The global High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) adhesives market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across packaging, construction, automotive, and consumer goods industries. According to Grand View Research, the global hot melt adhesives market—of which HDPE-based formulations are a key segment—was valued at USD 10.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the increasing need for fast-setting, durable, and recyclable bonding solutions, particularly in automated manufacturing processes. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that the Asia Pacific region is emerging as a dominant force, supported by expanding industrial activity and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. As demand for high-performance polyethylene-based adhesives continues to rise, a select group of manufacturers has distinguished itself through innovation, scalability, and product consistency. Here are the top 10 HDPE glue manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 High Density Polyethylene Glue Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Product and Brand Catalog
Domain Est. 1992
Website: dow.com
Key Highlights: Explore Dow’s extensive portfolio of solutions by category, product or brand….
#2 Industrial, Construction & DIY Adhesives
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bostik.com
Key Highlights: A comprehensive adhesive offering for the construction industry, providing reliable, flexible and waterproof joints for a broad range of applications….
#3 Adhesives, Sealants and Coatings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: masterbond.com
Key Highlights: Master Bond is a leading manufacturer of epoxy adhesives, sealants, coatings, potting and encapsulation compounds. Master Bond specializes in epoxies, ……
#4 Specialty Polymer & Thermoplastic Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: avient.com
Key Highlights: Global manufacturer of advanced composites, specialty polymers, color and additive systems, and thermoplastic and polymer compounds that enhance performance ……
#5 Compatible Substrates Surfaces High Density Polyethylene Hdpe
Domain Est. 2023
Website: hbfullerproducts.com
Key Highlights: H.B. Fuller is a leading global adhesives provider focusing on perfecting adhesives, sealants and other specialty chemical products to improve products and …Missing: glue manufa…
#6 Adhesives for Polyethylene
Domain Est. 1996
Website: permabond.com
Key Highlights: Permabond has developed a line of specialty acrylic adhesives for polyethylene that form strong bonds without surface treatment….
#7 Synthomer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: synthomer.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading supplier of high-performance, highly specialised polymers and ingredients that play vital roles in growing sectors that serve billions of end ……
#8 SCGC™ HDPE
Domain Est. 2006
Website: scgchemicals.com
Key Highlights: SCGC™ HDPE offers high strengths thus be able to withstand high impact, heat, and chemicals while maintain stiffness and easy processing….
#9 Polymers
Domain Est. 2007
Website: lyondellbasell.com
Key Highlights: Polyethylene is flexible, lightweight, and resists moisture, UV rays, chemicals and contaminants. Our offerings include high-density (HDPE), low-density (LDPE) ……
#10 HDPE Glue
Website: innerduct.com
Key Highlights: Pro-Poly is a high strength polyethylene adhesive for coupling of HDPE pipe using standard PVC couplings, HDPE couplings and other non-standard materials….
