The global laser beam welding (LBW) market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, high-speed joining technologies across the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 4.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing, and the need for energy-efficient and clean welding processes. As industries prioritize accuracy and production efficiency, laser beam welding has emerged as a preferred solution for critical applications requiring minimal heat distortion and superior joint quality. With key players investing heavily in R&D and next-generation laser systems, the competitive landscape is rapidly evolving. In this dynamic environment, identifying the top manufacturers shaping innovation in laser beam welding technologies becomes essential for stakeholders across the industrial spectrum.
Top 9 How Does Laser Beam Welding Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 What Is Laser Welding and How Does the Technique Work?
Website: esab.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding technology uses a laser beam as a high-concentrated heat source to join materials. The applied laser beam heats and melts the edges of the ……
#2 What is Laser Welding and How Does It Work?
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: It uses a high-energy laser beam to fuse metals together, creating a strong metallurgical bond. As the energy from the laser beam is absorbed by ……
#3 NIST Research Sparks New Insights on Laser Welding
Website: nist.gov
Key Highlights: This high-speed video shows a weld made with 360 watts of focused laser power. The laser (not visible) heats the metal until it melts and forms ……
#4 Laser Welding Explained
Website: fractory.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding or laser beam welding (LBW) is a process that uses a concentrated heat source in the form of a laser to melt the materials, which fuse together ……
#5 Laser Welders
Website: dnelaserusa.com
Key Highlights: How Laser Welding Works. Laser welding is a high-precision welding technique that uses a focused laser beam to join pieces of metal together….
#6 An Introduction to Laser Welding
Website: camvaceng.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a versatile joining process to fuse materials through the application of a highly focussed beam of light (a laser)….
#7 Laser welding
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: A laser beam can join metal in different ways. It can join workpieces at the surface or produce deep weld seams. It can be combined with conventional welding ……
#8 Learning about laser welding systems, innovations, and hazards
Website: thefabricator.com
Key Highlights: “People should take a laser welding training course to build the skills needed for safe, precise welding in industries like automotive, medical, ……
#9 [PDF] Process Specification and Operator Qualification for Laser Beam …
Website: pubs.aws.org
Key Highlights: The information contained in this Process Specification and Operator Qualification for Laser Beam Welding has been compiled and reviewed by the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Does Laser Beam Welding Work
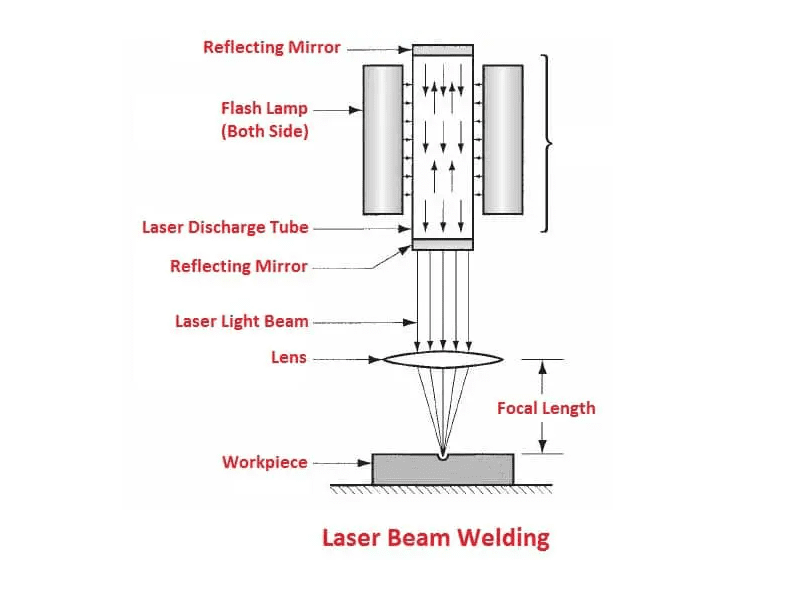
H2: 2026 Market Trends for How Does Laser Beam Welding Work
As we approach 2026, the understanding and dissemination of technical processes such as laser beam welding are evolving rapidly due to advancements in industrial automation, digital learning platforms, and increased demand for precision manufacturing. While “How Does Laser Beam Welding Work” is an educational and technical inquiry, market trends are shaping how this knowledge is produced, consumed, and applied across industries.
