The global high-pressure steam boiler market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising energy demands across industrial and power generation sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global steam boiler market size was valued at USD 16.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing adoption in chemical processing, food and beverage, and power plants, where high-efficiency and reliable steam generation are critical. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects steady market expansion, citing advancements in boiler technology and a global shift toward cleaner, more efficient energy systems as key contributors. As demand for high-pressure steam boilers rises, manufacturers are focusing on innovation, fuel flexibility, and compliance with stringent emissions standards. In this evolving landscape, the following nine companies have emerged as leading manufacturers, distinguished by their technological expertise, global footprint, and consistent performance in delivering high-pressure steam solutions.
Top 9 High Pressure Steam Boiler Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Clayton Industries
Domain Est. 1997
Website: claytonindustries.com
Key Highlights: Clayton Industries is proud to be a leading industrial steam boiler manufacturer at the forefront of steam technology delivering unparalleled efficiency, ……
#2 Hurst Boiler
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hurstboiler.com
Key Highlights: Hurst Boiler, Inc. is the leading manufacturer of gas, oil, wood, coal, solid fuel, solid waste, biomass and hybrid fuel-fired steam and hot water boilers….
#3 Page ⋆ Burnham Commercial Boilers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: burnhamcommercial.com
Key Highlights: Burnham Commercial is a leading manufacturer of high-quality boilers and boiler control systems for commercial and industrial applications….
#4 New Yorker Boiler
Domain Est. 2000
Website: newyorkerboiler.com
Key Highlights: New Yorker Boiler manufactures residential heating products, such as high efficiency water and steam boilers and water heaters….
#5 U.S. Boiler Company
Domain Est. 2010
Website: usboiler.net
Key Highlights: U.S. Boiler Company is a leading manufacturer of home heating equipment, water boilers, steam boilers, hot water heaters, radiators and boiler control systems….
#6 Fulton: High
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fulton.com
Key Highlights: Trusted globally, Fulton engineers high-efficiency steam and hydronic boilers, thermal fluid heaters, and custom heat transfer systems….
#7 All Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: weil-mclain.com
Key Highlights: Steam; /; Water. 88 High Efficiency Series 3 Commercial Gas Oil Boiler. Fuel Type: Gas; /; Oil. Heat Exchanger Material: Cast Iron. Heating Range: 960-5440 MBH ……
#8 Superior Boiler
Domain Est. 1997
Website: superiorboiler.com
Key Highlights: Superior Boiler solves your most complex boiler challenges so you can get down to business – sterilizing essential hospital equipment, heating large facilities….
#9 Cleaver
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cleaverbrooks.com
Key Highlights: Cleaver-Brooks is your total solution provider for boilers and boiler room systems, including rentals, maintenance programs, parts, and training….
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Pressure Steam Boiler
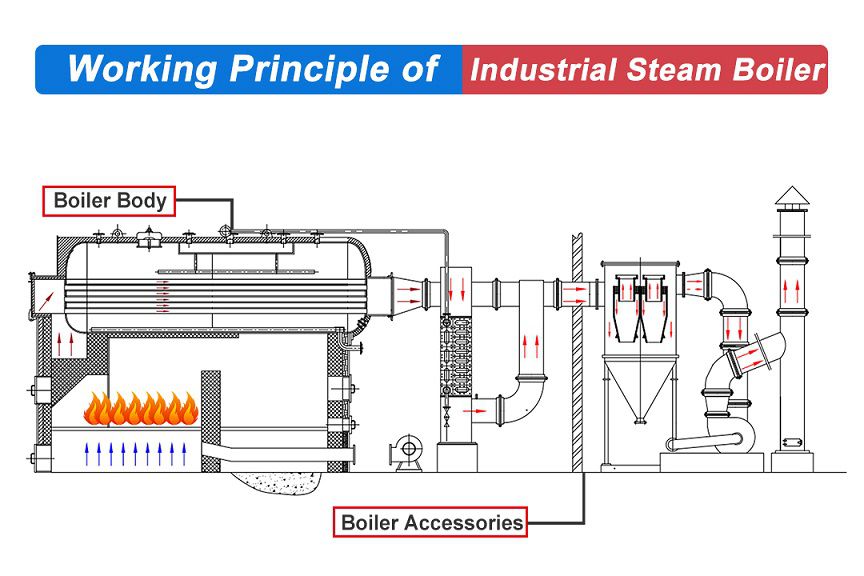
H2: 2026 Market Trends for High-Pressure Steam Boilers
The global high-pressure steam boiler market is anticipated to experience significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving energy demands, technological innovation, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and efficiency. Below is a comprehensive analysis of the key market trends expected to shape the industry during this period:
1. Increased Demand from Industrial and Power Generation Sectors
High-pressure steam boilers remain critical in power plants (especially coal, biomass, and waste-to-energy), refineries, chemical processing, and manufacturing. As emerging economies expand their industrial base and developed nations modernize aging infrastructure, demand for reliable, high-efficiency steam generation systems is projected to rise. The push for energy security will further bolster investments in robust boiler solutions capable of supporting base-load and peak-load operations.
