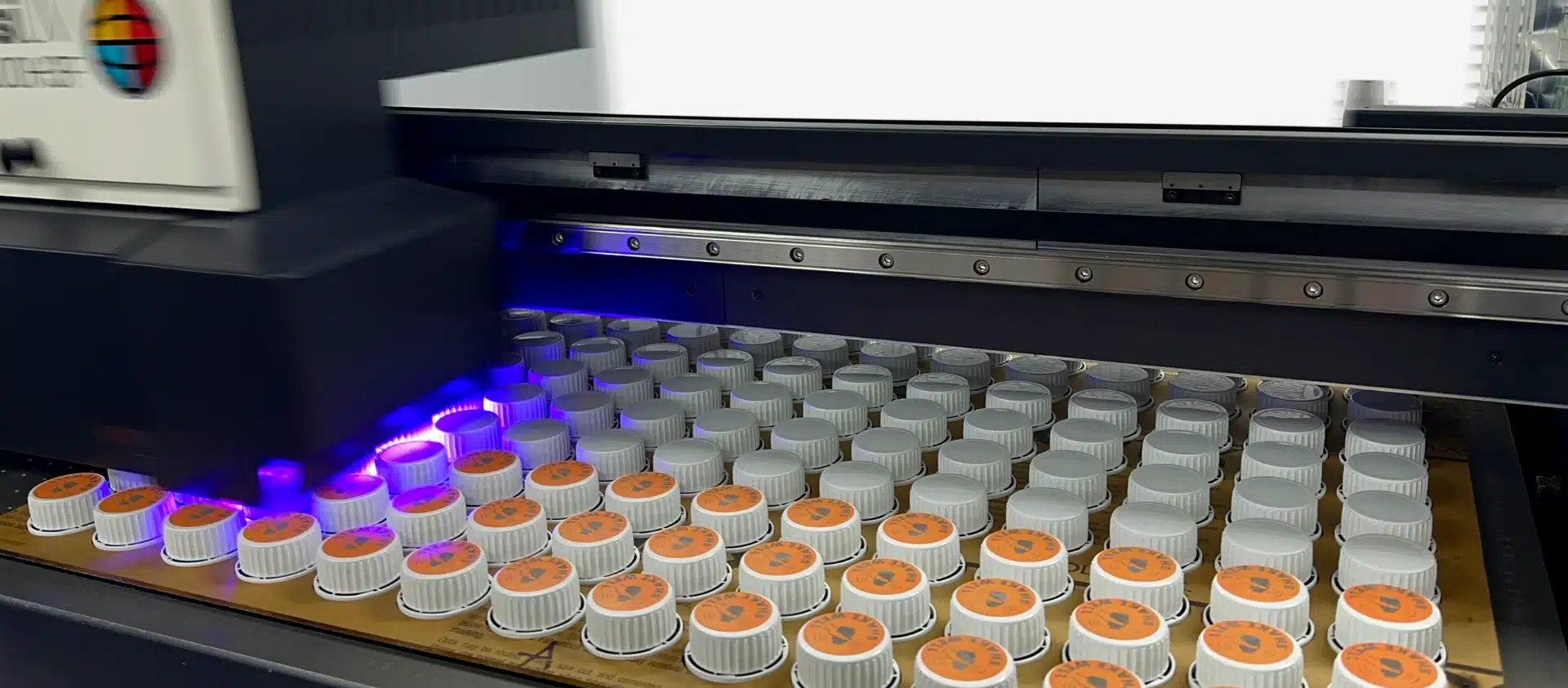
The UV printer market has experienced robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-speed, energy-efficient printing solutions across industries such as packaging, signage, and textiles. According to Grand View Research, the global UV printing market was valued at USD 10.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in UV-curable inks, increasing adoption of digital printing technologies, and a shift toward sustainable printing methods with lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. As industrial and commercial users prioritize precision, durability, and operational efficiency, manufacturers are innovating rapidly to enhance printhead technology, curing systems, and software integration. In this competitive landscape, nine key players have emerged as leaders in developing UV printers that exemplify cutting-edge engineering and performance—shaping the future of digital printing.
