The global high oleic canola oil market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for healthier cooking oils with improved oxidative stability and longer shelf life. According to Grand View Research, the global canola oil market size was valued at USD 11.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2023 to 2030, with high oleic variants gaining traction due to their favorable fatty acid profile and functional performance in food processing. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of approximately 4.8% for the canola oil market over the 2024–2029 forecast period, citing increased consumer awareness around heart-healthy fats and the expansion of applications in the bakery, snacks, and ready-to-eat food sectors. This surge in demand has catalyzed innovation and scale among manufacturers specializing in high oleic canola oil, positioning key players to capitalize on shifting dietary preferences and clean-label trends. Below are the top seven high oleic canola oil manufacturers leading this transformation through advanced breeding technologies, sustainable practices, and strategic market positioning.
Top 7 High Oleic Canola Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Maverik Oils
Domain Est. 2015
Website: maverikoils.com
Key Highlights: Maverik Oils offers a vast selection of the finest organic and non-GMO specialty oils and ingredients to food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical manufacturers….
#2 Oils
Domain Est. 2017
Website: synovaoil.com
Key Highlights: Synova oils are specifically designed for industrial baking and food preparation. Experience the best cooking oil for your bakery….
#3 High Oleic Oils – Canola, Soybean, Sunflower – North America
Domain Est. 1994
Website: cargill.com
Key Highlights: Cargill’s Clear Valley high oleic oils offer high stability, superior performance and clean flavor. Plus, the low levels of saturated fat per serving of our ……
#4 Major supplier of oilseeds
Domain Est. 1999
Website: viterra.com
Key Highlights: We also produce high-quality, speciality oils such as high oleic sunoil, high oleic canola oil and non-GMO canola oil. Biodiesel. We process rape methyl ester ……
#5 Richardson introduces high oleic canola oil with natural antioxidants
Domain Est. 2007
Website: richardson.ca
Key Highlights: Richardson’s new high oleic canola oil with natural antioxidants offers high stability and functionality that can extend product shelf life….
#6 Canola Oil
Domain Est. 2016
Website: cataniaoils.com
Key Highlights: Our portfolio includes conventional, organic, Non-GMO, expeller-pressed, and high-oleic options so you get the exact profile your process and label require….
#7 Oilseed Crops
Domain Est. 2017
Website: corteva.com
Key Highlights: With high oleic soybean seeds and canola seed from Corteva Agriscience™, farmers can realize the high-profit potential of the Omega-9 Oils market, supported by ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Oleic Canola
H2: Projected Market Trends for High Oleic Canola in 2026
By 2026, the global market for High Oleic Canola (HOC) is expected to experience significant growth, driven by evolving consumer preferences, regulatory shifts, and advancements in agricultural biotechnology. High Oleic Canola, valued for its enhanced stability, heart-healthy fatty acid profile, and versatility in food and industrial applications, is poised to expand its footprint across multiple sectors.
1. Rising Demand in the Food Industry
The food manufacturing sector is increasingly adopting High Oleic Canola oil as a replacement for partially hydrogenated oils and tropical oils high in saturated fats. With the U.S. FDA’s full enforcement of the ban on artificial trans fats and similar regulations in other regions, food producers are turning to HOC for its naturally long shelf life, high smoke point, and clean flavor. By 2026, demand is projected to grow substantially in applications such as frying oils (particularly in the snack and fast-food industries), margarines, and bakery products.
2. Health and Wellness Trends
Consumer awareness of heart-healthy fats continues to rise, with nutrition labels and health claims influencing purchasing decisions. High Oleic Canola oil contains high levels of monounsaturated fats (up to 70–80%) and low levels of saturated fats (<7%), aligning with dietary guidelines from organizations such as the American Heart Association. This nutritional profile is expected to bolster market adoption, particularly in North America and Europe, where clean-label and functional food trends are strong.