Expert Sourcing Insights for High Density Polyethylene Glue
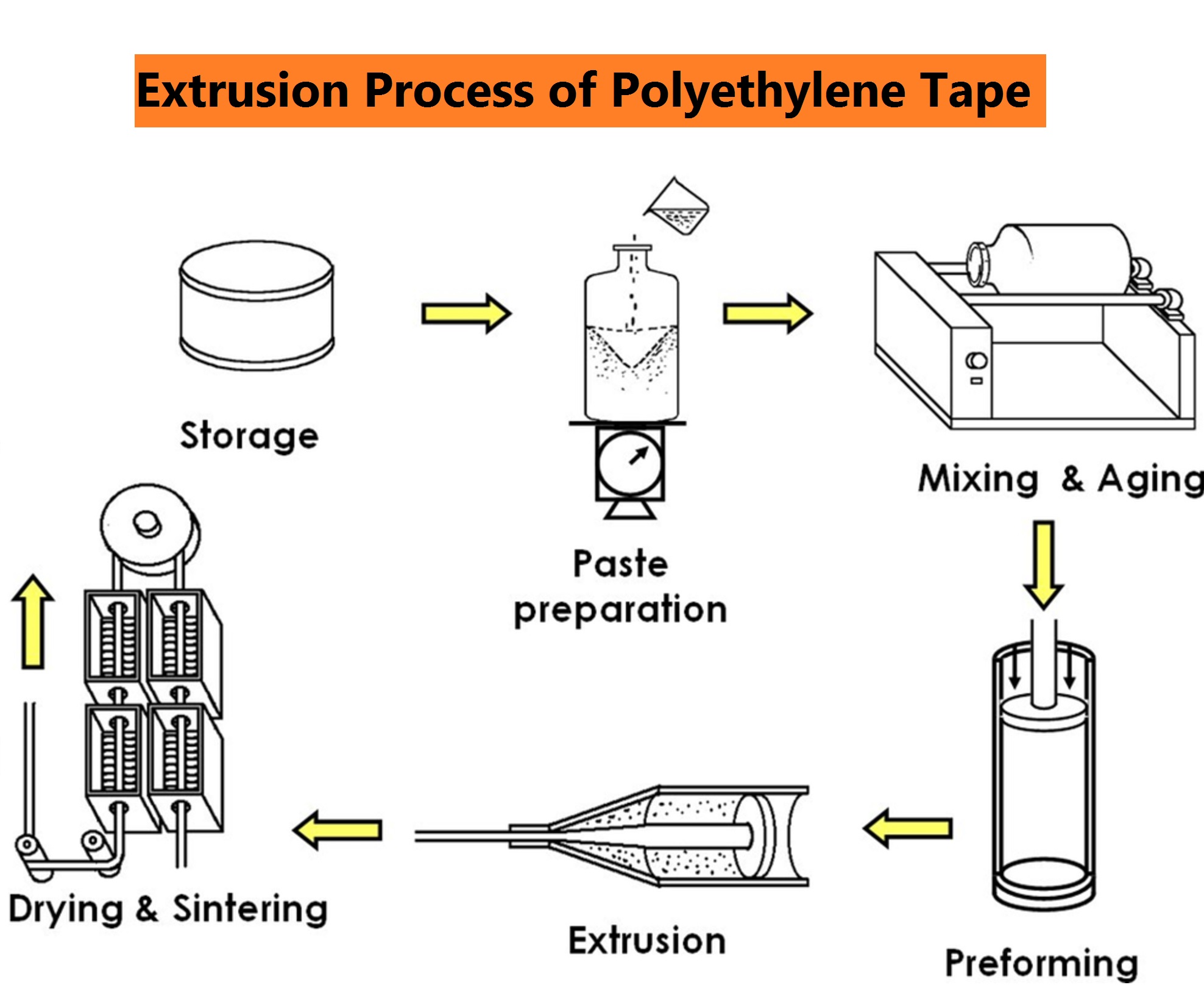
H2: Projected Market Trends for High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Glue in 2026
By 2026, the global market for High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) glue—adhesives specifically formulated for bonding HDPE plastics—is expected to undergo notable expansion and transformation, driven by evolving industrial demands, technological innovation, and sustainability imperatives.
-
Growing Demand in Packaging and Construction Sectors
The packaging industry, particularly in food and beverage, healthcare, and consumer goods, continues to rely heavily on HDPE due to its durability, chemical resistance, and recyclability. As manufacturers increasingly shift toward seamless, lightweight, and tamper-resistant packaging solutions, demand for high-performance HDPE glue is rising. In the construction sector, HDPE is widely used in geomembranes, piping systems, and insulation materials. The need for reliable bonding solutions in infrastructure projects—especially in water management and waste containment—will further fuel adhesive demand. -
Advancements in Adhesive Formulations
Innovation in adhesive chemistry will play a pivotal role in 2026. Manufacturers are investing in HDPE-compatible adhesives with improved bond strength, faster curing times, and enhanced resistance to environmental stressors such as moisture, UV exposure, and thermal cycling. Hybrid adhesives combining polyolefin-modified polymers or reactive hot melts are gaining traction, offering better adhesion to low-surface-energy plastics like HDPE without requiring surface treatment. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental regulations—such as extended producer responsibility (EPR) and restrictions on volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—are pushing formulators toward eco-friendly HDPE glue solutions. Water-based, solvent-free, and bio-based adhesives are expected to capture a larger market share by 2026. Additionally, recyclability of bonded HDPE products is becoming a key consideration, prompting development of debondable or reversible adhesives that support circular economy goals. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, will remain the fastest-growing market for HDPE glue due to rapid industrialization, urban development, and rising plastic consumption. North America and Europe will see steady growth, driven by infrastructure renewal, green building initiatives, and strict environmental standards favoring advanced adhesive technologies. -
Integration with Automation and Industry 4.0
The trend toward smart manufacturing and automated production lines will boost demand for adhesives compatible with robotic dispensing systems. HDPE glue formulations optimized for precision application, real-time curing monitoring, and compatibility with IoT-enabled equipment will gain prominence, especially in automotive and electronics assembly processes involving plastic components. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Alliances
Major chemical and adhesive manufacturers—including Henkel, 3M, Sika, and H.B. Fuller—are expected to expand their HDPE-specific product portfolios through R&D and strategic partnerships with plastic processors. Customized adhesive solutions tailored to specific HDPE grades and end-use applications will differentiate market leaders.