Top 9 How Does A Uv Printer Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 The Ins And Outs Of An LED UV Printing System
Website: bbpress.co.uk
Key Highlights: This printer apart from the competition is its unique UV curing technology and it allows you to print directly onto numerous different materials, in record ……
#2 UV Printing
Website: rolanddg.eu
Key Highlights: UV digital printing speeds up the print production process by instantly curing specially formulated UV inks on a vast range of materials using UV lamps….
#3 EUV lithography systems – Products
Website: asml.com
Key Highlights: Using extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light, our NXE and EXE systems deliver high-resolution lithography and make mass production of the world’s most advanced ……
#4 Debunking UV Printing Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
Website: rolanddga.com
Key Highlights: UV digital printing speeds up the print production process by instantly curing specially formulated UV inks using UV lamps. As with any ……
#5 How Does A Printer Work Step By Step
Website: en.gongzheng.com
Key Highlights: The UV printer uses specialized UV-curable inks that dry instantly when exposed to UV light. These inks are loaded into the printer’s ink cartridges. Gongzheng ……
#6 What is UV Printing? How Does it Work? What Can You Do With It?
Website: coldesi.com
Key Highlights: This method of printing uses a combination of ultraviolet (UV) light, and UV-curable inks to produce the final print….
#7 What is UV Printing?
Website: prtwd.com
Key Highlights: UV printing is a distinctive form of digital printing that involves the use of ultraviolet (UV) light to cure or dry UV ink almost as soon as it is applied to ……
#8 What Is UV Printing? A Complete Beginner’s Guide (2025 Update)
Website: truflatplywood.com
Key Highlights: UV printing sprays UV-curable ink directly onto the surface and immediately cures it with UV light. It works on rigid surfaces like wood, metal, and glass, as ……
#9 What is UV Printer? Know the Pros & Cons + Buyer’s Guide 2025
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Does A Uv Printer Work
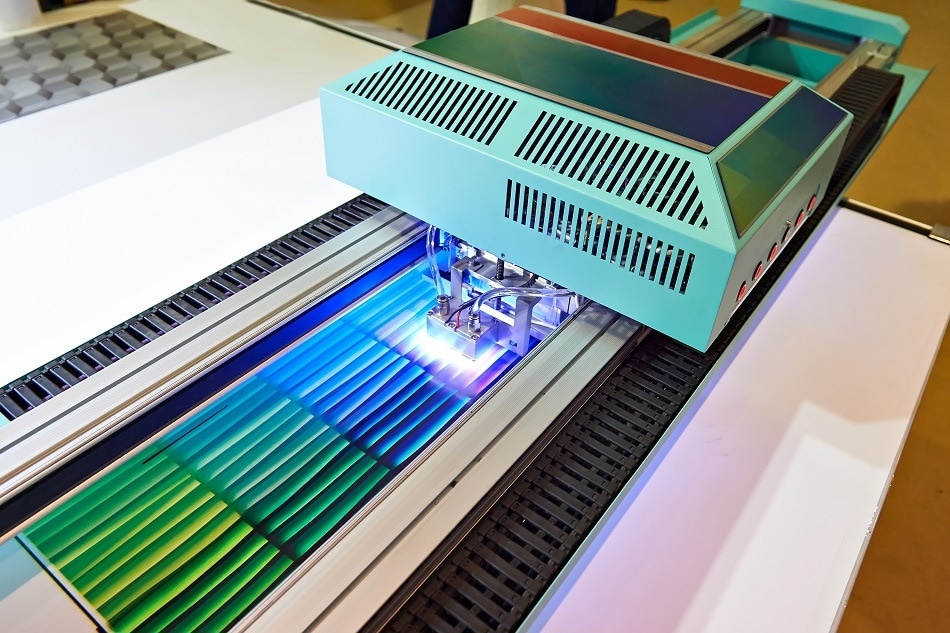

How Does a UV Printer Work: 2026 Market Trends Analysis
Understanding UV Printer Technology in 2026
As we move into 2026, the UV (ultraviolet) printing industry has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in digital printing, environmental regulations, and growing demand for high-quality, versatile printing across industries. At its core, UV printing uses ultraviolet light to instantly cure or dry ink as it is applied to a substrate. Unlike traditional solvent or latex inks that require time to air-dry, UV inks solidify almost immediately when exposed to UV lamps, enabling faster production speeds and reduced smudging.
