The high pressure die casting (HPDC) process has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, particularly in industries demanding high-volume production of complex, precision-engineered metal components. According to Grand View Research, the global die casting market was valued at USD 59.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2023 to 2030, driven by increasing demand from the automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors. This growth is further accelerated by the automotive industry’s shift toward lightweight aluminum die cast parts to improve fuel efficiency and support electric vehicle (EV) development. As a result, leading manufacturers specializing in high pressure die casting are expanding capabilities, investing in automation, and leveraging advanced simulation technologies to meet tighter tolerances and higher quality standards. These developments have elevated the strategic importance of HPDC players who can deliver scalable, repeatable, and sustainable casting solutions across critical applications—ranging from engine blocks and transmission cases to EV battery housings and structural components. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers excelling in the HPDC space, selected based on production capacity, technological innovation, global footprint, and market influence.
Top 10 High Pressure Die Casting Process Applicatoins Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Die Casting Process
Domain Est. 1995
Website: cwmdiecast.com
Key Highlights: The high-pressure die casting process is the solution if you’re looking for the most economical, efficient technology to produce your component in a durable ……
#2 Precision Die Casting Solutions
Domain Est. 1995
Website: dynacast.com
Key Highlights: Dynacast is a global leader in precision die casting solutions. Explore our innovative manufacturing processes and high-quality parts for diverse ……
#3 [PDF] Aluminum High Pressure Die Casting
Domain Est. 1991
Website: magna.com
Key Highlights: The body and chassis applications of the High-Q-Cast process add to Cosma’s proven track record of advancing the industry with innovative lightweight structures ……
#4 High Pressure Die Casting for Complex Parts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lesueurinc.com
Key Highlights: Our premier die casting services, including design support, prototype services, machining, and more, are completed in-house to save you time and money….
#5 High
