The global hydroponics market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable agriculture, urban farming, and efficient use of resources. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the hydroponics market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the market could reach USD 1.8 billion by 2030, fueled by advancements in controlled environment agriculture and rising adoption of soilless cultivation techniques. With this surge in demand, hydroponic equipment manufacturers are playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of food production. From precision nutrient delivery systems to advanced grow lights and scalable hydroponic platforms, innovation is accelerating across the sector. Based on market presence, technological advancement, product range, and customer reach, here are the top 10 hydroponic equipment manufacturers leading the industry’s transformation.
Top 10 Hydroponic Equipment Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CropKing Inc
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cropking.com
Key Highlights: Cropking Inc. has over 30 years of experience in commercial greenhouse and hydroponic manufacturing, sales, and customer support……
#2 Hydroponics System Supplier & Hydroponic Equipment …
Domain Est. 2023
Website: tuhopeta.com
Key Highlights: We are a hydroponics equipment factory, our price is relatively more advantageous . We offer factory wholesale prices for importers, distributors, wholesalers ……
#3 Nutraponics: Buy Hydroponic Tower Systems
Domain Est. 2008
Website: nutraponics.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsBuy premium indoor hydroponic tower systems. Grow fresh vegetables year-round. Free shipping, 60-day returns. Shop now! Nutraponics….
#4 AeroFarms
Domain Est. 2008
Website: aerofarms.com
Key Highlights: AeroFarms is an award-winning vertical farming company solving agriculture’s biggest challenges, specializing in nutrient-dense microgreens….
#5 FloraFlex
Domain Est. 2010
#6 Grow Light, LED Growlights, HPS Grow Lights, Grow Tents …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: growace.com
Key Highlights: As a leader in hydroponics equipment, we offer a range of items such as LED grow lights, grow tents, and HPS grow lights. Visit us online today at GrowAce….
#7 Hydroponic Growing Setup
Domain Est. 2011
Website: freightfarms.com
Key Highlights: Freight Farms provides high-tech hydroponic container farms and expert support to help anyone grow fresh food anywhere—no experience required. Freight Farms ……
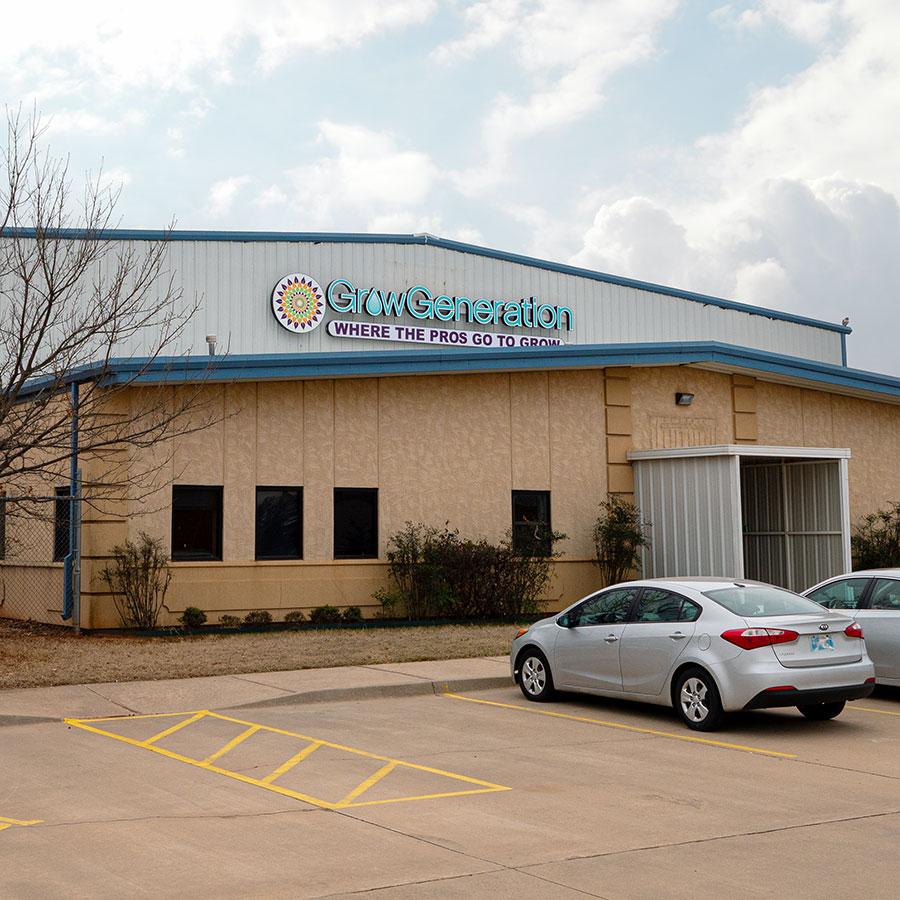
#8 Grow Generation
Domain Est. 2014
Website: growgeneration.com
Key Highlights: 7-day returnsExplore GrowGeneration, the largest hydroponics store in the U.S., offering grow lights, nutrients, tents & more. Shop online or find a store near you….
