The global ice production market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across foodservice, hospitality, and healthcare sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global packaged ice market was valued at approximately USD 3.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% through 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing consumer preference for convenience, heightened hygiene standards, and the expansion of cold chain infrastructure in emerging economies. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, scalability, and product quality. These top ice vendor manufacturers are not only meeting current market needs but are also shaping the future of ice production through energy-efficient designs, smart technology integration, and sustainable practices. In this analysis, we identify the top 10 ice vendors manufacturers leading the industry based on production capacity, global reach, technological advancements, and market share.
Top 10 Ice Vendors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Reddy Ice
Domain Est. 1998
Website: reddyice.com
Key Highlights: Reddy Ice is the largest manufacturer and distributor of packaged ice products in the United States – offering a scope of service ranging from packaged ice to ……
#2 Page
Domain Est. 1999
Website: homecityice.com
Key Highlights: Home City Ice is an ice manufacturer and delivery service with a local feel and attention to detail but with the resources and network of a large company….
#3 AAA ICE
Domain Est. 2001
Website: aaaice.com
Key Highlights: As the oldest manufacturer of ice in Maryland, we can supply ice at the lowest cost in the area. Whether you need ice sculptures, ice luges or blocked ……
#4 Hoshizaki America
Domain Est. 2003
Website: hoshizakiamerica.com
Key Highlights: Hoshizaki America, trusted ice machine manufacturers with over 70 years of experience, delivers reliable, high-quality ice makers….
#5 Follett Ice
Domain Est. 1998
Website: follettice.com
Key Highlights: Follett Horizon Elite ice machine, Ice Machines, Follett Symphony Plus ice and water dispenser, Ice and Water Dispensers, beverage dispenser, Ice and Beverage ……
#6 Arctic Glacier® Premium Ice
Domain Est. 1999
Website: arcticglacier.com
Key Highlights: Whether it’s snow scenes, ice sculptures or event rentals, we have a range of specialized ice products, solutions and services available in select regions….
#7 Ice Industries
Domain Est. 2001
Website: iceindustries.com
Key Highlights: Looking for a purchaser with a long-term ownership perspective to take over your metal-forming business, look no further than Ice Industries….
#8 Hundredweight Big Ice
Domain Est. 2011 | Founded: 2011
Website: hundredweightice.com
Key Highlights: The World’s Premier Crystal-clear cocktail ice production and delivery company. Serving New York City and Beyond since 2011…
#9 Mixology Ice
Domain Est. 2015
Website: mixologyice.com
Key Highlights: $10 deliveryMixology Ice, the clear ice company you love! · Calculate the Right Ice For Your Event · Share Ice Budget with your Clients · Take the Quiz, Get Discounts!…
#10 Crystal Ice Company
Domain Est. 2018
Website: crystalicecompany.com
Key Highlights: We offer the best in new commercial ice making, storage, and dispensing equipment and parts. Crystal Ice Company offers full service after the sale….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ice Vendors

2026 Market Trends for Ice Vendors: A Strategic Outlook
As the global economy and consumer behaviors evolve, the ice vending industry is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by technological innovation, heightened environmental awareness, and shifting retail dynamics, ice vendors must adapt to remain competitive and profitable. Below are the key market trends shaping the future of the industry.
Rising Demand in Outdoor and Recreational Sectors
The expansion of outdoor dining, pop-up events, and recreational travel is fueling consistent demand for bagged ice. With more consumers engaging in camping, boating, and road trips post-pandemic, ice vending machines located near marinas, parks, and campgrounds are seeing increased foot traffic. By 2026, strategic placement in high-traffic leisure zones will be critical for maximizing sales.
Technological Integration and Smart Vending Solutions
Ice vending is undergoing digital transformation. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of IoT-enabled machines that offer remote monitoring, real-time inventory tracking, predictive maintenance, and mobile payment integration. These smart systems reduce operational costs, minimize downtime, and enhance customer experience through features like app-based purchasing and loyalty rewards.
Sustainability and Eco-Conscious Operations
Environmental responsibility is becoming a key differentiator. Consumers and regulators are pressuring vendors to reduce plastic waste and carbon emissions. In response, leading operators are transitioning to biodegradable ice bags, solar-powered machines, and energy-efficient refrigeration systems. By 2026, compliance with green standards and transparent sustainability reporting will be essential for brand credibility and regulatory approval.
Expansion into Underserved and Rural Markets
Urban markets are becoming saturated, prompting vendors to explore rural and suburban areas with limited access to convenient ice. These regions present high-margin opportunities due to lower competition and steady local demand. Mobile ice vending units and modular kiosks are expected to grow in popularity, enabling rapid deployment in emerging markets.
Increased Competition and Brand Differentiation
As barriers to entry lower and franchise models expand, competition among ice vendors is intensifying. To stand out, vendors are focusing on branding, premium product offerings (e.g., clear ice, flavored ice), and superior machine hygiene. By 2026, customer trust and brand loyalty—built through cleanliness, reliability, and community engagement—will be decisive success factors.
