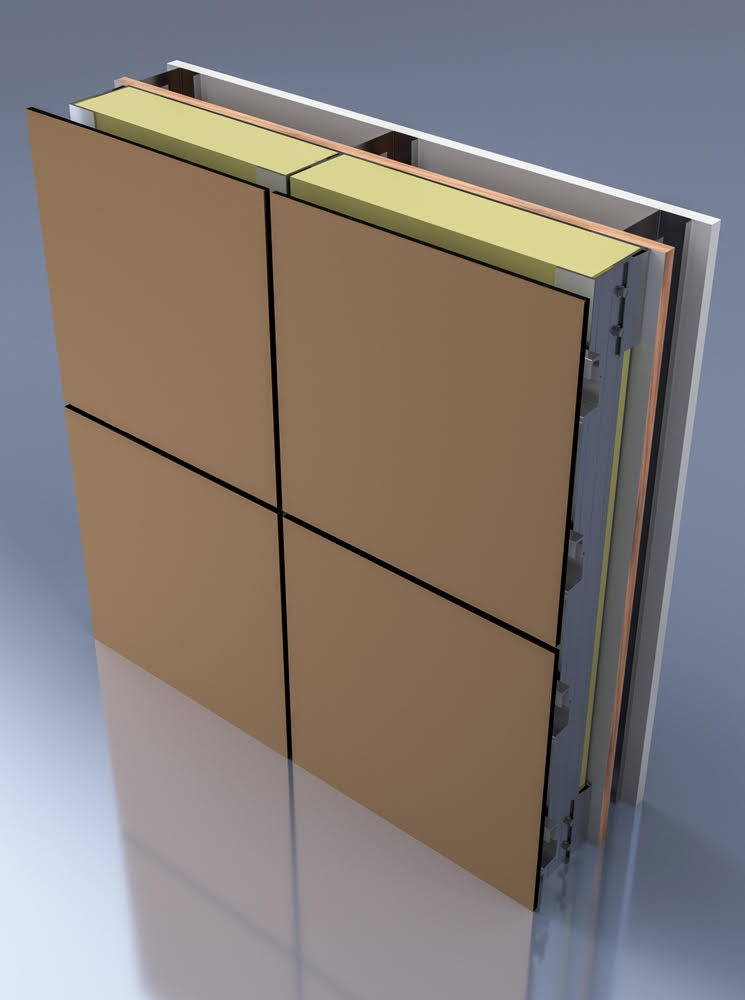
The global HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) panels market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in construction, interior design, and furniture industries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 8.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing urbanization, modern architectural trends, and the material’s durability, aesthetic versatility, and cost-efficiency. With sustainability becoming a key focus, manufacturers are also adopting eco-friendly production processes and materials, further boosting market appeal. As demand surges across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, a select group of global leaders have emerged at the forefront of innovation and market share. Here are the top 9 HPL panel manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 9 Hpl Panels Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 High Pressure Laminate
Domain Est. 2014
Website: kmldesignerfinishes.com
Key Highlights: More than just a producer of high-pressure laminate, KML is your source for on-trend, eco-friendly HPL panels and TFL panels all under one roof….
#2 High-quality HPL panels
Domain Est. 1996
Website: trespa.com
Key Highlights: Trespa International B.V. is a premier developer of high-quality panels HPL panels for exterior cladding, decorative façades, sidings and scientific surface ……
#3 HPL (High Pressure Laminate)
Domain Est. 1997
Website: panolam.com
Key Highlights: Our High Pressure Laminate (HPL) products are manufactured under extreme pressure to deliver a decorative surface that is strong and durable, yet flexible and ……
#4 Laminated Panels
Domain Est. 2002
Website: genesisproductsinc.com
Key Highlights: High pressure laminate (HPL) is considered one of the most durable decorative surface materials. Available in both vertical and horizontal grades….
