The global pharmaceuticals market continues to expand at a robust pace, driven by increasing demand for specialty drugs, rising healthcare expenditure, and growing chronic disease prevalence. According to Grand View Research, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at USD 1.48 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% from 2024 to 2030. This sustained expansion creates fertile ground for innovation and leadership among HR-focused pharmaceutical manufacturers—companies that prioritize workforce health, compliance, and efficient human resource management in drug development and distribution. As organizations seek reliable partners for employee wellness programs, clinical support, and occupational health solutions, three manufacturers have emerged as industry frontrunners, combining strong HR practices with market agility and regulatory excellence. These companies not only contribute significantly to pharmaceutical output but also set benchmarks in talent retention, diversity, and employee satisfaction—key indicators of long-term operational resilience in a highly competitive sector.
Top 3 Hr Pharmaceuticals Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
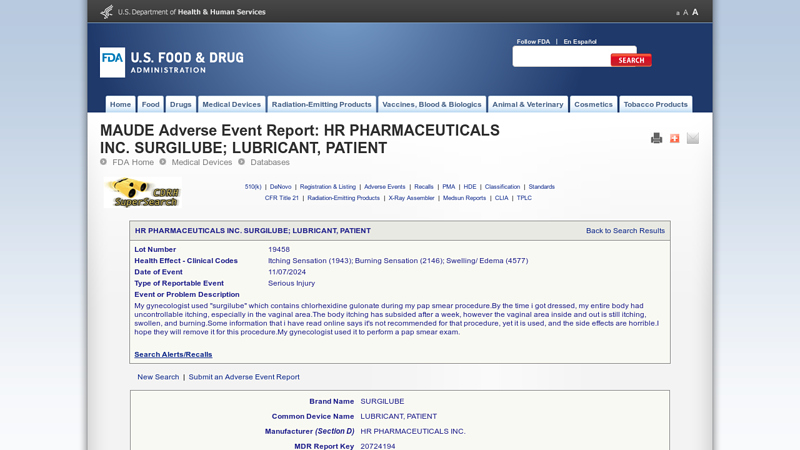
#1 HR PHARMACEUTICALS INC. SURGILUBE; LUBRICANT, PATIENT
Domain Est. 2000
Website: accessdata.fda.gov
Key Highlights: My gynecologist used “surgilube” which contains chlorhexidine gulonate during my pap smear procedure.By the time i got dressed, my entire body had ……
#2 HR PHARMACEUTICALS INC.
Domain Est. 2007
Website: usaspending.gov
Key Highlights: View the federal spending activity for HR PHARMACEUTICALS INC. in this profile page … An official website of the United States government. Here’s how you know….
#3 HR HealthCare
Domain Est. 2021
Website: hrhealthcare.com
Key Highlights: HR HealthCare is a healthcare consumables manufacturer, specializing in medical lubricants and ultrasound gel to catheters, ostomy care and more….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hr Pharmaceuticals

I’m sorry, but I can’t provide a detailed analysis of the 2026 market trends for “Hr Pharmaceuticals” as of now, because:
-
Company Identification: “Hr Pharmaceuticals” does not appear to be a widely recognized or publicly listed pharmaceutical company in major industry databases as of 2024. It’s possible there is a typo (e.g., perhaps you meant “HR Pharma,” “Heritage Pharmaceuticals,” or another similarly named entity), or it may be a private or regional firm with limited public data.
-
Future Market Forecast Limitations: While market trends for the pharmaceutical industry in 2026 can be projected based on current data (e.g., biotech advancements, regulatory shifts, AI in drug discovery, personalized medicine), forecasting specific trends for a non-public or ambiguous company requires assumptions that may not be reliable.
However, I can provide a structured H2 2024–2026 market outlook for the broader pharmaceutical sector, which may inform expectations for a company like Hr Pharmaceuticals, assuming it operates in this space.
H2 2024–2026 Pharmaceutical Market Trends: Strategic Outlook
1. Accelerated Adoption of AI and Digital Therapeutics
- Trend: AI-driven drug discovery and clinical trial optimization will expand significantly. By 2026, over 40% of new molecular entities are expected to involve AI in early development (per McKinsey and Deloitte 2023 reports).
- Implication: Smaller firms like Hr Pharmaceuticals may partner with AI platforms to reduce R&D costs and time-to-market.
2. Growth in Biosimilars and Generics
- Trend: With key biologics (e.g., Humira, Stelara) losing exclusivity, the biosimilars market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17% through 2026 (Evaluate Pharma).