Domain Est. 1998
Website: dycastspec.com
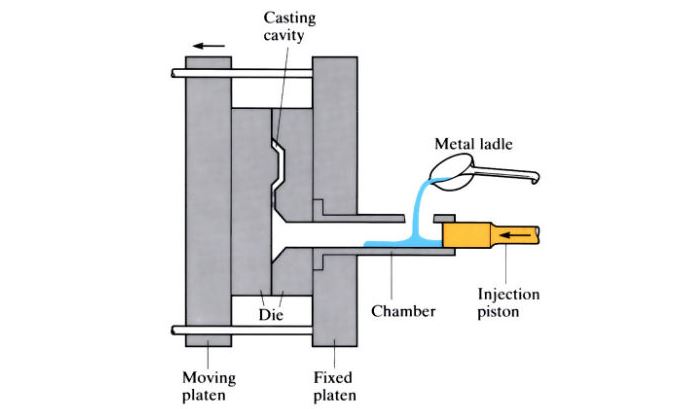
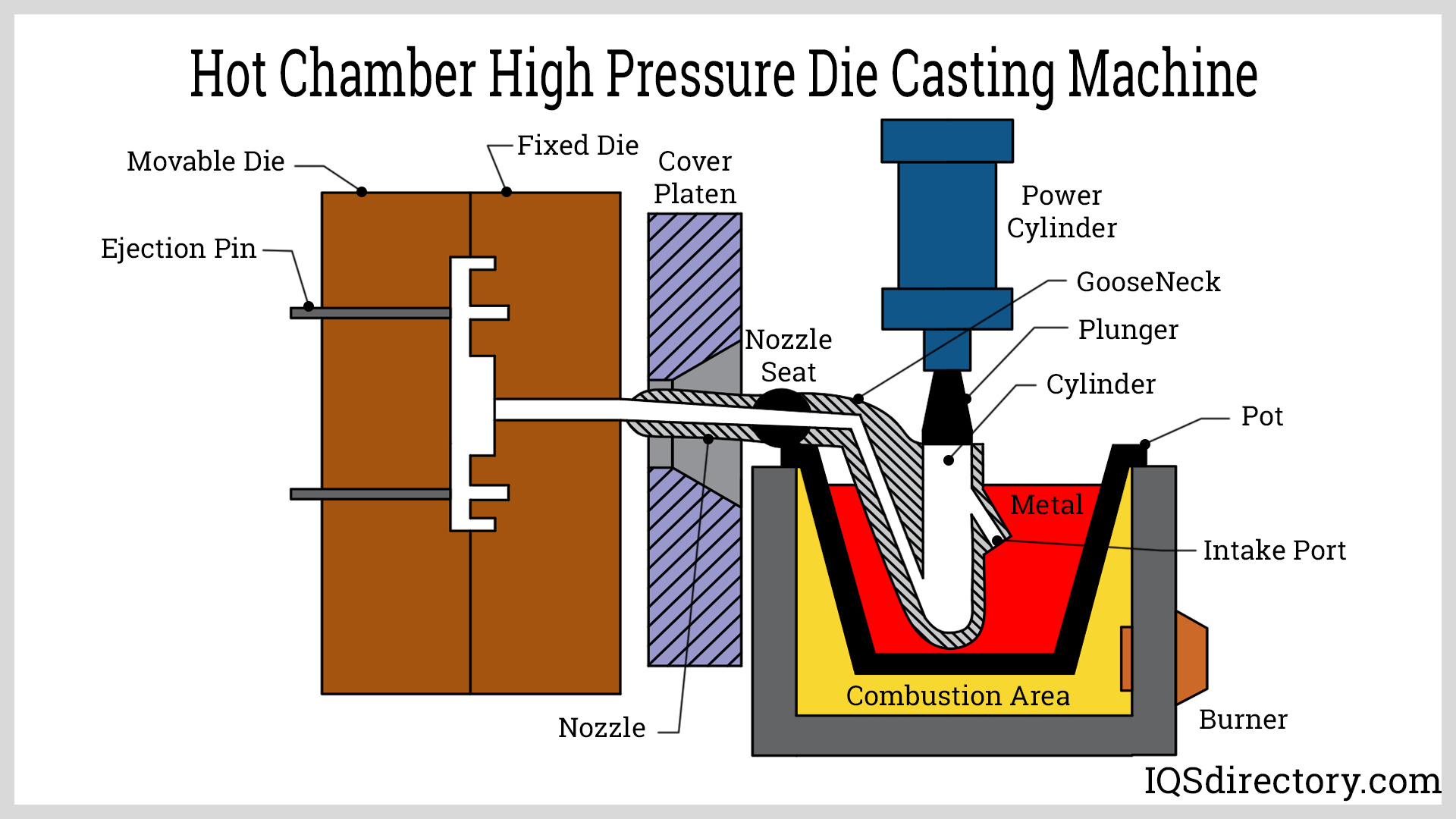
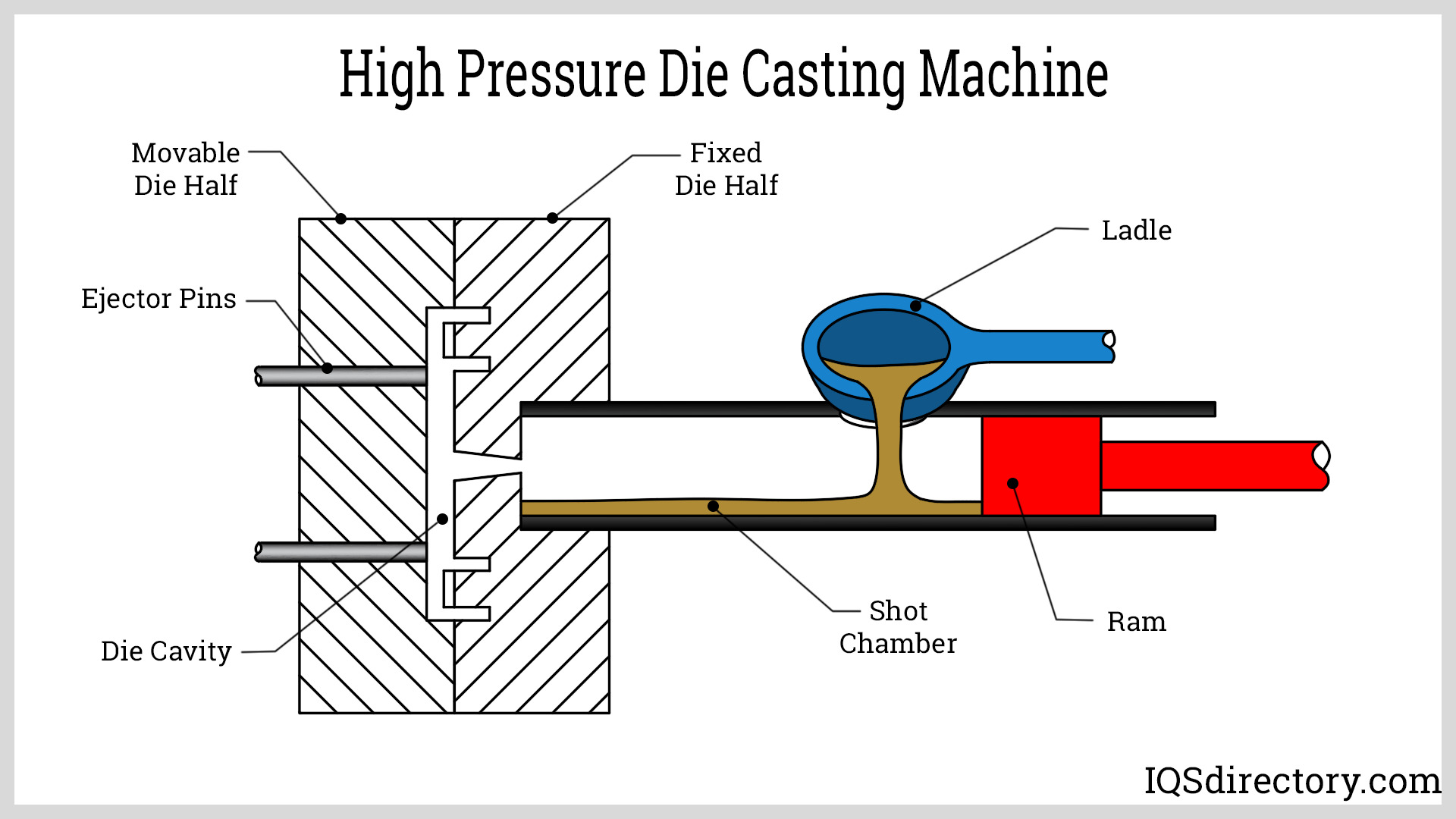
Key Highlights: High pressure die casting is a process where molten metal is forced into a mold cavity at very high pressure until the metal becomes solid. This process is ……
#6 High
Domain Est. 1998
Website: decoprod.com
Key Highlights: The high-pressure die casting production process is similar across all alloys. A cavity is machined out of blocks of steel, leaving an empty ……
#7 Ryobi
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ryobidiecasting.com
Key Highlights: Ryobi is the global leader of high quality, technically complex aluminum casting products for the automotive industry….
#8 Light Metal High Pressure Die Casting
Domain Est. 2008
Website: paceind.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture high volume, innovative and lightweight die casting solutions to serve every industry and application….
#9 High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fathommfg.com
Key Highlights: HPDC is an ideal choice for high-volume, high-performance manufacturing. It produces parts that are light and have a high-quality surface finish….
