The global thermal imaging market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across defense, industrial, and commercial sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the high-resolution thermal camera market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029, fueled by advancements in infrared sensor technology and increasing adoption in predictive maintenance, surveillance, and autonomous vehicles. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the overall thermal imaging market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.2% through 2030. With resolution capabilities now exceeding 1280×1024 pixels and integration of AI-powered analytics, manufacturers are pushing the boundaries of performance and application breadth. As demand surges for precision thermal data across harsh environments and critical infrastructure, a select group of innovators has emerged as leaders in high-resolution thermal imaging technology. Here are the top nine manufacturers shaping the future of thermal vision.
Top 9 High Resolution Thermal Camera Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
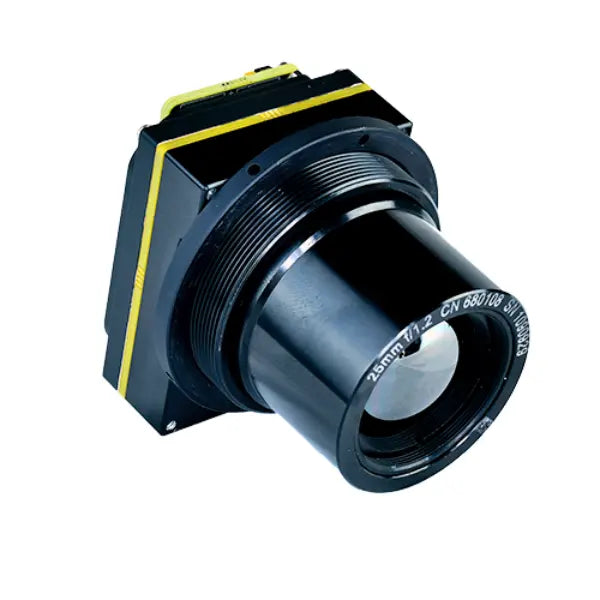
#1 Infrared Cameras Inc.
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 1995
Website: buy.infraredcameras.com
Key Highlights: Explore the best in thermal imaging and infrared systems with ICI. Trusted since 1995, we deliver unmatched accuracy, reliability, and innovation for ……
#2 Flir
Domain Est. 1993
Website: flir.com
Key Highlights: High-Speed Thermal Imaging · Material Research & Testing · Target Tracking & Long Range Measurements. Security. Back Security Overview. Applications & ……
#3 Seek Thermal
Domain Est. 1993
Website: thermal.com
Key Highlights: Highest resolution, most full-featured thermal imaging camera in its class. Learn more. Picture. Premium performance, easy to integrate, and ……
#4 Thermal
Domain Est. 2002
Website: hikvision.com
Key Highlights: Hikvision Thermal Cameras guarantee layered situational awareness across a range of scenarios such as perimeter protection, temperature measurement, and fire ……
#5 Infrared Camera Models 2025
Domain Est. 2007
Website: infratec-infrared.com
Key Highlights: You are interested in buying an infrared camera? At InfraTec you can choose from an extensive range of over 30 models with a wide variety of features!…
#6 Pulsar Vision
Domain Est. 2010
Website: pulsarvision.com
Key Highlights: Pulsar: global leader in premium night vision & thermal imaging. For hunters, nature lovers & pros seeking precision and innovation….
#7 FOTRIC
Domain Est. 2015
Website: fotric.com
Key Highlights: FOTRIC leads in innovating and manufacturing advanced thermal and acoustic imaging cameras, redefining reliability testing and maintenance….
#8 Sierra
Domain Est. 2021
Website: sierraolympia.com
Key Highlights: Our engineering focus drives performance. We combine optical, mechanical, and electronic design expertise to deliver dependable infrared imaging solutions ……
#9 Best Thermal Imaging Cameras
Domain Est. 1986
Website: fluke.com
Key Highlights: Fluke infrared thermal imaging cameras provide you with high-quality thermal images for industrial inspection. You can discover faults and failures before they ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Resolution Thermal Camera

H2: Key 2026 Market Trends for High-Resolution Thermal Cameras
The high-resolution thermal camera market is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding applications, and evolving industry demands. Key trends shaping this landscape include:
1. Proliferation of High-Resolution Microbolometers (1024×768 and Beyond):
* Mainstreaming of HD+ Formats: While 640×480 remains common, 1024×768 resolution microbolometers are rapidly transitioning from niche to mainstream. By 2026, they are expected to become the de facto standard for professional and industrial applications, offering significantly improved detail, longer detection ranges, and better image clarity.
