The global laser welding equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining technologies across automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.87 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of automation, advancements in fiber laser technology, and the push for more energy-efficient and accurate welding solutions. As industries shift toward lightweight materials and high-speed production lines, laser welding has emerged as a critical process due to its minimal heat distortion, superior seam quality, and compatibility with robotic systems. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation by enhancing beam quality, system integration, and process control. Here, we examine the top nine companies shaping the future of laser welding technology—firms that combine engineering excellence with data-driven performance metrics to redefine manufacturing precision.
Top 9 How Does A Laser Welder Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 What is Laser Welding and How Does It Work?
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: It uses a high-energy laser beam to fuse metals together, creating a strong metallurgical bond. As the energy from the laser beam is absorbed by ……
#2 A Little Light Construction: Laser Welding in Three Acts
Website: nist.gov
Key Highlights: The laser welding process begins, as one might imagine when a laser is focused to the surface of a metal….
#3 What Is Laser Welding and How Does the Technique Work?
Website: esab.com
Key Highlights: In the laser welding process, a highly concentrated beam of light is focused on the cavity between the materials to be joined. The powerful laser beam melts the ……
#4 Laser Welding Explained
Website: fractory.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding or laser beam welding (LBW) is a process that uses a concentrated heat source in the form of a laser to melt the materials, which fuse together ……
#5 Laser Welders
Website: dnelaserusa.com
Key Highlights: How Laser Welding Works. Laser welding is a high-precision welding technique that uses a focused laser beam to join pieces of metal together….
#6 Laser Welding Basics
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a type of fusion welding. It uses its small beam and deep penetration to rapidly melt and join materials together without excessive distortion….
#7 How Does Laser Welding Work
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of combining metal or thermoplastic parts using high-intensity laser beam energy. This welding technique emerged in the early 1960s ……
#8 A Guide to Handheld Laser Welding
Website: theo.inc
Key Highlights: This guide offers insights into laser welding’s benefits and challenges, providing a straightforward view on its role in modern manufacturing and safety….
#9 The Complete Guide to Laser Welders
Website: xtool.com
Key Highlights: Laser welders can operate in continuous mode and pulsed mode. Depending on your needs, you need to check the modes the machine offers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Does A Laser Welder Work
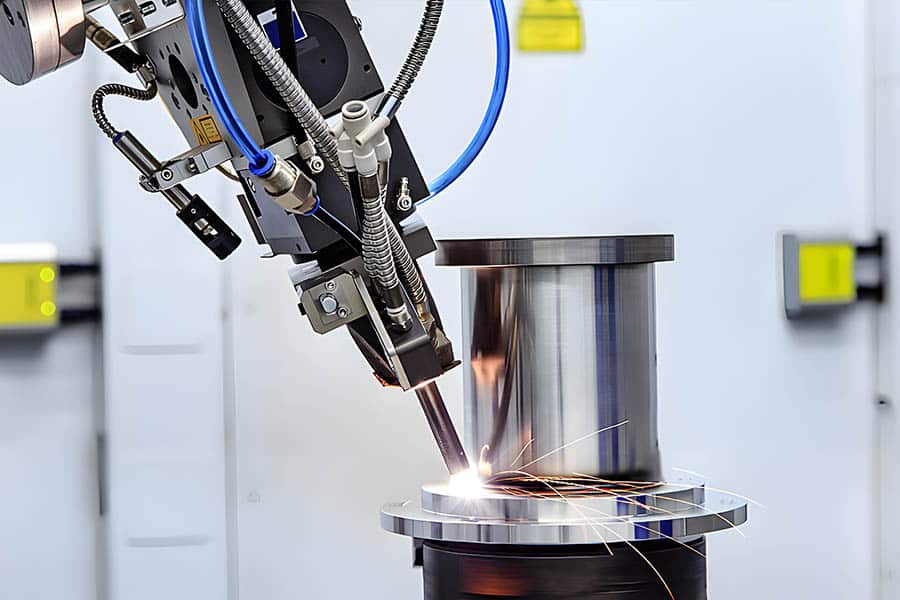

How Does A Laser Welder Work: 2026 Market Trends
As the manufacturing and industrial automation sectors continue to evolve, laser welding technology is poised for significant advancements and market expansion by 2026. Understanding how a laser welder works is fundamental to appreciating its growing role across industries, from automotive and aerospace to consumer electronics and medical devices. This analysis explores the operational principles of laser welding and identifies key trends expected to shape the market in 2026.