3. Expansion in Genetically Modified and Non-GMO Varieties
Seed technology companies are investing heavily in both genetically modified (GM) and non-GMO high oleic canola varieties to meet diverse market needs. By 2026, increased availability of non-GMO HOC will cater to the growing natural and organic food sectors, especially in the European Union and among U.S. consumers seeking non-GMO Project verified products. Simultaneously, GM HOC varieties will gain traction in regions with high agricultural efficiency demands, such as Canada and Australia.
4. Geographic Market Growth
Canada remains the largest producer and exporter of High Oleic Canola, supported by strong research initiatives and farmer adoption. The U.S. is expected to see increased domestic production due to rising demand from food processors and government incentives for heart-healthy oilseed crops. In South America, Argentina and Uruguay may expand HOC acreage, leveraging existing canola infrastructure. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific markets—particularly China and India—are anticipated to become key import destinations due to growing middle-class populations and urban foodservice expansion.
5. Sustainability and ESG Considerations
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are influencing supply chain decisions. High Oleic Canola offers advantages in crop rotation, soil health, and carbon sequestration compared to other oilseed crops. By 2026, sustainability certifications and traceability will become critical differentiators, with food brands seeking HOC from verified sustainable sources to meet corporate responsibility goals.
6. Price Volatility and Supply Chain Dynamics
While demand rises, supply constraints could lead to price volatility. Weather patterns, global trade policies, and competition with other oilseeds (e.g., soybean, sunflower) may impact production yields. However, improved agronomic traits—such as drought resistance and higher oil content—expected in next-generation HOC varieties will help stabilize supply.
Conclusion
By 2026, the High Oleic Canola market is forecasted to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8–10%, reaching a global market value exceeding $1.8 billion. Innovation in seed technology, regulatory tailwinds, and consumer demand for healthier, sustainable oils will be the primary drivers. Stakeholders across the value chain—from seed developers to food manufacturers—will need to align on quality, scalability, and sustainability to capitalize on this growth trajectory.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing High Oleic Canola (Quality, IP)
Sourcing High Oleic Canola (HOC) presents unique challenges compared to conventional canola due to its specialized genetics, stringent quality requirements, and strict Identity Preservation (IP) protocols. Overlooking these factors can lead to significant financial losses, supply chain disruptions, and reputational damage. Key pitfalls include:
1. Compromised Identity Preservation (IP) Integrity
HOC’s value hinges on maintaining genetic purity and preventing commingling with conventional or GMO canola. Weaknesses in the IP chain—such as inadequate segregation during harvesting, storage, transport, or handling—can result in contamination. Without robust documentation, chain-of-custody verification, and third-party audits, buyers risk receiving off-spec material unsuitable for premium markets.
2. Inconsistent Oil Profile and Quality Variability
HOC is prized for its high oleic acid content (>70%) and stability. However, inconsistent growing conditions, variable seed genetics, or poor agronomic practices can lead to off-spec oil profiles. Buyers may receive product with insufficient oleic levels or elevated polyunsaturates, undermining performance in applications like frying or shelf-stable foods. Lack of batch-specific certification exacerbates this risk.
3. Insufficient Testing and Verification Protocols
Relying solely on supplier declarations without independent lab testing invites fraud or error. Without regular, validated testing for oleic acid content, GMO presence, and impurities (e.g., moisture, foreign material), buyers cannot confirm compliance with technical specifications. Delayed or infrequent testing also hampers timely quality interventions.
4. Overlooking Contractual and Regulatory Compliance
Ambiguous contracts that fail to define quality specs, IP requirements, testing methods, and liability for non-conformance leave buyers exposed. Additionally, navigating evolving global regulations on GMO labeling and food safety (e.g., EU, USDA) without expert oversight can result in rejected shipments or legal penalties.
5. Supply Chain Fragmentation and Traceability Gaps
Sourcing HOC from fragmented or opaque supply networks increases traceability risks. Without end-to-end visibility—from seed source to delivered product—verifying claims becomes difficult. This is especially critical for brands marketing clean-label or non-GMO attributes, where consumer trust depends on transparency.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires proactive supplier vetting, enforceable contracts, rigorous testing, and investment in traceable, audited supply chains.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for High Oleic Canola
This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling, transportation, and documentation of High Oleic Canola (HOC), a specialty oilseed with unique market demands and regulatory requirements.
