The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for high-precision joining technologies across automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, increased automation in production lines, and the shift toward lightweight materials requiring non-contact, high-speed welding solutions. As industrial players seek reliable, scalable, and energy-efficient joining methods, the competitive landscape among laser welding manufacturers has intensified. This analysis identifies the top 10 companies shaping the industry, evaluating their technological capabilities, production capacity, innovation pipelines, and global market presence to determine who stands strongest in this evolving sector.
Top 10 How Strong Is Laser Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 How Strong Is Laser Welding
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: Yes, laser welding is often stronger (and better) than Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) and Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding….
#2 NIST Research Sparks New Insights on Laser Welding
Website: nist.gov
Key Highlights: NIST scientists discuss their ambitious project to understand the basic principles of laser welding better than ever before….
#3 Is Laser Welding Strong?
Website: cobot.systems
Key Highlights: Laser welding can be stronger than MIG and TIG welding for adequate applications. Unlike arc welding processes, laser welding uses heat far more efficiently….
#4 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Whether for precision or structural welding, laser welding is an easily automated solution for creating excellent quality welds rapidly and reliably. Laser ……
#5 Traditional Versus Laser Welding
Website: advancedmanufacturing.org
Key Highlights: With much faster processing speeds and higher quality, you might think laser welding would quickly take over the field. But traditional welding hangs on….
#6 What is Laser Welding and How Does It Work?
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a precise process that produces very little deformation compared to traditional welding methods….
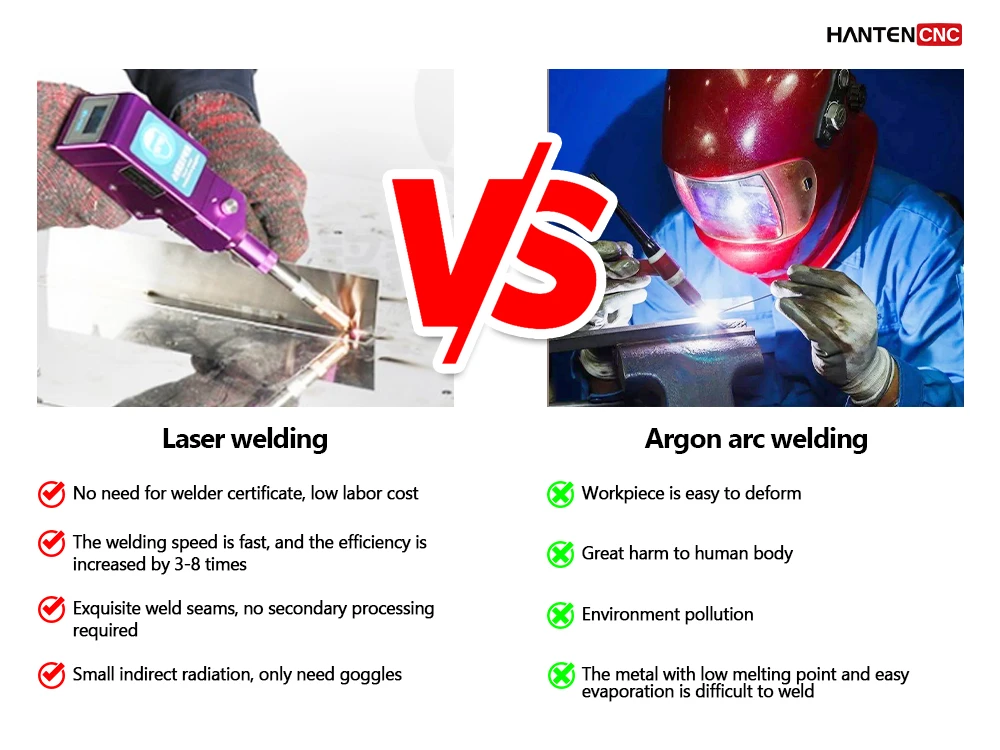
#7 How Strong Is Laser Welding
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: The laser welding strength typically depends on the thickness and the type of metals you are using. How strong is laser welding? Learn more….
