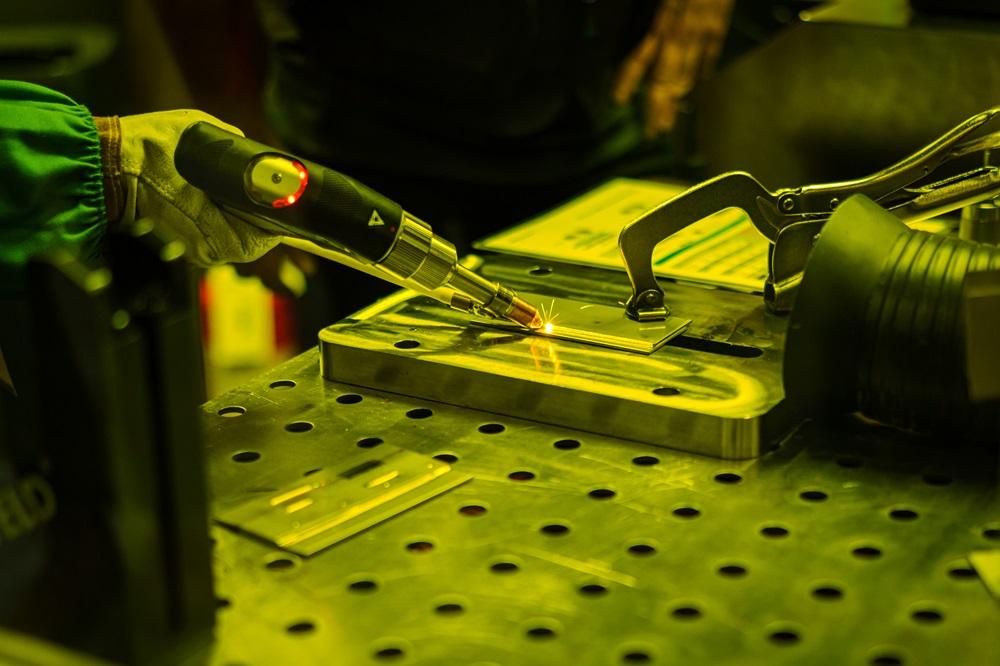
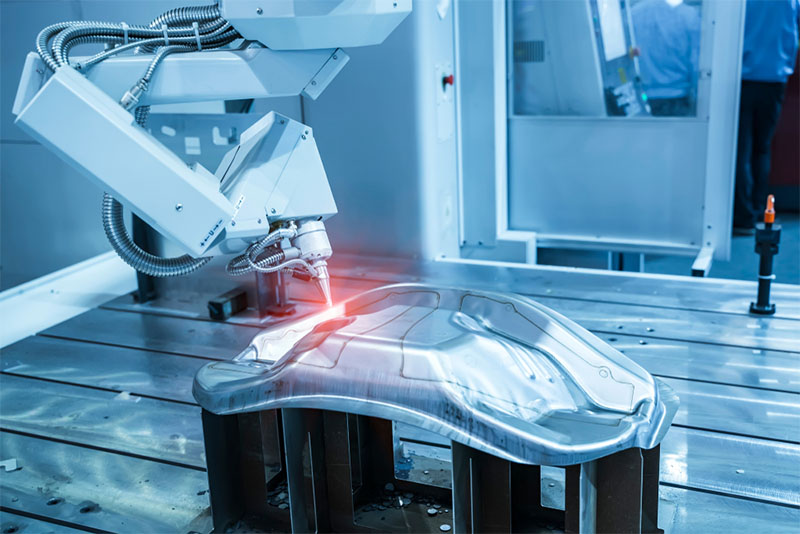
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 6.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. Factors such as advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in production processes, and the shift toward lightweight materials in electric vehicles are accelerating adoption. As manufacturers seek higher efficiency, minimal heat distortion, and superior weld quality, laser welding has become a critical solution. This growing demand has fostered a competitive landscape featuring both established industrial powerhouses and innovative technology-driven firms. In this analysis, we spotlight the top 9 manufacturers leading the charge in laser welding innovation, evaluating their technological capabilities, market presence, and contributions to shaping the future of advanced manufacturing.