#9 Hydroponic Growing Systems
Domain Est. 2016
Website: growrillahydroponics.com
Key Highlights: 14-day returnsGrowrilla Hydroponics is a 100% Italian brand of hydroponic growing systems, designed and manufactured in Italy by growers for growers….
#10 Wholesale Hydroponic Supplies Distributor
Domain Est. 2017
Website: hydrotekhydroponics.com
Key Highlights: Wholesale Hydroponic Supplies Distributor for All Your Commercial Needs. Since the 90s, Hydrotek Hydroponics has been North America’s choice for quality ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hydroponic Equipment

Hydroponic Equipment Market Trends in 2026
The hydroponic equipment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing demand for sustainable agriculture, and increasing urbanization. This analysis explores key trends shaping the industry in the coming years.
Rising Demand for Urban and Vertical Farming
Urban populations are expanding rapidly, creating pressure on traditional agriculture to deliver fresh produce within city limits. By 2026, vertical farming—powered by hydroponic systems—is expected to become a mainstream solution. Governments and private investors are increasingly funding indoor farming initiatives, especially in regions with limited arable land such as East Asia and the Middle East. This shift is fueling demand for compact, energy-efficient hydroponic equipment tailored for skyscraper farms and repurposed urban spaces.
Integration of Smart Technology and Automation
The fusion of hydroponics with Internet of Things (IoT) technology is a defining trend for 2026. Smart hydroponic systems equipped with sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automated nutrient delivery are becoming standard. These systems allow real-time monitoring of pH levels, temperature, humidity, and nutrient concentrations, minimizing human error and optimizing crop yields. Cloud-based platforms enable remote management, making advanced hydroponics accessible even to novice growers. Equipment manufacturers are focusing on user-friendly interfaces and modular designs to support scalability.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental concerns are pushing hydroponic equipment manufacturers to prioritize sustainability. By 2026, there is a growing preference for renewable energy-powered systems, such as solar-integrated grow lights and low-energy LED spectrums tailored to plant growth stages. Water recycling mechanisms and closed-loop systems are also gaining traction, reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional farming. Regulatory incentives and consumer demand for eco-friendly food production methods are accelerating this trend.
Expansion of the Consumer-Grade Market
While commercial hydroponic systems continue to grow, the consumer and home gardening segment is experiencing explosive growth. Affordable, plug-and-play hydroponic kits for herbs, leafy greens, and vegetables are becoming popular in households across North America and Europe. By 2026, this segment is expected to be a major revenue driver, supported by e-commerce platforms and educational content promoting food self-sufficiency. Equipment brands are investing in design aesthetics and space-saving solutions to appeal to urban dwellers.
Regional Growth and Emerging Markets
North America and Europe remain leaders in hydroponic technology adoption, but Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are emerging as high-growth regions. Countries like China, India, and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in controlled environment agriculture to enhance food security. Government subsidies, public-private partnerships, and agricultural modernization programs are creating favorable conditions for hydroponic equipment deployment. Local manufacturing hubs are also emerging, reducing import dependency and lowering costs.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite positive momentum, the hydroponic equipment market faces challenges such as high initial setup costs, technical complexity, and lack of skilled labor. However, these barriers are being addressed through leasing models, training programs, and turnkey solutions. Equipment providers that offer comprehensive support—from installation to crop consulting—are likely to gain a competitive edge in 2026.