#5 High
Domain Est. 2004
Website: fundermax.com
Key Highlights: High-pressure laminates are available in various sizes, thicknesses, decors and surfaces. The HPL panels are certified in accordance with EN 438-3. Discover ……
#6 Fundermax: Phenolic & High
Domain Est. 2011
Website: fundermax.us
Key Highlights: Fundermax’s phenolic panels are perfect for exterior, interior and lab surfaces. Create powerful and durable designs with our high pressure laminate panels….
#7 HPL Laminates
Domain Est. 2012
Website: distributorserviceinc.com
Key Highlights: DSI sells Formica® Brand, Nevamar and Pionite HPL high pressure laminates HPL, fiber reinforced laminate FRL, pressure laminate HPL resins and other surfacing ……
#8 HPL Compact
Domain Est. 2017
Website: puricelli-group.com
Key Highlights: HPL can be manufactured in a wide range of thicknesses, generally from 0.8 mm up to 25/30 mm. Thin thicknesses are ideal for wall coverings, ……
#9 High
Domain Est. 2017
Website: ceimaterials.com
Key Highlights: We fabricate high pressure laminate panels—durable, fade-resistant, and design-flexible façade solutions engineered for commercial, institutional, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hpl Panels

H2: Key Market Trends Shaping the HPL Panels Industry in 2026
By 2026, the High-Pressure Laminate (HPL) panels market is poised for significant transformation, driven by evolving consumer demands, technological advancements, and global sustainability imperatives. Here are the dominant trends expected to define the landscape:
1. Sustainability & Circularity as Core Drivers:
Environmental responsibility will be paramount. Demand for HPL panels made with recycled content (especially post-consumer paper and resins) will surge. Manufacturers will prioritize FSC-certified or PEFC-certified wood fibers and bio-based resins. End-of-life considerations will gain traction, with increased focus on recyclability and take-back schemes. Products featuring EPDs (Environmental Product Declarations) and robust sustainability certifications (e.g., Cradle to Cradle, Declare) will become essential for market access, particularly in green building projects targeting LEED, BREEAM, or similar standards.
2. Advanced Functionalities Beyond Aesthetics:
HPL will move beyond basic decoration to incorporate high-value functional properties. Expect widespread adoption of:
* Enhanced Hygiene & Antimicrobial Properties: Critical in healthcare, food service, and public spaces, with integrated silver ions or other technologies.
* Improved Scratch, Impact, and Wear Resistance: Especially for high-traffic commercial and industrial applications.
* Easy-Clean & Stain-Resistant Surfaces: Low-maintenance finishes will be standard.
* Enhanced Fire Performance: Development and demand for HPL meeting stricter international fire safety codes (e.g., higher Euroclass ratings) will grow, particularly in public buildings.
* Acoustic Solutions: Integration of sound-absorbing properties for interior panels in offices and educational facilities.
3. Digitalization & Customization Revolution:
Digital printing technology will mature, enabling unprecedented design flexibility:
* Hyper-Realistic & Custom Designs: Seamless wood grain, stone, concrete, and abstract patterns with unique customization options for architects and designers.
* Mass Customization: Shorter production runs and faster turnaround times for bespoke projects.
* Integration with BIM: Seamless incorporation of HPL specifications into Building Information Modeling workflows for efficient project planning and execution.
4. Dominance of Large-Format & Thinner Panels:
Driven by efficiency and modern aesthetics:
* Large-Format Sheets: 6’x12′ and larger sizes will become standard, minimizing seams, reducing installation time, and enabling sleek, continuous surfaces in furniture and wall cladding.
* Thinner, Lightweight Options: Development of structurally sound but thinner HPL (e.g., 0.5mm-0.8mm) for applications in transportation (aviation, rail), lightweight furniture, and renovation projects where weight is a constraint.
5. Strategic Focus on Emerging Markets & Urbanization:
Rapid urbanization in Asia-Pacific (especially India, Southeast Asia), Latin America, and parts of Africa will fuel demand. The expanding middle class and growth in affordable housing, retail, and commercial infrastructure will create significant opportunities for cost-effective, durable HPL solutions. Localized manufacturing and distribution networks will be key competitive advantages.