2. Adoption of Advanced Materials and Design Technologies
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to increasingly adopt advanced materials such as high-temperature alloys, corrosion-resistant composites, and nano-coatings to enhance boiler durability under extreme pressure and temperature conditions. Innovations in boiler design—such as ultra-supercritical (USC) and advanced ultra-supercritical (A-USC) technologies—will enable higher thermal efficiency (up to 45–50%), reduced fuel consumption, and lower emissions. These designs will be especially prominent in new-build power plants aiming to meet stringent environmental standards.
3. Integration of Digitalization and IoT
Smart boiler systems equipped with IoT sensors, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance algorithms, and AI-driven control systems are expected to become standard by 2026. These digital solutions optimize combustion, improve safety, reduce downtime, and streamline operations. Remote diagnostics and cloud-based analytics will enable operators to enhance performance and respond proactively to potential failures, increasing overall system reliability and reducing operational costs.
4. Shift Toward Low-Carbon and Renewable Fuels
With global decarbonization goals intensifying, there will be a notable shift toward using high-pressure boilers compatible with low-carbon fuels such as biomass, biogas, hydrogen blends, and synthetic gases. Retrofitting existing boilers for hydrogen co-firing (up to 20–30%) is expected to gain traction, particularly in Europe and North America. Some new installations may be designed as “hydrogen-ready,” anticipating future full hydrogen conversion as infrastructure develops.
5. Stringent Emission Regulations Driving Innovation
Environmental regulations such as the EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), U.S. EPA standards, and China’s Ultra-Low Emissions (ULE) policies will compel boiler manufacturers and end-users to adopt cleaner technologies. This includes integrating advanced flue gas treatment systems (e.g., SCR, FGD, and ESP) with high-pressure boilers to minimize NOx, SOx, and particulate emissions. Compliance will be a key purchase driver, especially in urban and environmentally sensitive areas.
6. Growth in Modular and Prefabricated Boiler Systems
To reduce installation time and costs, modular high-pressure boiler units are expected to gain popularity. These prefabricated systems offer scalability, easier maintenance, and flexibility in deployment—particularly in remote or temporary industrial sites. The trend aligns with the broader industrial shift toward modular construction and fast-track project delivery.
7. Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific: Expected to dominate the market due to rapid industrialization in India, Southeast Asia, and ongoing coal-to-clean transitions in China. Government initiatives promoting efficient power generation will drive demand.
- Europe: Focus will be on retrofitting and replacing old boilers with high-efficiency, low-emission models, supported by EU Green Deal funding and carbon pricing mechanisms.
- North America: Steady demand from industrial sectors and power generation, with an emphasis on digitalization and hydrogen compatibility.
- Middle East & Africa: Growth driven by expanding petrochemical industries and investments in power infrastructure.
8. Supply Chain and Raw Material Challenges
Volatility in the prices of steel, nickel, and other critical materials may impact manufacturing costs. However, by 2026, increased localization of production and strategic supplier partnerships are expected to mitigate supply chain risks. Recycling of boiler components and circular economy principles may also influence procurement strategies.
9. Rising Focus on Energy Efficiency and Heat Recovery
High-pressure boilers will increasingly be integrated into combined heat and power (CHP) and waste heat recovery systems to maximize energy utilization. Industries aiming for net-zero targets will prioritize systems that reduce energy waste and improve overall plant efficiency.