#10 DIE CASTING
Domain Est. 2024
Website: cofanthermal.com
Key Highlights: Cofan’s high-pressure casting delivers accurate dimensions, smooth surfaces, and intricate features by injecting molten metal under high pressure into a ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Pressure Die Casting Process Applicatoins
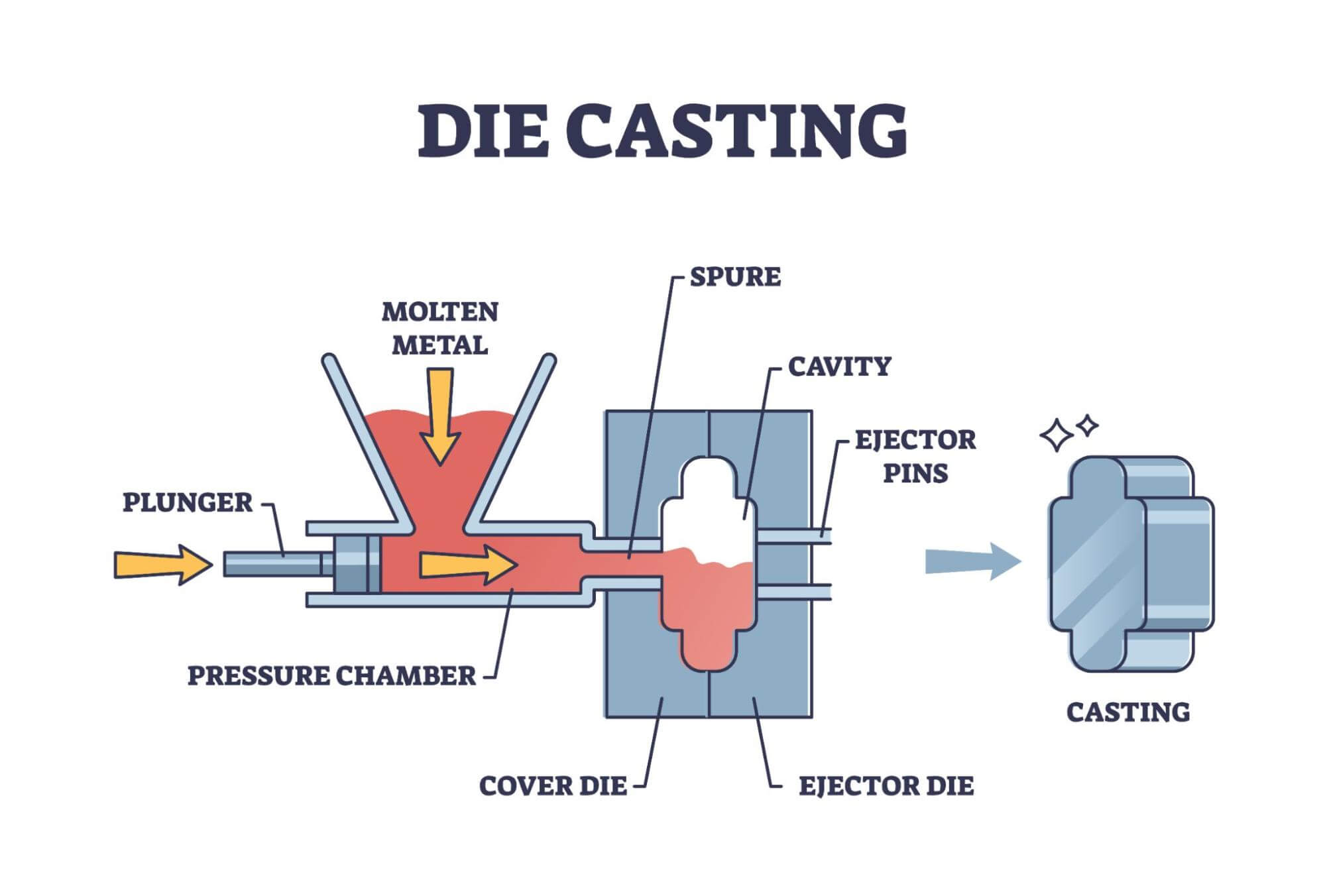
H2: 2026 Market Trends in High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Process Applications
As the global manufacturing sector advances toward lightweight, high-strength, and cost-efficient production methods, High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is poised to play a pivotal role across multiple industries by 2026. Driven by technological innovation, sustainability mandates, and evolving end-user demands, HPDC applications are undergoing significant transformation. This analysis explores key market trends expected to shape HPDC applications through 2026.
