The global peptide therapeutics market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for targeted treatments in oncology, metabolic disorders, and regenerative medicine. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 48.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% through 2028. A key contributor to this expansion is the rising interest in research-grade peptides such as IGF-1 LR3, known for its enhanced stability and potency in cellular growth and repair studies. As demand surges, particularly in preclinical research and biopharmaceutical development, identifying reliable manufacturers with stringent quality control, high purity standards, and transparent sourcing has become critical. Based on market analysis and performance metrics, the following five manufacturers have emerged as leaders in producing high-quality IGF-1 LR3 peptide, combining scientific rigor with scalable production capabilities.
Top 5 Igf 1 Lr3 Peptide Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
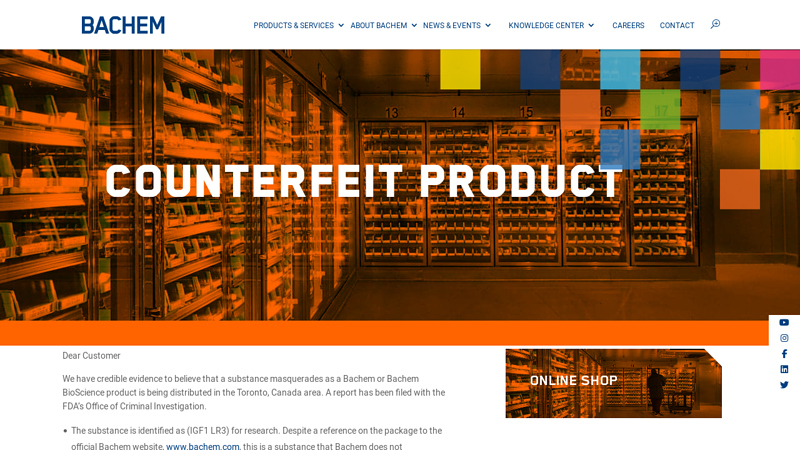
#1 Counterfeit product
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bachem.com
Key Highlights: Counterfeit product · The substance is identified as (IGF1 LR3) for research. · The substance within the packaging is unknown. · None of Bachem’s research products ……
#2 Human LR3
Domain Est. 1999
Website: innov-research.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryR3 IGF-1 is an 83 amino acid analog of IGF-1 comprising the complete human IGF-1 sequence with the substitution of an Arg (R) for the Glu(E) at position three…
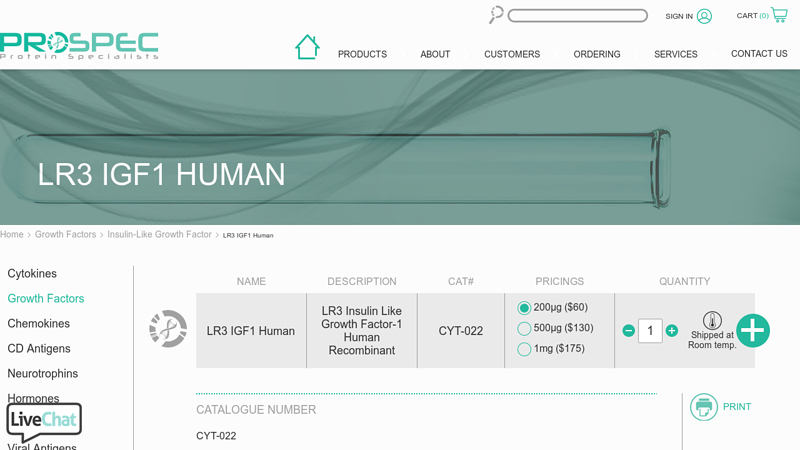
#3 IGF1 LR3
Domain Est. 2006
Website: prospecbio.com
Key Highlights: Recombinant Human Long R3 Insulin Like Growth Factor-1 produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 83 amino acids….
