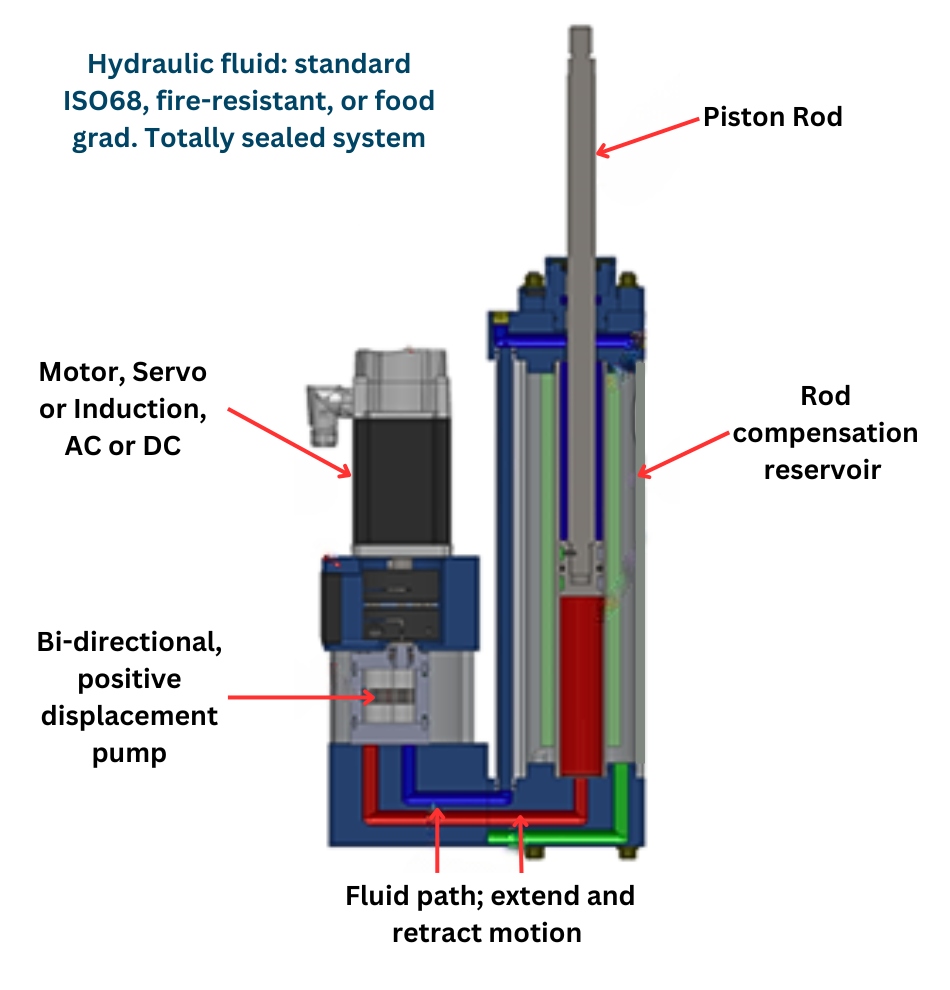
The global hydraulic linear actuator market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across industrial automation, construction, agriculture, and material handling sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the hydraulic actuators market was valued at USD 8.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 11.3 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% during the forecast period. This expansion reflects the increasing need for high-force, reliable motion control solutions in heavy-duty applications where precision and durability are critical. As industries continue to modernize and automate, hydraulic linear actuators remain a cornerstone technology due to their ability to deliver substantial thrust under extreme conditions. With North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific leading in both production and adoption, the competitive landscape is shaped by manufacturers who combine engineering excellence with innovation in energy efficiency and system integration. In this evolving market, sourcing the right supplier is key to optimizing performance and reliability—here are the top 10 hydraulic linear actuator manufacturers leading the industry in technology, scalability, and application expertise.
Top 10 Hydraulic Linear Actuator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tolomatic
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tolomatic.com
Key Highlights: Tolomatic is a US manufacturer of linear motion solutions made to last. Design engineers rely on us for mission-critical automation….
#2 Biffi Actuators
Domain Est. 1998
Website: biffi.it
Key Highlights: Biffi is one of the world’s leading manufacturers of valve actuators. With an engineering pedigree of 70 years plus and a truly global presence….
#3 Hydraulic Actuator Division
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parker.com
Key Highlights: Parker’s Hydraulic Actuator Division designs and manufactures the largest selection of actuators, accumulators, coolers and compact hydraulic power units in ……
#4 Hydraulic Actuators
Domain Est. 1995
Website: emerson.com
Key Highlights: Hydraulic actuators are used to control flow in a system. Our portfolio includes rotary vane, helical spline, linear, scotch yoke, and rack and pinion designs….