Top 9 How Do Laser Welders Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 What Is Laser Welding and How Does the Technique Work?
Website: esab.com
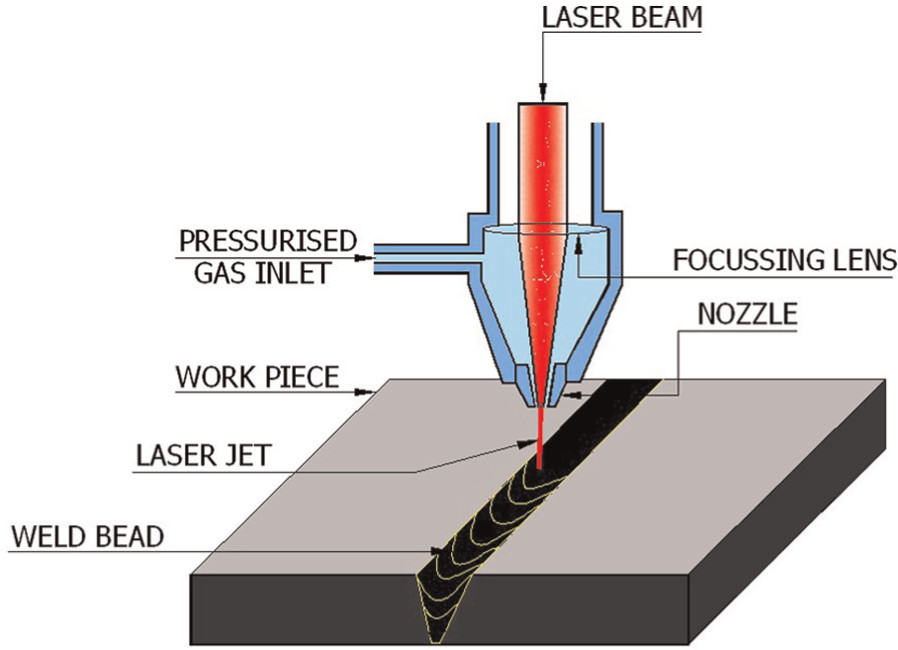
Key Highlights: Laser welding technology uses a laser beam as a high-concentrated heat source to join materials….
#2 What is Laser Welding and How Does It Work?
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: It uses a high-energy laser beam to fuse metals together, creating a strong metallurgical bond. As the energy from the laser beam is absorbed by ……
#3 Laser Welding Explained
Website: fractory.com
Key Highlights: Laser beam welding works on the principle of using a laser with high power density to apply heat to a joint between the surface of two metals….
#4 NIST Research Sparks New Insights on Laser Welding
Website: nist.gov
Key Highlights: On its surface, the work is deceptively simple: Shoot a high-power laser beam onto a piece of metal for a fraction of a second and see what ……
#5 Laser Welders
Website: dnelaserusa.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a high-precision welding technique that uses a focused laser beam to join pieces of metal together. The laser provides a ……
#6 Learning about laser welding systems, innovations, and hazards
Website: thefabricator.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding—including hand-held laser welding—has grown in relevance and use in metal fabricating. Images: FABTECH….
#7 What Is Laser Welding and How Does It Work?