-
Accelerated Adoption in the Electric Vehicle (EV) Sector
The automotive industry, particularly the EV segment, remains the primary driver of HPDC demand. By 2026, automakers are projected to increasingly use HPDC for large structural components such as battery enclosures, chassis parts, and integrated front-end modules. The need for lightweighting to extend EV range and reduce battery costs is pushing manufacturers toward aluminum and magnesium-based HPDC solutions. Innovations like “mega-casting”—exemplified by Tesla’s Giga Press technology—are expected to become more widespread, reducing part count, assembly time, and production costs. -
Material Innovations and Alloy Development
By 2026, advancements in high-performance alloys—such as high-strength aluminum (e.g., Al-Si-Cu-Mg systems) and next-generation magnesium alloys—will enhance the structural integrity and thermal performance of HPDC components. These materials will enable thinner wall sections and improved durability, particularly in powertrain and safety-critical applications. Moreover, research into recyclable and low-carbon alloys aligns with sustainability goals, further boosting HPDC adoption in regulated markets. -
Integration of Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
HPDC operations are expected to become more connected and data-driven by 2026. The integration of IoT-enabled sensors, real-time process monitoring, AI-driven defect prediction, and digital twin technologies will optimize casting quality, reduce scrap rates, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Foundries investing in smart HPDC cells will gain competitive advantages through predictive maintenance and adaptive process control. -
Growth in Non-Automotive Applications
While automotive dominates HPDC usage, demand is rising in aerospace, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment. In aerospace, HPDC is being explored for non-critical structural parts due to improved porosity control and consistency. In consumer electronics, HPDC is used for durable, intricately shaped housings (e.g., smartphones, laptops), benefiting from high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finish. Industrial applications, including hydraulic components and power tools, will also see growth due to the need for high-volume, reliable metal parts. -
Sustainability and Environmental Regulations
Environmental pressures are shaping HPDC’s future. Stricter emissions standards and circular economy policies are pushing companies to adopt energy-efficient HPDC machines, closed-loop recycling of aluminum, and low-emission furnace technologies. By 2026, manufacturers using recycled aluminum in HPDC processes are expected to gain market preference, especially in Europe and North America. Additionally, lifecycle assessments (LCA) of HPDC components will become integral to procurement decisions. -
Regional Market Shifts and Capacity Expansion
Asia-Pacific—led by China, India, and Southeast Asia—will remain the largest HPDC market due to robust automotive and electronics manufacturing. However, nearshoring and supply chain resilience efforts will drive HPDC capacity growth in North America and Eastern Europe. Localized production of EV components will spur investments in high-tonnage HPDC machinery, particularly in the U.S. and Germany. -
Challenges in Porosity and Post-Processing
Despite its advantages, HPDC still faces challenges related to internal porosity and heat treatment limitations. By 2026, advancements in vacuum-assisted HPDC, semi-solid casting integration, and high-integrity casting (HIC) processes are expected to mitigate these issues. These improvements will expand HPDC’s applicability to safety-critical components requiring high fatigue resistance.
Conclusion
By 2026, the High Pressure Die Casting process will be increasingly defined by its role in enabling lightweight, scalable, and sustainable manufacturing—especially in the EV revolution. Technological advancements, material science improvements, and digitalization will broaden HPDC’s application scope and efficiency. Companies investing in innovation, sustainability, and smart production systems will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving market dynamics.