In summary, the HDPE glue market in 2026 will be shaped by innovation, sustainability, and industrial modernization. Companies that prioritize performance, environmental compliance, and digital integration are poised to lead in this evolving sector.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Adhesives: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing high-performance adhesives for bonding High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) presents unique challenges due to the material’s inherent chemical resistance and low surface energy. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to project failures, safety risks, and legal liabilities. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
H2: Poor Adhesion Due to Inadequate Surface Preparation Compatibility
One of the most frequent failures occurs when the adhesive system does not align with proper HDPE surface treatment requirements. HDPE’s non-polar, low-energy surface resists bonding unless modified. A major pitfall is sourcing an adhesive without verifying its compatibility with surface activation methods such as plasma, corona, or flame treatment. Adhesives marketed as “HDPE-compatible” may still fail if they are not designed to bond effectively with treated surfaces. Always confirm with the supplier whether the adhesive is validated for use with specific surface treatments and request adhesion test data under realistic conditions.
H2: Substandard Raw Materials and Inconsistent Batch Quality
Low-cost suppliers may use inferior or recycled resin components in the adhesive formulation, leading to inconsistent viscosity, pot life, cure time, and final bond strength. Variations between production batches can result in unpredictable performance, especially in critical applications like medical devices or pressure vessels. To mitigate this risk, require detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for each batch and consider conducting independent third-party testing. Avoid suppliers who are unwilling or unable to provide full transparency on raw material sourcing and manufacturing controls.
H2: Misrepresentation of Performance Claims and Lack of Validation Data
Some suppliers exaggerate adhesive performance, claiming high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, or structural strength without supporting data. Pitfalls include relying on generic datasheets not specific to HDPE substrates or lacking long-term aging and environmental exposure testing (e.g., UV, moisture, thermal cycling). Always request application-specific test reports, such as lap shear strength on HDPE after humidity aging or exposure to relevant chemicals. Beware of vague claims like “excellent for polyolefins” without quantitative proof.
H2: Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing adhesives from unverified manufacturers, particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement, can expose your company to legal action. Some suppliers may replicate patented formulations, such as specific primer-adhesive systems or proprietary coupling agents (e.g., chlorinated polyolefins or specialty silanes). Using such adhesives—even unknowingly—can lead to infringement lawsuits, product recalls, or supply chain disruptions. Conduct due diligence by verifying the supplier’s IP ownership or licensing agreements and consider including indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
H2: Inadequate Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Depending on the application (e.g., food contact, medical, automotive), HDPE adhesives must meet strict regulatory standards such as FDA, REACH, or UL. A common oversight is failing to confirm that the adhesive formulation complies with relevant regulations across all target markets. Suppliers may provide outdated or incomplete compliance documentation. Always request up-to-date regulatory certificates and ensure the adhesive is fully traceable through its bill of materials (BOM), especially if substitutions are made without notification.
By proactively addressing these H2-level pitfalls—focusing on compatibility, material consistency, performance validation, IP integrity, and compliance—companies can significantly reduce risks and ensure reliable, durable bonds in HDPE applications.