Core Functionality: How Does a Laser Welder Work?
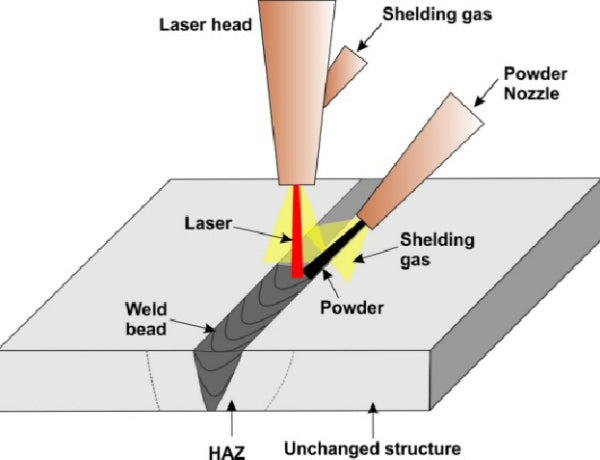
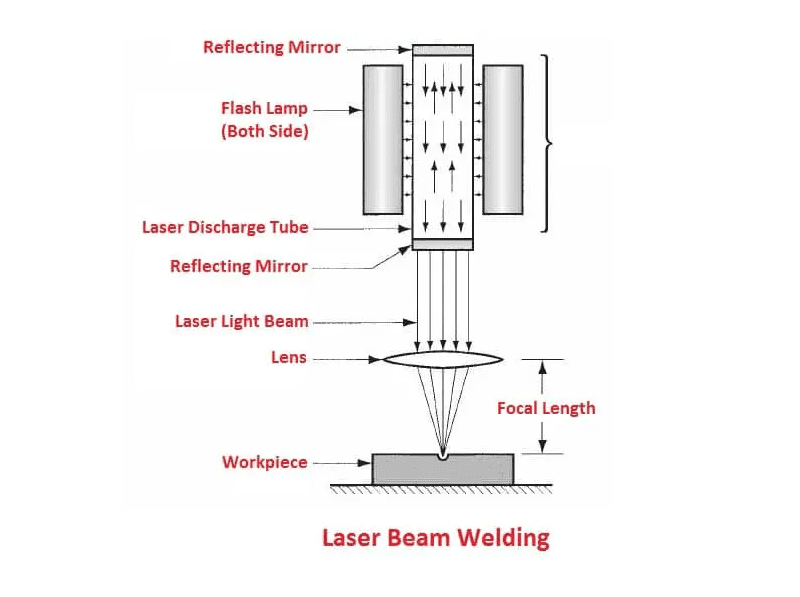
A laser welder operates by focusing a high-intensity laser beam onto a precise point on the workpiece, generating intense heat that melts and fuses materials together. The process typically involves three main components: a laser source (commonly fiber, CO₂, or disk lasers), a delivery system (such as mirrors or optical fibers), and a control system that manages beam intensity, duration, and positioning.
The laser beam is directed through a collimating lens and then focused by a focusing lens to create a concentrated spot—often less than 1 mm in diameter—producing temperatures sufficient to melt metals with minimal heat-affected zones. This precision enables clean, strong welds on thin or complex materials, making it ideal for high-tolerance applications.
Rising Demand for Precision and Automation
By 2026, the global push toward automation and smart manufacturing is expected to drive demand for laser welding systems. Industries are increasingly adopting robotic laser welding cells that integrate seamlessly with Industry 4.0 technologies. These systems offer unparalleled precision, repeatability, and speed, reducing human error and increasing throughput. The ability of laser welders to perform intricate welds on lightweight and high-strength materials—such as aluminum and advanced high-strength steels—makes them essential in electric vehicle (EV) production, a sector projected for explosive growth.
