The global microwave oven market continues to expand, driven by rising demand for convenient cooking solutions and technological advancements in appliance efficiency. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global microwave oven market was valued at USD 10.67 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. This growth trajectory directly fuels demand for critical components such as high-voltage capacitors, which are essential for the safe and efficient operation of microwave magnetrons. As manufacturers prioritize reliability, energy efficiency, and compact design, the high-voltage capacitor segment has witnessed increased innovation and competition. This report identifies the top eight manufacturers leading the space, evaluated based on production capacity, technological capabilities, global supply reach, and adherence to international safety standards such as UL and IEC. These companies are instrumental in supporting the next generation of microwave ovens across consumer and commercial applications.
Top 8 High Voltage Capacitor For Microwave Oven Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Capacitor
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata offers ceramic, polymer aluminum, single-layer microchip, variable, silicon, film, and various other types of capacitors. See selection guide….
#2 Cornell Dubilier
Domain Est. 1995
Website: cde.com
Key Highlights: Type BLS DC Link capacitors use the most advanced construction and technology to meet the challenges of harsh environments with operating temperatures to 125°C….
#3 Microwave Capacitors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: capacitorindustries.com
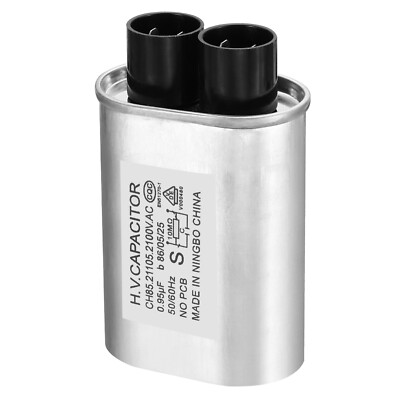
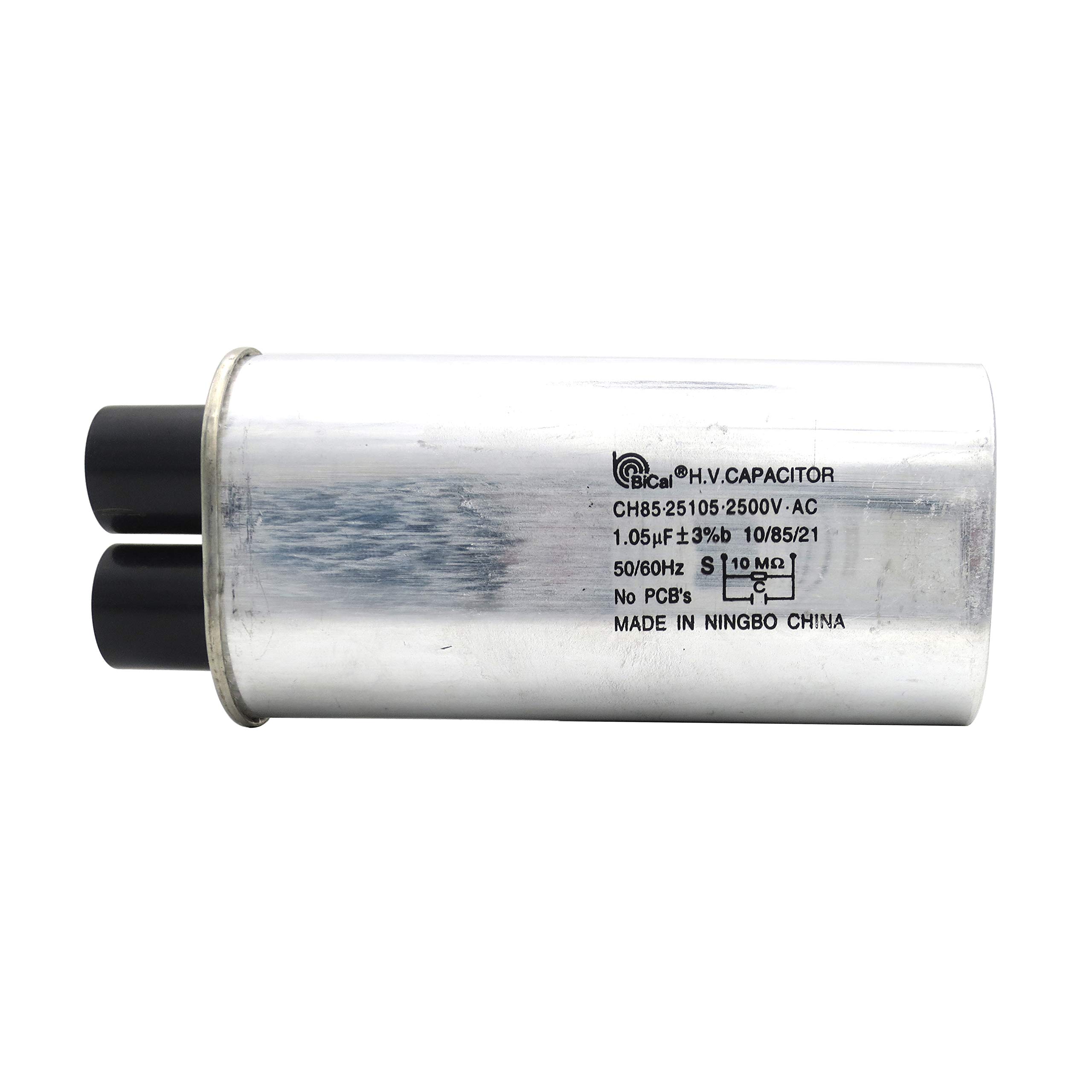
Key Highlights: CH85 High Voltage Capacitors are designed to meet the mechanical, electrical, and performance requirements of microwave oven manufacturers….
#4 Presidio High Voltage Capacitors Chips, Stacks and Radial Leaded
Domain Est. 1997
Website: presidiocomponents.com
Key Highlights: Presidio Components High Voltage Capacitors, one of the world’s leading manufacturers of high quality ceramic capacitors for space, military, microwave, ……
#5 Passive Plus
Domain Est. 2005
Website: passiveplus.com
