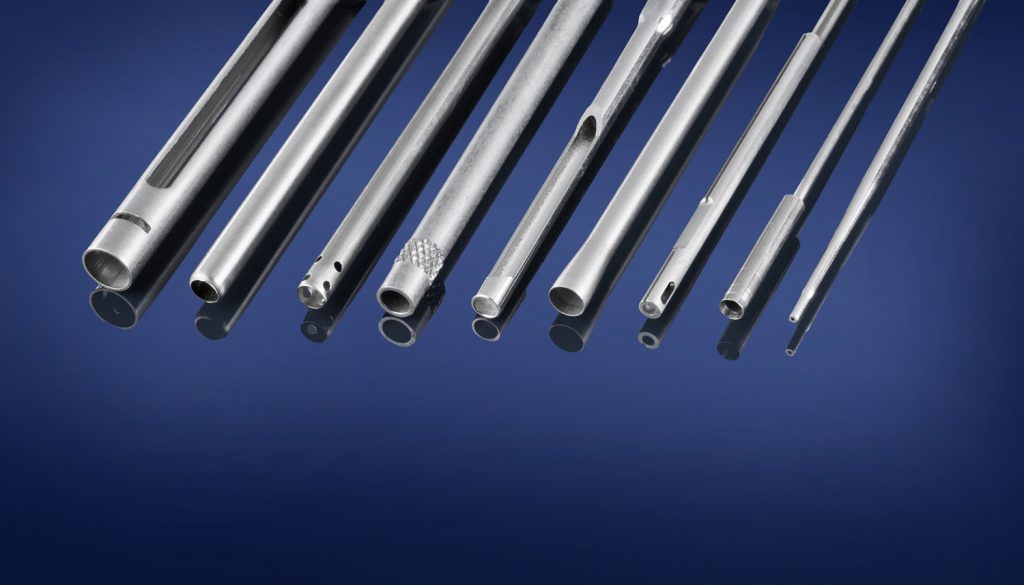
The global hypo tubing manufacturing market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries. According to Grand View Research, the global stainless steel tubing market was valued at USD 28.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030, with hypo tubing playing a critical role in precision applications such as drug delivery systems and diagnostic devices. Additionally, the increasing focus on biocompatible, high-purity tubing for parenteral solutions has intensified competition among manufacturers to offer tightly toleranced, ASTM-compliant products. As outsourcing of drug development and device manufacturing rises, so does the reliance on specialized hypo tubing suppliers capable of meeting stringent regulatory standards. This growing demand underscores the importance of identifying leading manufacturers who combine precision engineering, regulatory compliance, and scalable production capacity. The following list highlights the top nine hypo tubing manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape.
Top 9 Hypo Tubing Manufacturing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hypodermic Tubing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: microgroup.com
Key Highlights: MicroGroup hypodermic tubing is ideal for medical and industrial components applications that require strength, uniformity, and corrosion resistance….
#2 Precision and Custom Tubing
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1974
Website: k-tube.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1974, K-Tube has been a pioneer in the world of precision tubing and hypotube manufacturers for 50 years. Every inch of our tubing meets strict ……
#3 Small Diameter Tubing & Cannula Needle Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: vitaneedle.com
Key Highlights: Vita Needle is a small diameter tubing and cannula needle manufacturer, and our company provides tube products for a wide range of industries….
#4 Hypodermic Metal Tubing for Medical Applications
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: TE’s hypodermic tubing are welded and drawn to tight OD and ID tolerances and stocked in gauge sizes. We maintain both 304 and 316 stainless steels tubing ……
#5 Tubing Fabrication
Domain Est. 1996
Website: paragonmedical.com
Key Highlights: Full-service tubing fabrication for parts up to 16 inches long. Our services include hypodermic tubing and needle flaring….
#6 Medical Metal Tubing Designed for Devices
Domain Est. 1997
Website: wytech.com
Key Highlights: We provide precision hypotubes in a variety of configurations from burr-free cut to length tubing, to complex machined, laser-cut, and needle-pointed ……
#7 Steel Hypodermic Tubing for Medical Industry
Domain Est. 1998
Website: eagletube.com
Key Highlights: Eagle Stainless offers and extensive selection of hypodermic tubing in sizes ranging from 3 gauge to 33 gauge. Contact us today to learn more!…
#8 Medical and Small Diameter Hypodermic Tubing
Domain Est. 2000
Website: pjtube.com
Key Highlights: PJ Tube’s hypodermic tubing is available off-the-shelf for quick shipping. Our small diameter tube products are manufactured in North America….