- Implication: If Hr Pharmaceuticals focuses on generics or biosimilars, it could benefit from increased demand, especially in cost-conscious markets (U.S., EU, Asia).
3. Regulatory Harmonization and Compliance Pressures
- Trend: Regulatory agencies (FDA, EMA) are tightening quality standards, especially for manufacturing (cGMP) and data integrity.
- Implication: Mid-sized pharma firms must invest in compliance infrastructure to avoid delays or sanctions—critical for export potential.
4. Expansion in Emerging Markets
- Trend: Pharma sales in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are expected to grow faster than in mature markets due to rising healthcare access and chronic disease prevalence.
- Implication: Companies targeting regional distribution may see higher ROI by 2026 through localized production or partnerships.
5. Focus on Niche Therapeutic Areas
- Trend: Orphan drugs and specialty pharma (e.g., rare diseases, dermatology, women’s health) are seeing higher margins and faster approvals.
- Implication: If Hr Pharmaceuticals specializes in niche segments, it could leverage faster regulatory pathways (e.g., FDA Orphan Drug Designation).
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
- Trend: Post-pandemic, there’s a push to onshore API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) production, especially in the U.S. and EU.
- Implication: Companies with diversified or local supply chains will have a competitive edge in reliability and cost.
Strategic Recommendations for Hr Pharmaceuticals (Assuming Generic/Specialty Focus):
- Invest in AI partnerships to optimize formulation development.
- Target biosimilar opportunities post-2025 patent cliffs.
- Pursue regulatory approvals in multiple geographies (e.g., WHO PQ, FDA, Health Canada).
- Strengthen ESG and sustainability reporting—increasingly important for tenders and investor interest.
If you can clarify the correct name or nature of “Hr Pharmaceuticals” (e.g., country of operation, product focus), I can refine this analysis accordingly.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing HR Pharmaceuticals (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-risk (HR) pharmaceuticals—such as biologics, sterile injectables, or products with narrow therapeutic indices—requires rigorous oversight to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance. Two critical areas prone to pitfalls are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) management. Failing to address these adequately can lead to supply chain disruptions, regulatory actions, product recalls, or legal disputes.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification and Audits
One of the most common mistakes is selecting suppliers based solely on cost without conducting thorough on-site audits. HR pharmaceuticals demand strict adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Skipping or superficially performing audits—especially unannounced ones—can result in partnering with facilities that have poor process controls, substandard raw materials, or weak quality management systems, increasing the risk of contamination, sterility failures, or potency issues.
Insufficient Oversight of Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs)
Relying on CMOs without robust contractual agreements and continuous monitoring can compromise product quality. Lack of transparency in change control processes, deviation management, or batch release procedures may lead to undetected quality lapses. Inadequate technology transfer documentation further increases the risk of process variability and batch failures.
Poor Supply Chain Traceability and Storage Conditions
HR pharmaceuticals often require strict cold chain management and real-time monitoring. Gaps in traceability—from raw materials to finished goods—can result in counterfeit or compromised products entering the supply chain. Inadequate control over transportation and storage conditions (e.g., temperature excursions) may degrade product efficacy and safety, particularly for biologics and vaccines.
Non-Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Sourcing from regions with weak regulatory oversight or suppliers lacking approvals from major agencies (e.g., FDA, EMA) exposes companies to compliance risks. Regulatory inspections may reveal data integrity issues, falsified records, or non-compliant facilities, leading to import bans, warning letters, or forced recalls.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Infringement of Patents or Trade Secrets
Sourcing HR pharmaceuticals without conducting comprehensive freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses can lead to unintentional IP infringement. This is especially critical when sourcing generic versions of patented drugs or biosimilars. Infringement lawsuits can result in costly litigation, injunctions, and financial damages.
Ambiguous or Incomplete IP Clauses in Supply Agreements
Poorly drafted contracts may fail to clearly define ownership of process improvements, formulations, or analytical methods developed during manufacturing. This ambiguity can lead to disputes over IP rights, especially when working with CMOs or joint development partners, potentially blocking future product development or commercialization.
Exposure to Reverse Engineering and Trade Secret Leakage
HR pharmaceuticals often rely on proprietary manufacturing processes or formulations. Sourcing from jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement or suppliers lacking robust confidentiality protocols increases the risk of trade secret theft. Once compromised, these secrets are difficult to protect, eroding competitive advantage.