6. Smart & Interactive Surfaces (Niche but Growing):
While still emerging, integration of HPL with conductive elements or sensors for simple touch-activated lighting, data transmission, or environmental monitoring in high-end architectural and furniture applications will begin to appear, representing the frontier of innovation.
7. Intensified Competition & Consolidation:
The market will see increased competition between established global players (e.g., Formica, Wilsonart, Pfleiderer, Arpa) and regional manufacturers, particularly from Asia. This will drive innovation but also potentially lead to consolidation as companies seek economies of scale and broader material portfolios (e.g., combining HPL with other engineered surfaces).
Conclusion:
By 2026, the HPL panel market will be characterized by a fundamental shift towards sustainability, enhanced performance, and digital-enabled customization. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate in eco-materials, integrate advanced functionalities, leverage digital design and production, and efficiently serve the growing demands of urbanizing emerging economies. HPL will solidify its position not just as a decorative surface, but as a high-performance, sustainable building block for modern interiors.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing HPL Panels (Quality, IP)
Sourcing High-Pressure Laminate (HPL) panels can be cost-effective and efficient, but buyers often encounter significant challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure a reliable supply chain and protects brand integrity.
Quality Inconsistencies
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing HPL panels—especially from lower-cost or less-regulated regions—is inconsistency in material quality. This includes variations in thickness, surface finish, color accuracy, and durability. Panels may exhibit warping, delamination, or poor resistance to moisture, heat, and impact, which can lead to premature failure in applications. Suppliers might use substandard resins or core materials to cut costs, resulting in non-compliance with international standards such as EN 438 or ANSI/HPDC CS-1. Without rigorous quality control and third-party certification verification, buyers risk receiving non-conforming batches that compromise project timelines and end-user satisfaction.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Another critical risk involves intellectual property (IP) violations. Many premium HPL designs—particularly wood grains, patterns, or branded finishes—are protected by copyrights, trademarks, or design patents. Unethical suppliers may replicate these designs without authorization, offering “look-alike” panels at lower prices. Purchasing such counterfeit products exposes the buyer to legal liability, including customs seizures, fines, or litigation from original manufacturers. Additionally, using infringing materials can damage a company’s reputation, especially in markets that value authenticity and design integrity. Due diligence in verifying supplier legitimacy and requesting IP compliance documentation is essential to mitigate this risk.
Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain
Many suppliers, particularly intermediaries or trading companies, lack visibility into their raw material sources and manufacturing processes. This opacity makes it difficult to verify claims about sustainability, formaldehyde emissions (e.g., CARB P2, E1), or recyclability. Buyers may unknowingly support environmentally harmful practices or fail to meet regulatory requirements in their target markets. Ensuring supply chain transparency through site audits, material traceability, and direct engagement with manufacturers can help avoid reputational and compliance risks.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Some sourced HPL panels come with falsified or generic certifications that don’t match the actual product performance. Relying solely on supplier-provided test reports without independent verification can lead to specifications being missed—particularly for fire ratings (e.g., Class A, BS 476), antibacterial properties, or outdoor durability (e.g., Exterior Grade HPL). Always require up-to-date, product-specific test reports from accredited laboratories and consider third-party testing for critical applications.
Hidden Costs and MOQ Challenges
While initial pricing may appear attractive, hidden costs such as non-standard packaging, extended lead times, or high minimum order quantities (MOQs) can erode savings. Small or custom orders may be difficult to fulfill, forcing buyers into bulk purchases of unwanted colors or textures. Additionally, poor logistics planning or unclear Incoterms can result in unexpected freight, customs, or handling fees. Clear communication and detailed contracts are essential to avoid budget overruns.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through vetting suppliers, demanding documentation, and investing in quality assurance—buyers can secure HPL panels that meet both performance expectations and legal standards.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for HPL Panels
HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) panels are widely used in furniture, cabinetry, and architectural applications due to their durability and aesthetic versatility. Efficient logistics and strict compliance are essential to ensure product quality, safety, and regulatory adherence throughout the supply chain.
