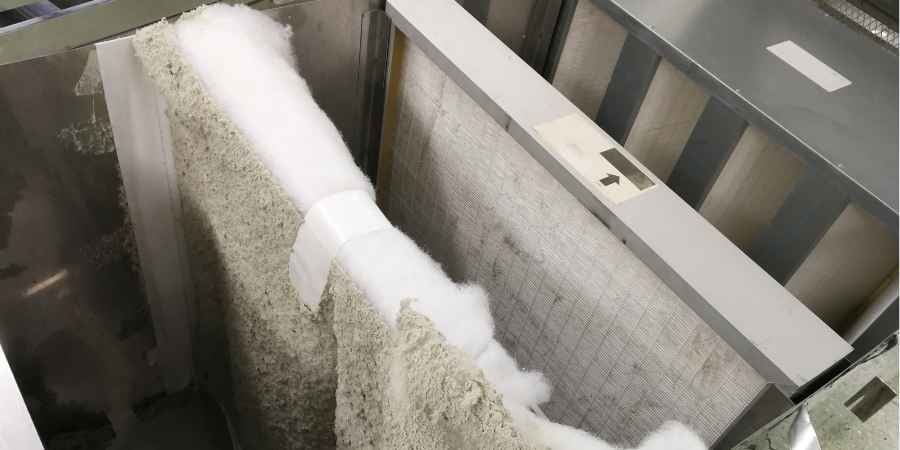
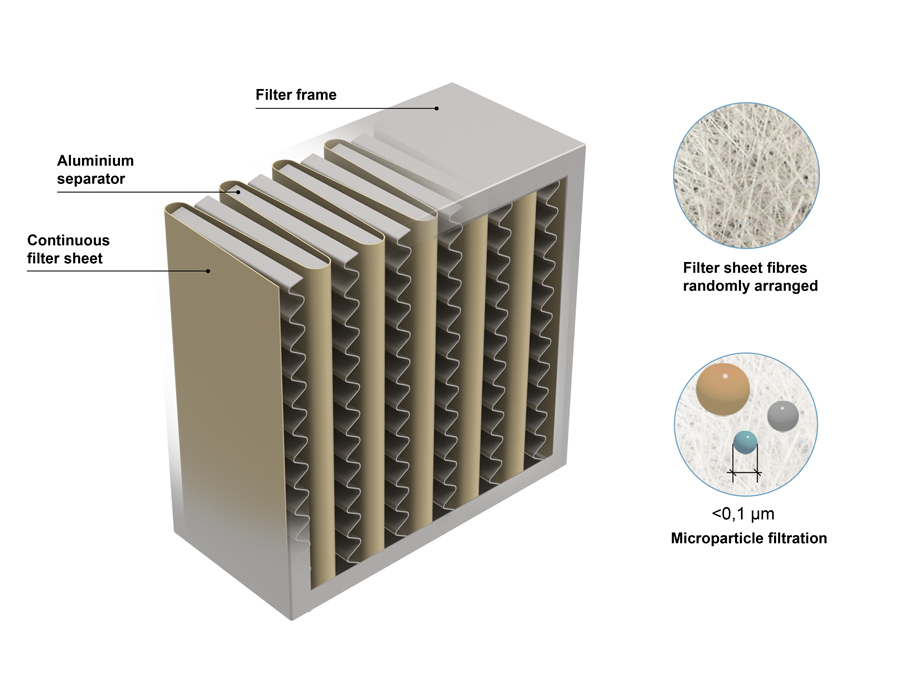
The global HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filter market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising air pollution levels, increasing regulatory standards for indoor air quality, and growing demand across healthcare, industrial, and residential sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the HEPA filter market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 6.6 billion. This expansion is further supported by heightened awareness of airborne health risks and the increasing adoption of HEPA filtration in cleanrooms, HVAC systems, and air purifiers. With technological advancements and regional growth—particularly in Asia-Pacific due to rapid urbanization and industrialization—the competitive landscape is evolving. Based on market presence, innovation, and global reach, here are the top 10 HEPA filter manufacturers leading this expansion.
Top 10 Hepa High Efficiency Particulate Air Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Air Filters for Clean Air
Domain Est. 2002
Website: cleanair.camfil.us
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer of premium clean air solutions, we provide commercial and industrial systems for air filtration and air pollution control that improve ……
#2 High Purity (HEPA) Filtration
Domain Est. 1997
Website: aafintl.com
Key Highlights: AAF’s High Purity line includes high-performing HEPA filters engineered for critical environments such as data centers, healthcare facilities and ……
#3 What is a HEPA filter?
Domain Est. 1997
Website: epa.gov
Key Highlights: HEPA is a type of pleated mechanical air filter. It is an acronym for high efficiency particulate air [filter] (as officially defined by the US Dept. of Energy ……
#4 EPA HEPA ULPA filters
Domain Est. 1998
Website: airfiltration.mann-hummel.com
Key Highlights: Highly effective EPA, HEPA and ULPA filter systems can remove up to 99.99999% of particles. They do what we do best: Separate the useful from the harmful….
