The global peptide therapeutics market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for targeted treatments in oncology, metabolic disorders, and regenerative medicine. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 48.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.9% from 2023 to 2030. A key contributor to this expansion is the rising interest in research peptides such as IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Long Arg3), widely studied for its potential in muscle growth, tissue repair, and metabolic regulation. With growing investment in peptide synthesis technologies and heightened R&D activities, particularly in North America and Asia-Pacific, the demand for high-purity, research-grade IGF-1 LR3 has spurred the emergence of specialized manufacturers focused on quality, scalability, and regulatory compliance. As the competitive landscape evolves, identifying reliable suppliers with proven analytical rigor and traceable production practices has become critical for research institutions and biotech developers alike.
Top 5 Igf Lr3 Peptide Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Counterfeit product
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bachem.com
Key Highlights: Bachem offers a large selection of peptides, amino acid derivatives, and biochemicals from stock that are ready to ship from our US or European locations….
#2 IGF
Domain Est. 2007
#3 Recombinant Human LR3 IGF
Domain Est. 2013
Website: apexbt.com
Key Highlights: Free 365-day returnsThe LR3IGF-1 is a long-term analog of human IGF-1, specifically designed and manufactured for mammalian cell culture to support large-scale manufacturing of ……
#4 IGF
Domain Est. 2024
Website: alphaomegapeptide.com
Key Highlights: IGF-LR3 1MG is a research-grade IGF-1 analog studied for cell growth, repair, and longevity. For in vitro research use only, not for human use….
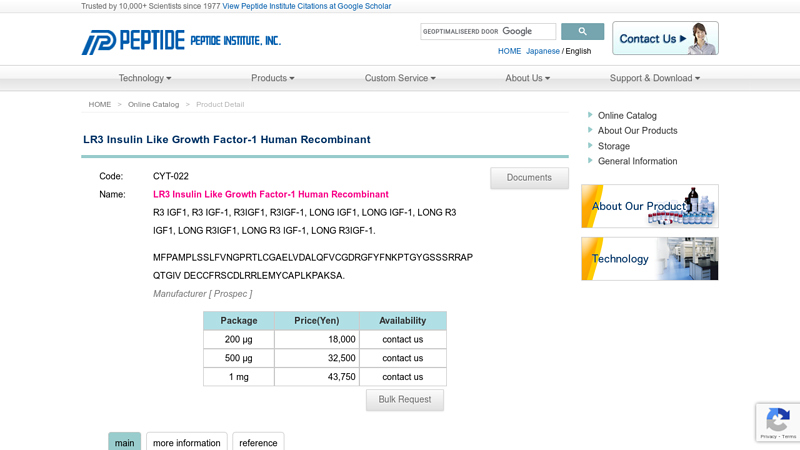
#5 LR3 Insulin Like Growth Factor
Website: peptide.co.jp
Key Highlights: The LR3 is a long-term analog of human IGF-1, specifically designed and manufactured for mammalian cell culture to support large-scale manufacturing of ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Igf Lr3 Peptide

H2: 2026 Market Trends for IGF-1 LR3 Peptide
The global market for IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Long Arginine 3) peptide is poised for notable evolution by 2026, driven by increasing demand in biopharmaceutical research, regenerative medicine, and performance enhancement sectors. This synthetic analog of human IGF-1 is valued for its prolonged half-life and enhanced bioavailability, making it a focal point in both clinical and non-clinical applications.
1. Expansion in Biomedical Research and Therapeutic Development
By 2026, IGF-1 LR3 is expected to play a critical role in advancing research related to muscle regeneration, neuroprotection, and metabolic disorders. Its ability to stimulate cell growth and differentiation supports ongoing studies in age-related muscle atrophy (sarcopenia), nerve injury repair, and diabetes management. Pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions are increasingly investing in preclinical trials involving IGF-1 LR3, which will likely accelerate its transition from research tool to therapeutic candidate.
2. Growth in Regenerative and Anti-Aging Medicine
The anti-aging and wellness industries are key drivers of IGF-1 LR3 demand. As consumer interest in longevity and cellular rejuvenation intensifies, clinics offering peptide therapies are incorporating IGF-1 LR3 into customized treatment regimens. By 2026, the peptide is anticipated to be a staple in regenerative medicine protocols, particularly in markets with lenient regulatory frameworks such as certain regions in Europe, Southeast Asia, and private concierge medical practices in North America.
