The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-based surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the market size was valued at USD 358.2 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.4% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is attributed to the technology’s advantages over traditional cleaning methods—such as reduced waste, minimal substrate damage, and no need for chemical solvents. As industries prioritize sustainability and operational efficiency, manufacturers of laser cleaning systems are scaling innovation to meet evolving performance standards. This dynamic landscape has given rise to a competitive field of players, with the top nine companies leading in R&D investment, product diversification, and global market reach.
Top 9 How Does Laser Cleaning Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
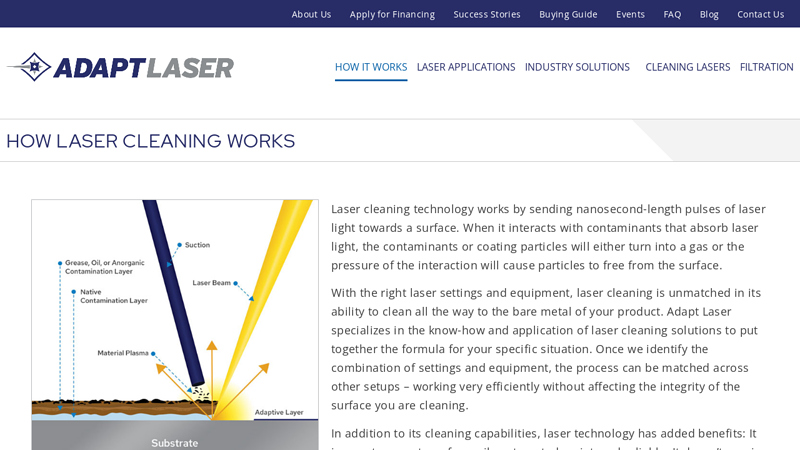
#1 How Laser Cleaning Works
Website: adapt-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning technology works by sending nanosecond-length pulses of laser light towards a surface. When it interacts with contaminants that absorb laser ……
#2 What are Laser Cleaning Machines?
Website: dustlessblasting.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is a non-contact cleaning technology that uses laser beams to remove contaminants, rust, paint, and other surface coatings. A ……
#3 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#4 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: The laser process removes dirt and cover layers without leaving any residue only by means of bundled light. No chemicals (as with washing or pickling) or other ……
#5 How Laser Cleaning Works
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is a modern surface preparation method that utilizes focused laser beams to efficiently remove contaminants, coatings, and unwanted materials ……
#6 How Does Laser Cleaning Work in 5 Steps
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning is an eco-friendly process used to remove rust, paint, oxide and other contaminants from metal surfaces….
#7 What Is Laser Cleaning? Advantages & How It Works
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning uses a technique known as laser scanning, which rapidly directs or “scans” a laser beam along a path or across a wider zone. This means that the ……
#8 Laser cleaning
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: How to achieve the perfect weld seam: laser cleaning allows you to very gently clean metal components of dirt, as well as oxidation and functional layers….
#9 Laser cleaning frequently asked questions
Website: laserforcleaning.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning uses concentrated laser radiation to evaporate impurities from the layer. Ultra-short laser pulses (μs-ms) are applied to the contaminants, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Does Laser Cleaning Work

H2: How Does Laser Cleaning Work in the Context of 2026 Market Trends?
As the industrial and manufacturing sectors evolve toward greater automation, sustainability, and precision, laser cleaning has emerged as a transformative surface treatment technology. By 2026, the adoption of laser cleaning is expected to accelerate significantly due to advancements in laser efficiency, falling equipment costs, and increasing regulatory pressure to eliminate environmentally harmful cleaning methods. Understanding how laser cleaning works is essential to appreciating its growing market relevance.
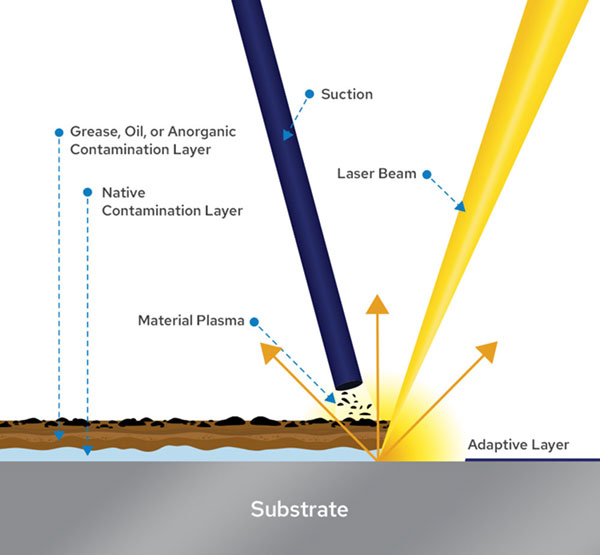
Laser cleaning operates on the principle of laser ablation. A high-intensity pulsed laser beam is directed at the surface of a material, where it rapidly heats and vaporizes contaminants such as rust, paint, oil, oxides, or coatings. The energy from the laser is absorbed by the contaminant layer but reflected or transmitted by the underlying substrate (e.g., metal, stone, or composite), ensuring selective removal without damaging the base material. The process generates minimal waste—typically just particulate matter that can be captured by integrated filtration systems—making it an eco-friendly alternative to sandblasting or chemical solvents.