#4 IGF
Domain Est. 2007
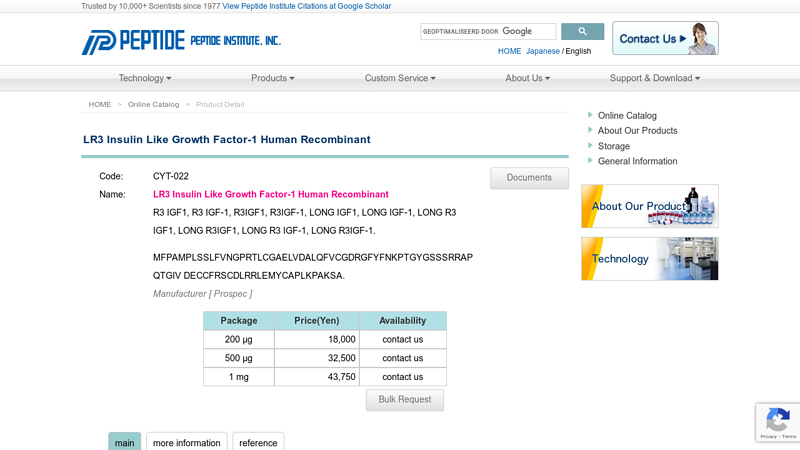
#5 LR3 Insulin Like Growth Factor
Website: peptide.co.jp
Key Highlights: The LR3 is a long-term analog of human IGF-1, specifically designed and manufactured for mammalian cell culture to support large-scale manufacturing of ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Igf 1 Lr3 Peptide
H2: 2026 Market Trends for IGF-1 LR3 Peptide
As we approach 2026, the global market for IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Long Arginine 3) peptide is poised for significant evolution, driven by advances in biotechnology, increasing demand in regenerative medicine, and shifting regulatory landscapes. This synthetic analog of IGF-1, known for its enhanced stability and prolonged activity, is attracting interest across multiple sectors, including anti-aging therapies, sports performance enhancement, and clinical research.
1. Rising Demand in Regenerative Medicine and Longevity Research
The growing emphasis on cellular repair, tissue regeneration, and longevity science is a major catalyst for the IGF-1 LR3 market. By 2026, increased investment in age-related disease research—such as muscle atrophy, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes—is expected to expand the therapeutic applications of IGF-1 LR3. Biotech startups and research institutions are leveraging the peptide’s myogenic and neuroprotective properties in preclinical trials, particularly in sarcopenia and wound healing.
2. Expansion in Cosmetic and Aesthetic Applications
IGF-1 LR3 is gaining traction in the cosmetic industry due to its potential to stimulate collagen production and enhance skin elasticity. By 2026, dermatological formulations incorporating peptide-based actives, including IGF-1 LR3, are projected to see increased adoption in anti-aging skincare products, especially in North America and Asia-Pacific regions. However, efficacy claims will remain under scrutiny by regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA.
3. Regulatory and Safety Concerns
Despite its popularity, IGF-1 LR3 remains unapproved for human use in most jurisdictions, classified primarily as a research chemical. By 2026, stricter enforcement against unauthorized sale and use—especially in sports and unregulated wellness clinics—is anticipated. The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) continues to list IGF-1 LR3 as a prohibited substance, which may limit its use in athletic performance but reinforce ethical sourcing in clinical research.
4. Growth in Peptide Manufacturing and Supply Chain Innovation
Technological improvements in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and purification techniques are reducing production costs and increasing purity levels. This advancement is expected to boost the commercial availability of high-grade IGF-1 LR3, particularly from contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) in India and China. Transparency in sourcing and third-party testing will become key differentiators in the competitive peptide marketplace.
5. Niche Use in Veterinary and Agricultural Research
Beyond human applications, IGF-1 LR3 is being explored in veterinary science for muscle development in livestock and tissue repair in performance animals. While still in early stages, agricultural biotechnology firms may drive new demand by 2026, especially in countries investing in food security and sustainable farming practices.
6. Market Competition and Intellectual Property Developments
As patent landscapes evolve, companies may seek proprietary delivery systems (e.g., transdermal patches, liposomal encapsulation) to differentiate IGF-1 LR3-based products. Although the peptide itself is not patentable in many regions, formulation innovations could lead to new commercial opportunities.