* Emergence of 1280×1024 and Higher: 1280×1024 (SXGA) sensors, currently premium offerings, will see increased adoption in critical sectors like defense, aerospace, and advanced R&D. Early commercialization of 1920×1080 (Full HD) thermal sensors will begin, primarily in defense and specialized scientific applications, setting the stage for future consumerization.
* Cost Reduction: Economies of scale and manufacturing improvements will gradually reduce the cost premium of high-resolution sensors, making them more accessible to mid-tier industrial and commercial users.
2. Miniaturization and Integration:
* Smaller Form Factors: Demand for drones, handheld devices, wearables, and embedded systems (e.g., in vehicles, robots) will drive the development of smaller, lighter, and lower-power high-resolution cores. Wafer-Level Packaging (WLP) and advanced MEMS fabrication will be crucial.
* System-on-Chip (SoC) and Smart Sensors: Integration of processing, memory, and connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G) directly onto the sensor package or core module will create “smart thermal cameras.” These enable edge AI processing, reducing latency, bandwidth needs, and system complexity.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Integration:
* On-Device Analytics: AI algorithms will be increasingly embedded directly into camera hardware or edge processors. This enables real-time automated detection, classification (e.g., human vs. animal, equipment fault types), anomaly detection, and predictive maintenance without relying on cloud connectivity.
* Enhanced Image Processing: AI will improve image quality through noise reduction, super-resolution (effectively enhancing perceived resolution), dynamic range optimization, and fusion with visible light data.
* Automated Workflows: AI-driven analytics will automate inspection processes in manufacturing, building diagnostics, and security, improving speed, consistency, and reducing reliance on operator expertise.
4. Expansion into New and Evolving Applications:
* Automotive (ADAS & Autonomous Driving): High-resolution thermal (especially 640×480+) will be critical for L3+ autonomous vehicles, providing robust night vision, pedestrian/animal detection in challenging conditions (fog, smoke, glare), and cabin occupancy monitoring. Integration with LiDAR and radar (sensor fusion) is key.
* Industrial Automation & Predictive Maintenance: Wider adoption for monitoring electrical substations, manufacturing processes (e.g., semiconductor, composites), and complex machinery. High resolution enables precise hotspot identification on crowded panels and early fault detection on smaller components.
* Smart Cities & Infrastructure: Use in traffic monitoring (congestion, incident detection), building energy audits, bridge/structural inspections, and perimeter security for critical infrastructure.
* Consumer & Prosumer: While lower resolution dominates, high-res thermal (driven by smartphone attachments and premium drones) will gain traction among enthusiasts, home inspectors, and security-conscious consumers as prices fall.
5. Advancements in Materials and Technologies:
* Quantum Dot Infrared Photodetectors (QDIPs): Potential to offer lower-cost, high-resolution alternatives to microbolometers in the longer term, though 2026 may see more R&D and niche prototypes.
* Improved NETD and Frame Rates: Ongoing improvements in sensor sensitivity (lower Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference – NETD) and faster frame rates (beyond 60Hz) will enhance performance in dynamic scenarios and low-contrast environments.
* Multi-Spectral & Fusion: Increased integration of thermal with visible light, SWIR, and LiDAR sensors in single platforms, providing richer contextual data. Advanced algorithms will seamlessly fuse these data streams.
6. Market Consolidation and Competitive Dynamics:
* Consolidation: The high-resolution segment requires significant R&D investment. Expect continued consolidation as larger players (e.g., Teledyne FLIR, Leonardo DRS, Seek Thermal) acquire innovative sensor startups or smaller competitors to secure IP and manufacturing capacity.