By 2026, key market trends are enhancing the functionality and appeal of laser cleaning systems:
-
Increased Automation Integration: Laser cleaning is being seamlessly integrated into robotic production lines, especially in automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. Its precision and repeatability align with Industry 4.0 standards, supporting smart factories.
-
Portable and Handheld Systems: The demand for flexible, on-site cleaning solutions has driven innovation in compact, user-friendly laser devices. These are gaining popularity in heritage restoration, shipbuilding, and maintenance operations.
-
Sustainability Regulations: With global emphasis on reducing VOC emissions and hazardous waste, industries are shifting toward non-chemical, dry cleaning methods. Laser cleaning meets strict environmental regulations, positioning it as a future-proof technology.
-
Improved Laser Sources: Advances in fiber laser technology have led to higher peak powers, better beam quality, and longer system lifespans. These improvements enhance cleaning speed and efficiency, making laser systems more cost-competitive.
-
AI and Real-Time Monitoring: Emerging systems incorporate machine learning algorithms and sensors to optimize laser parameters in real time, ensuring consistent results and minimizing human error.
In summary, by 2026, the market growth of laser cleaning is being fueled by its clean, precise, and automated operation. The underlying mechanism—targeted laser ablation—enables superior surface preparation and maintenance across diverse applications, aligning perfectly with the industrial world’s move toward green manufacturing and digital integration.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Cleaning Technology: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser cleaning systems, businesses often focus on performance and cost, overlooking critical aspects related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP). Failing to address these can lead to operational failures, legal disputes, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Sourcing
Many low-cost laser cleaning solutions on the market use substandard components—such as low-grade optics, unreliable cooling systems, or poor laser diodes—which degrade quickly under industrial use. Buyers may be attracted by competitive pricing but later face frequent breakdowns, inconsistent cleaning performance, and high maintenance costs. It’s crucial to verify the origin and quality certifications of core components and request third-party test reports or reliability data before procurement.
Insufficient Verification of Laser Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate key performance metrics like laser power, pulse energy, beam quality (M² factor), or cleaning speed. Misleading specifications can lead to underperforming systems that fail to meet production needs. Always demand independent verification through technical documentation, on-site demonstrations, or trial runs under real-world conditions. Be wary of vague claims and ensure specifications are backed by measurable, standardized testing.
Ignoring Safety and Compliance Standards
Laser cleaning systems must comply with international safety standards such as IEC 60825 (laser safety) and regional regulations like CE, FCC, or RoHS. Sourcing from vendors who lack proper certifications can expose buyers to safety hazards and regulatory penalties. Ensure the supplier provides full compliance documentation and that safety features—like emergency stops, interlocks, and protective enclosures—are integrated and tested.
Underestimating After-Sales Support and Serviceability
High-quality laser systems require ongoing maintenance, spare parts, and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers with limited local presence or poor service networks can result in extended downtimes. Evaluate the vendor’s service infrastructure, warranty terms, and availability of trained technicians. Avoid vendors who outsource critical support or fail to offer long-term service agreements.
Falling into Intellectual Property Infringement Traps
A major risk when sourcing from manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement is purchasing systems that infringe on patented technologies. Some suppliers reverse-engineer or clone proprietary laser designs, putting the end-user at risk of legal action, especially in jurisdictions with strong IP laws. Always conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio, request proof of legitimate licensing, and include IP indemnification clauses in contracts.
Relying on Vague or Incomplete Technical Documentation
Poor documentation—missing operation manuals, unclear maintenance procedures, or absent software interfaces—hampers integration and troubleshooting. This is common with low-cost suppliers who prioritize speed-to-market over product maturity. Demand comprehensive technical packages, including software SDKs, error code lists, and system schematics, before finalizing purchases.
Conclusion
To mitigate risks in sourcing laser cleaning technology, prioritize vendors with proven quality control, transparent specifications, robust safety compliance, and clear IP legitimacy. Conduct thorough technical audits, request customer references, and consider third-party inspections. Investing time in due diligence upfront prevents costly setbacks and ensures reliable, legally sound deployment.

