improved energy efficiency. Additionally, building strong supplier relationships fosters long-term reliability and responsiveness to future needs.
In conclusion, a strategic, informed approach to sourcing industrial heating elements not only enhances operational effectiveness but also supports sustainable and cost-efficient industrial operations. Prioritizing quality, compatibility, and supplier expertise ensures that heating systems meet current demands and can adapt to evolving industrial requirements.