Website: prototek.com
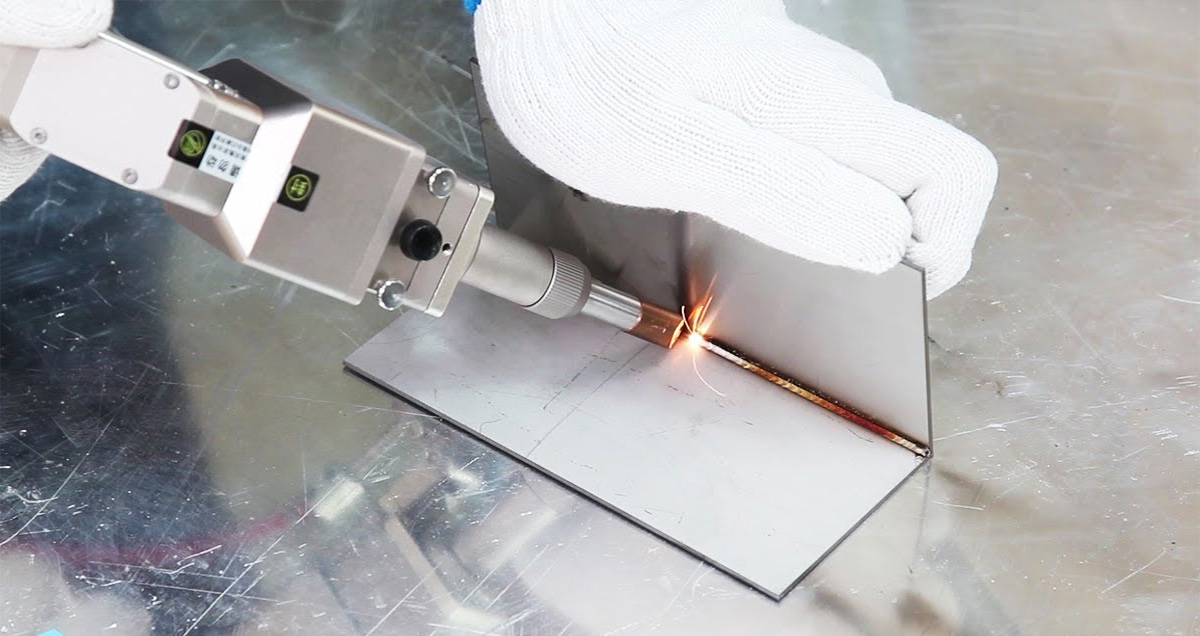
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a process that focuses a laser beam to melt and fuse metal and certain plastics with precision and speed. With minimal heat input, it creates ……
#8 How Does Laser Welding Work
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: The laser welder (or laser welding machine) emits a laser beam concentrated on a particular spot of the material’s surface. · The concentrated beam produces heat ……
#9 A Guide to Handheld Laser Welding
Website: theo.inc
Key Highlights: The welding laser beam is directed, or “wobbled” by a moving mirror within the hand torch dozens or even hundreds of times per second over the weld joint, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for How Do Laser Welders Work

How Do Laser Welders Work: 2026 Market Trends
As industrial automation and precision manufacturing continue to evolve, laser welding technology is poised for significant transformation by 2026. This analysis explores the emerging market trends shaping the understanding and application of how laser welders work, emphasizing technological advancements, industry adoption, and educational demand.
Advancements in Laser Source Technology
By 2026, fiber and disk lasers are expected to dominate the market due to their superior energy efficiency, beam quality, and lower maintenance requirements. These advancements make laser welders more accessible and reliable, deepening public understanding of their operational mechanics. Innovations such as multi-kilowatt continuous-wave (CW) lasers and ultra-short pulse lasers are expanding applications in aerospace, electric vehicles (EVs), and medical devices—driving interest in how these systems generate and direct high-intensity light for precise fusion welding.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Automation
A key trend is the integration of AI-driven process monitoring and real-time control systems into laser welding equipment. By 2026, smart laser welders will utilize machine learning algorithms to optimize weld parameters such as power, speed, and focus—automatically adjusting based on material properties and joint geometry. This shift not only improves weld quality but also enhances transparency into how laser welders function, as digital twins and simulation tools allow operators and engineers to visualize beam-material interactions in real time.