#5 Linear actuators
Domain Est. 1997
Website: linak-us.com
Key Highlights: Linear actuators convert rotational motion in motors into movements. Shop our selection of different types and models in high quality here….
#6 EDrive Actuators
Domain Est. 1998
Website: joycedayton.com
Key Highlights: The Eliminator HD is a ball screw linear actuator designed to replace hydraulic presses. It has a rated thrust up to 25,000 lbf and a high velocity up to 20 in/ ……
#7 H
Domain Est. 2008
Website: thomsonlinear.com
Key Highlights: Our H-Track electro-hydraulic linear actuator is an all-in-one, self-contained system that can tolerate extreme shock loads, prevents leaks and features a ……
#8 Kyntronics Actuation
Domain Est. 2016
Website: kyntronics.com
Key Highlights: Kyntronics’ Hybrid Linear Actuation (SHA) systems offer an innovative solution—combining the best features of hydraulic and electro-mechanical actuators to ……
#9 Hydraulic
Website: ahp.de
Key Highlights: The e-ahp electro-hydraulic linear actuator combines the advantages of electric (clean, maintenance-free, easy connection) and hydraulic drive systems….
#10 Best Electric Hydraulic Linear Actuators Manufacturers From China
Domain Est. 2021
Website: hydrauliclinearactuator.com
Key Highlights: Highv is best electric hydraulic linear actuators manufacturers and factory from China for selling electro-hydraulic pushers, valves, unloaders and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hydraulic Linear Actuator

2026 Market Trends for Hydraulic Linear Actuators
The global hydraulic linear actuator market is poised for steady evolution by 2026, driven by enduring industrial demand, technological advancements, and shifting priorities in key end-use sectors. While facing competition from electric alternatives, hydraulic systems maintain critical advantages in high-force and rugged applications. Here are the key trends shaping the market:
1. Sustained Demand in Heavy-Duty and Mobile Applications
Hydraulic linear actuators will remain the dominant choice in industries requiring immense force and reliability under extreme conditions. Construction machinery (excavators, loaders), agricultural equipment (tractors, combines), mining, and offshore oil & gas operations will continue to drive significant demand. The inherent high power density and tolerance to shock loads make hydraulics indispensable in these sectors, ensuring stable market growth through 2026.
2. Integration of Smart Hydraulics and IoT Connectivity
A major trend is the integration of sensors, embedded controls, and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities into hydraulic actuation systems. By 2026, smart hydraulic actuators equipped with pressure, position, and temperature sensors will enable real-time performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics. This enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports Industry 4.0 initiatives, particularly in manufacturing and process industries.
3. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Environmental Compliance
Growing regulatory pressure and sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to improve the energy efficiency of hydraulic systems. Trends include the adoption of variable displacement pumps, load-sensing systems, and advanced valve technologies to minimize energy losses. Additionally, the development of biodegradable hydraulic fluids and leak-resistant sealing solutions will gain traction to meet environmental standards, especially in ecologically sensitive regions.
4. Material Innovation and Compact Design
To meet demands for lighter weight and higher performance, hydraulic actuator manufacturers are investing in advanced materials such as high-strength alloys, composites, and surface coatings. These innovations enhance durability, reduce weight, and improve corrosion resistance. Compact, modular designs are also emerging to facilitate easier integration into space-constrained applications without sacrificing power output.
5. Regional Growth Disparities and Emerging Markets
Geographically, Asia-Pacific (particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia) will lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and expansion of manufacturing and construction sectors. North America and Europe will see moderate growth, driven by equipment modernization, automation adoption, and maintenance of aging infrastructure. Investments in renewable energy (e.g., hydroelectric and offshore wind) will also contribute to regional demand.
6. Competitive Pressure from Electrification
While hydraulics dominate high-force applications, electric linear actuators are gaining ground in precision, clean, and energy-efficient environments such as packaging, laboratory automation, and some aerospace applications. This competition is pushing hydraulic manufacturers to innovate and highlight their unique advantages—particularly in force density and ruggedness—while also exploring hybrid solutions that combine both technologies for optimal performance.
In summary, the hydraulic linear actuator market in 2026 will be characterized by technological sophistication, a strong focus on efficiency and connectivity, and resilience in heavy-industry applications. Companies that embrace digitalization, sustainability, and advanced engineering will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Hydraulic Linear Actuators (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing hydraulic linear actuators requires careful evaluation to ensure performance, reliability, and legal compliance. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant operational and financial risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Verification
Many buyers assume that published specifications reflect real-world performance, leading to the procurement of substandard actuators. Common quality-related pitfalls include:
- Overreliance on Manufacturer Claims: Accepting performance data (e.g., load capacity, stroke length, cycle life) without independent validation or third-party certification.