Key Highlights: PPI is a manufacturer of high-performance RF/Microwave passive components. Quick delivery, competitive pricing. Find out how PPI Components can work for ……
#6 Advanced Electronic Components & Solutions
Domain Est. 2021
Website: kyocera-avx.com
Key Highlights: KYOCERA AVX is a leading global manufacturer of advanced electronic components engineered to accelerate technological innovation and build a better future….
#7 High Voltage Capacitor 8206562
Domain Est. 2001
Website: partselect.ca
Key Highlights: In stockHigh Voltage Capacitor – Whirlpool 8206562 – This is an electronic device that holds a charge of electricity….
#8 LG 0CZZW1H004B Microwave Oven High Voltage Capacitor
Domain Est. 2004
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Voltage Capacitor For Microwave Oven

H2: 2026 Market Trends for High Voltage Capacitors in Microwave Ovens
As the global appliance market evolves through technological innovation and shifting consumer demands, the high voltage capacitor segment for microwave ovens is expected to experience significant transformation by 2026. These components, essential for stepping up voltage in magnetron-based microwave systems, are influenced by trends in energy efficiency, miniaturization, cost optimization, and the broader transition toward smart and sustainable appliances.
1. Rising Demand for Energy-Efficient and Compact Microwave Ovens
By 2026, increasing consumer preference for energy-efficient kitchen appliances will drive demand for high-performance, compact high voltage capacitors. Manufacturers are focusing on capacitors with higher capacitance density and reduced energy loss, enabling smaller microwave designs without sacrificing power output. This trend is particularly strong in urban markets where space-saving appliances are in higher demand.
2. Technological Advancements in Capacitor Materials
The adoption of advanced dielectric materials—such as polypropylene film with improved thermal stability and self-healing properties—is expected to accelerate. These materials enhance capacitor reliability, extend lifespan, and reduce failure rates in microwave ovens, especially under fluctuating voltage conditions. Innovations in nanocomposite dielectrics may also begin to enter commercial production by 2026, offering superior performance in high-stress environments.