Growth in Electric Vehicle and Battery Manufacturing
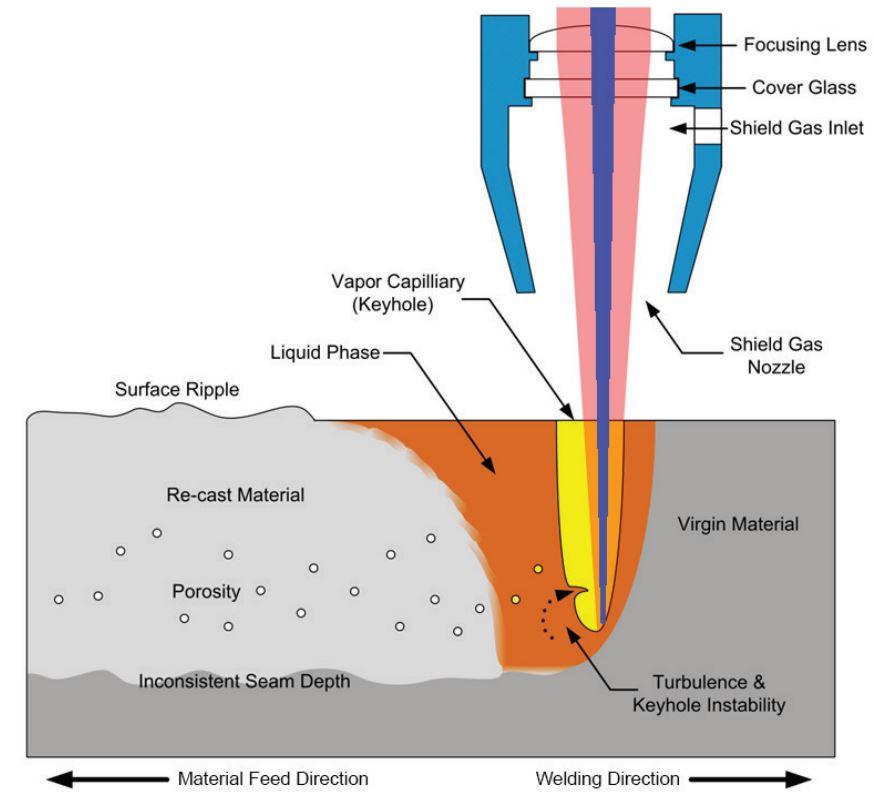
The surge in EV production is a major driver of laser welding demand, particularly for battery pack assembly and lightweight component joining. By 2026, manufacturers will increasingly rely on laser welding for its ability to join dissimilar metals and thin materials without distortion. This trend is increasing public and technical interest in how laser welders achieve deep penetration with minimal heat-affected zones, especially through techniques like conduction and keyhole welding.
Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing industries toward cleaner manufacturing technologies. Laser welding, known for its low material waste and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional methods, aligns with green manufacturing goals. By 2026, market trends will highlight how laser welders contribute to energy-efficient production, spurring educational content and training programs focused on their eco-friendly operation and lifecycle advantages.
Expansion of Training and Online Educational Content
With growing complexity and adoption, there is a rising demand for accessible education on how laser welders work. By 2026, e-learning platforms, augmented reality (AR) training modules, and manufacturer-led certification programs are expected to proliferate. These resources will demystify core principles such as beam generation, focusing optics, shielding gas usage, and weld pool dynamics—making the technology more approachable for technicians, engineers, and students.
Regional Market Developments
Asia-Pacific, led by China and Japan, will remain a hotspot for laser welding adoption due to strong manufacturing bases and government support for advanced technologies. North America and Europe will see growth driven by reshoring initiatives and investments in high-tech industries. These regional dynamics will influence how laser welding principles are taught and applied, with localized content emerging to explain operational nuances in different industrial contexts.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market trends surrounding laser welding will center on smarter, cleaner, and more precise manufacturing solutions. As industries adopt these advanced systems, the demand to understand how laser welders work—from beam generation to metallurgical fusion—will grow significantly. Enhanced transparency through AI, simulation, and education will shape a new era of skilled adoption and innovation in laser-based joining technologies.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing How Do Laser Welders Work (Quality, IP)
When sourcing information or educational content on “How Do Laser Welders Work,” especially with concerns around quality and intellectual property (IP), several common pitfalls can undermine the reliability and legality of the materials obtained. Being aware of these issues helps ensure accurate, safe, and compliant use of the content.
Overlooking Content Accuracy and Technical Depth
One major pitfall is sourcing content from unreliable or non-technical sources that oversimplify or misrepresent how laser welding functions. Many websites, blogs, or low-quality videos may provide inaccurate explanations of key components—such as the laser source (e.g., fiber, CO₂, or diode), beam delivery systems, or the interaction between the laser and metal. This lack of precision can mislead learners or engineers relying on the information for practical applications. Always verify content against reputable technical publications, academic sources, or trusted industry manufacturers.