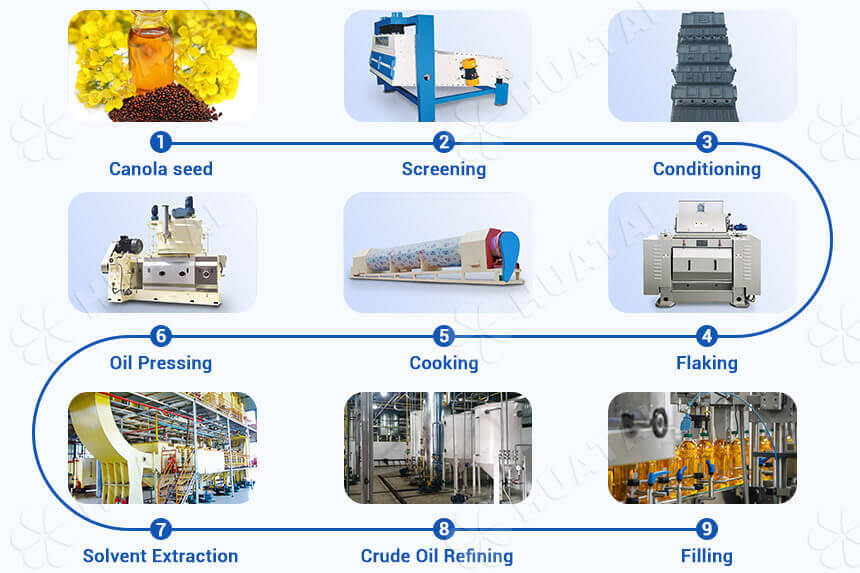
Storage and Handling
High Oleic Canola requires careful handling to maintain its premium quality and extended shelf life. Proper storage prevents degradation of the oil profile and minimizes contamination risks.
- Dry & Clean Facilities: Store only in thoroughly cleaned, dry bins, silos, or containers. Residual moisture or foreign material (especially from conventional canola or other oilseeds) can lead to spoilage and downgrading.
- Temperature Control: Maintain storage temperatures as low and consistent as possible (ideally below 15°C / 59°F). Elevated temperatures accelerate oxidation and can degrade the high oleic acid content, reducing value.
- Aeration: Utilize aeration systems to manage moisture and temperature uniformity, preventing hot spots and condensation.
- Segregation: Strictly segregate HOC from conventional canola, other oilseeds, and grains throughout the supply chain (farm, elevator, transport, port). Co-mingling destroys its identity-preserved (IP) status and premium value. Dedicated equipment and lines are essential.
- Minimize Handling: Reduce the number of transfer points to minimize mechanical damage (cracking) and exposure to air and moisture.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor stored HOC for temperature, moisture content, and signs of spoilage (odor, heating).
Transportation
Transport logistics must prioritize the protection of HOC’s quality and ensure traceability from origin to destination.
- Clean Vehicles & Containers: All trucks, railcars, and shipping containers must be certified clean and free of residue from previous cargoes. Documentation of cleaning may be required.
- Covered Transport: Use covered trucks or railcars, and ensure shipping containers are watertight to protect against moisture ingress and contamination.
- Segregation During Transit: Ensure HOC is not loaded in adjacent holds or compartments to incompatible cargoes (e.g., strong-smelling goods, non-food items, conventional canola). Use dedicated or thoroughly cleaned transport whenever possible.
- Timeliness: Minimize transit time, especially in warm conditions, to reduce exposure to temperature fluctuations and potential quality loss.
- Documentation: Maintain accurate bills of lading and transport documents specifying “High Oleic Canola” clearly to prevent misrouting or co-mingling.
Quality Standards and Testing
HOC is traded based on specific quality parameters that define its value and suitability for high-performance food applications.
- Key Specifications: Typical buyer requirements include:
- Oleic Acid Content: Minimum 70-75% (often verified by NMR or GC testing).