3. Regulatory Scrutiny and Market Fragmentation
Despite its popularity, IGF-1 LR3 remains unapproved for human use by major regulatory bodies, including the U.S. FDA and EMA. This restricts its legal sale to research-only purposes. However, the black market and online peptide suppliers continue to thrive, creating a fragmented and often unregulated landscape. By 2026, increased enforcement and stricter import controls may curb illicit distribution, pushing demand toward licensed research institutions and GMP-compliant manufacturers.
4. Technological Advancements in Peptide Synthesis
Improvements in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and purification techniques are expected to reduce production costs and enhance purity levels of IGF-1 LR3. These advancements will support scalability and accessibility, particularly for research applications. Additionally, innovations in delivery systems—such as transdermal patches or nano-encapsulation—may improve peptide stability and absorption, potentially expanding its practical use.
5. Rising Demand in Sports and Bodybuilding (Despite Bans)
IGF-1 LR3 remains highly sought after in athletic and bodybuilding communities due to its anabolic effects. Although banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA), underground use persists. By 2026, detection methods are expected to become more sophisticated, increasing the risk for athletes. Nonetheless, demand in this segment will likely remain strong, sustained by online forums, private networks, and gray-market suppliers.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe will continue to dominate research-oriented demand, while Asia-Pacific—particularly China and India—is expected to emerge as a key manufacturing hub due to lower production costs and growing biotech infrastructure. Meanwhile, Latin America and the Middle East may see increased consumer uptake through private clinics offering off-label peptide therapies.
Conclusion
By 2026, the IGF-1 LR3 peptide market will reflect a dual trajectory: legitimate scientific advancement in regenerative medicine and persistent challenges related to regulation and ethical use. Stakeholders must navigate this complex landscape with emphasis on compliance, quality control, and ethical research practices to unlock the peptide’s full potential while minimizing misuse.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing IGF-1 LR3 Peptide: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Long Arg3), a synthetic peptide often used in research, carries significant risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Researchers and organizations must be vigilant to avoid these pitfalls.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Lack of Purity and Contaminants
One of the most critical risks is receiving peptides with low purity or harmful impurities. IGF-1 LR3 requires high purity (typically ≥95–98%) for reliable research outcomes. Poor-quality suppliers may provide products contaminated with:
– Residual solvents (e.g., acetonitrile, TFA)
– Incomplete synthesis byproducts
– Microbial contamination
Without proper Certificates of Analysis (CoA) verified by independent HPLC and mass spectrometry, users cannot confirm the peptide’s integrity, leading to unreliable data or safety hazards.
2. Inaccurate Concentration and Dosage
Many suppliers misrepresent the concentration or peptide mass. Underdosing leads to ineffective results, while overdosing may cause unintended biological effects. Always verify that the supplier provides accurate analytical data, including peptide content (not just crude weight), and consider third-party testing for validation.
3. Poor Handling and Stability
IGF-1 LR3 is sensitive to temperature and moisture. Improper storage (e.g., non-lyophilized form, exposure to heat during shipping) can degrade the peptide before it reaches the user. Ensure suppliers use cold chain logistics and provide stable, lyophilized powder in sterile vials with desiccants.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Sequences or Uses
While the base IGF-1 sequence is well-known, specific modifications, formulations, delivery methods, or therapeutic applications of IGF-1 LR3 may be protected by patents. Using or distributing the peptide without a license in patented contexts (e.g., certain medical applications) could result in legal action. Always conduct a freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis, especially if transitioning from research to commercial development.
2. Sourcing from Unlicensed or Grey-Market Suppliers
Many online vendors operate in legal grey zones, selling peptides without proper IP clearance. Purchasing from such sources may indirectly support IP violations. Reputable suppliers will disclose compliance with IP laws and avoid marketing peptides for human use where restricted.
3. Mislabeling and Counterfeit Products
Some suppliers falsely label generic or modified peptides as IGF-1 LR3 to circumvent IP protections. These counterfeit products not only risk legal exposure but also compromise research validity. Always verify the amino acid sequence (e.g., E-peptide-IGF-1 with Arg3 substitution) and demand transparency from the supplier.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, procure IGF-1 LR3 only from reputable, transparent suppliers that provide full analytical documentation and operate within legal and ethical frameworks. Conduct due diligence on both quality control processes and IP compliance to ensure research integrity and avoid legal complications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for IGF-1 LR3 Peptide
IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Long R3) is a synthetic peptide variant used primarily in research settings. Due to its regulatory status and potential for misuse, strict logistics and compliance protocols must be followed to ensure legal, safe, and ethical handling. This guide outlines key considerations for researchers, laboratories, suppliers, and institutions.