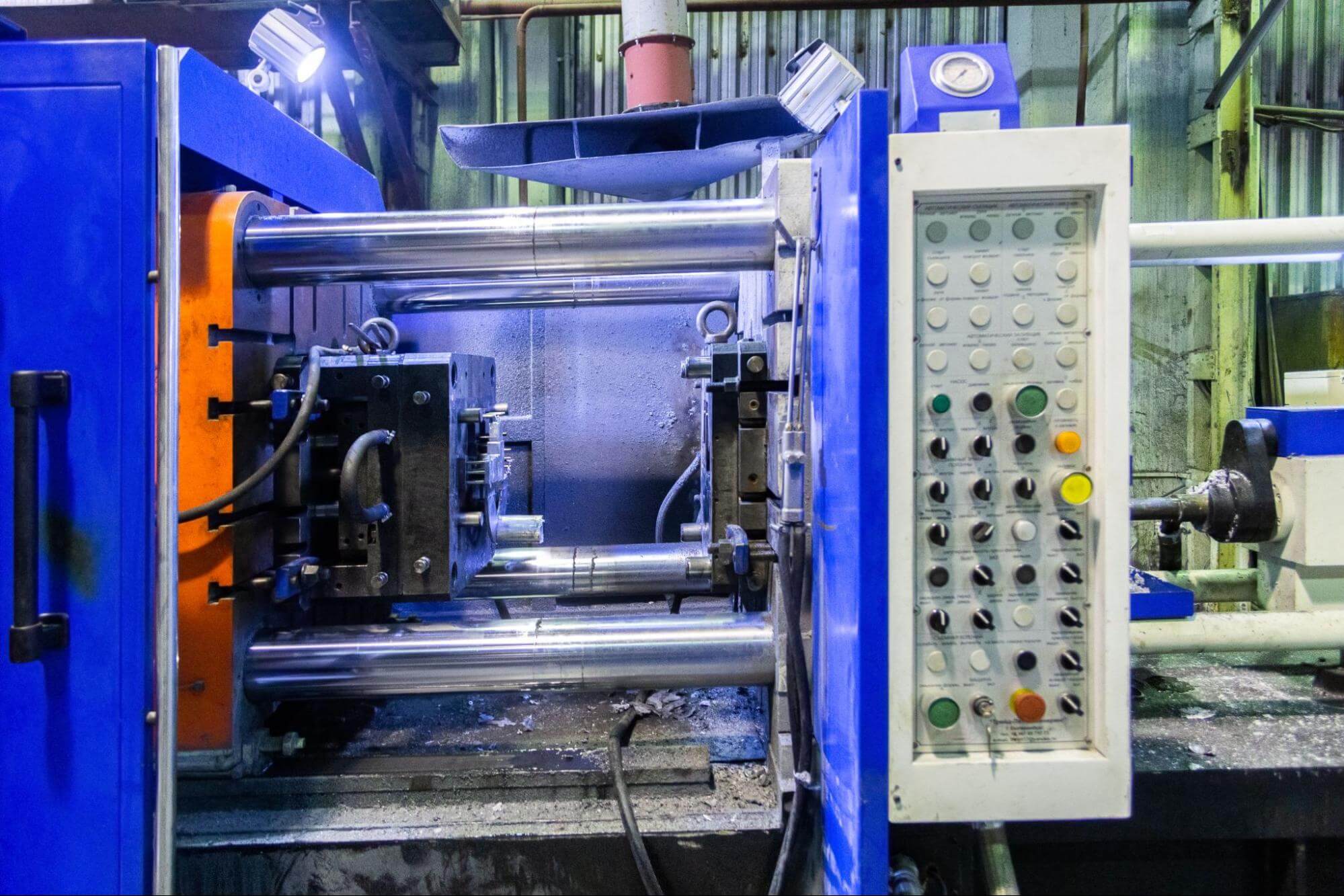

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Applications: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing high pressure die casting (HPDC) components offers significant benefits such as high production rates, excellent dimensional accuracy, and good surface finish. However, navigating the supply chain involves critical risks, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to costly failures, delays, and legal disputes.
