The global laser cutting equipment market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision machining across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser cutting machine market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology and rising adoption of automation in manufacturing processes. Complementing this, Grand View Research valued the global industrial laser market at USD 13.2 billion in 2022, with expectations of continued growth due to enhanced cutting speed, accuracy, and energy efficiency offered by next-generation systems. As competition intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront, shaping innovation and defining industry standards in how laser cutting works—from beam generation and focusing mechanisms to CNC integration and material compatibility. The following analysis highlights the top nine manufacturers leading this technological evolution.
Top 9 How Does Laser Cutting Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Numerically controlled laser cutting technology, industrial machining
Website: mecanumeric.com
Key Highlights: How laser cutting systems work. CNC laser cutting uses a high-powered laser beam to heat the surface of the material to be cut until it melts or evaporates….
#2 Laser Cutting
Website: 3ds.com
Key Highlights: As its name implies, laser cutting is a digital subtractive technique that uses laser technology to cut or engrave a variety of materials….
#3 Laser
Website: reiner.de
Key Highlights: Metal cutting by laser combines high processing speeds with extremely precise cuts – no longer needing the usual tool shop expenditures known from presses….
#4 Laser Cutting Services
Website: techfoundry.ucdavis.edu
Key Highlights: Laser cutting is a precise subtractive manufacturing process that uses a high-powered laser to cut (through or engrave) a variety of sheet- ……
#5 8 Steps of the Laser Cutter Process (Laser Cutting)
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: A laser cutter uses a coherent light source to produce a collimated beam of light energy. It is then focused on a small spot on the surface of the material to ……
#6 Laser cutting
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: Laser cutting is a slitting process with which it is possible to cut metallic and non-metallic raw materials of different material thicknesses….
#7 What can laser cutting do? Everything you need to know about laser …
Website: seeedstudio.com
Key Highlights: Once the laser cutter received the file, the machine uses a laser beam to cut into or etch into the material on the cutting bed. Laser cutters ……