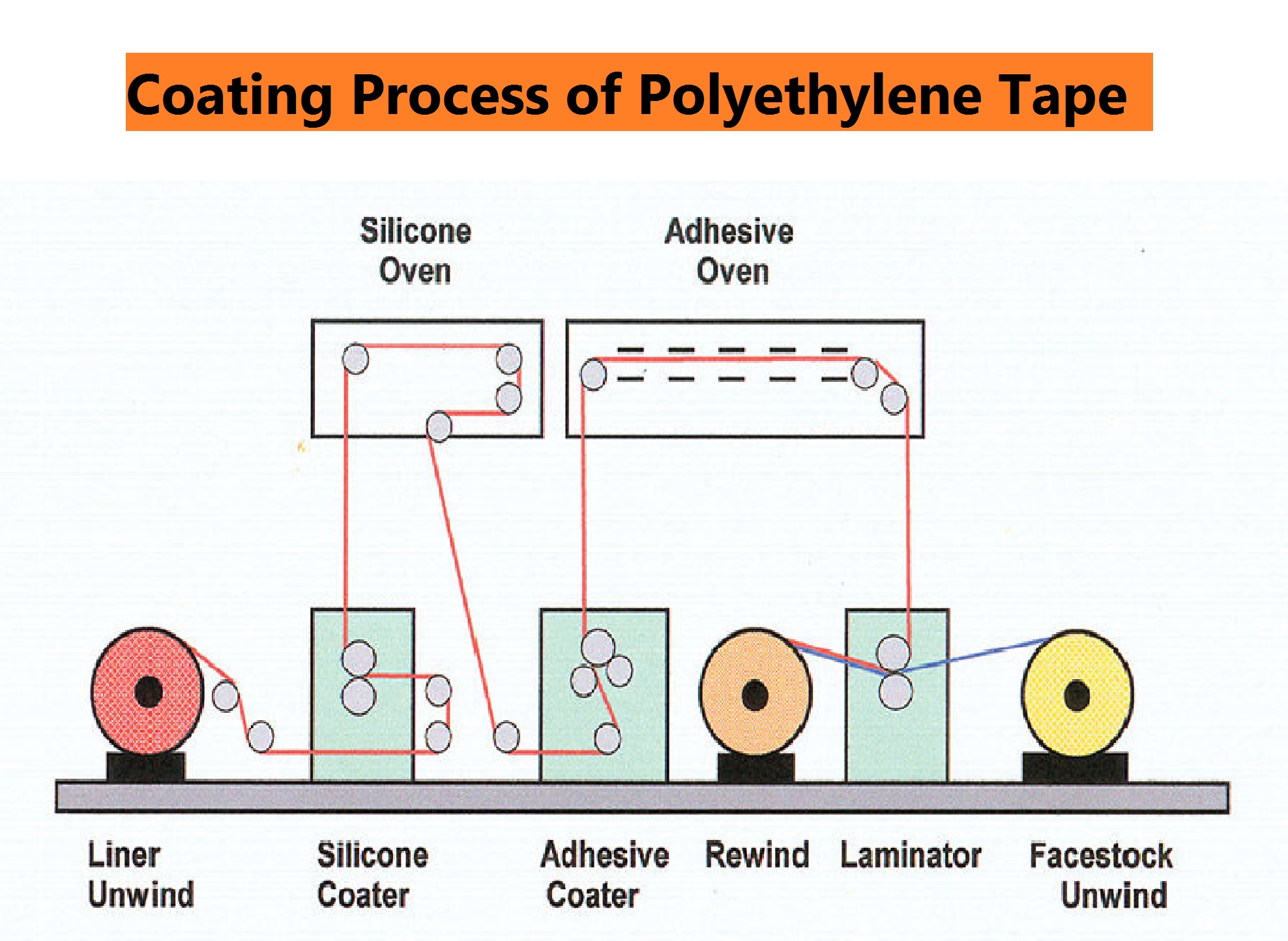
Logistics & Compliance Guide for High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Glue
(Using H2 Heading Style)
Logistics & Compliance Guide for High-Density Polyethylene Glue
1. Product Overview
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) glue refers to adhesives specifically formulated for bonding HDPE plastics. These glues are typically solvent-based, cyanoacrylate (super glue), or two-part epoxy systems designed to overcome the low surface energy of HDPE, ensuring durable bonds. Proper handling, storage, transport, and compliance with regulatory standards are critical due to potential chemical hazards.
2. Classification & Regulatory Compliance
2.1. Hazard Classification (GHS)
Depending on formulation, HDPE glues may fall under the following Globally Harmonized System (GHS) classifications:
– Flammable liquids – Category 2 or 3 (H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapor)
– Skin irritation – Category 2 (H315: Causes skin irritation)
– Eye damage – Category 1 (H318: Causes serious eye damage)
– Specific target organ toxicity (single exposure) – Category 3 (H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness)
Note: Always refer to the specific Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for exact classifications.