Advancements in Laser Technology
Fiber laser technology continues to dominate the market due to its high efficiency, lower maintenance, and superior beam quality. By 2026, expect broader adoption of ultrafast and green lasers, especially in micro-welding applications for electronics and medical devices. These advancements allow laser welders to work with reflective materials like copper and gold more effectively, overcoming previous challenges related to beam absorption and back-reflection.
Expansion in Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional manufacturing, new applications are emerging in renewable energy, battery production, and additive manufacturing. Laser welding is critical in sealing battery cells for EVs and energy storage systems, where hermetic seals and minimal thermal distortion are vital. The growth of solid-state batteries and 3D-printed metal components will further increase reliance on laser welding, as these technologies require highly controlled joining processes.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt cleaner production methods. Laser welding consumes less energy than traditional arc welding and produces fewer emissions and waste. By 2026, energy-efficient laser systems with intelligent power management and closed-loop feedback systems are expected to become standard, aligning with global carbon reduction targets.
Regional Market Growth
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the largest market for laser welding equipment, driven by electronics manufacturing and automotive production. North America and Europe are also expected to see strong growth due to investments in advanced manufacturing and defense technologies.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser welding market will be shaped by technological innovation, automation integration, and expanding applications across high-growth industries. As understanding of how a laser welder works becomes more widespread, its adoption will accelerate, offering manufacturers a competitive edge through precision, speed, and sustainability. Companies that invest in next-generation laser welding solutions today will be well-positioned to lead in the manufacturing landscape of tomorrow.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing “How Does a Laser Welder Work” Content (Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns)
When sourcing content explaining how a laser welder works—whether for technical documentation, marketing materials, or educational resources—organizations often encounter challenges related to content quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Understanding these common pitfalls can help ensure that the information is both accurate and legally compliant.
Pitfall 1: Poor Technical Accuracy and Over-Simplification
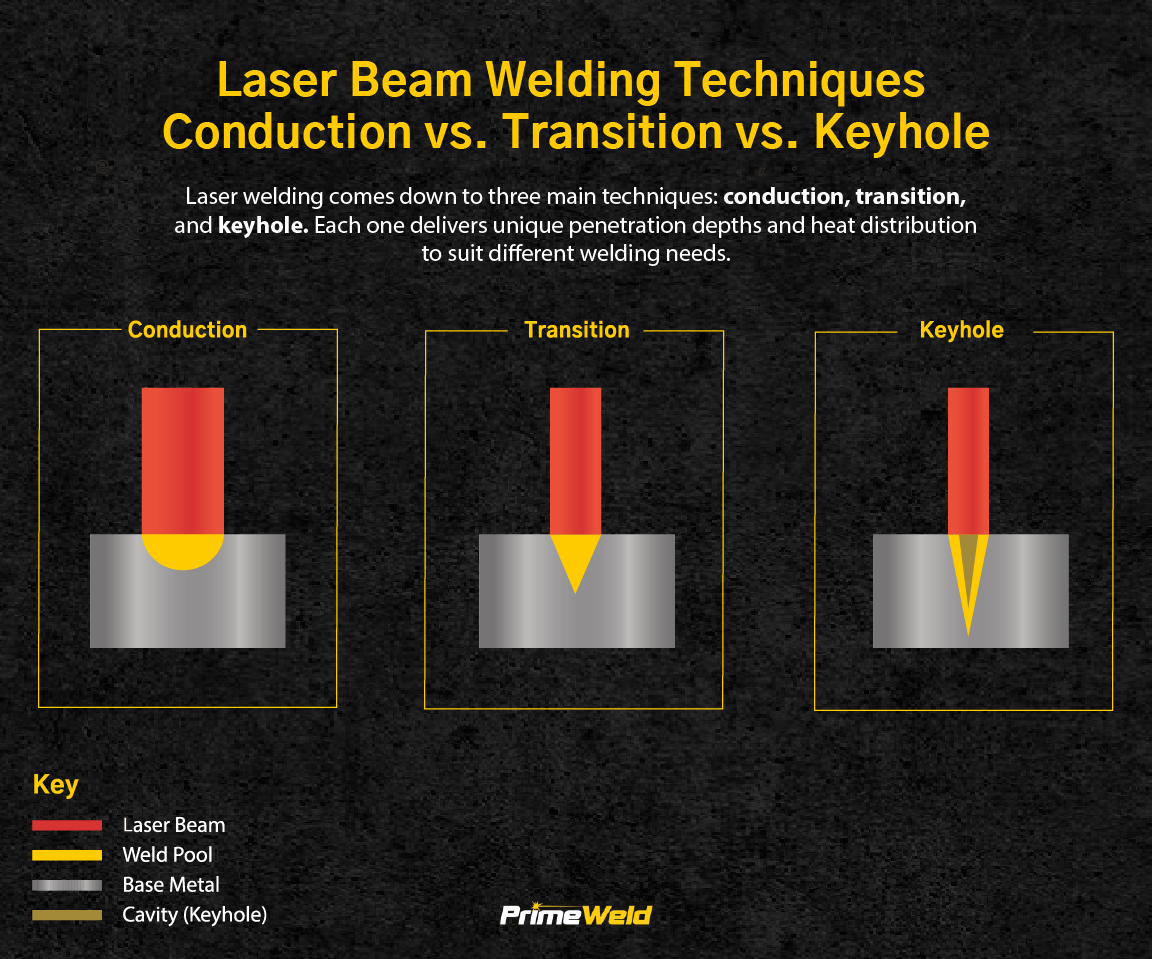
One of the most frequent quality issues is content that oversimplifies or inaccurately describes the laser welding process. Laser welding involves complex physics, including beam focusing, material absorption, keyhole formation, and thermal dynamics. Sourced content may omit critical details or contain technical errors, especially when created by non-specialists. This can mislead readers and damage the credibility of the publisher.