Regulatory Classification and Legal Status
IGF-1 LR3 is not approved for human use by the U.S. FDA, EMA, or other major regulatory bodies. It is classified as a research chemical and is regulated under various controlled substance or peptide regulations depending on jurisdiction. In many countries, including the United States, possession or distribution for non-research purposes may violate laws enforced by the DEA or equivalent agencies. Always verify local, national, and international regulations before acquiring, storing, or transporting IGF-1 LR3.
Licensing and Authorization Requirements
Access to IGF-1 LR3 typically requires institutional authorization. Researchers must operate under approved protocols from an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), as applicable. Suppliers may require proof of institutional affiliation and research intent prior to sale. Never purchase IGF-1 LR3 from unverified vendors or for personal use, as this may constitute a legal violation.
Procurement and Supplier Verification
Only procure IGF-1 LR3 from reputable, certified suppliers that provide:
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
– Purity and identity verification (e.g., HPLC, mass spectrometry)
– Clear labeling indicating “For Research Use Only – Not for Human or Veterinary Use”
Verify supplier compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or equivalent standards. Maintain documentation of all purchase records for audit purposes.
Storage and Handling Protocols
- Storage Conditions: Store lyophilized IGF-1 LR3 at -20°C in a dedicated, locked freezer. Protect from light and moisture.
- Reconstitution: Use sterile, endotoxin-free water or appropriate buffer. Aliquot to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- Labeling: Clearly label all containers with chemical name, concentration, date of reconstitution, and hazard warnings.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use gloves, lab coat, and eye protection when handling. Work in a biosafety cabinet when generating aerosols.
Transportation and Shipping Compliance
Shipments of IGF-1 LR3 must comply with:
– International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations (if applicable)
– National postal and customs regulations
– Use of cold chain logistics (dry ice or cold packs) with insulated, tamper-evident packaging
– Accurate labeling: “Research Chemical – Not for Human Use”
– Avoid international shipping without verifying import permits in the destination country
Recordkeeping and Audit Trail
Maintain comprehensive records including:
– Purchase invoices and CoAs
– Inventory logs with usage tracking
– Storage temperature logs
– Disposal records
These records must be retained for a minimum of 5 years or as required by institutional policy and local laws.
Disposal and Waste Management
Dispose of unused IGF-1 LR3 and contaminated materials as biohazardous or chemical waste in accordance with local environmental and safety regulations. Use licensed medical or hazardous waste disposal services. Never dispose of down drains or in regular trash.
Ethical and Institutional Oversight
IGF-1 LR3 has performance-enhancing potential and is banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). Ensure strict separation between research use and any clinical or athletic application. Institutions must enforce policies preventing misuse and report any suspected violations to appropriate oversight bodies.
Conclusion
IGF-1 LR3 peptide requires careful logistical planning and strict adherence to compliance standards. Researchers and institutions must prioritize regulatory compliance, safety, and ethical integrity throughout the supply chain — from procurement to disposal. Regular training and internal audits are recommended to maintain compliance and prevent legal or safety incidents.
Conclusion for Sourcing IGF-1 LR3 Peptide:
In summary, sourcing IGF-1 LR3 peptide requires careful consideration of quality, legality, and safety. Due to its status as a research peptide not approved for human use by regulatory agencies such as the FDA, it is essential to obtain IGF-1 LR3 only from reputable, trusted suppliers that provide third-party testing (such as HPLC and mass spectrometry) and transparent Certificates of Analysis (CoA). Potential buyers should be cautious of counterfeit or contaminated products, which are common in unregulated markets.
Furthermore, understanding the legal and ethical implications of purchasing and using IGF-1 LR3 is crucial, especially in competitive sports where it is banned by WADA and other athletic organizations. Individuals should prioritize harm reduction, use the peptide strictly for legitimate research purposes, and consult healthcare or scientific professionals when applicable.
Ultimately, responsible sourcing involves due diligence, adherence to legal guidelines, and a commitment to safety and integrity in research or personal use contexts.