#9 Teshima International Corporation
Domain Est. 2009
Website: teshimaintl.com
Key Highlights: We supply standard and custom cuts of medical-grade hypodermic stainless steel tubes that fit various medical devices….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hypo Tubing Manufacturing

H2: Projected Market Trends in Hypodermic Tubing Manufacturing for 2026
The global hypodermic (hypo) tubing manufacturing market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in medical technology, rising healthcare demands, and evolving regulatory landscapes. This analysis outlines key market trends expected to shape the hypo tubing manufacturing industry in 2026 under the H2 framework, focusing on Health Innovation, Healthcare Demand, and High-Performance Materials.
H2.1: Health Innovation – Advancements in Precision and Miniaturization
By 2026, innovation in medical device engineering will continue to push the boundaries of hypo tubing design. Manufacturers are expected to prioritize ultra-thin wall tubing and micro-bore precision to meet the growing demand for minimally invasive procedures and wearable drug delivery systems. Technological improvements in laser cutting, electropolishing, and automated drawing processes will enhance dimensional accuracy and surface finish, reducing patient trauma and improving drug delivery efficiency. Integration with smart medical devices—such as insulin pens with embedded sensors—will drive demand for tubing compatible with digital health ecosystems.
H2.2: Healthcare Demand – Expanding Access and Chronic Disease Prevalence
Global healthcare systems are witnessing a surge in demand for injectable therapies due to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. By 2026, the aging population and increased biologics utilization will amplify the need for high-quality hypo tubing in pre-filled syringes, auto-injectors, and infusion systems. Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America will contribute significantly to volume growth, as healthcare infrastructure improves and government initiatives expand access to injectable medications. This shift will pressure manufacturers to scale production while maintaining compliance with ISO and FDA standards.
H2.3: High-Performance Materials – Shift Toward Specialty Alloys and Coatings
Material innovation will be a key differentiator in the 2026 hypo tubing market. While 316L stainless steel remains dominant, manufacturers are increasingly adopting specialty alloys (e.g., nitinol, cobalt-chromium) and applying advanced coatings (e.g., hydrophilic, anti-thrombogenic) to enhance biocompatibility and performance. There is also growing interest in alternative materials such as medical-grade polymers for specific applications requiring flexibility and MRI compatibility. Sustainability concerns will drive R&D into recyclable materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes, aligning with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the hypo tubing manufacturing sector will be shaped by the convergence of Health Innovation, rising Healthcare Demand, and the adoption of High-Performance Materials. Companies that invest in precision engineering, scalable production, and sustainable materials will be best positioned to capture market share in an increasingly competitive and regulated environment. Strategic partnerships with pharmaceutical firms and medtech developers will further accelerate innovation and commercialization across global markets.
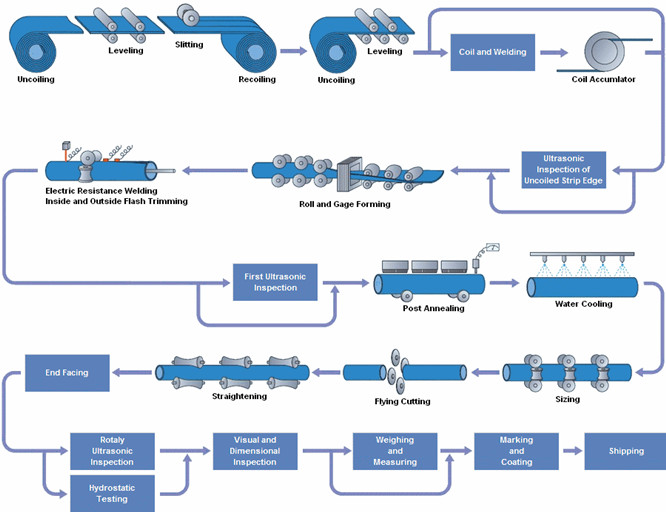
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Hypo Tubing Manufacturing: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing hypo tubing (hypodermic tubing) from external manufacturers, especially overseas, offers cost and scalability benefits but introduces significant risks. Overlooking quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection can lead to product failures, regulatory non-compliance, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality Control and Compliance Shortfalls
One of the most critical areas where sourcing can go wrong is in maintaining the high standards required for medical-grade hypo tubing. Inadequate oversight often results in subpar products.
