The global High-Efficiency Vehicle (HEV) charging station market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing electric vehicle adoption, supportive government policies, and advancements in charging infrastructure. According to Grand View Research, the global electric vehicle charging station market size was valued at USD 23.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34.9% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a CAGR of over 35% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, underscoring the accelerating demand for reliable and scalable charging solutions. As nations push toward carbon neutrality and automakers phase in electrified fleets, the role of HEV charging station manufacturers has become pivotal. This growth trajectory has fueled intense innovation and competition, positioning a select group of manufacturers at the forefront of technology, scalability, and global deployment. The following list highlights the top 10 HEV charging station manufacturers shaping the future of sustainable mobility.
Top 10 Hev Charging Station Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Principles of e-mobility charging technology
Domain Est. 1996
Website: phoenixcontact.com
Key Highlights: Charging station: Stand-alone charging system in a manufacturer-specific housing. Mostly for public or semi-public AC and/or DC charging including billing ……
#2 GM Electric Vehicles, Charging & Technology
Domain Est. 1992
Website: gm.com
Key Highlights: Our GM Energy PowerShift charger is bidirectional, so when paired with the GM Energy V2H Enablement Kit, your properly equipped home can draw on energy from ……
#3 EV Charging
Domain Est. 1990
Website: new.abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB offers a total ev charging solution from compact, high quality AC wallboxes, reliable DC fast charging stations with robust connectivity….
#4 Cummins EV Charging Solutions
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cummins.com
Key Highlights: Our reliable EV charging solutions are tailored to you, with expert service to keep your system running smoothly. Power up with confidence….
#5 EV/HEV Charging and Batteries: Powering eMobility Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: boydcorp.com
Key Highlights: Boyd is an ideal partner in developing and manufacturing products that help seal, protect, and control energy flow in an electric vehicle….
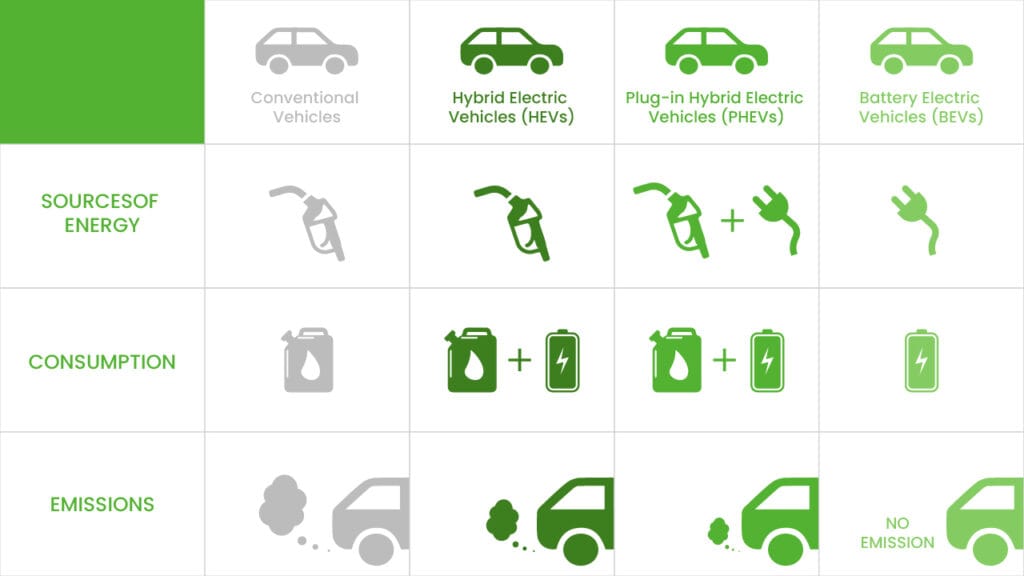
#6 Types of Electric Vehicles: BEVs, PHEVs, HEVs
Domain Est. 2002
Website: evgo.com
Key Highlights: Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs). Similar to a Hybrid, but with a larger battery and electric motor. Has a gas tank and a charging port….