Solution: Always verify content with subject matter experts or engineers familiar with laser technology. Use reputable sources such as academic journals, industry standards (e.g., ISO 13577), or documentation from established equipment manufacturers.
Pitfall 2: Lack of Clarity and Audience Misalignment
Content may fail to match the intended audience’s knowledge level. Excessively technical jargon can confuse beginners, while overly simplistic explanations may not satisfy engineers or technical buyers. This mismatch reduces the effectiveness of the material.
Solution: Define your target audience upfront (e.g., students, technicians, procurement managers) and tailor the explanation accordingly. Use diagrams or analogies to aid understanding, but ensure they remain technically sound.
Pitfall 3: Plagiarism and Copyright Infringement
A major IP risk arises when content is copied directly from manufacturer websites, technical manuals, or educational platforms without proper authorization or attribution. Even paraphrasing without credit can lead to copyright issues, especially if the structure or unique explanations are replicated.
Solution: Create original content or license material from reputable sources. When referencing existing work, use proper citations and consider transformative use that adds new insight or value.
Pitfall 4: Use of Proprietary or Patent-Protected Information
Some explanations of laser welding may inadvertently disclose proprietary techniques or patented processes (e.g., specific beam modulation methods or hybrid laser-arc systems). Using such details without permission can lead to legal liability.
Solution: Avoid detailing patented methods unless publicly documented and properly attributed. Focus on general principles that are widely accepted in the industry.
Pitfall 5: Outdated or Obsolete Information
Laser welding technology evolves rapidly, with advances in fiber lasers, real-time monitoring, and automation. Sourced content may rely on outdated principles or obsolete equipment designs, leading to misinformation.
Solution: Prioritize recent publications (within the last 3–5 years) and consult OEM documentation or industry white papers to ensure relevance.
Pitfall 6: Misuse of Images and Diagrams
Visuals explaining laser welder operation (e.g., beam focusing, weld pool dynamics) are often sourced from copyrighted materials. Using such images without a license—even if the accompanying text is original—can result in IP violations.
Solution: Use royalty-free or licensed images from reputable sources, or create custom illustrations. Always verify the licensing terms of any visual content.
By addressing these common pitfalls—ensuring technical accuracy, respecting IP rights, and tailoring content appropriately—organizations can source or create high-quality, compliant explanations of how laser welders work.

How Does a Laser Welder Work: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding how a laser welder functions is essential not only for operational efficiency but also for ensuring safe logistics and regulatory compliance throughout its lifecycle—from procurement and transportation to installation, use, and disposal. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements associated with laser welding systems.