-
Inconsistent Material Purity and Dimensional Accuracy: Hypo tubing demands strict adherence to material specifications (e.g., ASTM F899 for stainless steel) and micron-level dimensional tolerances. Suppliers may use inferior-grade materials or lack precision manufacturing capabilities, leading to variations in outer diameter, wall thickness, or inner diameter. These inconsistencies can compromise needle performance, drug delivery accuracy, and patient safety.
-
Poor Surface Finish and Defects: A smooth, defect-free internal and external surface is essential to prevent particle generation, ensure biocompatibility, and allow smooth plunger movement in syringes. Sourcing from manufacturers without rigorous finishing processes (e.g., electropolishing) or inspection systems increases the risk of surface scratches, burrs, or residual contaminants.
-
Lack of Validated Processes and Traceability: Reputable medical tubing requires validated manufacturing processes (e.g., drawing, annealing, cutting) and full material traceability (mill certs, lot tracking). Suppliers may not maintain proper documentation or validation records required by regulatory bodies like the FDA or notified bodies under MDR/IVDR, jeopardizing your product approval.
-
Inadequate Quality Management Systems (QMS): Partnering with a supplier lacking ISO 13485 certification or a robust QMS increases the risk of systemic quality failures. Without regular audits and corrective action processes, recurring defects may go undetected until they reach end users.
Intellectual Property Exposure and Misappropriation
Hypo tubing designs, proprietary alloys, or specialized manufacturing techniques represent valuable IP. Sourcing without proper safeguards can lead to theft or unauthorized use.
-
Insufficient IP Protection in Contracts: Failing to include comprehensive IP clauses in manufacturing agreements is a major risk. Contracts must clearly define ownership of designs, tooling, process know-how, and any improvements made during production. Without explicit language, suppliers may claim rights or use your IP for other clients.
-
Weak Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): NDAs that are too broad, poorly enforced, or not jurisdiction-specific may offer little legal recourse if a supplier leaks sensitive information. Ensure NDAs cover all aspects of your design, materials, and processes, and specify governing law and dispute resolution mechanisms.
-
Tooling and Design Replication: Suppliers may replicate your custom tooling or dies and produce identical tubing for competitors—especially in regions with lax IP enforcement. To prevent this, retain ownership of tooling, limit access to design files, and conduct unannounced audits.
-
Reverse Engineering and Market Competition: Once a supplier has manufactured your tubing, they may reverse engineer the product and launch a competitive version. This is particularly dangerous when sourcing from regions known for IP infringement. Proactive strategies such as patent filings in key markets and monitoring for counterfeit products are essential.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls—through rigorous supplier vetting, enforceable contracts, ongoing audits, and robust legal protections—companies can mitigate risks and ensure the reliable, compliant, and secure sourcing of hypo tubing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hypo Tubing Manufacturing
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the manufacturing and distribution of hypo tubing, a critical component in medical devices, pharmaceutical delivery systems, and laboratory applications. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product safety, regulatory compliance, and supply chain efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance Framework
Hypo tubing must comply with a range of international and regional regulations due to its use in healthcare and sensitive environments. Key regulatory standards include:
- FDA 21 CFR (U.S. Food and Drug Administration): Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) under 21 CFR Part 820 is mandatory for tubing used in medical devices. Materials must be biocompatible and meet device classification requirements.
- ISO 10993 (Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices): Required for assessing the biocompatibility of tubing materials, including cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation testing.
- ISO 13485 (Medical Devices – Quality Management Systems): Certification to this standard demonstrates a robust QMS tailored to medical device manufacturing, including design controls, risk management, and traceability.
- REACH & RoHS (EU Regulations): Ensure tubing materials comply with restrictions on hazardous substances (e.g., phthalates, heavy metals) under REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances).
- USP Class VI Certification: For plastic tubing used in pharmaceutical or medical applications, USP <87> and <88> testing ensures material safety through systemic toxicity, intracutaneous, and implantation testing.
Manufacturers must maintain comprehensive technical documentation, including material specifications, test reports, and risk assessments, to support regulatory submissions and audits.
Material Sourcing & Supplier Qualification
Reliable sourcing of raw materials is critical to product quality and compliance. Key practices include:
- Approved Supplier List (ASL): Establish and maintain a list of qualified suppliers for polymers (e.g., PTFE, silicone, PVC, FEP), additives, and dyes.