Conclusion
By 2026, the IGF-1 LR3 peptide market will be shaped by a convergence of scientific innovation, regulatory oversight, and ethical considerations. While its therapeutic potential remains promising, market growth will depend on clinical validation, compliance with regulatory standards, and responsible commercialization. Stakeholders—from researchers to manufacturers—must navigate this dynamic environment with a focus on safety, efficacy, and transparency.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing IGF-1 LR3 Peptide: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Long R3) peptide—commonly used in research and performance enhancement—can present significant challenges, particularly in ensuring product quality and avoiding intellectual property (IP) violations. Researchers, laboratories, and developers must navigate these pitfalls carefully to maintain compliance, safety, and efficacy.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Lack of Purity Verification
One of the most common issues is receiving peptides with insufficient purity or unverified claims. IGF-1 LR3 should typically be ≥95% pure for research use, but some suppliers may provide misleading HPLC or mass spectrometry data. Always request and review independent Certificates of Analysis (CoA) from third-party laboratories.
2. Contamination Risks
Contamination with endotoxins, bacterial residues, or other peptides is a serious concern, especially with poorly manufactured products. This can compromise experimental results or pose safety risks in preclinical studies. Ensure the supplier follows Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or ISO standards.
3. Inaccurate Peptide Sequence or Modification
IGF-1 LR3 includes a specific amino acid substitution (arginine replaces glutamic acid at position 3) and an extended 13-amino acid N-terminal extension. Errors in synthesis can lead to biologically inactive or inconsistent results. Confirm the exact sequence and modification via mass spectrometry.
4. Improper Storage and Handling
Peptides are sensitive to temperature, light, and moisture. Suppliers that do not use lyophilized form with proper packaging (e.g., vacuum-sealed vials with desiccants) or fail to ship with cold chain logistics risk delivering degraded product.
5. Mislabeling and Counterfeit Products
The unregulated peptide market is rife with counterfeit or mislabeled substances. Some vendors may sell standard IGF-1 instead of IGF-1 LR3, or dilute the peptide with fillers. Verify supplier reputation and consider using trusted research chemical distributors.
Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
1. Patent Infringement Risks
IGF-1 LR3 and its applications may be covered by active patents, particularly in therapeutic or commercial use contexts. For example, certain formulations, delivery methods, or medical uses could be protected. Using or developing IGF-1 LR3 without due diligence may expose individuals or organizations to legal action.
2. Research-Use Limitations
Many suppliers label IGF-1 LR3 as “for research use only” (RUO) to avoid regulatory scrutiny. However, even RUO use can infringe IP if the research leads to commercial development. Always assess whether your intended application falls within patent claims.
3. Geographic Variability in IP Enforcement
Patent protections vary by country. A peptide legally available in one jurisdiction may be under patent in another. Sourcing from or shipping to regions with strong biotech IP laws (e.g., U.S., EU) requires particular caution.
4. Supplier IP Compliance
Reputable suppliers should be able to confirm that their manufacturing process does not infringe on existing patents. Lack of transparency here may indicate IP risks in the supply chain.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
– Source from reputable, transparent suppliers with verifiable CoAs.
– Conduct independent testing when possible.
– Consult legal counsel regarding IP status before commercial development.
– Use peptides strictly within permitted research contexts.
– Stay informed about patent expirations and regulatory updates.
By addressing both quality and IP challenges proactively, stakeholders can minimize risks and ensure the integrity of their work involving IGF-1 LR3 peptide.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for IGF-1 LR3 Peptide
The handling, distribution, and use of IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Long Arginine 3) peptide require strict adherence to legal, safety, and logistical protocols due to its status as a research compound with potential regulatory implications. This guide outlines best practices for logistics and compliance when working with IGF-1 LR3.
Regulatory Classification and Legal Status
IGF-1 LR3 is not approved for human use by major regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), or other national health authorities. It is classified as a research chemical and is intended solely for laboratory research purposes.
- United States: Regulated under the FDA and the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) if intended for human consumption. Sale or distribution for human use is illegal.
- Europe: Subject to the EU Medicines Directive; not authorized for medicinal use. Member states may have additional restrictions.
- Australia: Listed as a Schedule 4 (prescription-only) substance under the Poisons Standard when intended for human use.
- Other Jurisdictions: Regulations vary; import/export may require permits or be prohibited.
Always verify local laws before purchasing, shipping, or storing IGF-1 LR3.
Intended Use and Labeling
- Research-Only Labeling: Products must be clearly labeled “For Research Use Only – Not for Human or Veterinary Use.”
