The global UV printing market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, high-speed, and high-resolution printing solutions across industries such as packaging, automotive, electronics, and signage. According to Grand View Research, the global UV printing market size was valued at USD 21.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the adoption of energy-efficient UV-LED curing technologies, stricter environmental regulations promoting low-VOC printing methods, and the rising need for durable, scratch-resistant prints in industrial applications. As manufacturers continue to innovate in UV curing mechanisms, ink formulation, and printer precision, a select group of industry leaders has emerged at the forefront of this transformation. Below, we spotlight the top 9 manufacturers that are shaping how UV printing works—through cutting-edge engineering, scalable solutions, and a commitment to sustainable advancement.
Top 9 How Does Uv Printing Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 UV Printing
Website: rolanddg.eu
Key Highlights: UV digital printing speeds up the print production process by instantly curing specially formulated UV inks on a vast range of materials using UV lamps….
#2 A Look at UV Printing Technology: What It Is & How It Works
Website: coldesi.com
Key Highlights: UV printing is a type of printing technology that uses a combination of ultraviolet (UV) light, and UV-curable inks to print directly onto an object or a ……
#3 What is UV Printing? UV Curable Inks for Packaging
Website: troygroup.com
Key Highlights: UV printing is an advanced digital technology that cures specially designed inks using UV light. This process creates sleek, vibrant designs that dry instantly….
#4 The Ins And Outs Of An LED UV Printing System
Website: bbpress.co.uk
Key Highlights: As the substrate begins feeding through the press, each compartment of the system applies colour to the image on top of each other to complete the image. When ……
#5 Debunking UV Printing Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
Website: rolanddga.com
Key Highlights: UV digital printing speeds up the print production process by instantly curing specially formulated UV inks using UV lamps. As with any ……
#6 EUV lithography systems – Products
Website: asml.com
Key Highlights: Using extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light, our NXE and EXE systems deliver high-resolution lithography and make mass production of the world’s most advanced ……
#7 How Does UV Ink Work?
Website: mimakiusa.com
Key Highlights: With UV printing, ultraviolet light is used to cure and dry ink, which occurs virtually in an instant. By comparison, traditional solvent inks take time to dry….
#8 How it works – UV curing for printing
Website: alpha-cure.com
Key Highlights: UV curing dries the ink but doesn’t let it absorb, etch or scratch into the substrate material. This means printers can now print on a huge range of materials….
#9 What Is UV Printing? A Complete Beginner’s Guide (2025 Update)
Website: truflatplywood.com
Key Highlights: UV printing sprays UV-curable ink directly onto the surface and immediately cures it with UV light. It works on rigid surfaces like wood, metal, and glass, as ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Does Uv Printing Work

How Does UV Printing Work: 2026 Market Trends Analysis
Understanding UV Printing Technology in 2026
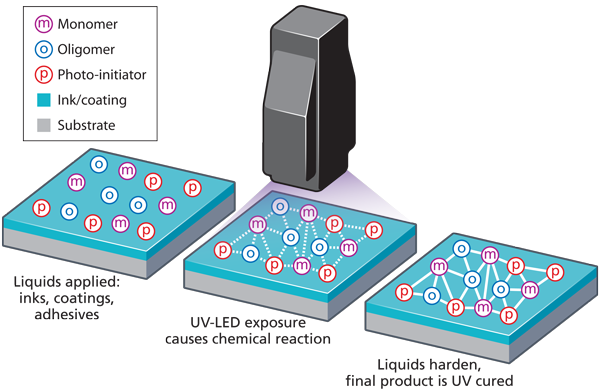
UV printing, or ultraviolet printing, is a form of digital printing that uses ultraviolet lights to dry or cure ink as it is printed. Unlike traditional solvent-based inks that dry through evaporation, UV inks polymerize—transforming from liquid to solid—when exposed to UV light. This immediate curing process allows for faster production speeds, reduced drying time, and the ability to print on a wide variety of substrates, including plastic, glass, metal, wood, and even some fabrics.
As we look toward 2026, advancements in UV LED technology, environmental regulations, and growing demand for high-quality, sustainable printing solutions are reshaping the market landscape.
Key Technological Advancements Driving UV Printing
In 2026, UV printing technology continues to evolve with significant improvements in UV LED curing systems. These systems offer lower energy consumption, longer lifespans, and reduced heat output compared to traditional mercury-vapor UV lamps. This makes them ideal for heat-sensitive materials and supports compact, more efficient printer designs.
Additionally, ink formulations have become more eco-friendly, with increased adoption of low-migration and food-safe UV inks—critical for packaging applications. Integration with automation, AI-driven color calibration, and IoT-enabled monitoring systems also enhances precision and reduces operational costs across industrial and commercial printing sectors.
