The global hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as construction, personal care, pharmaceuticals, and oil & gas. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global cellulose ethers market—of which HEC is a key component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Factors fueling this expansion include the increasing use of water-soluble polymers in eco-friendly construction materials and formulations requiring enhanced viscosity and stability. Similarly, Grand View Research valued the global cellulose ethers market at USD 4.9 billion in 2022, with continued growth anticipated due to advancements in green building technologies and rising consumer demand for high-performance personal care products. As supply chains adapt to meet this demand, identifying the leading hydroxyethyl cellulose manufacturers becomes critical for sourcing reliable, high-quality materials. The following list highlights the top 10 HEC manufacturers based on production capacity, global reach, innovation, and market reputation.
Top 10 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Hec Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CELLOSIZE™ Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC)
Domain Est. 1992
Website: dow.com
Key Highlights: Dow’s CELLOSIZE ™ HEC technology allows you to modify rheology and build pleasing textures in shampoos, conditioners, body washes, hair colorants, creams and ……
#2 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC)
Domain Est. 2001
Website: mikem.com
Key Highlights: Mikem is a trusted manufacturer of hydroxyethyl cellulose, offering a range of HEC powder grades tailored to diverse applications. Our HEC delivers excellent ……
#3 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2018
Website: kimacellulose.com
Key Highlights: Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) is a thickener and emulsifier commonly used in skin care products which can help to improve the texture, hydration, and overall ……
#4 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose(HEC) Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2021
Website: ihpmc.com
Key Highlights: Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) is a white or light yellow, odorless, non-toxic fibrous or powdered solid, prepared by etherification of alkaline cellulose and ……
#5 hydroxyethyl cellulose suppliers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hpmc.com
Key Highlights: Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) is a gelling and thickening agent derived from cellulose. HEC is a non-ionic water-soluble material with good thickening, suspension ……
#6 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC)
Domain Est. 1998
Website: gantrade.com
Key Highlights: Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) is a water-soluble, non-ionic polymer derived from cellulose, a natural polymer obtained from wood or cotton….
#7 CELLOSIZE™ Hydroxyethyl Cellulose
Domain Est. 1999
Website: chempoint.com
Key Highlights: CELLOSIZE™ Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) is a nonionic, water-soluble polymer used for thickening, film forming, and water retention in many applications….
#8 Hydroxyethyl cellulose
Domain Est. 2004
Website: setylose.com
Key Highlights: Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) are manufactured by the etherification of cellulose with ethylene oxide….
#9 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC)