Relying on Outdated or Non-Specialized Sources
Laser welding technology evolves rapidly, and sourcing outdated material can result in obsolete information—such as references to older laser types or pre-digital control systems. Additionally, generic engineering overviews may not address nuances like keyhole vs. conduction welding, pulse modulation, or the role of shielding gases. Ensure that sources are current and specific to laser welding, preferably published within the last 5–10 years by recognized authorities in manufacturing or photonics.
Ignoring Intellectual Property Rights
A critical legal pitfall involves using diagrams, animations, or technical descriptions without proper licensing or attribution. Many high-quality visual explanations of laser welding processes (e.g., beam focusing, melt pool dynamics) are protected by copyright or patents. Unauthorized reproduction—even for educational use—can lead to IP infringement claims. Always check the licensing terms of images, videos, or text, and prefer open-licensed (e.g., Creative Commons) or royalty-free resources when possible.
Sourcing from Unverified User-Generated Content
Platforms like YouTube, forums, or crowd-sourced websites often host user-generated content that may look professional but lacks technical validation. Misleading animations or incorrect terminology (e.g., confusing laser welding with laser cutting) are common. These sources rarely undergo peer review, increasing the risk of propagating errors. Cross-reference such content with authoritative sources such as equipment manufacturers (e.g., IPG Photonics, Trumpf), academic journals, or technical training materials.
Failing to Verify Source Credibility and Affiliation
Another common issue is sourcing information from websites that appear authoritative but lack clear authorship or institutional backing. Be cautious of content produced by unknown entities, affiliate marketers, or vendors with a sales agenda, as they may exaggerate capabilities or omit safety and operational limitations. Prioritize content from accredited educational institutions, professional engineering organizations (e.g., AWS, ASME), or established technology providers.
Neglecting Language and Localization Quality
When sourcing non-English content or translated materials, poor translation can distort technical meaning—especially with terms like “beam divergence” or “penetration depth.” Machine-translated documents may introduce critical errors. Always use professionally translated or natively authored content, and if possible, have technical translations reviewed by subject-matter experts.
By avoiding these pitfalls, organizations and individuals can ensure they source accurate, high-quality, and legally compliant information on how laser welders work—supporting both educational integrity and innovation within the field.
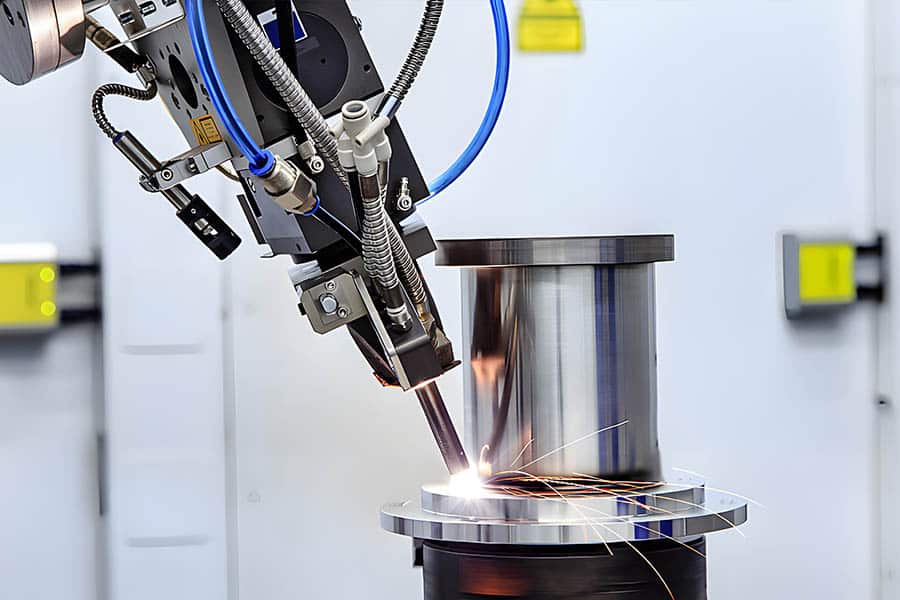

Logistics & Compliance Guide for “How Do Laser Welders Work”
Understanding the operation of laser welders is essential not only for technical proficiency but also for ensuring safe, compliant, and efficient use in industrial and manufacturing environments. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations when working with or explaining laser welding technology.