#8 STR Laser 【strongest Laser 】
Website: strlaser.com
Key Highlights: STRION LASER delivers integrated laser welding solutions, featuring handheld, automated, and hybrid laser welding. We provide a one-stop service that ensures ……
#9 6 Disadvantages of Laser Welding
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: The downsides to laser welding include high cooling rates, partially completed fusion and penetration, material sensitivity, and joint design limitations….
#10 Is Laser Welding Strong Comparing Durability and Weld Quality
Website: dynalaserstech.com
Key Highlights: Overall, laser welding offers high-quality weld strength, faster processing speeds, and less heat impact, making it the best choice for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Strong Is Laser Welding

H2: Market Growth and Demand Driving the Strength of Laser Welding in 2026
By 2026, laser welding is projected to demonstrate significant strength in the global manufacturing and industrial sectors, driven by accelerating market demand, technological advancements, and industry-wide shifts toward automation and precision engineering. The global laser welding market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8–10% from 2022 to 2026, reaching a market value exceeding USD 12 billion. This expansion underscores the increasing reliability and adoption of laser welding across high-tech industries.
One of the primary drivers of laser welding’s strength in 2026 is its integration into the electric vehicle (EV) and battery manufacturing sectors. As automakers ramp up EV production to meet regulatory and consumer demands, the need for high-speed, high-precision joining methods has surged. Laser welding offers superior seam quality, minimal heat-affected zones, and the ability to weld dissimilar and thin materials—essential for battery tab and cell assembly. Major automotive and battery producers, including Tesla, BYD, and CATL, are increasingly investing in high-power fiber laser systems, reinforcing laser welding’s critical role in next-generation manufacturing.
Moreover, advancements in fiber and disk laser technologies have enhanced power efficiency, beam quality, and process stability, making laser welding more accessible and cost-effective. Smart factories leveraging Industry 4.0 principles are incorporating laser welding systems with real-time monitoring, AI-driven process control, and robotic integration. This convergence strengthens laser welding’s position as a cornerstone of automated production lines in aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—will remain the dominant market for laser welding due to robust industrial infrastructure and government support for advanced manufacturing. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are seeing increased adoption in defense and renewable energy sectors, where material integrity and precision are paramount.
In summary, the strength of laser welding in the 2026 market lies in its alignment with key industrial trends: automation, sustainability, and digitalization. As manufacturers prioritize efficiency, quality, and scalability, laser welding is not just a competitive advantage—it’s becoming a necessity.

H2. Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Welding (Quality and IP Concerns)
When sourcing laser welding services or equipment, businesses often encounter several critical pitfalls related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these challenges is essential to ensuring reliable performance and safeguarding proprietary information.
1. Inadequate Quality Control Standards
One of the most common issues is partnering with suppliers that lack stringent quality control processes. Laser welding demands precision, and inconsistent parameters—such as power density, beam focus, or travel speed—can lead to weak joints, porosity, or cracking. Without certifications like ISO 9001 or adherence to industry-specific standards (e.g., ASME, AWS), there’s a higher risk of subpar weld integrity.
2. Lack of Process Validation and Traceability
Many suppliers fail to provide full process documentation or real-time monitoring data. Without traceability—such as weld logs, parameter records, or non-destructive testing (NDT) reports—it becomes difficult to verify weld strength or troubleshoot failures. This opacity undermines confidence in the final product’s structural reliability.
3. Insufficient Material and Application Expertise
Laser welding performance varies significantly based on material type, thickness, and joint design. Sourcing from vendors without proven experience in your specific application (e.g., medical devices, automotive components) can lead to poor weld penetration, distortion, or metallurgical incompatibility, ultimately compromising strength and durability.
4. Intellectual Property Exposure
Sharing detailed designs or proprietary manufacturing data with third-party laser welding providers poses a significant IP risk. Without strong legal agreements—such as Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and clear IP ownership clauses—companies may lose control over sensitive technology, especially when sourcing internationally where enforcement of IP laws is weak.
5. Hidden Costs from Rework and Failure
Low initial pricing can be misleading. Poorly executed laser welds often result in field failures, recalls, or the need for costly rework. These downstream expenses far outweigh upfront savings, particularly in high-reliability industries where weld failure can have safety implications.
6. Inconsistent Equipment and Technology
Not all laser welding systems are equal. Differences in laser type (fiber vs. CO₂), power output, and beam delivery systems impact weld quality. Sourcing from vendors using outdated or poorly maintained equipment can lead to inconsistent results, reducing the overall strength and repeatability of welds.