-
Increased Demand Driven by Industry 4.0 and Automation
By 2026, the global manufacturing sector is projected to deepen its integration of smart technologies under Industry 4.0. Laser beam welding (LBW), known for its precision, speed, and minimal heat distortion, is being widely adopted in automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. This growing industrial reliance on LBW is increasing public and professional interest in understanding how the technology works. As a result, content explaining the fundamentals of LBW—including beam generation, material interaction, and weld pool dynamics—is seeing higher demand in both academic and vocational training markets. -
Growth in Digital and Interactive Educational Content
Market trends indicate a shift toward immersive and interactive learning tools. By 2026, AR (augmented reality), VR (virtual reality), and 3D simulations are expected to dominate technical education platforms. Companies and educational institutions are investing in visual explainers and animated tutorials that break down complex processes like laser beam welding. These tools help users visualize key components such as the laser source (CO₂, fiber, or disk lasers), beam focusing optics, and shielding gas use—making the learning curve less steep for engineers and technicians. -
Expansion of Online Learning and Skill Development Platforms
With the rise of platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and specialized engineering portals, there is a surge in demand for concise, high-quality content explaining laser welding principles. By 2026, microlearning modules focusing on “How Does Laser Beam Welding Work” are expected to become standard in vocational training programs. These modules often integrate real-world case studies, performance metrics, and comparisons with traditional welding methods like MIG or TIG, catering to a global audience of students, hobbyists, and professionals. -
Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As industries move toward greener manufacturing practices, laser beam welding is gaining attention for its energy efficiency and reduced material waste. Market analysis shows that by 2026, content explaining how LBW contributes to sustainable production—through precise energy delivery and lower emissions—will be increasingly integrated into technical overviews. This trend is shaping not only how the process is taught but also how it is marketed and adopted. -
Regional Market Growth and Localization of Technical Content
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and South Korea, are investing heavily in advanced manufacturing. This regional growth is fueling demand for localized, multilingual content that explains laser beam welding in accessible terms. By 2026, expect to see more region-specific educational materials, translated guides, and government-backed training initiatives focusing on LBW technology and its underlying principles. -
Integration with AI and Predictive Maintenance Training
A key trend by 2026 is the convergence of laser welding systems with AI-driven monitoring and predictive maintenance. As a result, educational content is expanding beyond the basic mechanics of LBW to include how sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time feedback optimize weld quality. This shift is redefining what it means to “understand” how laser beam welding works, now encompassing system intelligence and data analytics.
Conclusion:
The 2026 market landscape for “How Does Laser Beam Welding Work” reflects a broader transformation in technical education and industrial training. The focus is no longer just on static explanations but on dynamic, application-oriented learning experiences. As laser beam welding becomes more central to high-tech manufacturing, the market for clear, accurate, and engaging educational content will continue to expand, driven by innovation, sustainability goals, and global skills development needs.
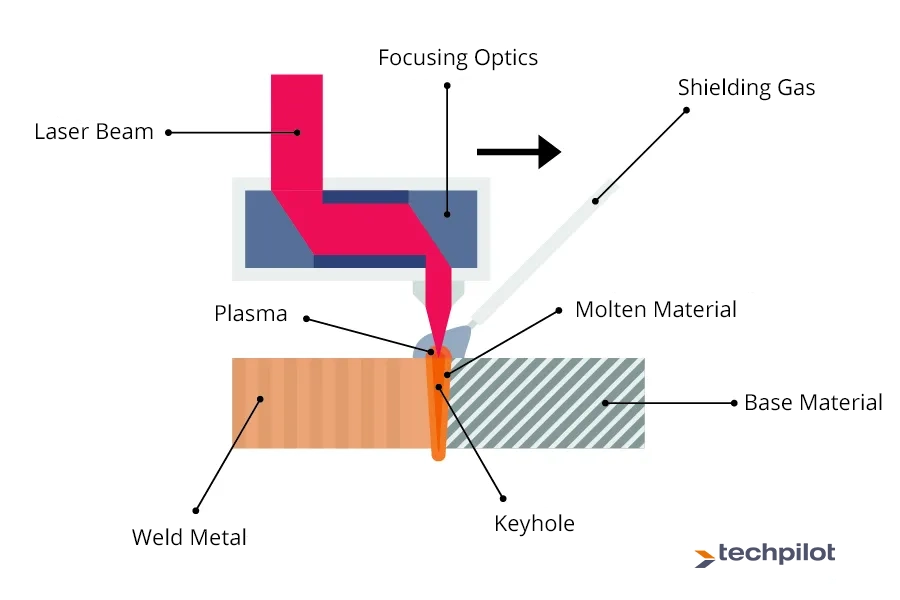
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Beam Welding: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
When sourcing laser beam welding (LBW) technology or services, businesses often focus on cost and delivery timelines but overlook critical aspects related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. These oversights can lead to significant technical, legal, and financial setbacks. Below are common pitfalls related to both quality and IP that should be carefully addressed during the sourcing process.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Process Validation and Documentation
One of the most frequent quality issues arises from insufficient validation of the LBW process by the supplier. Laser welding parameters—such as power density, beam focus, travel speed, and shielding gas—are highly sensitive and require precise control. Sourcing from a vendor without comprehensive process documentation (e.g., Welding Procedure Specifications, WPS) or lack of process qualification (e.g., according to ISO 15614 or AWS D17.1) increases the risk of inconsistent weld quality, porosity, cracking, or incomplete penetration. Always require documented evidence of process validation and access to in-process monitoring data.