- Moisture: Usually ≤ 9.5% (critical for safe storage).
- Oil Content: Often specified (e.g., ≥ 40%).
- Impurities/Foreign Material: Very low tolerance (e.g., ≤ 2%).
- Damaged Kernels: Low limits (e.g., ≤ 2%).
- Free Fatty Acids (FFA): Low levels indicate good handling and storage.
- Identity Preservation (IP) Verification: Mandatory testing (often at multiple points: load, destination) to verify oleic acid content and confirm the cargo is indeed HOC and not conventional canola. Third-party verification is common.
- Sampling: Use approved, representative sampling methods (e.g., automatic samplers on grain legs, probe sampling for containers) to ensure test results are accurate.
- Certified Laboratories: Utilize accredited laboratories for official quality and oleic acid testing. Retain sample duplicates.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to national and international regulations is crucial for market access and avoiding penalties.
- Phytosanitary Requirements: Comply with import/export phytosanitary regulations of both origin and destination countries. This may include requirements for pest-free areas, treatments (e.g., fumigation – though rarely needed for canola if clean and dry), and official phytosanitary certificates issued by the national plant protection organization (e.g., CFIA in Canada, APHIS in the US).
- Grading Standards: Adhere to official grain grading standards (e.g., Canada Grain Act, US Grain Standards Act) which define canola quality factors (moisture, damaged kernels, foreign material). HOC may follow the same base grade (e.g., No. 1 Canada) but with additional IP specifications.
- Food Safety Regulations: Comply with relevant food safety laws (e.g., FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) in the US, SFCR in Canada, EU General Food Law). This includes Preventive Controls (FSMA), traceability requirements, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) during handling.
- Labeling and Documentation: Ensure all commercial documents (contracts, invoices, bills of lading, certificates) accurately declare the commodity as “High Oleic Canola.” Mislabeling can lead to rejection and legal issues.
- Traceability: Implement a robust traceability system capable of tracking HOC batches from farm/origin elevator through processing to the final customer. This is critical for recalls, quality investigations, and IP program audits.
- Country-Specific Regulations: Be aware of and comply with any specific import requirements of the destination country (e.g., GMO regulations – note that most commercial HOC varieties are non-GMO, but verification is key; maximum residue limits (MRLs) for pesticides; specific import licensing).
Identity Preservation (IP) Program Management
Maintaining the integrity of the HOC supply chain is paramount for accessing premium markets.
- Enrollment: Producers and handlers must be enrolled in a certified IP program managed by a seed company, processor, or third-party auditor.
- Audit Trail: Maintain comprehensive records for every batch, including seed source, field location, planting date, harvest date, storage location, transport details, test results, and final destination.
- Audits: Be prepared for regular audits by the IP program administrator to verify compliance with all segregation, handling, cleaning, and documentation protocols.
- Chain of Custody: Implement strict chain-of-custody procedures at every transfer point, with clear documentation and verification steps.
By meticulously following these logistics and compliance guidelines, stakeholders can ensure High Oleic Canola reaches its market in optimal condition, maintains its premium value, and meets all regulatory and customer requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing high oleic canola oil presents a strategic opportunity for food manufacturers, retailers, and health-conscious consumers seeking a sustainable, heart-healthy, and performance-driven oil alternative. Its superior oxidative stability, extended fry life, and reduced need for hydrogenation make it ideal for a wide range of food applications, from frying to baking and processed foods. Additionally, its favorable nutritional profile—low in saturated fat and high in monounsaturated fats—aligns with evolving dietary guidelines and consumer demand for cleaner labels and improved health outcomes.
Moreover, advancements in plant breeding have made high oleic canola more accessible and scalable, supporting consistent supply chains and competitive pricing. As global regulatory and consumer pressures continue to drive the elimination of trans fats and unhealthy oils, high oleic canola stands out as a responsible and forward-thinking choice. By sourcing high oleic canola, stakeholders can meet health, sustainability, and performance goals while staying ahead of market trends and regulatory developments.