The fundamental mechanism involves several key components: printheads that deposit UV-curable ink, UV lamps (or increasingly, LED-UV systems) that cure the ink, and a precision motion system that controls the movement of the print head or substrate. This process allows UV printers to print on a vast array of materials—including plastic, glass, metal, wood, and acrylic—without requiring pre-treatment in most cases.
Advancements in UV LED Technology Driving Market Growth
One of the most significant trends shaping the UV printing market in 2026 is the widespread adoption of UV LED curing systems. Compared to traditional mercury-vapor UV lamps, UV LED systems offer longer lifespans, lower energy consumption, reduced heat output, and zero emission of ozone. These benefits have made LED-UV printers the preferred choice for manufacturers focused on sustainability and operational efficiency.
By 2026, nearly 75% of new UV printers introduced to the market are expected to use LED-UV curing technology. This shift is particularly impactful in environments such as retail signage, packaging, and industrial manufacturing, where low heat output allows printing on heat-sensitive substrates like thin plastics and foams.
Expansion into New Applications and Industries
The versatility of UV printing is fueling its penetration into emerging markets. In 2026, we see UV printers being increasingly used in:
- Customized Consumer Goods: From personalized phone cases to printed footwear and eyewear, UV printers enable on-demand, short-run production with vibrant, durable results.
- Industrial Manufacturing: UV printing is now used for coding, marking, and decorating automotive parts, electronics, and appliances due to its resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and weathering.
- Packaging and Labels: Growing demand for sustainable, high-resolution packaging has boosted the use of UV printing in folding cartons, rigid plastic packaging, and pressure-sensitive labels.
These applications benefit from the instant curing process, which increases throughput and reduces production bottlenecks.
Integration of Automation and Smart Technologies
By 2026, UV printers are no longer standalone machines but part of smart, interconnected production ecosystems. Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies—such as IoT sensors, AI-driven color calibration, and automated material handling—has enhanced precision, reduced waste, and improved uptime.
For example, predictive maintenance systems monitor printhead performance and UV lamp output in real time, alerting operators before failures occur. Additionally, cloud-based workflow software enables remote job submission, monitoring, and color management, increasing operational flexibility for print service providers.
Sustainability and Regulatory Influence
Environmental concerns continue to shape the UV printing landscape. With global regulations tightening around VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions, UV printing—especially LED-UV—offers a near-zero VOC alternative to solvent-based printing. In 2026, eco-certifications and green manufacturing standards are influencing buyer decisions, with businesses favoring UV printers that meet ISO 14001 and other environmental benchmarks.
Moreover, advancements in bio-based and recyclable UV inks are supporting circular economy goals, making UV printing more sustainable across the product lifecycle.
Conclusion: UV Printing as a Cornerstone of Digital Manufacturing
In 2026, understanding how a UV printer works is essential not just for print professionals but for manufacturers across sectors embracing digital transformation. The combination of rapid curing, material versatility, and evolving smart features positions UV printing as a key enabler of customization, efficiency, and sustainability. As technology continues to advance, UV printers will play an increasingly central role in the future of on-demand and industrial digital printing.