Quality-Related Pitfalls in HPDC Sourcing
Achieving consistent, high-quality HPDC parts requires stringent process control and supplier expertise. Common quality pitfalls include:
Inadequate Supplier Qualification and Audit Processes
Selecting HPDC suppliers based solely on cost or proximity without thorough technical and quality system evaluation is a major risk. Suppliers may lack the necessary experience with specific alloys, part complexity, or required quality standards (e.g., IATF 16949 for automotive). Skipping on-site audits can hide deficiencies in process control, equipment maintenance, and metrology capabilities.
Insufficient Understanding of Process Variability
HPDC is sensitive to numerous parameters—die temperature, injection speed, pressure, lubrication, and cooling rates. Poorly managed variations can lead to internal porosity, shrinkage, cold shuts, or inconsistent mechanical properties. Sourcing partners may not fully document or control these variables, resulting in batch-to-batch inconsistencies that affect part performance.
Inadequate Inspection and Testing Protocols
Relying solely on visual or dimensional checks without comprehensive non-destructive testing (NDT) like X-ray or ultrasonic inspection increases the risk of hidden defects. Failure to define and enforce appropriate sampling plans, acceptance criteria, and traceability (e.g., lot tracking) can allow defective parts to reach end-use applications, especially in safety-critical sectors like aerospace or medical devices.
Poor Die Design and Maintenance Oversight
The die is central to HPDC quality. Sourcing without involvement in or approval of die design can result in premature wear, parting line mismatch, or ejection issues. Additionally, unclear agreements on die maintenance, repair responsibilities, and life expectancy can lead to deteriorating part quality over time.
Intellectual Property (IP) Protection Risks in HPDC Sourcing
HPDC often involves complex, proprietary part designs and tooling, making IP protection essential yet frequently mishandled.
Lack of Robust Legal Agreements
Failing to establish comprehensive contracts that explicitly define IP ownership—especially for custom dies, fixtures, and product designs—can lead to disputes. Jurisdictional differences in IP law may further complicate enforcement, particularly when sourcing internationally. Without clear clauses on confidentiality, use limitations, and reverse engineering prohibitions, suppliers may misuse or replicate designs.
Unsecured Design Data and Tooling Access
Sharing CAD models and manufacturing data without proper digital rights management (DRM), encryption, or controlled access exposes designs to unauthorized use or leakage. Similarly, allowing suppliers to retain physical possession of dies without contractual safeguards increases the risk of tooling misuse or unauthorized production runs.
Insufficient Control Over Sub-Tier Suppliers
Many HPDC suppliers subcontract secondary operations (e.g., machining, heat treatment, plating). If these sub-tier vendors are not bound by the same IP protections, design information can be inadvertently or deliberately compromised. Lack of transparency in the supply chain exacerbates this risk.
Ambiguous Ownership of Process Improvements
Innovations developed during production—such as optimized gating systems or cycle time reductions—may be claimed by the supplier if not addressed in the original agreement. This can erode competitive advantage and limit future sourcing flexibility.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, sourcing teams should:
– Conduct thorough technical audits and require certifications relevant to the industry.
– Define clear quality requirements, inspection methods, and acceptance criteria in procurement contracts.
– Implement robust IP protection through legally vetted NDAs, IP ownership clauses, and controlled data sharing.
– Maintain ownership of tooling and audit die maintenance records regularly.
– Extend IP and quality requirements to sub-tier suppliers through flow-down clauses.
Proactively addressing quality and IP concerns ensures reliable supply, protects innovation, and supports long-term product success in HPDC applications.