2.2. Regulatory Frameworks
- OSHA (USA): Compliant with Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200)
- REACH (EU): Registered under Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006
- CLP Regulation (EU): Properly classified, labeled, and packaged per Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
- DOT (USA): Compliant with 49 CFR for transportation of hazardous materials
- ADR/RID/IMDG/IATA: Applicable for road, rail, sea, and air transport (classification typically under UN 1133, Adhesives, flammable, n.o.s.)
3. Packaging & Labeling Requirements
3.1. Primary Packaging
- Use solvent-resistant, leak-proof containers (typically HDPE or metal with secure seals)
- Internal liners may be required for aggressive formulations
3.2. Labeling (GHS-Compliant)
Each container must display:
– Product identifier
– Signal word (e.g., “Danger”)
– GHS pictograms (e.g., flame, exclamation mark, corrosion)
– Hazard statements (e.g., H225, H318)
– Precautionary statements (e.g., P210, P305+P351+P338)
– Supplier information
4. Storage Guidelines
4.1. Environmental Conditions
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area
- Temperature range: 10°C to 25°C (50°F to 77°F)
- Avoid direct sunlight and heat sources (远离火源 / Keep away from heat)
4.2. Segregation
- Store away from oxidizers, strong acids, and bases
- Keep in flammable storage cabinets if volume exceeds local regulatory thresholds
4.3. Shelf Life
- Typically 12–24 months; check manufacturer’s expiration date
- Monitor for viscosity changes or phase separation
5. Transportation & Logistics
5.1. Domestic Transport (USA – DOT)
- Proper shipping name: “Adhesives, flammable, n.o.s.”
- UN Number: UN 1133
- Hazard Class: 3 (Flammable liquid)
- Packing Group: II or III (based on flash point)
- Required markings and placards per 49 CFR
5.2. International Transport
- Air (IATA): Class 3, Packing Instruction 355
- Sea (IMDG): Class 3, UN 1133, PG II
- Road (ADR): Class 3, UN 1133, Limited Quantity exemptions may apply
Note: Small quantities (< 1L) may qualify for limited or excepted quantities with reduced labeling.
6. Handling & Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
6.1. Safe Handling Practices
- Use only in well-ventilated areas or with local exhaust ventilation
- Avoid inhalation of vapors and direct skin/eye contact
- Ground containers during transfer to prevent static discharge
6.2. Required PPE
- Chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile or neoprene)
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Lab coat or protective clothing
- Respiratory protection (organic vapor cartridge) if ventilation is inadequate
7. Emergency Procedures
7.1. Spill Response
- Contain spill with absorbent materials (e.g., spill pillows, vermiculite)
- Do not allow into drains or waterways
- Collect waste in labeled, sealed container for hazardous disposal
7.2. Fire Response
- Extinguishing media: Dry chemical, CO₂, foam
- Evacuate area; vapors may be heavier than air and travel to ignition sources
- Cool containers with water spray from a safe distance
7.3. First Aid
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention if breathing is difficult
- Skin contact: Wash with soap and water; remove contaminated clothing
- Eye contact: Rinse immediately with water for at least 15 minutes; consult a physician
- Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting; seek immediate medical help
8. Disposal & Environmental Considerations
- Dispose of waste and empty containers in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations
- Empty containers may retain product residue—treat as hazardous waste
- Do not incinerate unless in approved hazardous waste incinerators
- Follow RCRA (USA), Waste Framework Directive (EU), or equivalent regulations
9. Documentation & Recordkeeping
- Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all adhesive products (minimum 3 years)
- Ensure transport documents include proper shipping name, UN number, class, and emergency contact
- Train employees annually on hazard communication, spill response, and fire safety
10. Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for HDPE glue ensures safety, regulatory adherence, and environmental protection. Always consult the manufacturer’s SDS and stay updated with current regulations in all regions of operation.
In conclusion, sourcing high-density polyethylene (HDPE) glue requires careful consideration of quality, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. HDPE-based adhesives are valued for their strong bonding capabilities, chemical resistance, and durability, making them suitable for demanding applications in packaging, automotive, construction, and manufacturing. To ensure optimal performance, it is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who provide consistent material specifications and technical support. Additionally, evaluating environmental impact and exploring sustainable sourcing options can align procurement practices with broader corporate responsibility goals. A strategic sourcing approach—balancing performance requirements, supply chain resilience, and total cost of ownership—will ensure reliable access to high-quality HDPE glue, supporting long-term operational success.