In conclusion, the 2026 hydroponic equipment market is characterized by innovation, sustainability, and democratization. As food systems evolve to meet global challenges, hydroponic technology will play a central role in shaping the future of agriculture.
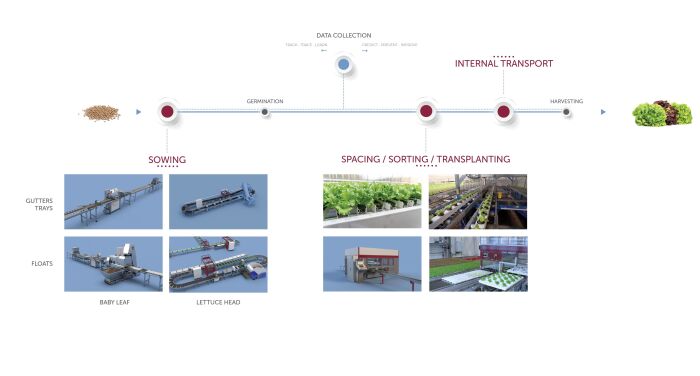
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Hydroponic Equipment (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing hydroponic equipment can be complex, and overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to operational failures, legal issues, and financial losses. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Substandard Materials and Construction
Many low-cost suppliers use inferior plastics, metals, or coatings that degrade quickly when exposed to water, nutrients, and UV light. This can result in leaks, structural failures, and contamination of the nutrient solution, ultimately harming plant health and system longevity.
Inaccurate or Unreliable Components
Sensors (pH, EC, temperature), pumps, and timers are critical for system performance. Cheap or poorly calibrated components deliver inconsistent readings or fail prematurely, leading to improper nutrient dosing, water circulation issues, and crop loss due to undetected environmental imbalances.
Lack of Durability and Weather Resistance
Outdoor or greenhouse hydroponic systems require equipment rated for harsh environments. Sourcing non-weatherproof or non-UV-stabilized components can result in rapid deterioration, especially in pumps, grow trays, and lighting housings.
Poor Design and Incompatibility
Equipment may not be designed with scalability or integration in mind. Purchasing components from multiple vendors without verifying compatibility (e.g., pipe diameters, electrical connections, control protocols) leads to assembly challenges, inefficiencies, and increased maintenance.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Reputable hydroponic equipment should meet safety and performance standards (e.g., IP ratings for water resistance, UL/CE certification). Sourcing from suppliers who do not provide or adhere to these standards increases the risk of electrical hazards, water damage, or non-compliance with local regulations.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Infringement of Patented Technologies
Some advanced hydroponic systems incorporate patented designs, such as unique drip emitters, aeroponic misting nozzles, or automated control algorithms. Sourcing knock-off versions without verifying IP status can expose your business to legal action, product seizures, or costly litigation.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
Unverified suppliers may sell counterfeit versions of well-known brands or reverse-engineer proprietary systems. These products often underperform and may carry hidden legal risks, especially if marketed under misleading branding.
Lack of Licensing Agreements
If you’re scaling up or commercializing a system based on proprietary technology, failing to secure proper licensing rights can block future operations or expansion. Always confirm whether the equipment includes licensed technology and whether sub-licensing is permitted.
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When working with manufacturers to develop custom hydroponic equipment, contracts must clearly define IP ownership. Without explicit agreements, the manufacturer may claim rights to design improvements, limiting your ability to produce, modify, or sell the equipment independently.
Failure to Conduct IP Due Diligence
Skipping patent searches or trademark checks before sourcing can result in unintentional infringement. Conducting due diligence helps identify existing IP and ensures your supply chain is legally sound.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, businesses and growers can ensure reliable system performance, avoid legal complications, and protect long-term investments in hydroponic operations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hydroponic Equipment
Understanding Hydroponic Equipment Classifications
Hydroponic equipment encompasses a wide range of products, including grow lights (LED, HID), water pumps, air pumps, timers, nutrient dosing systems, grow trays, reservoirs, environmental controllers, and sensors. Proper classification is essential for logistics and compliance. Most hydroponic equipment falls under specific Harmonized System (HS) codes based on function and components. For example:
– Electric pumps: HS 8413
– Electric lighting equipment: HS 8539 or 9405
– Electronic controllers and sensors: HS 8537 or 8543
Accurate classification ensures correct tariff application and regulatory adherence during international shipping.