#8 How Does a Laser Cutting Machine Work
Website: ametals.com
Key Highlights: All laser cutting machines work in a similar way. It all starts with a laser source, which produces a powerful, consistent light that can be adjusted quickly ……
#9 How Does Laser Cutting Work?
Website: gemathis.com
Key Highlights: Laser cutting machines generate a ¾-inch wide laser beam. This beam is pushed through a nozzle, which contains compressed oxygen, nitrogen, or ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Does Laser Cutting Work
H2: 2026 Market Trends: How Does Laser Cutting Work?
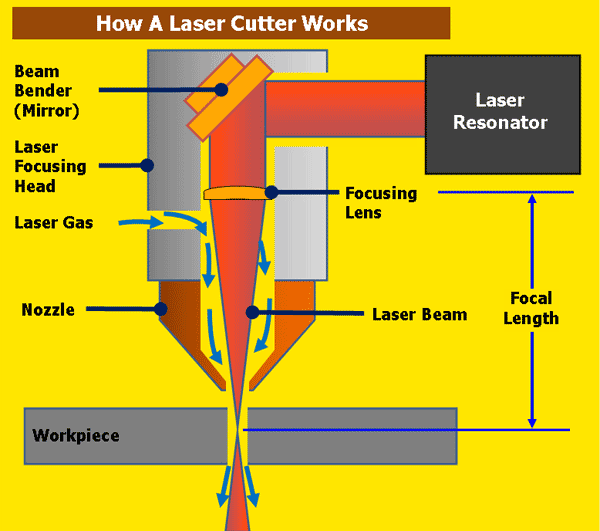
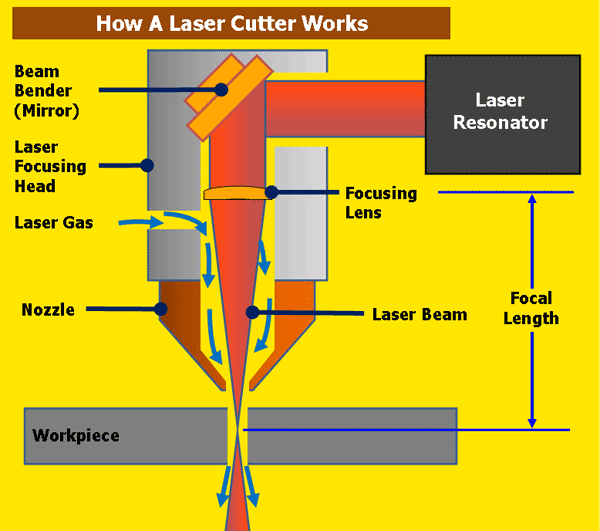
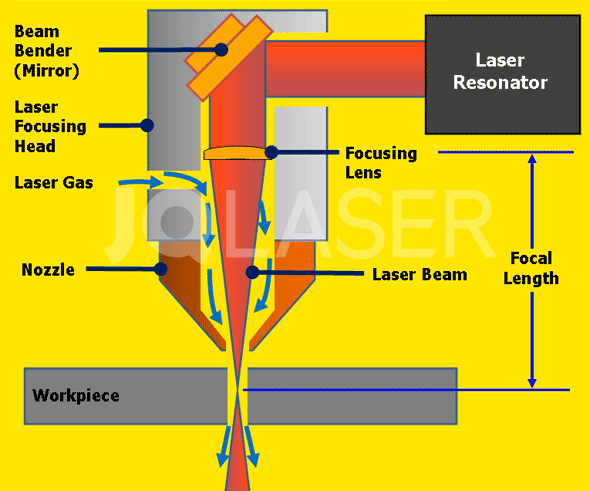
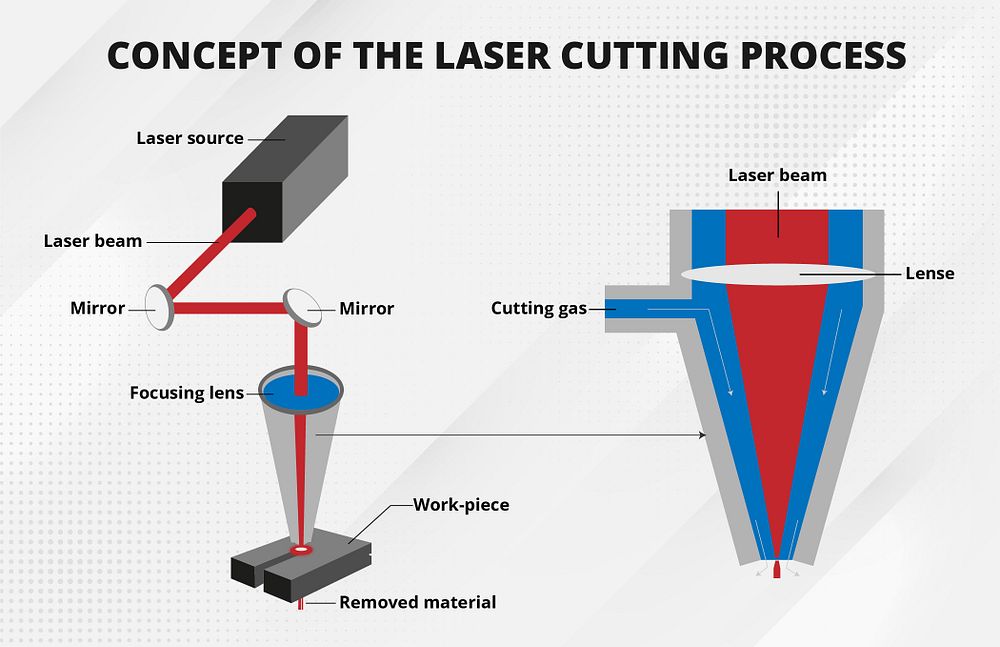
As we approach 2026, the laser cutting industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology, increased demand for precision manufacturing, and growing adoption across diverse sectors. Understanding how laser cutting works is essential to appreciating its expanding role in modern production environments. At its core, laser cutting uses a high-powered laser beam directed through optics and controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) systems to melt, burn, or vaporize materials, resulting in clean, precise cuts. The process typically involves three main components: a laser source (commonly CO2, fiber, or crystal lasers), a motion control system that guides the laser beam, and a nozzle that delivers assist gas to remove molten material and improve cut quality.
In 2026, several market trends are shaping the evolution and application of laser cutting technology. First, fiber laser adoption is accelerating due to its superior energy efficiency, lower maintenance requirements, and enhanced cutting speed—especially for reflective metals like aluminum and copper. Fiber lasers now dominate the market, accounting for over 70% of industrial laser sales, according to industry reports.
Second, automation and integration with Industry 4.0 systems are becoming standard. Smart factories are incorporating AI-driven monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time quality control into laser cutting systems. This shift not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces waste and downtime.
Third, there is a growing demand for portable and compact laser cutters in small and medium enterprises (SMEs), as well as in the education and prototyping sectors. These systems offer affordability and ease of use, broadening the accessibility of laser cutting technology.