Sustainability and Regulatory Influences
Environmental concerns are shaping the UV printing market profoundly by 2026. With growing regulations on VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions in regions like the EU and North America, UV printing is gaining favor as a near-zero VOC solution. Its energy-efficient LED curing systems align with corporate sustainability goals, making UV printers a preferred choice for eco-conscious brands.
Moreover, recyclability of UV-printed materials has improved due to innovations in ink chemistry, further supporting circular economy initiatives. As governments push for greener manufacturing practices, the demand for UV printing in packaging, signage, and product decoration is expected to rise.
Expanding Market Applications
By 2026, UV printing is no longer limited to niche applications. It has expanded into mainstream packaging, especially in food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries, where durability and compliance are paramount. The ability to print high-resolution graphics directly onto 3D objects is fueling growth in promotional products and customized goods.
The rise of mass customization and on-demand printing is another driver. E-commerce platforms and print-on-demand services increasingly rely on UV printers for fast turnaround and vibrant, long-lasting prints on diverse materials.
Regional Market Outlook
North America and Europe remain dominant markets for UV printing in 2026, driven by advanced manufacturing infrastructure and strict environmental norms. However, Asia-Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth, particularly in China, India, and Southeast Asia, due to increasing industrialization, urbanization, and consumer demand for branded packaging.
Local manufacturers are adopting UV printing to compete globally, supported by government incentives for green technology adoption.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
Leading manufacturers such as Epson, HP, Agfa, and Mimaki are intensifying R&D efforts to enhance print speed, resolution, and substrate compatibility. In 2026, we see a trend toward hybrid printers that combine UV with other technologies like latex or aqueous inks, offering greater flexibility.
Smaller firms are entering the market with modular and desktop UV printers, democratizing access for small businesses and creative entrepreneurs. Cloud-based design platforms integrated with UV printing workflows are also emerging, enabling remote customization and seamless production.
Conclusion: The Future of UV Printing in 2026
UV printing is poised for robust growth in 2026, driven by technological innovation, environmental benefits, and expanding applications. As industries demand faster, cleaner, and more versatile printing solutions, UV technology stands out as a sustainable and high-performance option. With continuous improvements in ink chemistry, curing systems, and smart manufacturing integration, UV printing is not just keeping pace with market needs—it is leading the digital printing revolution.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing UV Printing Services (Quality and IP)
When sourcing UV printing services, businesses often encounter challenges related to both print quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding these pitfalls can help you make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
Inconsistent Print Quality Due to Poor Process Control
One of the most frequent issues is variability in print quality across different suppliers or even within the same production run. UV printing relies on precise control of UV-curable inks, curing lamps, and substrate preparation. Sourcing from vendors with inadequate equipment calibration or inconsistent curing processes can lead to problems like smudging, poor adhesion, color inaccuracy, or uneven gloss. Always verify a supplier’s quality assurance protocols and request physical samples before committing.
Limited Material Compatibility and Adhesion Issues
UV inks don’t adhere uniformly to all substrates. Some low-cost providers may claim broad compatibility but fail to perform proper surface treatment (e.g., plasma or flame treatment) on plastics, metals, or glass. This can result in flaking or peeling over time. Ensure your supplier tests adhesion on your specific material and communicates any limitations upfront to avoid product failures.
Inadequate Color Matching and Calibration
UV printers can produce vibrant colors, but achieving accurate color reproduction requires proper profiling and regular calibration. Sourcing from vendors without standardized color management systems (e.g., ICC profiles, spectrophotometer use) risks mismatched branding colors or inconsistent batches. Request a printed color chart or PANTONE matching verification to confirm fidelity.
Intellectual Property Risks from Unsecured Digital Files
When you provide digital artwork for UV printing, you’re sharing sensitive design files. Unscrupulous suppliers may lack secure data practices or even replicate your designs for unauthorized use or resale. This poses a serious IP risk, especially for proprietary or patented products. Always vet suppliers for data security policies, sign NDAs, and consider watermarking or encrypting design files when sharing.
Lack of IP Ownership Clarity in Contracts
Many sourcing agreements fail to explicitly state who owns the rights to digital print files, tooling, or customized print setups. Without clear contractual terms, the supplier may claim partial ownership or reuse your designs for other clients. Ensure your contract specifies that all IP related to your project remains your property and prohibits unauthorized use.
Hidden Costs from Minimum Order Requirements or Setup Fees
Some UV printing providers advertise low per-unit prices but impose high setup fees or require large minimum orders. These hidden costs can undermine cost-effectiveness, especially for prototypes or small batches. Clarify all fees upfront and assess total cost per project, not just the print price.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—through due diligence, clear contracts, and sample testing—you can ensure high-quality UV printing outcomes while protecting your intellectual property.