Poor Material and Joint Preparation Oversight
Laser beam welding demands exceptionally clean and precisely aligned joints. Contamination (oils, oxides, moisture) or misalignment can lead to defects. Suppliers may cut corners in cleaning procedures or fixturing, especially when under cost pressure. Ensure that material handling and joint preparation protocols are clearly defined in the sourcing contract and subject to audit. Lack of control at this stage often results in failed inspections or field failures.
Insufficient In-Process and Post-Weld Quality Control
Laser welding processes benefit from real-time monitoring systems (e.g., seam tracking, melt pool monitoring, back-reflectivity sensors). However, many third-party vendors do not invest in such systems or fail to provide data logs. Sourcing without demanding access to real-time quality data or non-destructive testing (NDT) reports (e.g., X-ray, ultrasonic testing) exposes buyers to latent defects. Define clear quality control benchmarks and data-sharing requirements in procurement agreements.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Ambiguous Ownership of Process-Specific IP
The development of a tailored laser welding procedure for a unique component may involve significant innovation. Without clear contractual terms, disputes can arise over who owns the IP—the buyer, the supplier, or both. For example, custom beam oscillation patterns, specialized fixturing, or adaptive control algorithms developed during prototyping might be claimed by the supplier. Always specify IP ownership in sourcing contracts, particularly for process innovations directly tied to your product design.
Unprotected Reverse Engineering and Knowledge Transfer
Laser welding parameters and process know-how are often considered trade secrets. When outsourcing, there is a risk that suppliers may reverse-engineer your components or extract proprietary information to serve competitors. Ensure that non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are comprehensive and that access to sensitive design data is limited to a need-to-know basis. Consider geographic restrictions or exclusivity clauses to mitigate competitive risks.
Use of Third-Party Patented Technologies Without Licensing
Some laser welding systems or techniques (e.g., remote laser welding, hybrid laser-arc processes) are protected by patents. A supplier might use such technologies without proper licensing, exposing your company to indirect infringement liability. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s equipment and methods to confirm they have the necessary licenses. Include indemnification clauses in contracts to shift liability in case of IP disputes.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls during the sourcing phase, organizations can ensure reliable, high-performance laser welding outcomes while safeguarding their competitive advantages and legal standing.