3. Consolidation of Supply Chains and Regional Manufacturing Shifts
Ongoing geopolitical dynamics and supply chain resilience concerns are prompting a regionalization of production. By 2026, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, South Korea, and India—is expected to dominate both production and consumption of high voltage capacitors for microwave ovens. Localized manufacturing reduces logistics costs and supports faster time-to-market, especially as microwave oven production grows in emerging markets.
4. Impact of Smart and Inverter Microwave Technologies
The growing adoption of inverter microwave ovens, which provide consistent power delivery and improved cooking control, is reshaping capacitor requirements. Inverter models demand capacitors capable of handling variable voltage loads and maintaining stable performance over extended cycles. This shift is increasing the average value per unit and encouraging capacitor manufacturers to develop specialized components tailored for inverter systems.
5. Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH are pushing manufacturers to eliminate harmful materials like PCBs and certain halogenated compounds from capacitor construction. By 2026, compliance with eco-design directives will be standard, promoting the use of lead-free soldering and recyclable housing materials. This not only reduces environmental impact but also aligns with consumer expectations for greener appliances.
6. Competitive Landscape and Pricing Pressures
While technological innovation supports premium product development, intense competition in the microwave oven market continues to exert downward pressure on component prices. Capacitor manufacturers are responding by optimizing production processes, investing in automation, and forming strategic partnerships with OEMs to secure long-term contracts and achieve economies of scale.
Conclusion
By 2026, the high voltage capacitor market for microwave ovens will be characterized by a balance between technological advancement and cost efficiency. Growth will be driven by demand for smarter, smaller, and more energy-efficient appliances, particularly in developing regions. Manufacturers who invest in material science, sustainability, and supply chain agility will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing High Voltage Capacitors for Microwave Ovens (Quality and Intellectual Property)

Logistics & Compliance Guide for High Voltage Capacitor For Microwave Oven
Product Overview
High Voltage Capacitors for microwave ovens are critical components used to store and deliver electrical energy in microwave magnetron circuits. Due to their high voltage rating (typically 2000–2200 VAC), these capacitors are subject to strict safety, handling, and regulatory requirements throughout their lifecycle—from manufacturing to end-of-life disposal.
Regulatory Compliance
International Safety Standards
High voltage capacitors must comply with key international safety and performance standards, including:
– IEC 60384-14: Fixed capacitors for use in electronic equipment – Part 14: Sectional specification – Fixed capacitors for electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression and connection to the supply mains.
– UL 60384-14: Safety standard for capacitors used in appliances, aligned with IEC standards under the UL recognition program.
– EN 60384-14: European version of IEC 60384-14, required for CE marking.
– RoHS (EU Directive 2011/65/EU): Restricts the use of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and certain flame retardants.
– REACH (EC 1907/2006): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in articles.
Capacitors must be certified by recognized bodies (e.g., UL, TÜV, CSA) and bear appropriate certification marks.
Environmental and Chemical Regulations
- RoHS Compliance: Ensure capacitors contain no restricted substances above threshold levels. Suppliers must provide material declarations and test reports.
- REACH SVHC Screening: Confirm absence of substances on the REACH Candidate List.
- Proposition 65 (California): If sold in California, ensure labeling requirements are met for chemicals like lead (common in older capacitor terminals).
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Packaging
- Use static-dissipative or anti-static packaging to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
- Capacitors must be individually insulated or spaced to avoid short-circuiting.
- Inner packaging should be moisture-resistant (e.g., sealed poly bags with desiccants) to prevent corrosion.
- Outer packaging must be robust (e.g., corrugated cardboard boxes) with sufficient cushioning to withstand transport vibration and drops.
Labeling
- Include:
- Manufacturer name and part number
- Capacitance value and voltage rating (e.g., 1.05 µF ±5%, 2100 VAC)
- Polarity marking (if applicable)
- Date of manufacture or lot code
- Compliance marks (UL, CE, RoHS, etc.)
- “Caution: High Voltage” warning symbol
- Labels must be durable and legible under normal storage and transport conditions.
Storage and Handling
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 5°C to 35°C, RH < 75%).