To mitigate these risks, businesses should conduct thorough due diligence, audit supplier capabilities, demand comprehensive quality documentation, and establish robust IP protection frameworks before finalizing any sourcing decision.

How Strong Is Laser Welding: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding the strength of laser welding is critical not only for engineering performance but also for ensuring safe, efficient logistics and compliance with industry standards. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and regulatory compliance factors tied to the strength and application of laser-welded components.
Material Compatibility and Handling
Laser welding excels with materials like steel, aluminum, and titanium, offering high-strength joints with minimal heat distortion. When planning logistics, ensure that raw materials and finished welded components are stored and transported under controlled conditions to prevent warping or contamination, which could compromise weld integrity. Use non-abrasive packaging and moisture-resistant wrapping, especially for sensitive alloys.
Transportation and Packaging Requirements
High-strength laser-welded parts often serve in critical applications (e.g., aerospace, automotive, medical devices), necessitating secure packaging to prevent mechanical stress during transit. Use custom cradles, foam inserts, or rigid containers to minimize vibration and impact. Clearly label packages with handling instructions, including “Fragile” and “Do Not Stack,” to protect weld zones from deformation.
Quality Control and Traceability
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 3834 (welding quality requirements), and AWS D1.1 (structural welding code) requires rigorous documentation of the welding process. Maintain traceability logs that include laser settings, material batch numbers, weld inspection results (e.g., ultrasonic or X-ray testing), and operator certifications. This ensures accountability and facilitates audits.
Regulatory Compliance by Industry
- Automotive: Adhere to IATF 16949 standards, which require validated welding procedures and strength testing of joints (e.g., tensile and fatigue tests).
- Aerospace: Comply with AS9100 and NADCAP accreditation, mandating non-destructive testing (NDT) and process control for high-integrity laser welds.
- Medical Devices: Follow FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485, requiring biocompatible materials and sterile handling where applicable.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Conform to AWS and EN 1090 standards, ensuring weld strength meets structural load requirements.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Considerations
Laser welding operations generate fumes and intense optical radiation. Logistics plans must include:
– Proper ventilation or fume extraction systems at production sites.
– Use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles.
– Compliance with OSHA (USA) or equivalent international regulations (e.g., EU Directive 2006/25/EC on artificial optical radiation).
Storage of gas lasers or fiber laser systems must follow fire safety codes, and disposal of metal particulates must comply with environmental regulations such as EPA or REACH.
Testing and Certification of Weld Strength
To validate the strength of laser welds, implement standardized testing procedures:
– Tensile testing to measure ultimate joint strength.
– Microhardness profiling to assess heat-affected zones.
– Fatigue testing for dynamic load environments.
Certify results through accredited third-party labs when required by industry regulations. Maintain certificates as part of the product compliance dossier.
Conclusion
The exceptional strength of laser welding brings significant performance benefits but demands careful attention to logistics and compliance. By aligning material handling, transportation, quality assurance, and regulatory requirements with the high-integrity nature of laser-welded components, organizations can ensure safety, reliability, and market readiness across global supply chains.
Conclusion: Strength of Laser Welding in Sourcing Decisions
Laser welding is a highly precise and powerful joining technique that offers exceptional strength and quality in welded joints, making it a compelling choice in sourcing decisions for high-performance applications. Its key advantages—such as high depth-to-width ratio, minimal heat-affected zones, and excellent repeatability—result in strong, durable welds with superior mechanical properties compared to many conventional welding methods. This makes laser welding particularly suitable for industries where structural integrity, precision, and reliability are critical, such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronics.
From a sourcing perspective, the strength of laser welding translates into longer product lifespans, reduced need for post-welding processing, and higher overall manufacturing efficiency. While initial investment and equipment costs can be high, the long-term benefits—including reduced material waste, lower rework rates, and improved product consistency—often justify the expense, especially for high-volume or high-precision production.
In conclusion, when evaluating manufacturing processes for sourcing, laser welding stands out as a robust and reliable option that delivers strong, high-quality joints. Its strength, precision, and scalability make it a strategic choice for suppliers and manufacturers aiming to enhance product performance and competitiveness in demanding markets.