Conclusion
By 2026, the high-pressure steam boiler market will be characterized by a convergence of efficiency, digitalization, and sustainability. While traditional fossil fuel-based systems will still hold significant market share, the industry will pivot toward cleaner fuels, smarter operations, and compliance with global environmental standards. Companies that invest in innovation, modular solutions, and low-carbon technologies will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing High-Pressure Steam Boilers (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a high-pressure steam boiler is a critical decision that impacts operational efficiency, safety, and long-term maintenance costs. While evaluating technical specifications and supplier reputation, buyers must also be vigilant about quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Below are the most common pitfalls in these two key areas:
- Compromised Quality Due to Substandard Materials or Manufacturing
- Pitfall: Selecting suppliers who use inferior materials (e.g., low-grade steel, inadequate insulation) to reduce costs, leading to reduced boiler lifespan, safety hazards, and frequent breakdowns.
- Risk: Increased downtime, higher maintenance costs, and potential non-compliance with pressure vessel codes (e.g., ASME, PED).
-
Mitigation: Require third-party certification (e.g., ASME “S” stamp), material test reports (MTRs), and factory acceptance testing (FAT). Conduct site audits of the manufacturer’s facility.
-
Inadequate Design Validation and Testing
- Pitfall: Accepting boiler designs without proper validation under real-world operating conditions or failure to verify performance data.
- Risk: Underperformance, inefficiency, or catastrophic failure under high-pressure conditions.
-
Mitigation: Insist on performance guarantees backed by test data, and ensure design compliance with recognized standards (e.g., ASME BPVC Section I).
-
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
- Pitfall: Incomplete or falsified documentation (e.g., missing weld logs, uncertified materials).
- Risk: Regulatory non-compliance, failed inspections, and liability in case of failure.
-
Mitigation: Require full documentation packs including design calculations, inspection records, and compliance certificates.
-
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement by Suppliers
- Pitfall: Unknowingly sourcing boilers that incorporate patented technologies (e.g., burner designs, control systems) without proper licensing.
- Risk: Legal action against the end-user, forced equipment removal, or costly retrofits.
-
Mitigation: Include IP indemnity clauses in contracts and verify that the supplier owns or licenses all critical technologies used.
-
Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
- Pitfall: Suppliers using cloned or copied components from reputable OEMs to cut costs.
- Risk: Poor reliability, lack of technical support, and voided warranties.
-
Mitigation: Specify OEM parts in procurement contracts and conduct technical audits of component sources.
-
Insufficient After-Sales Support and IP Restrictions on Maintenance
- Pitfall: Suppliers restricting access to technical drawings, control software, or spare parts through proprietary IP controls.
- Risk: Dependence on a single vendor for maintenance, inflated service costs, and operational delays.
-
Mitigation: Negotiate access to essential technical documentation and ensure software is licensable or open-standard based.
-
Ambiguity in Warranty and Liability for IP Violations
- Pitfall: Vague contractual terms that do not assign liability if the boiler infringes on third-party IP.
- Risk: Financial and operational exposure if litigation arises.
- Mitigation: Clearly define warranty terms, indemnification for IP claims, and require suppliers to provide proof of freedom-to-operate.
Conclusion
To avoid quality and IP pitfalls when sourcing high-pressure steam boilers, organizations must conduct thorough due diligence, enforce stringent contractual terms, and prioritize transparency and compliance. Engaging independent engineering consultants and legal experts during procurement can significantly reduce risks and ensure long-term operational integrity.
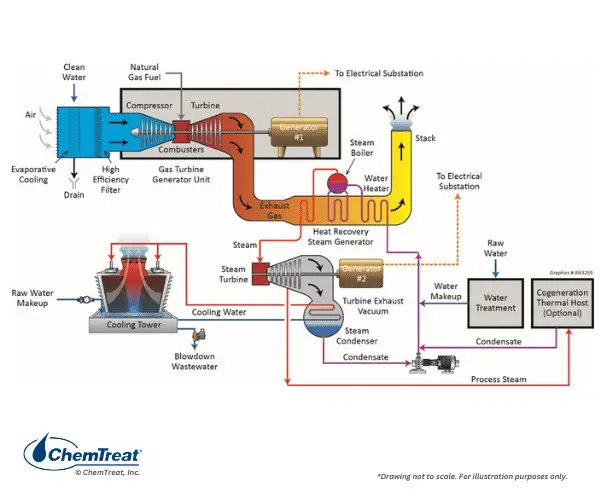
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for High Pressure Steam Boilers
High pressure steam boilers are critical assets in industrial, power generation, and commercial heating applications. Due to their operational risks and regulatory requirements, proper logistics and compliance protocols are essential to ensure safety, efficiency, and legal adherence. This guide outlines key considerations under the H2 framework—highlighting Hazard Management, Handling Procedures, and Health & Safety Compliance.