- Prohibited Claims: Marketing materials must not make therapeutic, performance-enhancing, or health benefit claims.
- Documentation: Maintain records showing the product is sold exclusively to qualified research institutions or laboratories.
Storage and Handling Requirements
Proper storage ensures compound stability and safety:
- Temperature: Lyophilized IGF-1 LR3 should be stored at -20°C in a dry, light-protected environment. Reconstituted solutions are stable for short periods at 4°C but should be used promptly.
- Containers: Use sterile, airtight vials to prevent contamination and degradation.
- Safety Protocols: Handle in a controlled environment (e.g., biosafety cabinet) using personal protective equipment (PPE): gloves, lab coat, and eye protection.
Shipping and Transportation
Shipping IGF-1 LR3 requires compliance with domestic and international regulations:
- Cold Chain Logistics: Use validated cold shipping methods (dry ice or cold packs) to maintain temperature integrity.
- Packaging: Use tamper-evident, insulated packaging with clear “Research Chemical” labeling. Avoid consumer-facing branding.
- Documentation: Include proper invoices, safety data sheets (SDS), and customs declarations indicating non-human use.
- Carrier Compliance: Use carriers experienced in shipping research chemicals. Avoid services that prohibit hazardous or regulated materials.
Import and Export Compliance
Cross-border movement of IGF-1 LR3 is highly regulated:
- Export Controls: Check if IGF-1 LR3 is listed under dual-use or chemical control regulations (e.g., Wassenaar Arrangement).
- Import Permits: Recipients in many countries must have permits from their national regulatory authority.
- Customs Declarations: Accurately declare the product as “Peptide for Research Use Only” with CAS number (if available) and quantity.
Record Keeping and Auditing
Maintain comprehensive records for compliance and traceability:
- Customer verification (e.g., institutional affiliation)
- Sales invoices and shipping logs
- Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for each batch
- SDS and labeling documentation
- Regulatory correspondence
These records should be retained for a minimum of 5 years, or as required by local law.
Quality Assurance and Testing
To ensure product integrity and compliance:
- Source IGF-1 LR3 from ISO-certified or GMP-like facilities.
- Require third-party HPLC and mass spectrometry testing for purity (>95% typical standard).
- Provide CoA with every shipment.
Risk Mitigation and Due Diligence
- Customer Vetting: Screen purchasers to ensure they are legitimate research entities.
- Prohibited Buyers: Do not sell to individuals, athletes, or supplement vendors.
- Legal Counsel: Consult regulatory experts when expanding into new markets.
- Insurance: Maintain liability insurance covering research chemical distribution.
Conclusion
IGF-1 LR3 peptide must be managed with rigorous attention to legal, logistical, and safety standards. By adhering to this compliance guide, organizations can minimize regulatory risk, ensure lawful distribution, and support ethical research practices. Always stay informed about evolving regulations and consult legal professionals when in doubt.
Conclusion on Sourcing IGF-1 LR3 Peptide:
Sourcing IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Long Arg3) requires careful consideration due to its status as a research peptide with potential regulatory, ethical, and health implications. While IGF-1 LR3 is commonly sought for its purported effects in muscle growth, tissue repair, and anti-aging research, it is not approved for human use by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and is typically intended solely for laboratory or research purposes.
When sourcing IGF-1 LR3, it is critical to prioritize reliability, purity, and transparency. Purchasing from reputable, well-reviewed suppliers that provide third-party testing (such as HPLC, mass spectrometry) and Certificates of Analysis (CoA) ensures product quality and reduces the risk of contamination or mislabeling. Avoiding unverified vendors, particularly on unregulated online marketplaces, is essential to maintaining safety and scientific integrity.
Additionally, researchers and individuals must be aware of the legal and ethical guidelines governing peptide use in their country, as possession or use outside of approved research contexts may violate regulations. Furthermore, the potential health risks—such as hypoglycemia, unwanted cell proliferation, or long-term safety concerns—underscore the importance of responsible use and medical supervision if applicable.
In summary, while IGF-1 LR3 may hold promise in scientific research, sourcing it demands diligence, adherence to legal standards, and a commitment to safety and ethical practices. It should be used strictly for legitimate research purposes, with informed awareness of its limitations and risks.