How Does UV Printing Work: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding UV Printing Technology
UV printing, or ultraviolet printing, is a digital printing method that uses ultraviolet lights to cure or dry ink as it is applied to a substrate. Unlike traditional solvent-based inks that dry through evaporation, UV inks solidify instantly when exposed to UV light. This process allows for high-quality, durable prints on a wide range of materials, including plastic, glass, metal, wood, and even three-dimensional objects.
The core components of a UV printer include a print head, UV lamps, and a conveyor or flatbed system. As the print head applies ink to the material, UV lamps immediately cure each layer, resulting in sharp, vibrant, and smudge-resistant prints.
Key Operational Logistics
Equipment Setup and Placement
UV printers require a controlled environment to operate efficiently. The equipment should be installed on a stable, level surface with adequate ventilation. While UV inks have low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, proper airflow reduces any residual odors and ensures operator safety.
Consider the following when setting up a UV printing operation:
– Space Requirements: Allow sufficient room for the printer, material handling, and curing zones.
– Power Supply: Ensure access to a stable electrical source compatible with the printer’s voltage and amperage needs.
– Environmental Controls: Maintain consistent temperature and humidity levels (typically 20–25°C and 40–60% RH) for optimal ink adhesion and curing.
Material Handling and Preparation
UV printing supports diverse substrates, but surface preparation is essential for print quality. Materials must be clean, dry, and free of oils or dust. Some surfaces may require pre-treatment (e.g., primers or corona treatment) to improve ink adhesion.
Logistics considerations:
– Implement a workflow for material inspection and cleaning before printing.
– Use compatible fixtures or vacuum tables to secure substrates during printing.
– Store materials in a climate-controlled area to prevent warping or moisture absorption.
Ink Management and Storage
UV inks are light-sensitive and must be stored away from direct sunlight and UV exposure to prevent premature curing. Follow these best practices:
– Store ink cartridges or bottles in closed, opaque containers.
– Maintain storage temperatures between 15–25°C.
– Rotate stock using a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to avoid expired inks.
Monitor ink usage and schedule regular maintenance to prevent clogs and ensure consistent print quality.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
UV Radiation Safety
UV printers emit ultraviolet light, which can pose health risks with prolonged exposure. Operators should:
– Never look directly at UV lamps during operation.
– Ensure safety interlocks and protective enclosures are functional.
– Use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as UV-blocking safety glasses when maintenance requires exposure.
Compliance with international safety standards such as IEC 62471 (Photobiological Safety of Lamps) is recommended.
Chemical Handling and Hazard Communication
Although UV inks are generally low in VOCs and non-flammable, they may contain acrylate monomers and photoinitiators that can cause skin or respiratory irritation.
To comply with OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) in the U.S. or CLP/GHS regulations in the EU:
– Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all inks and cleaning agents.
– Label containers properly.
– Train staff on safe handling, spill response, and emergency procedures.
Waste Disposal and Environmental Regulations
Used ink cartridges, cleaning wipes, and uncured ink residues are considered hazardous waste in many jurisdictions due to chemical content.
Compliance steps:
– Partner with licensed hazardous waste disposal providers.
– Follow local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S., Environment Agency in the UK).
– Avoid pouring ink or solvents down drains.
Recycling programs for cartridges and containers should be implemented where available.
Quality Control and Process Validation
To ensure consistent output and customer satisfaction, establish quality control protocols:
– Perform daily nozzle checks and calibration.
– Use color management software and定期校准 (periodic calibration) of printers.
– Conduct adhesion, scratch, and weather resistance tests on finished prints.
Document all quality checks and maintenance activities for traceability and compliance audits.
Training and Documentation
Staff must be trained on:
– Safe operation of UV printing equipment.
– Emergency shutdown procedures.
– Ink handling and waste management protocols.
Maintain up-to-date training records and standard operating procedures (SOPs). This documentation supports compliance with occupational health and safety standards such as ISO 45001 or ANSI/ASSP Z10.
Conclusion
UV printing offers significant advantages in speed, quality, and substrate versatility. However, successful implementation requires careful attention to logistics, safety, and regulatory compliance. By following this guide, businesses can optimize their UV printing operations while maintaining a safe, compliant, and environmentally responsible workflow.
In conclusion, understanding how UV printing works reveals its efficiency, precision, and versatility in modern printing applications. By using ultraviolet light to instantly cure or dry ink as it is applied to a surface, UV printing offers numerous advantages over traditional methods, including faster production times, reduced environmental impact due to lower VOC emissions, and the ability to print on a wide variety of materials such as plastic, glass, metal, and wood. The technology ensures high-quality, durable, and vibrant prints that are resistant to fading and scratching. As a result, UV printing has become a preferred choice across industries ranging from signage and packaging to custom product decoration. Its innovative approach to ink curing not only enhances print quality but also supports sustainable manufacturing practices, making UV printing a valuable advancement in digital printing technology.