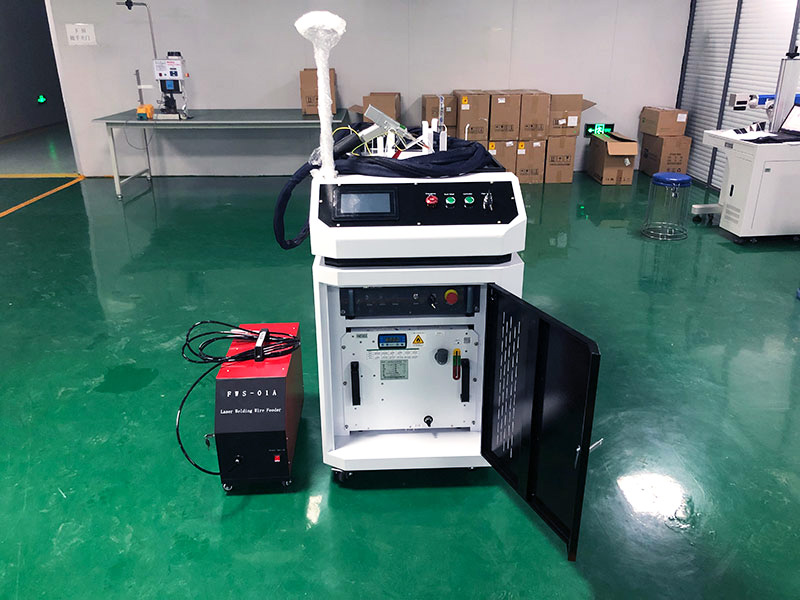
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 1.47 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the adoption of advanced laser technologies, rising automation, and the need for high-speed, low-distortion joining solutions in production environments. As industries prioritize efficiency and quality, the demand for reliable laser welder manufacturers has intensified. With a competitive landscape featuring both established players and emerging innovators, identifying the top manufacturers—evaluated on technology, output capacity, pricing, and application versatility—has become critical for businesses scaling their manufacturing capabilities.
Top 7 How Much Is A Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 How Much Does a Laser Welder Cost?
Website: cobot.systems
Key Highlights: Prices can range from $2,500 to $10,000 for basic models suitable for amateur use, around $21,000 to $25,000 for manufacturer-grade systems, ……
#2 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: Ultra-portable laser welding machine (48.5 lbs) with dual welding/seam cleaning. Patented CUAL laser ensures precision on thin metals. Pre-set modes +….
#3 How much does it cost for a handheld laser welder machine?
Website: kirinlaser.com
Key Highlights: A Kirin Laser handheld fiber laser welding machine ranges from $1,860 to $6,200, yet saves up to $3 per meter of weld and slices lead time in ……
#4 Laser Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: 6–7 day deliveryLaser Welders · Compare. Original price $5,200.00 – Original price $5,700.00 · Compare. Original price $21,900.00 – Original price $21,900.00 · Compare. Original …..
#5 36 Laser Welders & Accessories for sale from $5.59
Website: weldersupply.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $300 · 14-day returnsLincoln Welding Machines Lincoln Electric Flex Lase™ Handheld Laser Welding System Ready-Pak® (K5772-1). Save $7,951.20. $37,947.80. $45,89…
#6 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: As of 2024 this sells for around $34,900 with a wire feeder. Our G5-1500WC is also 1500W, and costs $14,000 with our wire feeder. In summary, you could buy 5 of ……
#7 How Much Does a Laser Welder Cost? (2025 Guide)
Website: gwklaser.com
Key Highlights: How much does a laser welder cost ; Fiber Laser Welding Machine, 1 kW, $5,000 ; Multi-Function 3 in 1, 1 kW, $6,500 ; High Speed 3-Axis Laser welder, 1 kW, $60,000….
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Much Is A Laser Welder
2026 Market Trends: How Much Is a Laser Welder
As we approach 2026, the global market for laser welding technology is undergoing significant transformation, directly influencing the pricing, accessibility, and demand for laser welders. Several economic, technological, and industrial factors are converging to reshape the cost landscape of laser welding systems. This analysis explores the key market trends expected to affect the price of laser welders in 2026.
Rising Demand in Advanced Manufacturing Drives Costs
The growing adoption of laser welding in industries such as electric vehicles (EVs), aerospace, medical devices, and renewable energy is a primary driver of market expansion. By 2026, the EV sector alone is projected to account for over 30% of new laser welding system installations. This surge in demand is placing upward pressure on prices, especially for high-precision fiber and hybrid laser welders. However, increased competition among manufacturers may help moderate price increases, particularly in the mid-tier equipment segment.