Domain Est. 2010
Website: celotech.com
Key Highlights: Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) is a non-ionic, water-soluble polymer critical for two demanding sectors: water-based coatings and oilfield operations….
#10 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Supplier
Domain Est. 2022
Website: wotaichem.com
Key Highlights: WOTAIchem is one of the leading hydroxyethyl cellulose suppliers in China. We provide various grades of HEC powder for your different uses….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Hec
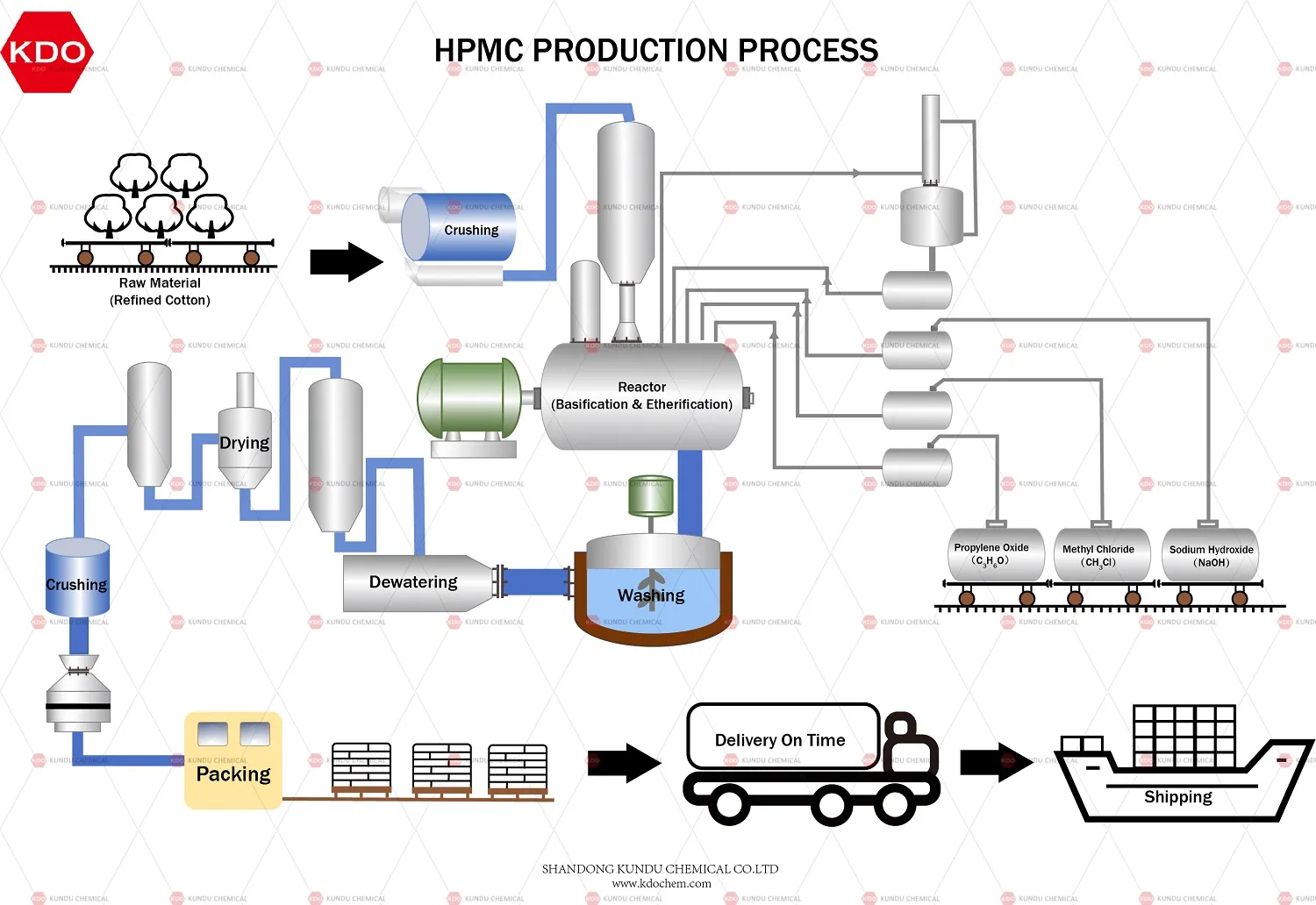
H2: Expansion of Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) Applications in Personal Care and Pharmaceuticals to Drive 2026 Market Growth
By 2026, the global Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) market is projected to experience significant growth, primarily driven by rising demand in the personal care and pharmaceutical industries. HEC, a water-soluble polymer derived from cellulose, is valued for its thickening, stabilizing, and emulsifying properties. In the personal care sector, increasing consumer preference for natural and non-irritating ingredients is boosting HEC adoption in formulations for shampoos, lotions, creams, and facial cleansers. Its hypoallergenic nature and compatibility with a wide range of surfactants and active ingredients make it a preferred choice for sensitive skin products.
In the pharmaceutical industry, HEC is gaining traction as a key excipient in ophthalmic formulations, oral suspensions, and topical gels. Its ability to enhance viscosity and control drug release kinetics supports the development of more effective and patient-friendly dosage forms. Regulatory approvals and the push for bio-based, sustainable polymers further reinforce HEC’s position in these high-value applications.
Additionally, Asia-Pacific—particularly China and India—is expected to lead regional market expansion due to rapid urbanization, growing middle-class populations, and expanding healthcare infrastructure. Manufacturers are also investing in R&D to improve HEC’s performance characteristics, such as enhanced thermal stability and shear resistance, broadening its applicability.
Environmental regulations favoring biodegradable chemicals over synthetic alternatives will further support HEC’s market penetration. As sustainability becomes a core criterion in product development, HEC’s renewable origin and low environmental impact will provide a competitive edge.
Overall, the confluence of technological advancements, regulatory support, and shifting consumer preferences toward safer and eco-friendly ingredients positions HEC for robust market expansion by 2026, with personal care and pharmaceuticals serving as primary growth engines.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC), a widely used water-soluble polymer in industries such as construction, personal care, pharmaceuticals, and oil & gas, involves several critical challenges. Buyers must be vigilant about both product quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) concerns to avoid performance failures, regulatory issues, or legal exposure.
Below are the common pitfalls under these two key areas:
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Inconsistent Viscosity and Substitution Degree (MS)
– HEC performance is highly dependent on its molar substitution (MS) and viscosity grade.