- Material Certifications: Require CoA (Certificate of Analysis) and CoC (Certificate of Conformance) for every batch, including compliance with USP, ISO, or FDA requirements.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Implement traceability from raw material to finished product (e.g., lot traceability). Conduct on-site audits of critical suppliers.
- Dual Sourcing Strategy: Where possible, qualify alternate suppliers to mitigate supply chain disruptions.
All incoming materials must undergo inspection and testing per defined quality plans before release into production.
Manufacturing Process Controls
Consistent production processes are essential for meeting dimensional tolerances, cleanliness, and performance standards.
- Cleanroom Environment: Manufacture in controlled environments (e.g., ISO Class 7 or 8 cleanrooms) when required for medical-grade tubing to prevent particulate and microbial contamination.
- Process Validation: Validate extrusion, cutting, packaging, and sterilization processes using IQ/OQ/PQ (Installation, Operational, Performance Qualification) protocols.
- In-Process Testing: Monitor critical parameters such as outer/inner diameter, wall thickness, tensile strength, and kink resistance using calibrated equipment.
- Defect Prevention: Implement statistical process control (SPC) and root cause analysis for non-conformances.
Documentation of all manufacturing steps must support full batch traceability.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling ensure product integrity and regulatory compliance throughout distribution.
- Sterile vs. Non-Sterile Packaging: Sterile tubing must be terminally sterilized (e.g., ETO, gamma) and packaged in validated, sterile barrier systems (e.g., peelable pouches).
- Labeling Compliance: Labels must include UDI (Unique Device Identification), lot number, expiration date (if applicable), manufacturer details, and symbols per ISO 15223-1.
- Environmental Protection: Packaging must protect against moisture, light, and physical damage during shipping and storage.
- Language & Regional Requirements: Ensure labeling meets local language and regulatory requirements for target markets (e.g., EU MDR, FDA UDI rules).
Logistics & Distribution Management
Efficient and compliant logistics ensure timely delivery while maintaining product quality.
- Cold Chain (if applicable): For temperature-sensitive materials or sterile products, maintain validated cold chain logistics with real-time monitoring.
- Transport Validation: Conduct shipping studies to validate packaging under various environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity, shock, vibration).
- Storage Conditions: Store products in controlled environments (e.g., dry, ambient temperature) with FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation.
- Customs & Import Compliance: Prepare accurate documentation (e.g., commercial invoice, packing list, CoO) and ensure conformity with import regulations in destination countries.
Post-Market Surveillance & Corrective Actions
Ongoing monitoring and response to field performance are required for compliance.
- Complaint Handling: Implement a formal system for receiving, investigating, and documenting customer complaints per 21 CFR 820.198 and ISO 13485.
- Field Corrections & Recalls: Establish procedures for initiating field actions when non-conforming products are identified, including notification to regulatory authorities (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED).
- CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action): Use data from complaints, audits, and non-conformances to drive continuous improvement and prevent recurrence.
Documentation & Record Retention
Maintain accurate and accessible records to demonstrate compliance.
- Retention Period: Retain quality records, batch documentation, and regulatory submissions for a minimum of the product’s shelf life plus two years, or per local regulatory requirements (e.g., EU MDR requires 10+ years).
- Electronic Records: If using electronic systems, ensure compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 (electronic records and signatures).
Adherence to this logistics and compliance guide ensures hypo tubing manufacturers meet global regulatory expectations, deliver safe and effective products, and maintain a resilient supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Hypo Tubing Manufacturing
In conclusion, sourcing hypo tubing manufacturing requires a strategic evaluation of material quality, manufacturing capabilities, regulatory compliance, and supplier reliability. Hypo tubing, commonly used in medical, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology applications, demands high precision, consistent dimensional accuracy, and biocompatible materials such as medical-grade stainless steel or specialty polymers. A successful sourcing strategy involves selecting suppliers with proven expertise in tight tolerance tubing production, adherence to ISO and FDA standards, and robust quality control processes.
Key considerations include cost-effectiveness without compromising on quality, scalability to meet production demands, and the supplier’s ability to provide technical support and documentation. Additionally, geographic location, lead times, and supply chain resilience play vital roles in ensuring timely delivery and business continuity.
Ultimately, partnering with a reputable and experienced hypo tubing manufacturer that aligns with regulatory requirements and performance standards ensures product safety, reliability, and long-term success in highly regulated industries. Comprehensive due diligence, supplier audits, and pilot testing are recommended to mitigate risks and establish a sustainable sourcing partnership.