- Lack of Material Traceability: Failing to verify the quality of internal components such as seals, piston rods, and cylinder materials, which can lead to premature failure under pressure or in corrosive environments.
- Insufficient Testing Documentation: Not requiring proof of pressure testing, fatigue testing, or environmental testing (e.g., salt spray, thermal cycling), especially for critical or harsh-duty applications.
- Poor Manufacturing Consistency: Sourcing from suppliers without robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), resulting in inconsistent product quality across batches.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Using or sourcing actuators that infringe on patented designs or proprietary technology exposes companies to legal action and supply chain disruptions:
- Unlicensed Copying or Reverse Engineering: Procuring “compatible” or “generic” actuators that mimic patented designs without authorization, potentially violating utility or design patents.
- Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs: Failing to secure written agreements confirming IP ownership when co-developing custom actuators with suppliers, risking disputes over design rights.
- Use of Proprietary Mounting Interfaces or Features: Incorporating actuators with protected mounting configurations, connection ports, or control systems without proper licensing, which may limit interoperability and future sourcing options.
- Grey Market or Counterfeit Products: Accidentally sourcing imitation products that replicate branded actuator designs, leading to warranty voids, safety hazards, and IP litigation.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, request certification and test reports, and consult legal experts when adopting non-OEM or custom solutions. Ensuring both quality compliance and IP integrity protects long-term operational reliability and legal standing.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hydraulic Linear Actuators
Product Classification and HS Code
Hydraulic linear actuators are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code 8412.21 or 8412.29, depending on the type and application. These codes cover hydraulic and pneumatic power engines and cylinders. Accurate classification is essential for import/export declarations, duty assessment, and adherence to trade regulations. Confirm the exact HS code with your customs broker based on product specifications such as bore size, stroke length, and operating pressure.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Hydraulic linear actuators must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use wooden crates or heavy-duty cardboard with internal foam or custom inserts to minimize movement. Seal ports with protective caps to avoid contamination from dirt or moisture. Label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.” Ensure all units are clean and dry before packaging to prevent internal corrosion during storage or shipping.
Shipping and Transportation
Transport hydraulic actuators via land, sea, or air depending on urgency, destination, and cost. For international shipments, comply with IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations as applicable. Although hydraulic actuators themselves are not hazardous, residual hydraulic fluid may require special handling if present. Confirm with the manufacturer whether units are shipped dry or pre-filled. Maintain stable temperatures during transport to avoid fluid expansion or seal damage.
Import and Export Documentation
Required documentation includes a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or air waybill, and certificate of origin. Some countries may require a conformity certificate or test report validating performance and safety standards. For exports from regulated regions (e.g., the U.S.), check if an export license is needed under EAR (Export Administration Regulations), particularly if the actuator has military or dual-use applications.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with relevant international and regional standards such as:
– ISO 6020/2 – Mounting dimensions and performance testing for hydraulic cylinders
– ISO 4413 – General rules for hydraulic fluid power systems
– CE Marking – Required for sales in the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards
– REACH & RoHS – Compliance with chemical substance restrictions (EU)
For the U.S. market, verify adherence to ANSI and NFPA standards where applicable.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Provide accurate product descriptions, value declarations, and country of origin to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Duties vary by destination country and trade agreements. Use an experienced customs broker to navigate tariff classifications, potential anti-dumping measures, and local regulatory requirements. Retain all compliance documentation for audit purposes.
Aftermarket and Warranty Considerations
Logistics planning should include reverse logistics for warranty returns or repairs. Define procedures for return authorization, packaging, and transportation of defective units. Clearly communicate warranty terms to customers, including conditions related to proper installation, maintenance, and environmental use.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
At end-of-life, hydraulic actuators may contain materials subject to environmental regulations. Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU for proper disposal or recycling. Ensure that hydraulic fluid is drained and disposed of according to local environmental laws to prevent contamination.
Conclusion for Sourcing Hydraulic Linear Actuators
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, operational conditions, supplier capabilities, and cost considerations, sourcing hydraulic linear actuators requires a balanced approach that prioritizes performance, reliability, and long-term value. Hydraulic linear actuators are ideal for high-force applications requiring durable and consistent linear motion in demanding environments such as heavy machinery, industrial manufacturing, and mobile equipment.
Key factors in successful sourcing include selecting actuators with appropriate force output, stroke length, pressure ratings, and seal materials compatible with the operating environment. Working with reputable suppliers who offer robust engineering support, proven product quality, and responsive after-sales service is critical to ensuring system efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—factoring in maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan—will lead to more sustainable and cost-effective procurement decisions. In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach that aligns technical specifications with reliable suppliers will ensure optimal performance and longevity of hydraulic linear actuator systems within the intended application.