Equipment Procurement and Supplier Compliance
When sourcing a laser welder, verify that the supplier adheres to international and regional safety and quality standards. Ensure the equipment complies with relevant certifications such as:
- CE Marking (Europe) – Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- FDA/CDRH Regulations (USA) – Classifies lasers and mandates reporting for manufacturers and importers.
- ISO 60825 – International standard for laser product safety, covering classification and labeling.
- ANSI Z136.1 – U.S. standard for safe use of lasers in manufacturing environments.
Confirm that the laser welder includes proper documentation, including user manuals, safety instructions, technical specifications, and compliance certificates.
Transportation and Handling Logistics
Laser welding systems, particularly industrial units, are often heavy and sensitive to shock, vibration, and environmental conditions. Follow these logistics best practices:
- Use crated and cushioned packaging designed for precision machinery.
- Label shipments with fragile and this side up indicators.
- Comply with hazardous materials regulations if the system includes high-voltage components or laser gases (e.g., CO₂ lasers may involve regulated gas cylinders).
- Ensure transport vehicles have climate control, especially for fiber-optic components sensitive to moisture and temperature extremes.
- Train logistics personnel on handling electrostatic-sensitive devices (ESD) to prevent damage during loading/unloading.
Installation and Facility Requirements
Before installation, assess the facility for compliance with safety and operational standards:
- Electrical Infrastructure: Verify power supply matches the laser welder’s requirements (voltage, phase, grounding). Install dedicated circuits if necessary.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Laser welding produces hazardous fumes and particulates. Install compliant fume extraction systems meeting OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent local regulations (e.g., COSHH in the UK).
- Laser Safety Zones: Designate controlled areas with proper signage (e.g., “Laser Radiation” warning signs). Use interlocks, barriers, and beam enclosures to prevent accidental exposure.
- Floor Space and Anchoring: Ensure adequate space for operation, maintenance access, and emergency egress. Anchor large units to prevent movement.
Operational Safety and Regulatory Compliance
During use, adherence to safety protocols is mandatory:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators must wear laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength (e.g., 1064 nm for fiber lasers).
- Training and Certification: Personnel must be trained per ANSI Z136.1 or IEC 60825 standards. Maintain training records for audits.
- Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a qualified LSO to oversee compliance, conduct risk assessments, and manage safety programs.
- Maintenance Logs: Keep detailed records of inspections, alignments, and repairs to ensure ongoing compliance and traceability.
Waste Disposal and End-of-Life Management
Dispose of laser welding components responsibly:
- Laser Optics and Fibers: Recycle or dispose via e-waste programs compliant with WEEE (EU) or RCRA (U.S.).
- Coolants and Lubricants: Manage used fluids as hazardous waste if applicable; use certified disposal vendors.
- Batteries and Electronics: Follow local regulations for handling and recycling electronic components.
- Laser Gas Cylinders: Return or recycle pressurized gas containers through authorized providers.
Documentation and Auditing
Maintain comprehensive records to support regulatory audits:
- Equipment compliance certificates
- Risk assessments and safety audits
- Operator training logs
- Maintenance and calibration records
- Incident reports (if any laser exposure or malfunction occurs)
Regular internal audits help ensure continuous compliance with OSHA, ISO, or other applicable standards.
Summary
Operating a laser welder involves more than understanding its technical function—it requires strict adherence to logistics and compliance protocols. From secure transportation and compliant installation to safe operation and responsible disposal, each phase demands attention to regulatory requirements and safety best practices. By following this guide, organizations can ensure efficient, legal, and safe use of laser welding technology.
In conclusion, understanding how a laser welder works involves sourcing information on its core principles, components, and operational processes. A laser welder operates by concentrating a high-intensity laser beam onto a small area of metal, generating intense heat that melts and fuses materials together with precision and minimal distortion. Key components such as the laser source (commonly fiber, CO2, or Nd:YAG), optical delivery system, focusing lens, and shielding gas play critical roles in ensuring a consistent and high-quality weld. Sourced technical literature, manufacturer documentation, and industry standards all confirm that laser welding offers advantages like deep penetration, high welding speeds, and excellent control, making it ideal for applications in automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. By gathering insights from reputable engineering sources and practical case studies, it becomes clear that laser welding is an advanced, efficient joining method rooted in precise energy delivery and material science.