Moreover, sustainability is emerging as a key driver. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing energy consumption and emissions, leading to the development of more eco-friendly laser systems with improved power-to-cut ratios and recyclable assist gases.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest market for laser cutting, fueled by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. However, North America and Europe are witnessing a resurgence in advanced manufacturing, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and medical device industries—sectors that require the high precision and repeatability laser cutting provides.
In summary, by 2026, the laser cutting market will be defined by smarter, faster, and more sustainable systems. As industries continue to prioritize precision, efficiency, and automation, the fundamental principles of how laser cutting works will remain central—but enhanced by digital innovation and green manufacturing practices.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Cutting Services (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser cutting services can significantly impact your product’s quality, cost, and time-to-market. While the technology offers precision and efficiency, several pitfalls—especially concerning quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection—can undermine your project. Being aware of these challenges helps in selecting the right partner and safeguarding your interests.
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
One of the most frequent issues when outsourcing laser cutting is inconsistent output due to weak or non-existent quality assurance protocols. Some suppliers may lack proper inspection tools, standardized procedures, or trained personnel to monitor tolerances, edge quality, and dimensional accuracy. This can result in parts that require rework, fail in assembly, or degrade final product performance—especially in high-precision industries like aerospace or medical devices.
Poor Material Handling and Contamination
Low-tier suppliers may not follow best practices in material handling, leading to scratches, oxidation, or contamination before or after cutting. For example, improper storage of sheet metal can introduce moisture or debris, which affects cut quality and surface finish. Without clear handling guidelines and clean work environments, even a high-quality laser cutter can produce subpar results.
Inaccurate or Outdated Equipment
Not all laser cutting machines are equal. Older or poorly maintained systems may suffer from beam misalignment, power fluctuations, or worn nozzles, resulting in inconsistent cuts, burrs, or thermal damage to materials. When sourcing, it’s crucial to verify the age, calibration status, and maintenance records of the equipment to ensure precision and repeatability.
Misalignment of Capabilities with Project Needs
Some suppliers may overpromise on capabilities—such as cutting thickness, speed, or material types—without the technical capacity to deliver. For instance, attempting to cut highly reflective materials like copper or aluminum with a CO₂ laser without proper settings can lead to poor edge quality or equipment damage. Always confirm that the provider’s technology (e.g., fiber vs. CO₂ laser) suits your specific material and tolerance requirements.
Lack of Transparency in Process Parameters
Reputable laser cutting providers document and optimize cutting parameters (power, speed, assist gas, focus position). However, some suppliers may use generic settings for all jobs, leading to compromised quality. A lack of transparency in how parameters are chosen can make it difficult to reproduce results or troubleshoot issues, especially during scale-up.
Insufficient Intellectual Property Protection
When sharing technical drawings, CAD files, or proprietary designs, you risk exposing sensitive IP. Many suppliers—especially in regions with weak IP enforcement—may not have confidentiality agreements (NDAs) in place or may reuse designs for other clients. Always ensure that a legally binding NDA is signed and clearly defines ownership, usage rights, and data handling procedures.
Data Security and Digital Vulnerabilities
Digital design files transmitted to suppliers can be vulnerable to cyber threats. If the provider lacks secure file transfer protocols, encryption, or cybersecurity policies, your IP could be intercepted or leaked. Ask about their data security measures, such as encrypted cloud storage, access controls, and secure communication channels.
Unverified Subcontracting Practices
Some laser cutting shops outsource work to third parties without informing the client. This not only breaks the chain of accountability but also increases IP exposure and reduces quality oversight. Always clarify whether the supplier performs work in-house and request transparency on subcontracting policies.
Absence of Traceability and Documentation
For regulated industries (e.g., automotive, medical), traceability of materials, processes, and inspections is critical. A lack of proper documentation—such as material certifications, cut logs, or inspection reports—can lead to compliance issues or failed audits. Ensure the supplier maintains detailed records and can provide them upon request.
Overlooking Post-Processing Requirements
Laser cutting often leaves behind burrs, slag, or heat-affected zones that require post-processing (e.g., deburring, sanding). Some suppliers may not include these steps in their quote or timeline, leading to unexpected delays or costs. Clarify whether finishing services are offered and included in the scope of work.
By identifying and addressing these common pitfalls early, businesses can mitigate risks, ensure high-quality output, and protect their intellectual property when sourcing laser cutting services. Due diligence, clear communication, and robust contractual safeguards are essential for a successful outsourcing relationship.