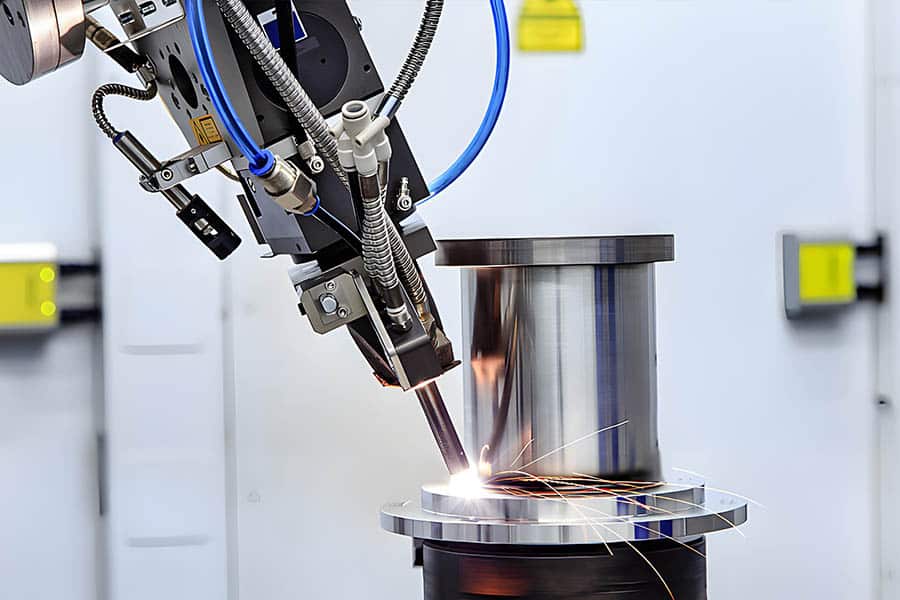

How Does Laser Beam Welding Work: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Laser Beam Welding (LBW) is a high-precision manufacturing process that uses a concentrated laser beam to join materials. Implementing LBW requires careful attention to equipment logistics, safety protocols, and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant operation of laser welding systems.
Equipment Logistics and Setup
Proper planning for the physical installation and integration of laser welding systems is essential for efficient operations.
- Space Requirements: Ensure adequate floor space for the laser source, workpiece handling system (e.g., robotic arm or CNC table), fume extraction unit, and control panel. Maintain clear access routes for maintenance and emergency egress.
- Power Supply: Verify that the facility provides stable, high-capacity electrical service matching the laser system’s voltage, phase, and amperage requirements. Consider backup power or surge protection for critical operations.
- Cooling Systems: Most high-power lasers require chiller units to prevent overheating. Plan for proper coolant lines, drainage, and ventilation for heat dissipation.
- Gas Supply: LBW often uses shielding gases (e.g., argon, helium, or nitrogen). Install gas lines with pressure regulators and leak detection systems. Store compressed gas cylinders securely in ventilated areas.
- Fume Extraction: Install high-efficiency local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems near the weld zone to capture hazardous airborne contaminants generated during welding.
Safety Protocols and Operator Training
Laser welding poses significant safety hazards, necessitating comprehensive training and protective measures.
- Laser Safety Classification: Confirm the laser’s safety class (typically Class 4 for industrial welding). Implement controls per ANSI Z136.1 or IEC 60825 standards.
- Protective Enclosures: Operate the laser within interlocked enclosures that halt the beam if opened. Use laser-resistant viewing windows with appropriate optical filters.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Require operators to wear laser safety goggles with the correct optical density for the laser wavelength (e.g., 1064 nm for Nd:YAG lasers), flame-resistant clothing, and face shields when appropriate.
- Training and Certification: Train all personnel on laser hazards, emergency procedures, and system operation. Maintain records of safety training and certifications.
- Beam Path Control: Ensure the beam path is enclosed or shielded to prevent accidental exposure. Use beam stops and alignment tools to minimize stray reflections.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
LBW operations must adhere to local, national, and international regulations to ensure workplace safety and environmental protection.
- OSHA Compliance (U.S.): Follow OSHA standards for general industry (29 CFR 1910), including requirements for machine guarding (1910.212), hazard communication (1910.1200), and respiratory protection (1910.134).
- Laser Safety Standards: Comply with ANSI Z136.1 (Safe Use of Lasers) and applicable sections of IEC 60825 (International Electrotechnical Commission).
- Air Quality and Emissions: Monitor and control fumes and particulates using certified filtration systems. Comply with EPA or local air quality regulations (e.g., NESHAP for metalworking).
- Hazardous Waste Handling: Collect and dispose of welding residues, filters, and coolant waste in accordance with RCRA or equivalent environmental regulations.
- Noise Exposure: Assess noise levels from cooling systems and automation; provide hearing protection if levels exceed permissible exposure limits (e.g., OSHA’s 85 dB TWA).
Maintenance and Documentation
Regular maintenance and detailed record-keeping support operational reliability and compliance audits.
- Preventive Maintenance: Follow manufacturer-recommended schedules for optics cleaning, laser alignment, coolant replacement, and system calibration.