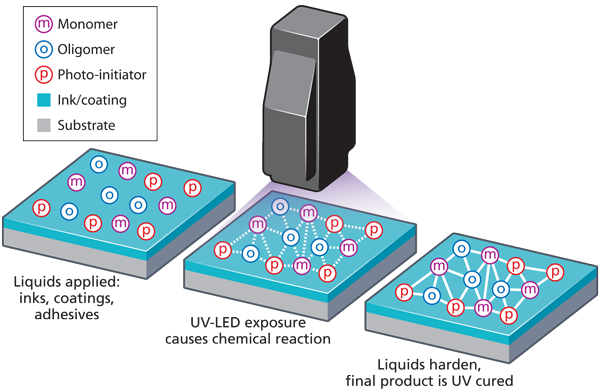
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing UV Printers: Understanding How They Work and Avoiding Quality & IP Issues
When sourcing UV printers—especially from overseas suppliers—businesses often overlook critical aspects related to quality, intellectual property (IP), and the technical functionality of the equipment. Understanding how a UV printer works is essential to avoid costly mistakes. Below are common pitfalls to watch for:
Pitfall 1: Misunderstanding UV Printer Technology
Many buyers source UV printers without fully understanding how they operate. UV printers use ultraviolet light to instantly cure or dry ink as it is printed. This allows printing on a wide range of rigid and flexible substrates, such as glass, metal, plastic, and wood. However, if the UV curing system is poorly calibrated or uses low-quality lamps/LEDs, it can result in incomplete curing, poor adhesion, or premature ink degradation. Buyers who don’t grasp these technical details may end up with underperforming machines.
Pitfall 2: Prioritizing Price Over Print Quality
Low-cost UV printers may seem attractive, but they often compromise on print head quality, software precision, and mechanical stability. Inferior print heads can cause banding, inconsistent color, or frequent clogging. Additionally, low-resolution optical encoders or stepper motors affect registration accuracy. Without testing sample prints or inspecting key components, buyers risk investing in equipment that fails to meet production standards.
Pitfall 3: Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Some suppliers, particularly in certain regions, produce UV printers that mimic branded systems (e.g., mimicking Epson or Ricoh print head integration or copying proprietary software interfaces). These clones may infringe on patents or software licenses, exposing the buyer to legal liability—especially when importing into regions with strict IP enforcement like the EU or the U.S. Always verify that the printer uses licensed components and original firmware.
Pitfall 4: Overlooking After-Sales Support and Spare Parts
UV printers have consumable parts—like print heads, UV lamps, and belts—that require regular maintenance or replacement. Sourcing from suppliers with poor technical support or limited spare parts availability can lead to extended downtime. Some manufacturers use proprietary parts that are difficult or impossible to source independently, creating long-term dependency and cost issues.
Pitfall 5: Inadequate Software and Driver Compatibility
How a UV printer works is not just about hardware—software plays a crucial role in color management, RIP (Raster Image Processing), and job automation. Many low-cost models come with outdated or non-upgradable software that lacks compatibility with industry-standard design tools. This can limit workflow efficiency and output quality, undermining the printer’s overall value.
Pitfall 6: Assuming All UV Inks Are Interchangeable
Suppliers may claim that their printers support “universal” UV inks, but ink formulation must match the printer’s curing system and print head specifications. Using incompatible inks can damage print heads, reduce color gamut, or create hazardous off-gassing. Reputable manufacturers often lock their systems to proprietary inks, so buyers should confirm ink availability and compatibility before purchasing.
Conclusion: Due Diligence Is Key
To avoid these pitfalls, thoroughly research the UV printer’s technology, demand transparency on components and software licensing, and verify the supplier’s reputation. Whenever possible, request live demonstrations, third-party inspections, and references. A clear understanding of how UV printers work—combined with attention to quality and IP concerns—will lead to a more reliable and legally sound investment.