H2.1 Hazard Management
Identifying and mitigating risks associated with high pressure steam boilers is fundamental.
- Pressure and Temperature Hazards:
High pressure boilers operate above 15 psi (per ASME standards), posing explosion and scalding risks. Ensure: - Pressure relief valves are correctly sized and tested annually.
- Temperature controls and safety cut-offs are calibrated regularly.
-
Pressure vessels comply with ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC), Section I.
-
Chemical Hazards:
Boiler water treatment chemicals (e.g., hydrazine, sodium hydroxide) may be corrosive or toxic. - Use appropriate PPE (gloves, goggles, face shields).
- Store chemicals in labeled, ventilated, and secure areas.
-
Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) on-site and train personnel.
-
Combustion and Emissions Risks:
Fuel types (natural gas, oil, biomass) produce flue gases containing CO, NOx, and SOx. - Install gas detection systems and ventilation.
- Conduct periodic emissions testing per EPA or local air quality regulations.
H2.2 Handling and Logistics Procedures
Efficient and safe logistics during installation, operation, maintenance, and decommissioning.
- Transportation and Installation:
- Use certified rigging and lifting equipment; boilers are heavy and require engineered lifting plans.
- Confirm site structural integrity can support boiler weight and vibrations.
-
Coordinate with utilities for gas, water, and electrical connections.
-
Fuel and Water Supply Chain:
- Ensure uninterrupted supply of treated feedwater meeting boiler specifications (e.g., low hardness, oxygen content).
- Secure fuel supply contracts with contingency plans.
-
Monitor fuel quality (e.g., BTU content, contaminants).
-
Spare Parts and Maintenance Logistics:
- Maintain an inventory of critical spares (gaskets, valves, sensors).
- Schedule preventive maintenance per manufacturer and regulatory timelines.
-
Use qualified technicians for repairs (e.g., NBIC “R” Stamp for repairs in the U.S.).
-
Decommissioning and Disposal:
- Follow environmental regulations for draining, cleaning, and dismantling.
- Recycle metals and dispose of hazardous waste (e.g., refractory materials, sludge) through licensed vendors.
H2.3 Health & Safety Compliance
Adherence to national and international standards ensures operational legality and personnel safety.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- ASME BPVC Section I: Mandatory for design, fabrication, and inspection.
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.168: Covers boiler operation, inspection, and safety controls.
- National Board Inspection Code (NBIC): Required for inspection, repair, and stamping.
-
Local Jurisdiction Requirements: Many states/counties require boiler registration and annual inspections.
-
Certification and Documentation:
- Maintain the ASME “S” Stamp for power boilers.
- Keep an updated Boiler Logbook recording operations, inspections, and incidents.
-
Retain National Board “R” Certificate of Authorization if performing repairs.
-
Operator Training and Certification:
- Operators must be trained and, in some jurisdictions, licensed (e.g., Chief Engineer license).
-
Conduct regular drills for emergency shutdown, blowdown procedures, and fire response.
-
Inspection and Testing Schedule:
- Internal inspection: At least once every 2 years (or per jurisdiction).
- External inspection: Annually.
- Hydrostatic test: After major repairs or as required by code.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for high pressure steam boilers hinge on proactive hazard management, disciplined handling procedures, and strict adherence to health and safety regulations. Implementing the H2 framework ensures operational reliability, regulatory compliance, and the safety of personnel and facilities. Always consult local authorities and certified professionals when planning or modifying boiler systems.
Conclusion: Sourcing a High-Pressure Steam Boiler
Sourcing a high-pressure steam boiler is a significant investment that requires careful consideration of technical specifications, safety standards, energy efficiency, supplier reliability, and long-term operational costs. A well-chosen boiler system ensures consistent performance, enhances process efficiency, and supports compliance with environmental and regulatory requirements.
Key factors such as steam demand, fuel type, available space, maintenance needs, and total cost of ownership must be evaluated thoroughly during the procurement process. Partnering with experienced and reputable suppliers who provide comprehensive after-sales support, warranties, and technical assistance further reduces risks and ensures system longevity.
Ultimately, selecting the right high-pressure steam boiler involves balancing upfront costs with long-term value. By conducting detailed market research, engaging in technical evaluations, and aligning the boiler specifications with operational needs, organizations can secure a reliable, efficient, and sustainable steam generation solution that supports their current and future requirements.