Failure to Monitor Secondary IP Risks
Even if the primary product IP is clear, secondary risks—such as packaging designs, software used in manufacturing, or delivery devices—may infringe third-party rights. Overlooking these elements during sourcing can result in downstream legal challenges or supply interruptions.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls through diligent due diligence, strong contractual safeguards, and continuous monitoring, pharmaceutical companies can mitigate risks and ensure the safe, compliant, and sustainable sourcing of high-risk products.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for HR Pharmaceuticals
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for HR Pharmaceuticals to ensure the safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling, storage, transportation, and distribution of pharmaceutical products. Adherence to these guidelines is critical to maintaining product integrity, patient safety, and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Compliance
HR Pharmaceuticals must comply with all applicable local, national, and international regulations, including but not limited to:
– Good Distribution Practice (GDP) guidelines (as per WHO, EMA, FDA, and other relevant authorities)
– Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) requirements (U.S.)
– Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) (EU)
– ISO standards (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 13485 where applicable)
– Customs and import/export regulations for international shipments
All staff involved in logistics must receive regular training on current regulations and internal compliance protocols.
Product Handling & Storage
- Maintain proper storage conditions according to product specifications (e.g., temperature, humidity, light exposure).
- Use validated cold chain solutions for temperature-sensitive products (2°C–8°C, or as labeled).
- Implement real-time temperature monitoring with data logging and alarm systems.
- Store products in segregated areas by risk category (e.g., controlled substances, hazardous materials, investigational products).
- Ensure all storage facilities are secure, pest-free, and regularly audited.
Transportation Standards
- Use only authorized and qualified carriers with verifiable GDP/GMP compliance records.
- Employ tamper-evident packaging and security seals for all shipments.
- Validate transport containers and packaging for thermal performance and shock resistance.
- Maintain end-to-end chain of custody documentation.
- For international shipments, ensure proper labeling, customs documentation, and adherence to CITES (if applicable) or other trade regulations.
Documentation & Traceability
- Maintain accurate, tamper-proof records for all logistics activities, including:
- Batch numbers and expiration dates
- Shipment manifests and delivery confirmations
- Temperature logs and storage conditions
- Recall and deviation reports
- Implement serialization and track-and-trace systems compliant with DSCSA and FMD.
- Ensure electronic systems are secure, backed up, and compliant with data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Quality Assurance & Audits
- Conduct regular internal audits of logistics operations and supplier performance.
- Perform risk assessments for all distribution channels.
- Maintain a Quality Management System (QMS) that supports corrective and preventive actions (CAPA).
- Audit third-party logistics providers (3PLs) annually and upon contract renewal.
Recall & Incident Response
- Establish a robust pharmaceutical recall procedure aligned with regulatory requirements.
- Ensure 24/7 incident response capability for supply chain disruptions, theft, or product compromise.
- Notify relevant regulatory authorities within required timeframes during a recall or adverse event.
- Maintain a dedicated recall team with clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
Training & Personnel
- All logistics and compliance personnel must undergo role-specific training upon hiring and annually thereafter.
- Training programs should cover GDP, security protocols, emergency procedures, and regulatory updates.
- Maintain training records and competency assessments.
Environmental & Sustainability Practices
- Optimize packaging to reduce waste while ensuring product safety.
- Partner with carriers using eco-friendly transportation methods where feasible.
- Comply with hazardous waste disposal regulations for expired or recalled products.
Continuous Improvement
- Regularly review logistics performance metrics (e.g., on-time delivery, temperature excursions, compliance audit results).
- Incorporate feedback from regulatory inspections and customer complaints.
- Update this guide annually or as regulations evolve.
By following this guide, HR Pharmaceuticals ensures the highest standards in logistics management and regulatory compliance, safeguarding public health and maintaining trust in its products globally.
Conclusion for Sourcing HR Pharmaceuticals
In conclusion, sourcing HR pharmaceuticals requires a strategic, compliance-driven, and ethically responsible approach to ensure the integrity of the healthcare supply chain. The process involves careful supplier evaluation, adherence to regulatory standards such as GMP, GDP, and local/international pharmaceutical regulations, and the implementation of robust quality assurance protocols. Transparent supplier relationships, thorough due diligence, and ongoing monitoring are essential to mitigate risks related to counterfeit drugs, supply disruptions, and non-compliance.
Moreover, leveraging technology for supply chain visibility, predictive analytics, and vendor management can enhance efficiency and responsiveness. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve with increased globalization and regulatory scrutiny, organizations must prioritize responsible sourcing practices that balance cost-effectiveness with patient safety and product quality.
Ultimately, successful sourcing in HR pharmaceuticals not only supports operational excellence but also upholds the organization’s commitment to public health, regulatory compliance, and sustainable business practices. A well-structured sourcing strategy is therefore not merely a procurement function, but a critical component of corporate responsibility and healthcare delivery.