How Does Laser Cleaning Work: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Laser cleaning is an advanced, non-abrasive method used to remove contaminants, oxides, coatings, and other unwanted materials from surfaces using high-intensity laser beams. As industries increasingly adopt this eco-friendly and precise cleaning technology, understanding the logistics and compliance aspects becomes essential for safe and efficient operation.
Understanding the Laser Cleaning Process
Laser cleaning works by directing a focused laser beam at the surface to be cleaned. The laser energy is absorbed by the contaminant layer, causing rapid thermal expansion and vaporization. The underlying substrate typically reflects or absorbs less energy, minimizing damage. This selective ablation effectively removes rust, paint, oil, and other residues without using chemicals or abrasive media.
Equipment Logistics and Setup
Proper logistics for laser cleaning operations begin with the selection and transportation of equipment. Laser cleaning systems vary in size—from handheld units to large automated industrial machines. Key logistical considerations include:
- Transportation and Handling: Ensure equipment is packed securely with protective casing. Follow manufacturer guidelines for temperature, humidity, and shock resistance during shipping.
- Installation Site Requirements: The operation area must have sufficient space, power supply (typically 3-phase electricity), ventilation, and cooling provisions.
- Accessories and Consumables: While laser cleaning has minimal consumables, spare parts (e.g., protective lenses, cooling units) should be stocked based on usage frequency and maintenance schedules.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Laser cleaning systems are classified under international laser safety standards, primarily IEC 60825. Compliance is crucial to protect personnel and ensure legal operation.
Laser Safety Classification
Most industrial laser cleaners fall under Class 4—high-power lasers capable of causing skin and eye injuries, as well as fire hazards. Required safety measures include:
- Installation of interlocks and emergency stop systems
- Use of laser safety enclosures or barriers
- Mandatory wearing of laser-protective eyewear with appropriate optical density (OD)
- Designation of controlled access zones with warning signs
Workplace Regulations
Operators must comply with local occupational health and safety regulations, such as OSHA (U.S.), HSE (UK), or equivalent bodies. Key actions include:
- Conducting a risk assessment before deployment
- Implementing a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) role where required
- Training personnel on laser hazards, emergency procedures, and proper operation
Environmental Compliance
One of the advantages of laser cleaning is its minimal environmental impact—no chemical solvents or secondary waste streams. However, fumes and particulates generated during ablation require attention:
- Fume Extraction Systems: Use high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration units to capture airborne particles, especially when removing hazardous coatings like lead-based paint.
- Waste Disposal: Collected debris may be classified as hazardous waste depending on substrate and contaminant. Follow local environmental regulations for disposal.
- Emissions Monitoring: Regularly inspect and maintain fume extraction to ensure compliance with air quality standards (e.g., EPA, REACH, RoHS).
Operational Best Practices
To ensure compliance and efficiency:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop documented workflows for setup, operation, shutdown, and maintenance.
- Maintenance Logs: Keep records of system performance, filter changes, and laser calibration.
- PPE Compliance: Enforce the use of protective gear including gloves, face shields, and flame-resistant clothing in high-risk environments.
Training and Certification Requirements
Personnel operating laser cleaning systems should undergo formal training covering:
- Laser physics and beam hazards
- Machine-specific operation and troubleshooting
- Emergency response and first aid
- Regulatory compliance standards
Certification from recognized bodies (e.g., Laser Institute of America) may be required depending on jurisdiction and application.
Conclusion
Laser cleaning offers a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional cleaning methods, but its deployment requires careful attention to logistics and compliance. By following safety standards, maintaining proper documentation, and training personnel, organizations can leverage this technology effectively while meeting all regulatory obligations.
Conclusion: How Does Laser Cleaning Work?
Laser cleaning is an advanced, non-abrasive technique that utilizes high-intensity laser beams to remove contaminants such as rust, paint, oxides, and coatings from various surfaces. The process works on the principle of laser ablation: when the laser beam is directed at a contaminated surface, the energy is absorbed by the unwanted layer, causing it to heat up rapidly, vaporize, and be ejected from the substrate. Because different materials absorb laser energy at different rates, the underlying base material remains largely unaffected if the correct settings—such as wavelength, pulse duration, and energy density—are used.
This method offers numerous advantages over traditional cleaning techniques, including precision, environmental friendliness (as it generates no chemical waste or secondary pollutants), and minimal damage to the substrate. It is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, conservation, and mold maintenance.
In summary, laser cleaning works by selectively removing surface contaminants through controlled laser-induced ablation, offering a clean, efficient, and sustainable alternative to mechanical or chemical cleaning methods. As technology advances, its accessibility and applications continue to grow, making it a promising solution for modern industrial and preservation needs.