How Does a UV Printer Work: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding UV Printer Technology
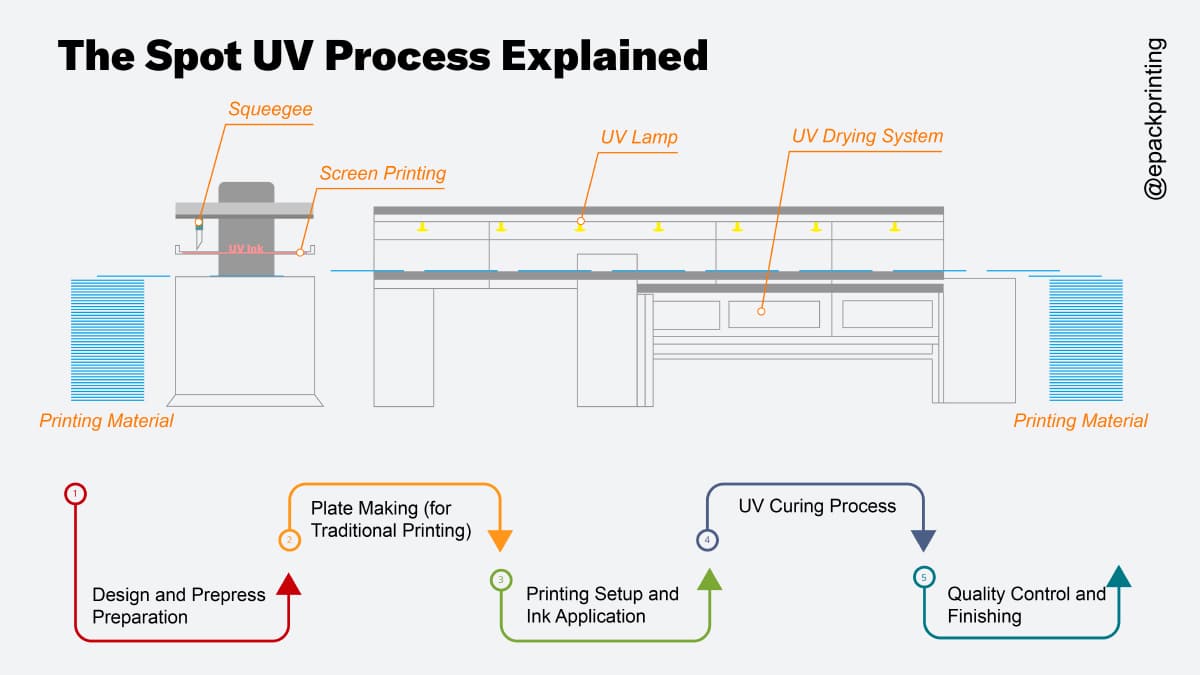
A UV (ultraviolet) printer is a digital printing machine that uses ultraviolet lights to cure or dry ink as it is printed onto a substrate. Unlike traditional printers that rely on solvent-based inks that air-dry, UV printers instantly cure inks using UV light, allowing for rapid production and high-quality prints on a wide range of materials.
The process begins when the printer applies UV-curable ink onto the printing surface—such as plastic, glass, metal, wood, or acrylic. As the ink is deposited, UV lamps located near the print heads emit ultraviolet light, causing the ink to polymerize and solidify almost immediately. This instant curing process eliminates drying time and reduces the risk of smudging or smearing.
Key Components of a UV Printer
Print Heads
UV printers typically use industrial-grade piezoelectric print heads that precisely spray microscopic droplets of UV ink. These heads must be regularly maintained to prevent clogging and ensure print quality.
UV Lamps
These lamps are positioned directly behind the print heads and emit UV light at specific wavelengths (usually between 200–400 nm) to instantly cure the ink. LED UV lamps are commonly used due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan.
Ink Delivery System
The printer contains a closed-loop ink system that supplies UV-curable inks from cartridges or bulk tanks to the print heads. These inks are formulated to remain liquid until exposed to UV light.
Conveyor or Flatbed System
UV printers can be flatbed or roll-to-roll. Flatbed models hold rigid substrates in place during printing, while roll-to-roll systems handle flexible materials like vinyl or banners.
Logistics Considerations for UV Printer Operation
Installation Requirements
- Space & Ventilation: While UV printers produce minimal fumes compared to solvent printers, proper ventilation is recommended, especially in enclosed workspaces.