- Avoid exposure to corrosive gases, direct sunlight, or extreme humidity.
- Shelf life: Typically 2–5 years; follow manufacturer guidelines. Periodic testing may be required for long-term storage.
Handling Precautions
- Always discharge capacitors before handling using a properly rated resistor (e.g., 10kΩ, 5W). Never short terminals with a conductor.
- Use ESD-safe tools, wrist straps, and work surfaces.
- Personnel must be trained in high-voltage component safety.
Transportation Logistics
Domestic and International Shipping
- UN/DOT Regulations: High voltage capacitors are generally not classified as hazardous materials if fully discharged and properly packaged. However, verify with manufacturer documentation.
- IATA/ICAO (Air Transport): Not typically restricted unless containing hazardous dielectrics (e.g., PCBs—now obsolete). Confirm exclusion from dangerous goods lists (e.g., IATA DGR, Class 9).
- IMDG Code (Sea Freight): Usually exempt; ensure packaging meets vibration, moisture, and stacking requirements.
Special Considerations
- Avoid extreme temperatures during transit (e.g., no cargo holds with temperatures >60°C).
- Use climate-controlled transport if necessary.
- Clearly mark packages as “Fragile” and “Do Not Stack” if required.
Import/Export Compliance
Customs Classification
- HS Code Example: 8532.29.00 (Fixed capacitors, other ceramic dielectric, other) or 8532.30.00 (Aluminum electrolytic capacitors). Confirm based on dielectric type and construction.
- Country-specific tariffs and rules of origin may apply (e.g., USMCA, EU preferences).
Documentation
- Commercial invoice with detailed technical specifications
- Packing list
- Certificate of Compliance (RoHS, REACH, UL/IEC)
- Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
- Material Declarations (e.g., SVHC, conflict minerals if applicable)
End-of-Life and Recycling
Disposal Regulations
- High voltage capacitors may contain small amounts of hazardous materials (e.g., dielectric fluids, lead terminals).
- Dispose of in accordance with local e-waste regulations (e.g., WEEE Directive in EU, EPA rules in US).
- Do not incinerate or landfill.
Recycling
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers who can safely recover metals and insulating materials.
- Capacitors should be discharged and physically damaged (punctured) before recycling to prevent accidental energizing.
Summary of Key Actions
- Verify full compliance with IEC/UL/EN 60384-14 and environmental directives (RoHS, REACH).
- Use ESD-safe, moisture-resistant packaging with clear safety labeling.
- Train personnel in safe handling and discharge procedures.
- Confirm non-hazardous classification for shipping; prepare full documentation.
- Ensure proper end-of-life management through certified e-waste channels.
By following this guide, businesses can ensure the safe, compliant, and efficient logistics of high voltage capacitors for microwave ovens across global supply chains.
Conclusion: Sourcing High Voltage Capacitors for Microwave Ovens
Sourcing a high voltage capacitor for a microwave oven requires careful consideration of safety, technical specifications, and supplier reliability. High voltage capacitors are critical components in the magnetron circuit, operating at voltages exceeding 2,000 volts and playing a vital role in efficient microwave generation. Therefore, selecting a capacitor that meets the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications—including capacitance value (typically 0.8–1.2 µF), voltage rating, physical dimensions, and safety certifications—is essential for both performance and user safety.
When sourcing replacement capacitors, it is strongly recommended to choose components from reputable manufacturers or suppliers who provide compliance with international safety standards such as UL, CSA, or IEC. Counterfeit or substandard capacitors pose significant risks, including overheating, short circuits, or catastrophic failure, which can lead to fire hazards or damage to other microwave components.
Additionally, consideration should be given to environmental and disposal regulations due to the presence of potentially hazardous dielectric materials in older capacitors. Opting for modern, RoHS-compliant components ensures environmental responsibility and regulatory compliance.
In summary, successful sourcing of a high voltage capacitor for a microwave oven hinges on prioritizing safety, matching technical specifications accurately, and procuring from trustworthy suppliers. Proper selection and installation not only ensure reliable appliance operation but also protect users from potentially dangerous electrical hazards.