– Poorly controlled manufacturing processes—especially among low-cost suppliers—can result in batch-to-batch variability.
– Pitfall: Using HEC with incorrect or inconsistent MS/viscosity leads to formulation failures (e.g., poor thickening, inadequate stability).
b. Residual Solvents and Impurities
– HEC is synthesized using ethylene oxide and solvents like isopropanol or acetone.
– Inadequate purification leaves behind residual solvents or unreacted chemicals, posing health and safety risks—especially in pharmaceutical or cosmetic applications.
– Pitfall: Non-compliant HEC may fail safety assessments or regulatory requirements (e.g., USP, EP, or REACH).
c. Poor Solubility and Hydration Rate
– Some HEC grades require specific pH or temperature conditions to dissolve properly.
– Off-spec or low-grade HEC may form “fish eyes” (undissolved lumps) or hydrate too slowly.
– Pitfall: Operational inefficiencies, clogged equipment, or inconsistent product performance in final applications.
d. Microbial Contamination
– HEC is prone to microbial degradation if not properly preserved or stored.
– Suppliers in humid climates or with poor manufacturing hygiene may deliver contaminated batches.
– Pitfall: Spoilage in water-based formulations, customer complaints, or recalls.
e. Lack of Regulatory Compliance Documentation
– Reputable suppliers provide certificates of analysis (CoA), safety data sheets (SDS), and regulatory support (e.g., FDA, KOSHER, HALAL).
– Pitfall: Sourcing from vendors without proper documentation risks non-compliance in regulated markets.
2. Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
a. Infringement of Patented Manufacturing Processes
– Major chemical companies (e.g., Ashland, Dow) hold patents on specific HEC production methods, purification techniques, or specialized grades.
– Some suppliers—particularly in regions with lax IP enforcement—may replicate patented processes without licensing.
– Pitfall: Buyers risk indirect liability or supply chain disruption if sourced HEC is later deemed infringing.
b. Misrepresentation of Product Origin or Grade
– Suppliers may falsely label generic HEC as equivalent to a patented or branded grade (e.g., “Ashland-equivalent”).
– This can constitute trademark or IP misrepresentation.
– Pitfall: Legal exposure and reputational damage, especially if performance does not match claims.
c. Use of Counterfeit or Diverted Material
– In some cases, HEC is diverted from original supply chains or counterfeit batches are introduced.
– These materials may lack traceability and quality assurance.
– Pitfall: Inconsistent quality, potential IP violations, and difficulty in recalls.
d. Absence of Freedom-to-Operate (FTO) Analysis
– Companies developing new formulations may unknowingly use HEC grades tied to enforceable patents.
– Pitfall: Risk of infringement lawsuits when commercializing end products.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Qualify Suppliers Rigorously: Audit manufacturing facilities, request full CoAs, and verify regulatory compliance.
- Demand Traceability: Ensure suppliers can provide documentation on raw materials and synthesis methods.
- Conduct IP Due Diligence: Work with legal counsel to assess whether sourced HEC grades are covered by third-party patents.
- Use Reputable Brands or Licensed Suppliers: When performance is critical, opt for established manufacturers with IP transparency.
- Test In-House or via 3rd Parties: Validate viscosity, MS, purity, and solubility before full-scale adoption.
Conclusion
Sourcing HEC involves balancing cost, performance, and compliance. Overlooking quality control or IP risks can lead to formulation failures, regulatory setbacks, or legal disputes. A proactive, due-diligence-driven approach is essential to ensure reliable, safe, and legally sound supply of Hydroxyethyl Cellulose.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC)
Using GHS Hazard Statement H2 (Not classified as hazardous under GHS)
1. Product Overview
- Chemical Name: Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC)
- CAS Number: 9004-62-0
- Formula: (C₆H₉O₄(OH)ₓ(OCH₂CH₂OH)ₙ)ₘ
- Appearance: White to off-white, odorless, free-flowing powder or granules
- Primary Uses: Thickener, stabilizer, and water retention agent in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, paints, construction materials, and oilfield applications.
2. GHS Classification & Hazard Statement (H2)
H2: NOT CLASSIFIED AS HAZARDOUS UNDER GHS
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose is not classified as hazardous according to the United Nations Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS).
Summary of GHS Classification:
- Physical Hazards: Not classified
- Health Hazards: Not classified
- Environmental Hazards: Not classified
- GHS Label Elements:
- Pictograms: None
- Signal Word: Not applicable
- Hazard Statements: None (H2 applies)
- Precautionary Statements: As per good industrial hygiene practices
Note: Some commercial HEC products may contain trace additives or processing aids. Always consult the specific Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the manufacturer.