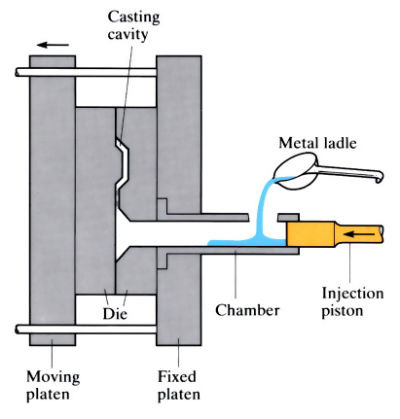
Logistics & Compliance Guide for High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Process Applications
Raw Material Sourcing and Transportation
Ensure all alloy ingots (e.g., aluminum, zinc, magnesium) are sourced from certified suppliers adhering to ASTM, ISO, or equivalent material standards. Maintain documented mill test reports (MTRs) for traceability. Transport materials in dry, covered vehicles to prevent contamination and moisture absorption, particularly critical for magnesium alloys due to flammability risks. Segregate incompatible materials during storage and transport to prevent chemical reactions.
In-Process Material Handling and Work-in-Progress (WIP) Flow
Implement standardized handling procedures for dies, ingots, and cast components using designated carts, lifts, and protective fixtures to prevent damage. Optimize WIP layout to minimize handling distances and reduce cycle times. Utilize barcode or RFID tracking systems to monitor component status, location, and process history in real time, supporting lean manufacturing principles and quality assurance.
Finished Goods Packaging, Storage, and Distribution
Package cast components according to customer specifications using anti-corrosion materials (e.g., VCI paper, desiccants) and protective dunnage to prevent surface damage during transit. Store finished goods in a controlled environment to avoid moisture exposure and thermal degradation. Label all shipments with lot numbers, material grades, and compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, REACH) to meet regulatory and traceability requirements. Coordinate with certified carriers experienced in handling industrial metal goods.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance
Adhere to OSHA, EPA, and local regulations for emissions control, waste management, and worker safety. Install and maintain effective ventilation and fume extraction systems to manage emissions from die lubricants and molten metal. Implement strict protocols for handling and disposal of spent die lubricants, dross, and scrap metal in accordance with hazardous waste guidelines. Conduct regular EHS audits and employee training to ensure compliance and promote a safety-first culture.
Regulatory and Industry Standards Adherence
Maintain certification to ISO 9001 (Quality Management), IATF 16949 (Automotive), and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) where applicable. Comply with material-specific regulations such as REACH (EU), RoHS (EU), and TSCA (USA) for restricted substances. Document and retain process parameters, inspection records, and non-conformance reports to support regulatory audits and customer requests for production evidence.
International Trade and Customs Compliance
For cross-border shipments, ensure accurate HS codes, export documentation (e.g., commercial invoices, packing lists), and adherence to Incoterms® rules. Verify that cast components meet destination country standards for material composition and product safety. Conduct regular reviews of export control lists (e.g., EAR, ITAR) to prevent unauthorized transfers of dual-use technologies or restricted materials.
Conclusion:
High pressure die casting (HPDC) remains a pivotal manufacturing process for producing high-precision, complex, and lightweight metal components across diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods. Its advantages—including high production rates, excellent dimensional accuracy, superior surface finish, and the ability to integrate multiple features into a single component—make it a preferred choice for mass production applications.
Sourcing HPDC components offers significant benefits, particularly in cost reduction and supply chain efficiency, especially when leveraging global manufacturing hubs with advanced tooling capabilities and cost-effective labor. However, successful sourcing requires careful consideration of factors such as material selection, tooling quality, process control, supplier credibility, and adherence to industry standards.
As demand for lightweight and energy-efficient products grows—driven by electric vehicles and sustainable manufacturing—HPDC will continue to evolve with innovations in materials (e.g., high-strength aluminum and magnesium alloys), process optimization, and digitalization (e.g., simulation and real-time monitoring).
In conclusion, sourcing high pressure die casting applications strategically enables companies to achieve high-quality, cost-effective production, provided that technical, logistical, and quality assurance aspects are thoroughly managed. With the right partners and processes in place, HPDC stands as a cornerstone technology for modern industrial manufacturing.

![[PDF] Aluminum High Pressure Die Casting](https://www.sohoinchina.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/pdf-aluminum-high-pressure-die-casting-858.jpg)