1. Equipment Logistics
1.1. Procurement and Installation
– Source laser welding systems from certified manufacturers compliant with international safety standards (e.g., ISO 11553, IEC 60825).
– Ensure proper facility planning: adequate space, power supply (typically 3-phase electrical connections), and ventilation for fumes.
– Install systems on stable, vibration-free platforms to maintain beam accuracy.
1.2. Maintenance and Calibration
– Schedule regular preventive maintenance to ensure laser optics, cooling systems, and motion components function optimally.
– Calibrate beam alignment and focus periodically to maintain weld quality and safety.
– Keep detailed service logs for compliance audits.
2. Safety Compliance
2.1. Laser Safety Standards
– Adhere to OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI Z136.1 (American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers).
– Classify laser systems according to IEC 60825 (Class 1 to Class 4); most industrial laser welders fall under Class 4, requiring strict controls.
2.2. Protective Measures
– Use appropriate laser protective eyewear with the correct optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength (commonly 1064 nm for fiber lasers).
– Install interlocks, emergency stop buttons, and beam shrouds to prevent accidental exposure.
– Enclose the welding area with light-tight barriers or curtains to contain laser radiation.
2.3. Fume and Ventilation Management
– Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems to capture hazardous fumes (e.g., metal oxides, ozone).
– Conduct air quality testing and maintain filtration systems to comply with OSHA PELs (Permissible Exposure Limits) and EPA regulations.
3. Operator Training and Certification
3.1. Required Training
– Train operators on laser safety, emergency procedures, and system operation per ANSI Z136.3 (Safe Use of Lasers in Health Care) and equivalent industrial standards.
– Include hazard communication (HazCom) training under OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1200.
3.2. Certification and Documentation
– Maintain records of operator certifications and refresher training.
– Designate a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) where required, especially for Class 3B and Class 4 lasers.
4. Regulatory and Documentation Requirements
4.1. Compliance Documentation
– Keep user manuals, safety data sheets (SDS) for materials being welded, and system conformity certificates (e.g., CE, UL).
– Document risk assessments and control measures as part of the facility’s safety management system.
4.2. Environmental and Waste Compliance
– Dispose of used laser filters, coolant fluids, and metal waste according to local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, REACH, RoHS).
– Recycle metal scraps and manage hazardous waste streams properly.
5. Quality Control and Process Validation
5.1. Process Monitoring
– Use in-process monitoring systems (e.g., cameras, sensors) to ensure weld consistency and detect defects.
– Implement quality assurance protocols aligned with ISO 3834 (Quality requirements for fusion welding) and ASME standards where applicable.
5.2. Record Keeping
– Maintain logs of weld parameters (power, speed, beam focus), inspection results, and non-conformance reports for traceability.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and strict compliance with safety, environmental, and operational standards are critical when utilizing or educating others about laser welding technology. By following this guide, organizations can ensure safe operation, regulatory adherence, and high-quality welding outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding how laser welders work involves sourcing information from technical manuals, industry publications, engineering resources, and expert insights. Laser welding operates by focusing a high-intensity laser beam onto a material’s surface, generating precise and concentrated heat that melts and fuses metals with minimal distortion. The process relies on the interaction between the laser light—typically from CO₂, fiber, or Nd:YAG sources—and the workpiece, often assisted by shielding gases to prevent oxidation. Key factors such as laser type, power, beam delivery systems, and material properties significantly influence weld quality and efficiency. By consulting credible sources like academic journals, manufacturer documentation, and certified welding organizations, one can gain a comprehensive understanding of the principles, applications, and advancements in laser welding technology. This informed approach ensures accurate knowledge acquisition for both educational and industrial purposes.