Regulatory and Health Compliance Pressures
Health and safety standards for automated ice production are tightening worldwide. Vendors must comply with food-grade material requirements, regular sanitation protocols, and water quality certifications. In 2026, non-compliant operators risk penalties and reputational damage, making investment in certified equipment and training programs a necessity.
Conclusion
The ice vending industry in 2026 will be shaped by innovation, sustainability, and strategic market positioning. Vendors who embrace technology, prioritize environmental responsibility, and expand intelligently into new territories will be best positioned to thrive. Success will depend not just on selling ice—but on delivering a reliable, clean, and convenient experience in an increasingly competitive and conscious marketplace.
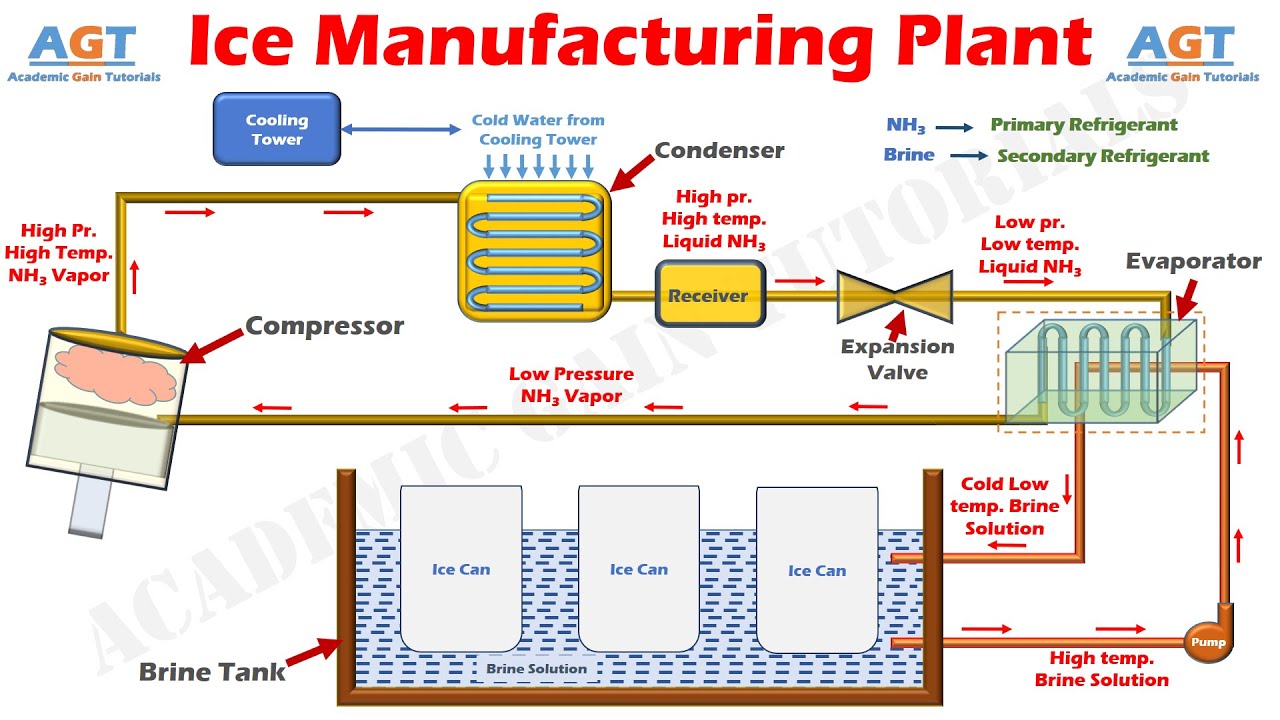
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ice Vendors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing ice from third-party vendors—particularly in industries like food service, healthcare, or logistics—can introduce significant risks if not managed carefully. Two critical areas of concern are product quality and intellectual property (IP) (especially when proprietary packaging, branding, or formulations are involved). Below are common pitfalls in these areas:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Ice Purity and Hygiene Standards
Many vendors may not adhere to stringent sanitation protocols, leading to ice contaminated with bacteria, mold, or chemicals. This risk is heightened if vendors use outdated equipment, poor water filtration, or inadequate storage practices.
2. Lack of Regulatory Compliance
Not all ice vendors comply with local health codes or international standards (e.g., FDA, NSF, ISO 22000). Sourcing from non-compliant vendors can expose your business to legal liability and public health risks.
3. Inadequate Cold Chain Management
Ice must be stored and transported at consistent sub-zero temperatures. Vendors with poor logistics can deliver partially melted or re-frozen ice, compromising texture, safety, and usability.
4. Variable Ice Type and Size
Different applications require specific ice forms (e.g., nugget, cube, flake). Sourcing from vendors who cannot consistently produce the correct type leads to operational inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction.
5. Poor Packaging and Contamination Risk
Low-quality packaging (e.g., non-food-grade bags, improper sealing) can expose ice to airborne contaminants or foreign particles during transport and storage.
IP-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Branded Packaging
If your business supplies custom-branded ice packaging (e.g., for cocktails or medical use), vendors may replicate or resell this design without permission, diluting your brand and violating IP rights.
2. Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts
Many sourcing agreements fail to explicitly assign ownership of custom molds, labels, or formulations to the buyer. This omission can result in disputes or loss of control over proprietary assets.
3. Reverse Engineering of Proprietary Ice Formulations
In niche markets (e.g., clear ice for premium bars), vendors might analyze and replicate your unique production methods, especially if no NDAs or trade secret protections are in place.
4. Third-Party Infringement Liability
If a vendor uses infringing designs, logos, or patented ice-making technology, your company could be drawn into legal disputes—even if unintentionally—by association.
5. Inadequate Audit and Monitoring Rights
Without contractual rights to audit a vendor’s facilities or processes, it’s difficult to ensure they’re not misusing your IP or sharing it with competitors.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough vendor audits (on-site or third-party) focusing on hygiene, equipment, and storage.
- Require certifications (e.g., HACCP, ISO) and verify compliance regularly.
- Include robust IP ownership, confidentiality, and audit clauses in sourcing contracts.
- Use watermarking or traceable packaging to deter unauthorized replication.
- Limit access to proprietary information on a need-to-know basis and under NDA.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, businesses can ensure safe, reliable ice supply while protecting their brand and innovations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ice Vendors
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for businesses involved in the production, storage, transportation, and sale of packaged ice. Adhering to these guidelines ensures product safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Facility and Production Requirements
All ice production facilities must be designed and maintained to prevent contamination. This includes using food-grade materials for equipment, implementing proper drainage systems, and ensuring regular cleaning and sanitation. Facilities should be inspected and licensed by the relevant health authority, such as the local or state Department of Health. Production areas must be enclosed and protected from environmental contaminants like dust, pests, and airborne pollutants.
Water Source and Quality Standards
The water used for ice production must meet potable (drinkable) water standards as defined by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or local public health regulations. Vendors must obtain water from an approved public supply or a licensed private well. Regular water testing—at least quarterly—is required to check for microbial and chemical contaminants. Records of water quality tests must be maintained for inspection.
Packaging and Labeling Compliance
Ice must be packaged in food-safe, tamper-evident materials that protect against contamination. Labels must include the following:
– Product name (“Packaged Ice” or similar)
– Net weight or volume
– Name and address of the manufacturer or distributor
– Production date or batch code
– Statement: “This product is made from potable water” (if required by local law)
Some jurisdictions may require additional language, such as allergy warnings or handling instructions.
Storage and Temperature Control
Packaged ice must be stored in clean, dry, temperature-controlled environments. Storage areas should be maintained at or below 40°F (4°C) to prevent microbial growth. Ice must be stored off the floor on racks or pallets and away from chemicals, raw foods, or other contaminants. Cross-contamination risks must be minimized through segregation and proper handling procedures.
Transportation and Distribution
Ice must be transported in vehicles designed for food-grade cargo. Delivery trucks should be insulated or refrigerated and kept clean. Vehicles must be inspected regularly for cleanliness, structural integrity, and temperature performance. During transport, ice must remain sealed and protected from heat, sunlight, and contamination. Drivers should follow strict hygiene practices and avoid storing non-food items in the same compartment.
Worker Hygiene and Training
All personnel involved in ice handling must follow strict personal hygiene protocols, including handwashing, wearing hairnets or hats, and using clean uniforms. Employees must receive training on food safety, sanitation practices, and proper handling procedures. Ill workers, particularly those with gastrointestinal symptoms, must be excluded from handling ice until cleared by a healthcare provider.
Regulatory Compliance and Inspections
Ice vendors are subject to routine inspections by health departments and may fall under federal regulations such as the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) if engaged in interstate commerce. Vendors must keep detailed records including:
– Water test results
– Cleaning and sanitation logs
– Employee training records
– Maintenance logs for equipment and vehicles
– Batch tracking and distribution records
Non-compliance can result in fines, product recalls, or closure of operations.
Environmental and Sustainability Practices
Consider sustainable practices such as using energy-efficient ice-making equipment, recycling packaging materials, and minimizing water waste. Some regions may require vendors to comply with environmental protection standards related to water usage and waste discharge.
Emergency Response and Recall Procedures
Develop a written recall plan in case of contamination or regulatory violation. The plan should include procedures for:
– Identifying affected batches
– Notifying customers and regulators
– Retrieving and disposing of unsafe product
– Corrective actions to prevent recurrence
Regular testing and mock recalls are recommended to ensure preparedness.
By following this logistics and compliance guide, ice vendors can ensure the safety and quality of their product, maintain regulatory compliance, and build trust with customers and authorities.
In conclusion, sourcing ice vendors requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, reliability, and scalability. Effective vendor selection involves thorough research, assessing certifications and hygiene standards, evaluating supply chain logistics, and conducting site visits when possible. Building strong relationships with multiple vendors can mitigate risks related to supply disruptions and demand fluctuations. Additionally, ongoing performance evaluation and clear communication ensure consistent product quality and adherence to delivery schedules. By implementing a structured sourcing process, businesses in industries such as hospitality, food and beverage, or events can secure a dependable ice supply that supports operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.