* Regional Competition: Intensifying competition, particularly from well-funded Asian manufacturers (China, South Korea) aiming to capture market share with competitive pricing and rapid iteration, potentially accelerating cost reduction.
7. Regulatory and Standardization Focus:
* Automotive Standards: Development and adoption of specific standards for thermal cameras in automotive applications (e.g., safety ratings, performance benchmarks) will be crucial for widespread OEM adoption.
* Data Privacy: Increased use in public spaces and consumer devices will heighten scrutiny on data collection, storage, and privacy, potentially leading to new regulations or best practices.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the high-resolution thermal camera market will be defined by higher sensor resolutions becoming standard, deeper integration of AI for intelligent analytics at the edge, significant miniaturization enabling new form factors, and explosive growth driven by automotive and industrial automation. While cost remains a factor, technological advancements and scale will continue to broaden accessibility. Companies that successfully innovate in sensor technology, AI integration, and cost-effective manufacturing will lead this dynamic and expanding market.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing High-Resolution Thermal Cameras (Quality & IP Considerations)
Sourcing high-resolution thermal cameras involves navigating complex technical, quality, and intellectual property (IP) landscapes. Overlooking key aspects can lead to performance shortfalls, legal risks, and project failures. Below are critical pitfalls to avoid:
H2: Overlooking Sensor Specifications and Real-World Performance
Purchasers often focus solely on advertised resolution (e.g., 640×480) without evaluating the underlying sensor quality and real-world thermal sensitivity. Low NETD (Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference) values—ideally below 40 mK—indicate superior ability to detect minute temperature differences, crucial for precision applications. Additionally, uncooled microbolometer sensors vary significantly in lifespan and stability. Choosing a camera based only on resolution may result in poor image clarity, reduced detection range, and inconsistent performance in challenging environments.
H2: Ignoring Genuine IP Protection and Firmware Authenticity
High-resolution thermal imaging technology is heavily protected by patents and proprietary firmware. Sourcing from manufacturers or suppliers without verified IP rights can expose buyers to infringement risks. Counterfeit or rebranded units may use stolen algorithms or unlicensed software, leading to legal liability, lack of updates, and compromised performance. Always verify the supplier’s authorization, request documentation of IP ownership or licensing, and assess firmware update policies to ensure long-term compliance and support.
H2: Underestimating Calibration and Long-Term Stability
High-resolution thermal cameras require precise factory calibration and periodic recalibration to maintain accuracy. Some low-cost suppliers cut corners by using inadequate calibration processes or omitting NIST-traceable certificates. Without proper calibration, temperature measurements drift over time, undermining the reliability of critical data. Ensure the supplier offers recalibration services, provides calibration reports, and uses stable sensor platforms designed for long-term deployment.
H2: Neglecting Software Development Kit (SDK) and Integration Rights
Many applications require integration with custom software, making the SDK a vital component. Hidden pitfalls include restrictive licensing terms, lack of source code access, or limited API functionality that hinders development. Some vendors charge exorbitant fees for commercial use of their SDKs or fail to protect your derivative software from IP claims. Evaluate SDK licensing thoroughly and confirm you retain ownership of your application code built on top of the provided tools.
H2: Assuming All High-Resolution Sensors Are Interchangeable
Not all thermal sensors of the same resolution deliver equivalent performance. Variations in pixel pitch, fill factor, and manufacturing processes affect image sharpness and thermal accuracy. Additionally, integration with the camera’s optics and processing engine significantly impacts output quality. Relying on generic datasheets without side-by-side testing or independent reviews can result in subpar image quality. Request sample units for evaluation under real operating conditions before finalizing procurement.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for High Resolution Thermal Camera
Regulatory Classification and Export Controls
High Resolution Thermal Cameras are subject to stringent international export regulations due to their potential dual-use applications in military, surveillance, and industrial contexts. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR): Cameras with resolutions exceeding certain thresholds (e.g., pixel counts above 640×480 or specific thermal sensitivity) may be classified under the U.S. Munitions List (USML), Category XII, requiring ITAR licensing for export.