#7 Electric & Hybrid Vehicles (EV/HEV)
Domain Est. 2002
Website: renesas.com
Key Highlights: We offer a broad and versatile range of solutions that address the full spectrum of EV charging needs—from onboard chargers and Level 1/2 units to DC fast ……
#8 Automotive & EV/HEV
Domain Est. 2003
Website: rogerscorp.com
Key Highlights: Rogers is a leading automotive and electric vehicle / hybrid electric vehicle advanced materials supplier with a wide range of industry solutions….
#9 EV and EVSE Charging Test Equipment and Solutions
Domain Est. 2012
Website: keysight.com
Key Highlights: Test and validate EV and EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment) charging systems with Keysight’s advanced solutions. Ensure compliance with the latest EV ……
#10 CharIN
Website: charin.global
Key Highlights: We are the leading global association with over 300 members dedicated to promote standards in the field of charging systems for charging EVs of all types….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hev Charging Station

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle (HEV) Charging Stations
As the global transition toward decarbonization accelerates, the heavy-duty electric vehicle (HEV) charging station market is poised for transformative growth by 2026. Driven by regulatory mandates, technological advancements, and increasing fleet electrification, several key trends are expected to shape the HEV charging infrastructure landscape over the next few years.
1. Regulatory Push and Zero-Emission Mandates
By 2026, stringent emissions regulations in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia will be a primary catalyst for HEV adoption. Policies such as the U.S. Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) rule, California’s 2035 zero-emission vehicle mandate, and the EU’s Fit for 55 package are compelling commercial fleets to transition to electric trucks and buses. These regulations are directly driving demand for high-power charging infrastructure capable of servicing heavy-duty vehicles, particularly depot and corridor-based charging stations.
2. Growth in High-Power Charging (HPC) Infrastructure
The need for rapid turnaround times in freight and public transport operations is fueling investment in high-power charging (HPC) systems. By 2026, 350–1,000 kW megawatt charging systems (MCS) will become standard at major freight hubs, logistics centers, and intercity corridors. These ultra-fast chargers, compatible with the Megawatt Charging System (MCS) standard developed by the CharIN association, will enable heavy-duty trucks to recharge in under an hour, significantly improving operational efficiency.
3. Expansion of Corridor Charging Networks
Public-private partnerships are accelerating the deployment of long-haul charging corridors. In the U.S., initiatives like the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) program are funding HEV-compatible stations along major freight routes (e.g., I-5, I-10, I-75). By 2026, these networks are expected to support seamless cross-country freight electrification, reducing range anxiety and enabling nationwide electric truck operations.
4. Fleet Electrification by Major Logistics and Transit Operators
Leading logistics companies (e.g., FedEx, Amazon, UPS) and public transit agencies are committing to full fleet electrification by 2030–2035. This shift is prompting large-scale investments in private depot charging infrastructure. By 2026, many major distribution centers will feature on-site charging hubs with integrated energy management systems to optimize load balancing and reduce peak demand charges.
5. Integration with Renewable Energy and Energy Storage
Sustainability goals are driving HEV charging stations to incorporate solar, wind, and battery energy storage systems (BESS). By 2026, hybrid charging stations that combine renewables with grid support will become more common, reducing carbon footprints and operational costs. Smart energy management platforms will enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) capabilities, allowing HEVs to act as mobile energy assets.
6. Standardization and Interoperability
The HEV charging ecosystem will see greater standardization by 2026, particularly with the widespread adoption of the MCS connector for trucks and buses. Interoperability across charging networks—enabled by roaming agreements and ISO 15118-20 protocols—will enhance user experience and support cross-border operations in regions like the EU and North America.
7. Increased Investment and Market Consolidation
The HEV charging market is attracting significant capital from automakers, energy companies, and infrastructure funds. By 2026, consolidation among charging hardware providers, software platforms, and energy service companies is expected, leading to integrated turnkey solutions for fleet operators. Partnerships between OEMs (e.g., Volvo, Daimler, Tesla) and charging providers (e.g., ChargePoint, ABB, Siemens) will further streamline deployment.