How Does Laser Cutting Work: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding the operational principles of laser cutting is essential, but equally important are the logistics and compliance aspects involved in deploying and operating such systems. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, efficient, and legally compliant laser cutting operations.
Equipment Selection and Installation
Choosing the right laser cutting system requires evaluating technical specifications against production needs. Factors include laser type (CO₂, fiber, or crystal), power output, cutting bed size, and material compatibility. Ensure the selected machine fits within available floor space and can be properly integrated into existing workflows. Installation should be conducted by qualified technicians, following manufacturer guidelines. This includes setting up proper power supplies, cooling systems, exhaust ventilation, and network connectivity for control software. Site preparation must also consider floor load capacity, environmental controls (temperature and humidity), and access for maintenance.
Facility Requirements and Layout Planning
Laser cutting operations demand dedicated space with specific environmental and safety controls. The workspace must accommodate the machine, material handling systems (e.g., loading/unloading tables or automated feeders), and safe clearance for operators. Adequate ventilation and fume extraction systems are mandatory to remove hazardous particulates and gases produced during cutting. Facilities should also provide sufficient lighting, emergency exits, and clear floor markings for safety zones. Consider noise levels and implement acoustic shielding if necessary. Layout planning should optimize material flow to minimize handling and reduce cycle times.
Safety Protocols and Operator Training
Laser cutting involves significant hazards, including high-intensity radiation, fire risks, and exposure to fumes. Strict safety protocols must be enforced. Operators must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety glasses with the correct optical density rating. Interlock systems on machine enclosures should prevent operation when doors are open. Comprehensive training programs must cover machine operation, emergency procedures, maintenance routines, and hazard recognition. Only certified personnel should operate or service laser equipment. Regular safety drills and refresher training ensure ongoing compliance and awareness.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Laser cutting operations must comply with national and international regulations. Key standards include:
– ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers) in the U.S.
– IEC 60825 (Safety of Laser Equipment) internationally.
– OSHA regulations regarding workplace safety and hazardous emissions.
– NFPA 70 (NEC) for electrical installations.
In addition, local environmental agencies may regulate air emissions, requiring permits or filtration certifications. Machines must carry proper laser classification labels (typically Class 1 or Class 4 with safety enclosures). Documentation, including risk assessments, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and maintenance logs, must be maintained for audits.
Material Handling and Waste Management
Proper handling of raw materials and byproducts is crucial for efficiency and compliance. Materials such as metals, plastics, and composites must be stored according to flammability and reactivity guidelines. Cut-offs and slag waste should be segregated and disposed of following environmental regulations. For instance, metal dust may be recyclable, while contaminated filters or hazardous fumes require special disposal. Implement a clear labeling and tracking system for waste streams. Fire prevention measures, including Class D extinguishers for metal fires, should be readily available.
Maintenance and Calibration Schedules
Regular maintenance ensures operational accuracy, prolongs equipment life, and maintains safety compliance. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for tasks such as lens and mirror cleaning, alignment checks, nozzle inspections, and coolant replacement. Calibration of the laser beam and motion control systems should be performed periodically to ensure cut quality and dimensional accuracy. Keep detailed service records and schedule downtime for preventive maintenance to avoid unplanned disruptions.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive documentation to support compliance and traceability. Required records include:
– Equipment manuals and safety data sheets (SDS) for materials.
– Operator training certifications.
– Maintenance and calibration logs.
– Emission test results and fume extraction system checks.
– Incident reports and corrective actions.
These documents are essential for internal audits, regulatory inspections, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Develop and implement an emergency response plan tailored to laser cutting operations. This should include procedures for laser fires, power failures, fume exposure, and mechanical malfunctions. Clearly mark emergency stops, fire extinguishers, and eyewash stations. Conduct regular drills and ensure all personnel know evacuation routes. Post emergency contacts and response protocols in visible locations throughout the facility.
In conclusion, laser cutting works by using a high-powered laser beam focused through a lens or curved mirror onto a material, which it melts, burns, or vaporizes to create precise and clean cuts. The process is typically controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) systems, allowing for high accuracy and repeatability in complex designs. The type of laser—CO2, fiber, or crystal—depends on the material being cut, with each offering advantages for specific applications. With its ability to cut a wide range of materials including metal, plastic, wood, and acrylic, laser cutting has become an essential technology in manufacturing, prototyping, and fabrication industries. Its efficiency, precision, and automation capabilities make it a preferred method for both small-scale projects and large-scale industrial production.