- Export Administration Regulations (EAR): Cameras not controlled by ITAR may fall under the Commerce Control List (CCL), typically under ECCN 6A003 or 6A993, depending on resolution, frame rate, and spectral range. A license may be required for certain destinations.
- Wassenaar Arrangement: Many countries adhere to this multilateral export control regime, which includes thermal imaging systems with high spatial resolution and sensitivity. Compliance ensures alignment with global standards.
Prior to shipment, verify the specific technical specifications against current control lists and obtain necessary export licenses from the relevant authority (e.g., U.S. Department of State or Bureau of Industry and Security).
Import Requirements and Customs Documentation
Importing a High Resolution Thermal Camera may trigger additional scrutiny depending on the destination country. Key considerations include:
- Customs Tariff Classification: Determine the correct Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 9030.39 or 8543.70, depending on function and design) to assess import duties and taxes.
- Import Permits: Some countries require prior authorization for dual-use technology. Examples include the EU Dual-Use Regulation (EU 2021/821) and similar frameworks in Canada, Australia, and Japan.
- Required Documentation: Prepare a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, export license (if applicable), technical specifications, and end-user statement. For ITAR-controlled items, a DSP-5 or equivalent authorization must accompany the shipment.
Ensure all documents clearly describe the item without technical ambiguity to prevent customs delays.
Transportation and Packaging Standards
Due to sensitivity and value, proper handling is critical during transit:
- Packaging: Use anti-static, shock-resistant packaging with internal cushioning. Include desiccants to prevent moisture damage. Clearly label with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not X-Ray” (if applicable).
- Shipping Methods: Use reputable carriers experienced in handling controlled technology (e.g., FedEx, DHL with special handling options). Air freight is recommended for speed and tracking.
- Temperature and Environmental Controls: Avoid extreme temperatures during transport; thermal cameras can be sensitive to cold or heat. Monitor environmental conditions if shipping across diverse climates.
End-Use and End-User Compliance
Compliance does not end at shipment. Ongoing obligations include:
- End-User Verification: Confirm the end-user is authorized and matches the license terms. Prohibited end-uses include military or intelligence applications unless explicitly permitted.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain records of export transactions, licenses, and communications for a minimum of five years (longer under ITAR).
- Red Flags: Be alert to suspicious requests such as unusual payment methods, lack of technical knowledge, or attempts to reroute shipments through third countries.
Country-Specific Restrictions
Certain countries face comprehensive embargoes or require special authorization:
- Prohibited Destinations: Do not ship to sanctioned countries (e.g., Iran, North Korea, Syria, Crimea region) without specific government authorization.
- License Exceptions: Evaluate eligibility for license exceptions such as ENC (Encryption Commodities) or TMP (Temporary Imports), though these rarely apply to high-resolution thermal cameras.
Always consult up-to-date country charts from the relevant regulatory body before initiating any shipment.
Compliance Best Practices
- Conduct regular internal audits of export processes.
- Train staff on export control regulations.
- Use classification tools and legal counsel to ensure accurate product categorization.
- Register with appropriate government agencies if handling ITAR or EAR-controlled items.
Adhering to this guide minimizes legal risk and ensures seamless international logistics for High Resolution Thermal Cameras.
Conclusion:
Sourcing a high-resolution thermal camera requires careful consideration of application needs, technical specifications, budget, and long-term value. High-resolution models offer superior thermal imaging capabilities, enabling precise temperature measurement, clearer visualization of thermal patterns, and reliable performance in demanding environments such as industrial maintenance, building diagnostics, electrical inspections, and research. While these cameras typically come at a higher initial cost, their enhanced accuracy and efficiency can lead to significant cost savings and improved decision-making over time.
When selecting a supplier or model, prioritize reputable manufacturers known for quality, reliability, and strong technical support. Key features to evaluate include thermal resolution (e.g., 640×480 or higher), thermal sensitivity, temperature range, lens options, and integration capabilities with analysis software. Additionally, consider warranty, calibration services, and available training.
In summary, investing in a high-resolution thermal camera is a strategic decision that enhances diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency. By aligning technical requirements with application goals and choosing a trusted provider, organizations can ensure optimal performance and a strong return on investment.