8. Workforce Development and Grid Readiness
As HEV charging infrastructure expands, challenges related to grid capacity and skilled labor will intensify. Utilities are investing in grid upgrades and smart grid technologies to support high-load charging sites. Meanwhile, training programs for electricians and fleet technicians will grow to meet the demand for qualified personnel to install and maintain HEV charging systems.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the HEV charging station market will be characterized by rapid infrastructure deployment, technological maturity, and strong policy support. The convergence of regulatory pressure, corporate sustainability goals, and advancements in charging technology will create a robust ecosystem for heavy-duty vehicle electrification. Stakeholders across the value chain—governments, utilities, fleet operators, and technology providers—must collaborate to ensure scalable, reliable, and sustainable charging solutions that support the future of freight and public transportation.
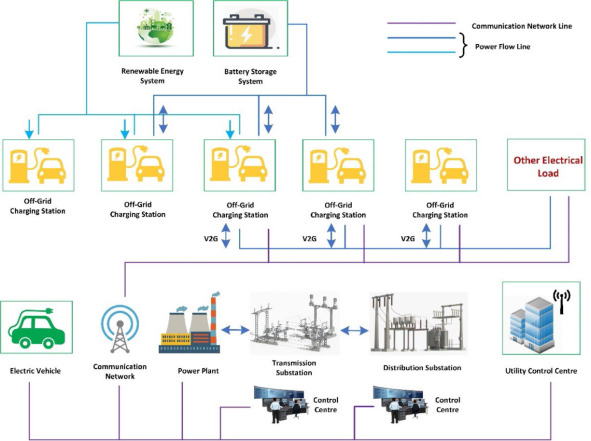
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing HEV Charging Stations (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) charging stations—though less common than full EV chargers, as HEVs typically charge through regenerative braking and internal combustion—can still involve significant risks, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for businesses, fleet operators, and procurement teams.
Poor Product Quality and Safety Risks
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing HEV charging solutions—especially from low-cost or unverified suppliers—is substandard product quality. Chargers may lack essential safety certifications (e.g., UL, CE, IEC), use inferior electrical components, or fail under continuous load. This increases the risk of overheating, electrical faults, or fire hazards. Additionally, inconsistent build quality can lead to frequent failures, high maintenance costs, and downtime, undermining the reliability expected from charging infrastructure.
Non-Compliance with Technical Standards
Many suppliers offer products that claim compatibility with HEV systems but do not adhere to established technical or communication protocols (e.g., ISO 15118, SAE J1772). This can result in interoperability issues, inefficient charging, or even damage to the vehicle’s battery management system. Sourcing without rigorous validation of technical compliance can lead to costly retrofits or replacement.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Sourcing from manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement raises the risk of procuring counterfeit or cloned products. Some suppliers may replicate designs, firmware, or software from established brands without authorization. Purchasing such equipment exposes the buyer to legal liability, potential seizure of goods, and reputational damage. Moreover, infringing products often lack proper support, updates, and warranties, further diminishing long-term value.
Lack of Firmware and Software Authenticity
Modern charging stations rely heavily on embedded software for authentication, load balancing, and remote monitoring. Sourcing from unreliable vendors may result in devices with pirated, outdated, or insecure firmware. This not only violates IP rights but also creates cybersecurity vulnerabilities, potentially exposing networks to hacking or data breaches.
Inadequate Documentation and Support
Low-quality suppliers often provide incomplete technical documentation, missing source code, or no access to software development kits (SDKs). This hinders integration into existing fleet management systems and limits customization. Furthermore, poor after-sales support makes troubleshooting and repairs difficult, increasing total cost of ownership.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including audits and reference checks.
– Require proof of certifications and compliance with international standards.
– Perform independent lab testing of sample units.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
– Prioritize vendors with transparent software licensing and open communication protocols.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally sound deployment of HEV charging infrastructure.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for HEV Charging Station
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the deployment, operation, and maintenance of Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) charging stations. While HEVs typically rely more on internal combustion engines and may not require external charging as frequently as Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), many modern HEVs (especially plug-in hybrids, or PHEVs) do support external charging. Therefore, establishing efficient logistics and adhering to regulatory compliance is essential for supporting this growing segment of the vehicle market.
Site Selection and Feasibility
- Accessibility: Choose locations with high visibility and convenient access, such as commercial centers, office parks, or multi-family dwellings.
- Grid Capacity Assessment: Conduct a utility site assessment to ensure the local power infrastructure can support charging loads.