Technological Advancements Reduce Long-Term Costs
Innovation in fiber laser efficiency, automation integration, and AI-powered process monitoring is making laser welders more capable and energy-efficient. By 2026, next-generation systems with improved beam quality and lower maintenance needs are expected to dominate the market. While these advanced models may carry higher initial price tags—ranging from $80,000 to over $250,000 for industrial-grade units—total cost of ownership (TCO) is decreasing due to reduced downtime and consumable usage. This shift is making laser welding more cost-competitive with traditional methods like MIG and TIG welding.
Regional Production and Supply Chain Shifts
Global supply chain reconfiguration, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America, is impacting laser welder pricing. Countries like China and India are expanding domestic production of laser components, which could lower costs for entry-level and mid-range systems. In contrast, tariffs, material costs (especially for rare-earth elements), and logistics in Western markets may keep prices elevated. By 2026, the average price for a standard portable laser welder is expected to range from $15,000 to $40,000, while fully automated turnkey systems could exceed $200,000.
Growth of Compact and Handheld Models
The rise of handheld laser welders is one of the most notable trends influencing affordability. These systems, popular in small fabrication shops and repair operations, are becoming more powerful and user-friendly. With prices ranging from $8,000 to $25,000 in 2026, they are democratizing access to laser welding technology. Increased competition among brands like IPG, Raycus, and Max Photonics is driving price reductions and feature enhancements, further accelerating adoption.
Conclusion: Price Variability with Downward Pressure
By 2026, the cost of a laser welder will depend heavily on type, power, automation level, and region. While high-end systems will remain a significant investment, broader market competition, manufacturing efficiencies, and technological improvements are expected to exert downward pressure on prices across most segments. Businesses can anticipate greater value for money, with more features available at lower price points than in previous years.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Welder (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a laser welder involves more than just comparing prices—especially when quality and intellectual property (IP) protection are critical. Overlooking key factors can lead to underperforming equipment, unexpected downtime, or even legal issues. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Price Over Quality and Long-Term Value
Choosing the cheapest option often leads to compromised components, poor build quality, and limited after-sales support. Low-cost laser welders may use inferior optics, unstable power sources, or lack proper cooling systems, resulting in inconsistent welds and frequent maintenance. Instead, evaluate total cost of ownership, including reliability, service availability, and expected lifespan.
2. Overlooking IP Protection and Genuine Technology
Some suppliers may offer laser systems that replicate patented technologies without proper licensing. Using such equipment exposes your business to IP infringement risks, legal challenges, or warranty voiding. Always verify that the manufacturer holds valid patents or certifications and uses original, traceable components.
3. Insufficient Verification of Manufacturer Credentials
Not all suppliers are original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Some rebrand machines from third parties without technical expertise. This can result in poor documentation, lack of software updates, or inability to customize. Request proof of manufacturing capability, certifications (e.g., ISO, CE), and references from existing clients.
4. Underestimating the Importance of After-Sales Support and Service
Laser welders require regular maintenance and occasional repairs. Sourcing from a supplier without a local service team or spare parts inventory can lead to extended downtime. Confirm the availability of technical support, training, and response times before purchase.
5. Ignoring Beam Quality and Process Stability
Beam quality (often measured by BPP—Beam Parameter Product) directly impacts weld precision and depth. Low-quality lasers may boast high power ratings but deliver inconsistent or divergent beams. Request beam profile data and real-world welding samples under conditions similar to your application.
6. Assuming All “IP65” Ratings Are Equal
Many suppliers claim high IP (Ingress Protection) ratings like IP65 for dust and water resistance. However, these claims aren’t always independently verified. In industrial environments, inadequate sealing can lead to contamination and failure. Ask for test reports or third-party certifications to validate IP claims.
7. Failing to Validate Safety and Compliance Standards
Laser systems must comply with safety regulations (e.g., IEC 60825, FDA, CDRH). Non-compliant machines pose safety risks and may be blocked at customs or prohibited from use. Confirm the welder includes proper interlocks, shielding, and documentation for your region.
8. Neglecting Software and Integration Capabilities
Modern laser welders rely heavily on software for parameter control, monitoring, and integration with production systems (e.g., PLCs, robotics). Closed or proprietary software can limit automation and data collection. Ensure the system offers open interfaces, updates, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures you source a reliable, compliant, and high-performing laser welder that protects your investment and intellectual property.
How Much Is A Laser Welder: Logistics & Compliance Guide
When evaluating the cost of a laser welder, it’s essential to consider not only the upfront purchase price but also the logistics and compliance factors that can significantly impact total ownership cost. Understanding these elements ensures a smooth acquisition, installation, and operation process while avoiding legal, safety, and financial pitfalls.