Transportation and Handling
Proper handling and transportation are critical to prevent damage to HPL panels, which are susceptible to scratches, warping, and edge chipping.
- Packing: Panels must be securely packed in moisture-resistant wrapping, ideally with interleaf paper between sheets. Use edge protectors and corner guards to prevent damage during transit.
- Stacking: Store and transport panels horizontally and flat. Avoid vertical stacking unless specifically designed for it. Limit stack height to prevent deformation.
- Forklift Handling: Use wide, padded forklift arms to distribute weight evenly. Never lift panels by the edges alone.
- Climate Control: Protect from extreme temperatures and high humidity. Avoid direct sunlight and moisture exposure to prevent warping or delamination.
Storage Requirements
- Environment: Store in a dry, well-ventilated area with stable temperature (15–25°C) and humidity (40–60% RH).
- Duration: Limit long-term storage. Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) to prevent aging or surface degradation.
- Surface Contact: Keep panels on flat, clean pallets or racks. Avoid direct contact with concrete floors to prevent moisture absorption.
Regulatory Compliance
HPL panels must meet various international and regional safety, environmental, and quality standards.
- Fire Safety: Comply with fire resistance standards such as ASTM E84 (USA), EN 13501-1 (EU), or local building codes. Class B or Class 1 ratings are commonly required.
- Emissions & VOCs: Ensure low formaldehyde and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Comply with CARB Phase 2 (California), EPA TSCA Title VI, or E1/E0 standards (Europe).
- REACH & RoHS: Confirm compliance with EU regulations restricting hazardous substances (e.g., phthalates, heavy metals).
- FSC or PEFC Certification: If using wood-based core materials (e.g., particleboard), ensure sustainable sourcing with chain-of-custody certification.
Customs and Import Regulations
For international shipments:
- HS Code Classification: Use correct Harmonized System codes (e.g., 3920.51 or 4412.31 depending on composition) to determine tariffs and duties.
- Documentation: Provide commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificates of origin. Include compliance certificates (fire, emissions, sustainability).
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with product details, handling instructions, country of origin, and safety warnings.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
- Batch Tracking: Maintain batch numbers and production dates for traceability in case of recalls or quality issues.
- Inspection Protocols: Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify dimensions, surface quality, color consistency, and compliance with specifications.
- Supplier Audits: Regularly audit suppliers to ensure adherence to quality and compliance standards.
Sustainability and Disposal
- Recycling: Encourage recycling programs where available. HPL is difficult to recycle due to resin content, but some facilities offer specialized processing.
- Waste Management: Follow local regulations for disposal of off-cuts and packaging materials. Avoid landfill when possible.
- Eco-Labeling: Consider environmental product declarations (EPDs) or Declare labels to support green building certifications (e.g., LEED, BREEAM).
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures safe, efficient distribution of HPL panels while meeting legal and environmental obligations across global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing HPL Panels:
Sourcing High-Pressure Laminate (HPL) panels requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and reliability. After evaluating various suppliers, product certifications, surface finishes, thickness options, and technical specifications, it is evident that selecting the right HPL panels goes beyond aesthetics—it impacts durability, safety, and long-term performance in applications such as interior design, furniture, and architectural surfaces.
Key factors to consider include compliance with international standards (such as ANSI/HPDC, ISO 4586), resistance to wear, moisture, and UV exposure, as well as the environmental credentials of the manufacturer (e.g., FSC certification, low VOC emissions). Partnering with reputable suppliers who offer consistent quality, timely delivery, and technical support ensures smooth project execution and customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing strategy for HPL panels—rooted in thorough supplier vetting, sample testing, and lifecycle considerations—leads to superior performance, enhanced design flexibility, and long-term value for both commercial and residential applications. Prioritizing sustainability and innovation in material selection also positions businesses ahead in an increasingly eco-conscious market.