- Zoning and Land Use: Verify local zoning laws permit installation of charging infrastructure; consult municipal planning departments.
- Traffic Flow: Design layout to minimize congestion and ensure safe ingress/egress for vehicles.
Infrastructure and Installation Logistics
- Equipment Procurement: Source UL-listed and Energy Star-certified charging equipment compatible with PHEV standards (e.g., SAE J1772).
- Electrical Upgrades: Coordinate with utility providers for necessary service upgrades, transformers, or demand management systems.
- Installation Contractors: Use licensed electricians and contractors experienced in EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment) installations.
- Permitting: Obtain all required building and electrical permits prior to construction. Maintain documentation for inspections.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
- National Electric Code (NEC): Installations must comply with NEC Article 625 (Electric Vehicle Charging Systems).
- ADA Accessibility: Ensure charging stations meet Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements for clear floor space, height, and reach.
- Local Building Codes: Adhere to municipal and state building codes, including fire safety setbacks and signage.
- OSHA Standards: Follow Occupational Safety and Health Administration guidelines for worker safety during installation and maintenance.
Environmental and Energy Regulations
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Conduct assessments if installation affects wetlands, historic sites, or protected areas.
- Utility Interconnection Agreements: Secure formal agreements with utility companies for grid connection and net metering (if applicable).
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Align with state-level clean energy initiatives and incentives (e.g., California’s Title 24).
- Renewable Integration: Where possible, integrate solar canopies or renewable energy sources to meet sustainability goals.
Data Management and Cybersecurity
- Networked Charging Systems: Use secure, encrypted communication protocols for stations with remote monitoring or payment systems.
- Data Privacy: Comply with data protection laws (e.g., CCPA, GDPR) when collecting user information or charging data.
- Cybersecurity Standards: Follow NIST or ISO 27001 guidelines to safeguard against unauthorized access and system breaches.
Operations and Maintenance
- Preventive Maintenance Schedule: Establish regular inspection and servicing protocols for connectors, cables, and electrical components.
- Fault Response Plan: Implement a 24/7 support system to address outages or malfunctions promptly.
- User Support: Provide clear instructions, signage, and customer service channels for troubleshooting.
- Software Updates: Regularly update firmware to ensure compatibility, security, and optimal performance.
Incentives and Funding Compliance
- Federal and State Incentives: Leverage programs such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s Clean Cities Coalition, NEVI Program, or state-specific rebates.
- Grant Reporting: Maintain accurate records and submit required documentation to comply with funding obligations.
- Tax Credits: Qualify for IRS Section 30C Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Credit where applicable.
Documentation and Auditing
- As-Built Drawings: Retain updated schematics and site plans post-installation.
- Compliance Logs: Keep records of inspections, permits, maintenance, and safety training.
- Audit Readiness: Prepare for periodic audits by regulators or funding agencies with organized digital and physical files.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of HEV (particularly PHEV) charging stations requires coordinated logistics planning and strict adherence to regulatory standards. By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure safe, compliant, and sustainable charging infrastructure that supports the transition to cleaner transportation. Regular review of evolving codes and technologies is recommended to maintain compliance and operational efficiency.
Conclusion for Sourcing HEV Charging Stations
In conclusion, sourcing HEV (Hybrid Electric Vehicle) charging stations requires a strategic approach that balances technical compatibility, cost-efficiency, scalability, and long-term sustainability. As the adoption of hybrid and electric vehicles continues to grow, organizations must prioritize reliable and future-ready charging infrastructure to support operational needs and environmental goals.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include identifying compatible charging standards (such as SAE J1772 or CCS), evaluating power output and charging speed, ensuring network connectivity for monitoring and management, and selecting reputable suppliers with proven track records in installation and maintenance. Additionally, incentives, rebates, and regulatory compliance should be factored into procurement decisions to optimize return on investment.
By conducting thorough market research, engaging with multiple vendors, and aligning procurement strategies with organizational objectives—such as reducing carbon footprint and enhancing fleet efficiency—businesses can successfully deploy HEV charging solutions that are both effective and scalable. Ultimately, proactive sourcing of HEV charging infrastructure positions organizations at the forefront of sustainable transportation, supporting a cleaner, more resilient energy future.