Equipment Sourcing & Procurement Logistics
Sourcing a laser welder involves careful planning around supplier selection, shipping, and importation. Prices vary widely—ranging from $10,000 for basic handheld units to over $100,000 for industrial robotic systems—so logistics must align with budget and operational needs. Purchasing internationally may offer cost savings but introduces shipping delays, customs duties, and import taxes. Ensure suppliers provide detailed technical specifications, compatibility data, and export documentation. Work with freight forwarders experienced in handling high-value, sensitive machinery to minimize damage risk. For overseas purchases, factor in lead times of 6–12 weeks, including customs clearance.
Import Regulations & Tariff Compliance
Importing a laser welder may be subject to tariffs and trade regulations depending on your country. In the United States, for example, laser systems may fall under Harmonized System (HS) code 8515.21 (resistance welding machines) or 8515.80 (other welding equipment), attracting variable duty rates. Some components, such as fiber lasers, could be subject to additional controls under export regulations like the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL) due to dual-use technology concerns. Ensure the seller provides an accurate commercial invoice, packing list, and Certificate of Origin. Consult a customs broker to determine applicable duties and avoid delays or penalties.
Safety Standards & Regulatory Compliance
Laser welders are classified as Class 4 laser products, posing significant safety risks including fire, radiation exposure, and eye injury. Compliance with safety standards is mandatory. In the U.S., adherence to the FDA’s 21 CFR 1040.10 and ANSI Z136.1 laser safety standards is required. The equipment must have proper labeling, interlocks, and an emergency stop. Employers must implement a Laser Safety Program, appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO), and provide operator training. In the EU, compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and CE marking is essential. Failure to comply can result in fines, operational shutdowns, or liability in case of injury.
Installation & Facility Requirements
Installing a laser welder involves more than just unboxing and powering up. These systems require stable power supplies (often 3-phase electrical), cooling systems (chillers), compressed air, and exhaust ventilation for fumes. Facility modifications may be needed to support weight load, flooring, and spatial clearance. Allow for at least 10–20% additional cost beyond the purchase price for installation, utility hookups, and safety enclosures. Site planning should include radiation shielding, access control, and proper signage. Confirm that the equipment meets local building and electrical codes to pass inspections.
Environmental & Waste Disposal Regulations
Laser welding generates hazardous byproducts, including metal fumes, particulate matter, and ozone. Compliance with environmental regulations such as OSHA permissible exposure limits (PELs) and EPA air quality standards is mandatory. Install certified fume extraction systems and conduct regular air monitoring. Spent filters and contaminated components may qualify as hazardous waste under RCRA (in the U.S.) or similar frameworks elsewhere, requiring proper disposal through licensed facilities. Maintain records of waste handling to demonstrate regulatory compliance during audits.
Training & Operational Certification
Operator training is both a safety necessity and a compliance requirement. Ensure all personnel are trained in laser operation, emergency procedures, and personal protective equipment (PPE) use. Certification programs from organizations like the Laser Institute of America (LIA) enhance competency and reduce accident risk. Document training sessions and maintain records to meet OSHA or equivalent workplace safety standards. Untrained operation can void warranties and increase liability exposure.
Maintenance & Regulatory Recordkeeping
Regular maintenance is crucial for performance and compliance. Follow the manufacturer’s service schedule and keep detailed logs of inspections, repairs, and calibration. Some jurisdictions require periodic certification of laser safety systems. Retain records for at least three years to comply with health and safety regulations. Unexpected downtime due to poor maintenance can negate initial cost savings, so factor service plans and spare parts availability into your purchasing decision.
Conclusion
The total cost of a laser welder extends far beyond its sticker price. Logistics challenges and compliance obligations significantly influence the investment. By planning for import duties, safety standards, facility upgrades, training, and maintenance, businesses can ensure a safe, legal, and cost-effective implementation. Always consult with legal, safety, and logistics experts when acquiring high-tech industrial equipment to avoid unforeseen expenses and regulatory issues.
In conclusion, the cost of a laser welder varies significantly depending on factors such as the type (fiber, CO2, diode), power output, brand, automation level, and intended application (industrial, commercial, or hobbyist use). Entry-level portable laser welders can start around $3,000 to $5,000, while high-powered, industrial-grade systems with advanced features can range from $20,000 to over $100,000. Additional costs may include training, maintenance, safety equipment, and integration into existing production lines. When sourcing a laser welder, it’s essential to assess your specific needs, production volume, material types, and long-term return on investment. Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers and considering financing or leasing options can also help in making a cost-effective decision that aligns with both technical requirements and budget constraints.