- Inspection Logs: Maintain logs for safety interlocks, fume extractors, and emergency stop functions. Document all maintenance and repairs.
- Compliance Audits: Conduct periodic internal audits to verify adherence to safety and environmental regulations. Keep records of training, inspections, and incident reports.
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a qualified LSO to oversee laser safety programs, conduct risk assessments, and manage compliance efforts.
By addressing these logistical and compliance aspects, organizations can ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant laser beam welding operations.
Conclusion: How Does Laser Beam Welding Work?
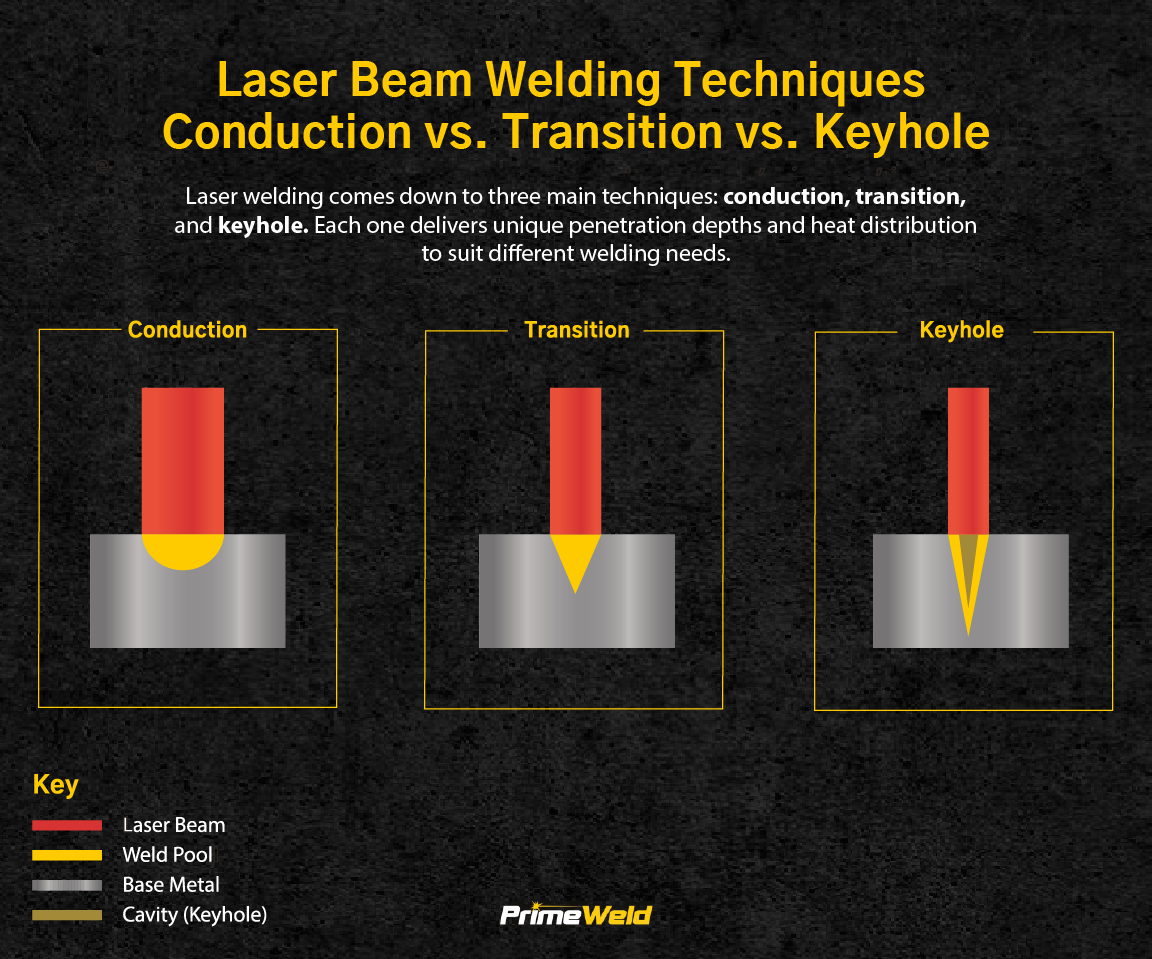
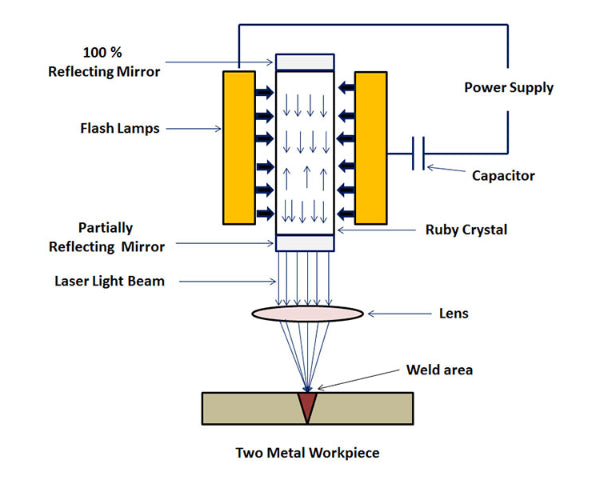
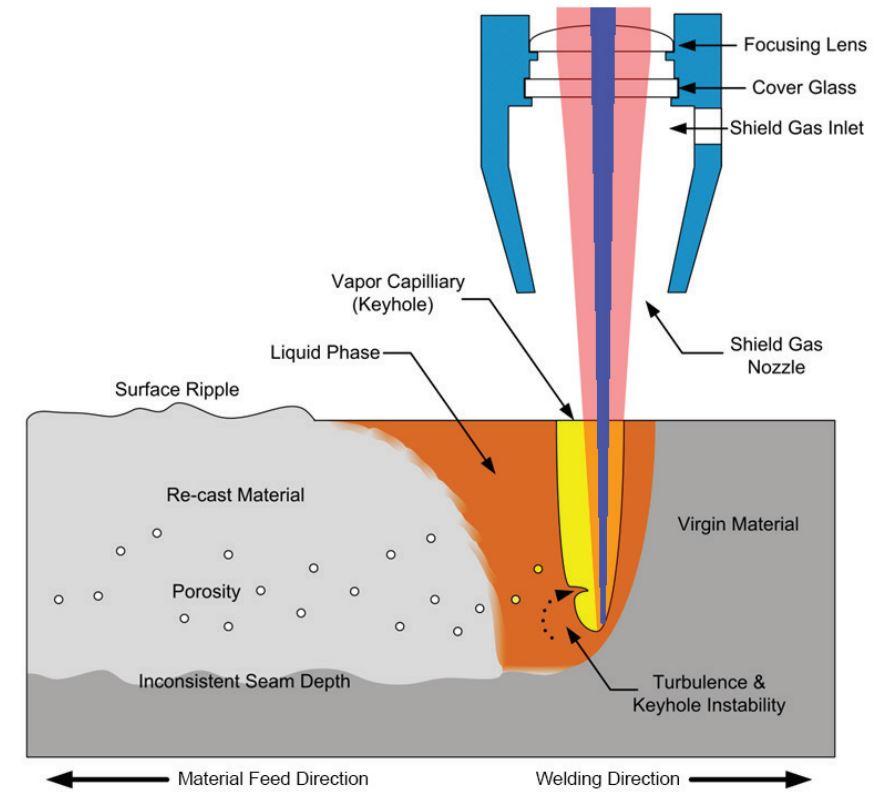
Laser beam welding (LBW) is a highly precise and efficient welding process that utilizes a concentrated beam of laser light to join materials. The process works by focusing a high-powered laser beam onto a small area of the workpiece, generating intense heat that melts and fuses the materials together. This is typically done in a controlled environment, often with the assistance of shielding gases to prevent oxidation and ensure weld integrity.
The key components of LBW include a laser source (commonly CO₂, Nd:YAG, or fiber lasers), an optical system to focus the beam, and a motion control system to guide the laser along the weld path. The process offers several advantages, such as deep penetration, narrow weld seams, minimal heat-affected zones, and high welding speeds, making it ideal for applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
In conclusion, laser beam welding works by harnessing the energy of coherent light to produce a precise and controllable heat source, enabling clean, strong, and repeatable welds in a variety of materials. Its accuracy and automation capabilities make it a vital technology in modern manufacturing.



![[PDF] Process Specification and Operator Qualification for Laser Beam ...](https://www.sohoinchina.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/pdf-process-specification-and-operator-qualification-for-laser-beam-197.png)