3. Transportation & Logistics
Regulatory Status:
- IMDG Code (Maritime): Not regulated as dangerous goods
- IATA DGR (Air): Not classified as hazardous; permitted as non-dangerous cargo
- ADR/RID (Road/Rail – Europe): Not subject to hazardous materials regulations
- 49 CFR (USA – DOT): Not regulated as a hazardous material
Packaging & Labeling:
- Packaging: Multi-wall paper bags, fiber drums, or bulk containers (lined with polyethylene)
- Labeling Requirements:
- Product name
- Manufacturer information
- Net weight
- Batch/lot number
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Keep dry”)
- GHS label not required due to H2 status unless local rules mandate otherwise
Storage & Handling:
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area. Protect from moisture and contamination.
- Shelf Life: Typically 24–36 months when stored properly.
- Handling: Use standard PPE (gloves, dust mask) to avoid inhalation of dust or skin/eye contact. Avoid generating dust.
4. Safety & Exposure Control
Exposure Limits:
- OSHA PEL (Particulates not otherwise regulated): 15 mg/m³ (total dust), 5 mg/m³ (respirable fraction)
- ACGIH TLV: 10 mg/m³ (inhalable particulate matter)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Respiratory Protection: Use N95 or equivalent if dust is generated
- Eye Protection: Safety goggles
- Skin Protection: Wear gloves and protective clothing to prevent irritation from prolonged exposure to dust
Ventilation:
- General ventilation sufficient under normal conditions. Local exhaust recommended in high-dust operations.
5. Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Ecotoxicity: Low toxicity to aquatic life; biodegradable over time
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local, regional, and national regulations. Can generally be landfilled as non-hazardous waste.
- Spill Management: Sweep or vacuum spilled material. Avoid creating dust. Do not flush large amounts into drains.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Global Regulations:
- REACH (EU): Registered substance (Registration number available from supplier)
- TSCA (USA): Listed on the TSCA Inventory
- China IECSC, South Korea K-REACH, etc.: Confirm compliance through supplier documentation
Food, Pharma, and Cosmetic Use:
- USP/NF, FCC, or Ph. Eur. grades available for regulated applications
- Documentation (e.g., DMF, CEP) available from manufacturers upon request
7. Documentation Requirements
Ensure availability of:
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Section 2 must reflect H2 status (“Not classified as hazardous”)
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
– Regulatory Compliance Statements (e.g., REACH, TSCA)
– Transport Documents: No DG declaration required, but commercial invoice and packing list needed
8. Emergency Response
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water.
- Eye Contact: Rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical advice if irritation continues.
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth. Do not induce vomiting. Seek medical advice if discomfort occurs.
9. Special Notes
- Although HEC is non-hazardous (H2), fine powder may pose a dust explosion risk under extreme conditions (high concentration, ignition source).
→ Dust explosion hazard: Assess if particle size < 500 µm and handling involves pneumatic transfer or high agitation.
→ Use appropriate ATEX-rated equipment if needed.
10. Conclusion
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) is a non-hazardous chemical (GHS H2) suitable for global transport and commercial use under standard industrial safety practices. No special hazardous materials handling or labeling is required, but prudent handling to minimize dust exposure is recommended.
Always refer to the manufacturer-specific SDS and comply with local regulations.
Prepared in accordance with GHS Rev. 9 (2020) and global transport regulations as of 2023.
Conclusion for Sourcing Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC):
Sourcing Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, and reliability. As a versatile water-soluble polymer widely used in industries such as construction, personal care, pharmaceuticals, and oil & gas, selecting the right HEC supplier is crucial for ensuring product performance and process efficiency. Key considerations include the supplier’s ability to provide consistent product specifications (such as viscosity, purity, and degree of substitution), compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements, and logistical capabilities for timely delivery.
After evaluating multiple suppliers, it is recommended to partner with manufacturers or distributors that have a proven track record of quality control, technical support, and sustainability practices. Establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers not only ensures a stable supply chain but also facilitates better customization and innovation support. Additionally, conducting periodic audits and sampling can help maintain quality assurance.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of HEC involves thorough due diligence, clear communication of specifications, and a focus on total value rather than just price. By prioritizing reliability, technical expertise, and supply chain resilience, organizations can secure high-performing HEC that meets their application needs and supports overall operational excellence.