- Power Supply: Ensure access to a stable electrical source compatible with the printer’s voltage and amperage requirements.
- Environmental Controls: Maintain a clean, temperature-controlled environment (typically 20–25°C) to prevent ink viscosity fluctuations and substrate warping.
Material Handling
- Substrate Preparation: Clean and dry substrates before printing to ensure proper ink adhesion.
- Loading & Fixturing: Use vacuum tables or clamps to secure materials, especially on flatbed printers, to prevent movement during printing.
- Post-Processing: Depending on the application, printed items may require finishing steps such as coating, cutting, or routing.
Ink & Consumables Management
- Ink Storage: Store UV inks in a cool, dark place to prevent premature curing. Follow manufacturer shelf-life guidelines.
- Waste Disposal: Used ink cartridges, cleaning solvents, and contaminated rags must be disposed of in accordance with local hazardous waste regulations.
Compliance and Safety Regulations
Occupational Safety
- UV Radiation Protection: Operators should avoid direct exposure to UV lamps. Most printers have safety interlocks that disable lamps when the cover is open.
- Eye and Skin Protection: Use protective eyewear and gloves when performing maintenance or handling uncured ink.
- Ventilation and Air Quality: Although UV inks are low-VOC, some applications may require local exhaust ventilation to capture trace ozone or fumes from the curing process.
Environmental Compliance
- Hazardous Waste Disposal: Uncured UV ink and cleaning agents may be classified as hazardous waste. Follow EPA (or local equivalent) guidelines for handling, labeling, and disposal.
- Chemical Handling: Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all inks and cleaning solutions. Train staff in safe handling procedures.
Regulatory Standards
- Electrical Safety: Ensure the printer meets regional electrical safety standards (e.g., UL in the U.S., CE in Europe).
- EMI/RFI Compliance: UV printers with electronic controls should comply with electromagnetic interference regulations to avoid disrupting nearby equipment.
- RoHS and REACH: Confirm that printer components and inks comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) directives if operating in the EU.
Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
Routine Maintenance
- Clean print heads regularly using manufacturer-recommended solutions.
- Inspect UV lamps for performance degradation and replace as needed.
- Calibrate the printer periodically to maintain print accuracy.
Training and Documentation
- Train operators on safe startup, operation, and shutdown procedures.
- Keep detailed logs of maintenance, ink usage, and compliance inspections.
Emergency Procedures
- Establish protocols for ink spills, equipment malfunctions, and UV exposure incidents.
- Ensure first-aid kits and emergency eyewash stations are accessible in the printing area.
Conclusion
Understanding how a UV printer works is essential for efficient and compliant operation. By following proper logistics protocols and adhering to safety and environmental regulations, businesses can maximize print quality, minimize downtime, and ensure a safe working environment. Always consult the printer manufacturer’s guidelines and local regulatory authorities to stay up to date with compliance requirements.
In conclusion, understanding how a UV printer works involves examining its core components and printing process, which rely on ultraviolet light to instantly cure or dry ink as it is applied to a variety of substrates. Unlike traditional printers that use solvent-based inks requiring time to dry, UV printers utilize UV-curable inks that harden immediately upon exposure to UV lamps, resulting in faster production, reduced smudging, and greater durability. This technology allows for high-quality, precise printing on materials such as plastic, glass, metal, wood, and ceramics—making it ideal for applications in signage, packaging, promotional items, and industrial manufacturing.
The integration of piezoelectric print heads, precision motion control, and targeted UV lamps ensures efficient, layer-by-layer printing with excellent color accuracy and adhesion. As a result, UV printing offers significant advantages in terms of versatility, speed, and environmental impact—particularly due to lower VOC emissions. When sourcing a UV printer, it’s essential to consider factors like print resolution, curing capability, substrate compatibility, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance for specific business needs. Overall, UV printing represents an advanced, efficient solution for modern digital printing demands.