Regulatory Compliance for Domestic and International Shipments
Hydroponic equipment shipped domestically or internationally must comply with various safety and environmental regulations. Key compliance standards include:
– Electrical Safety: Equipment must meet standards such as UL (USA), CE (Europe), or CSA (Canada) for electrical components.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Applies in the EU and other regions; restricts lead, mercury, cadmium, and other harmful substances in electronic devices.
– REACH: EU regulation on chemicals, relevant if equipment contains regulated substances.
– FCC Certification (USA): Required for electronic equipment that may emit radio frequency interference.
Ensure all products have appropriate certifications documented and labels affixed prior to shipping.
Import and Export Documentation Requirements
Complete and accurate documentation is critical for smooth customs clearance:
– Commercial Invoice: Must detail item descriptions, quantities, values, HS codes, and country of origin.
– Packing List: Includes weight, dimensions, and packaging details for each shipment.
– Certificate of Origin: May be required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements.
– Safety and Compliance Certificates: Copies of UL, CE, RoHS, or FCC certifications.
– Import/Export Licenses: Generally not required for standard hydroponic gear, but verify based on destination country and equipment type (e.g., high-power lighting may have additional controls).
Shipping and Handling Considerations
Hydroponic systems often include fragile or sensitive components (e.g., glass grow lights, electronic controllers). Follow best practices:
– Use durable, shock-absorbent packaging to prevent damage.
– Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
– Consider climate-controlled transport for temperature-sensitive electronics.
– Choose reliable logistics partners with experience in handling technical or agricultural equipment.
– Implement tracking systems for real-time shipment visibility.
Environmental and Sustainability Regulations
As sustainability becomes a priority, logistics operations must address:
– Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE): In the EU, sellers may be responsible for recycling end-of-life electronic components. Registration with national WEEE authorities may be required.
– Battery Regulations: If equipment includes rechargeable batteries, comply with transport rules (e.g., IATA for air freight) and local disposal laws.
– Packaging Waste Directives: Some regions require reduced packaging or use of recyclable materials.
Country-Specific Compliance Requirements
Regulations vary significantly by market. Key examples:
– United States: Compliance with FCC and UL standards; no federal restrictions on hydroponic gear, but state-level agricultural regulations may apply.
– European Union: CE marking, RoHS, REACH, and WEEE compliance are mandatory. Registration in national producer compliance schemes may be necessary.
– Canada: CSA or cETL certification for electrical safety; compliance with IC (Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada) for electromagnetic compatibility.
– Australia: Must meet RCM (Regulatory Compliance Mark) requirements for electronic products.
Risk Management and Due Diligence
To minimize logistics delays and compliance risks:
– Conduct regular audits of supplier certifications and product documentation.
– Train staff on export controls and customs procedures.
– Partner with customs brokers familiar with agricultural technology shipments.
– Monitor changes in trade regulations, especially for emerging markets adopting hydroponic farming.
Recordkeeping and Traceability
Maintain comprehensive records for at least 5–7 years, including:
– Product compliance certificates
– Shipment documentation (invoices, bills of lading)
– Customs correspondence
– Recalls or non-conformance reports
Robust traceability supports compliance audits and facilitates product recalls if necessary.
In conclusion, sourcing hydroponic equipment requires careful consideration of several key factors, including system type, quality of materials, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and long-term maintenance needs. Investing in high-quality, durable components from reputable suppliers ensures optimal performance, increased crop yields, and reduced downtime due to equipment failure. Additionally, evaluating local versus international vendors, warranty options, and customer support can significantly impact the success of a hydroponic operation. By conducting thorough research and aligning equipment choices with specific cultivation goals, growers can establish efficient, sustainable, and scalable hydroponic systems that support healthy plant growth and long-term profitability.