#5 High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filter Test Facility (FTF)
Domain Est. 1999
Website: energy.gov
Key Highlights: The Office of Quality Assurance has the responsibility to inspect and test all High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters….
#6 Airpura Industries
Domain Est. 2004
Website: airpura.com
Key Highlights: 7–11 day delivery 30-day returnsUV air purifiers, HEPA air purifiers, Air purifiers with carbon filters for removal of VOC’s formaldehyde, dust, odors, mold, virus, bacteria and mo…
#7 Elevating Indoor Air
Domain Est. 2006
Website: hepacart.com
Key Highlights: HEPA filters offer a powerful defense against indoor air pollutants and are research-backed and rigorously tested to effectively remove harmful particles from ……
#8 Honeywell Air Purifier
Domain Est. 2006
#9 ISO
Domain Est. 2020
Website: iso-aire.com
Key Highlights: ISO-Aire™ HEPA air purifiers are built with high-quality components for an effective, medical-grade and quiet solution. Utilizing proven 99.99% HEPA ……
#10 HEPA Filter
Domain Est. 2009
Website: oransi.com
Key Highlights: HEPA air filters are designed to clean the air of airborne particles. This includes things like pollen, mold spores, fine dust, pet dander, etc….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hepa High Efficiency Particulate Air

H2. Projected Market Trends for HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) Filters in 2026
The global HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filter market is poised for significant growth by 2026, driven by heightened awareness of air quality, technological advancements, and expanding applications across healthcare, residential, industrial, and commercial sectors. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape:
-
Rising Demand for Clean Air Solutions
Increased concerns over air pollution, allergens, and airborne pathogens—amplified by the long-term effects of the global pandemic—are fueling demand for advanced air purification systems. HEPA filters, known for capturing at least 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns, are becoming essential in homes, offices, and public spaces. Urbanization and deteriorating air quality in emerging economies are expected to further accelerate adoption. -
Growth in Healthcare and Life Sciences Applications
Hospitals, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and research laboratories continue to require stringent air quality standards. By 2026, HEPA filters remain critical in cleanrooms, operating theaters, and isolation units. Regulatory mandates for infection control and sterile environments are driving investments in high-performance filtration systems, particularly in developing regions expanding their healthcare infrastructure. -
Expansion of Residential Air Purifier Market
The consumer preference for healthier indoor environments is boosting the residential air purifier segment. Smart home integration, compact designs, and energy-efficient HEPA-based purifiers are gaining traction. Major electronics brands are incorporating HEPA technology into HVAC systems and standalone devices, contributing to market growth. -
Technological Innovations and Hybrid Filtration Systems
Manufacturers are investing in next-generation HEPA filters, including HEPA H13/H14 variants and hybrid systems combining HEPA with activated carbon, UV-C light, or ionization. These multi-stage systems offer enhanced efficiency in removing viruses, VOCs, and odors. Nanofiber-based HEPA filters are also emerging, offering lower airflow resistance and longer service life. -
Stringent Environmental and Safety Regulations
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter air quality standards. In regions like North America and Europe, regulations in construction, manufacturing, and healthcare are mandating the use of HEPA filtration. Similarly, Asia-Pacific countries such as China and India are tightening emission norms, creating new opportunities for HEPA filter deployment. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Recyclable Filters
Environmental sustainability is becoming a priority. By 2026, there is an increasing push for eco-friendly HEPA filter materials and recyclable components. Companies are exploring biodegradable media and energy-efficient designs to reduce environmental impact and meet corporate sustainability goals. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted manufacturers to localize production. Regional manufacturing hubs in Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, and North America are expected to expand, reducing dependency on single-source suppliers and improving delivery timelines. -
Growth in Electric Vehicles and Aerospace
Emerging applications in electric vehicles (EVs) and aerospace are creating new revenue streams. HEPA filters are being integrated into EV cabin air systems to improve passenger health, while aerospace applications require ultra-clean environments for sensitive instrumentation and crew safety.
In conclusion, the HEPA filter market in 2026 is expected to be characterized by strong growth, innovation, and diversification. With increasing health consciousness, regulatory support, and technological integration, the market is projected to exceed USD 15 billion by 2026, according to industry forecasts, cementing HEPA’s role as a cornerstone of modern air quality management.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) Filters (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-quality HEPA filters requires careful attention to technical specifications, supplier credibility, and application requirements. Overlooking key factors can lead to compromised air quality, regulatory non-compliance, and increased operational costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Filter Efficiency Classification
One of the most frequent mistakes is assuming that any filter labeled “HEPA” meets true high-efficiency standards. Not all HEPA filters are created equal. Sourcing filters without verifying the exact efficiency class (e.g., H13, H14 per EN 1822 or equivalent standards like ISO 29463) can result in insufficient particulate removal. Filters below H13 may not capture ≥99.95% of 0.3-micron particles, which is critical in cleanrooms, healthcare, and pharmaceutical applications.
Ignoring Integrity Testing (IP – Integrity Performance)
Many buyers overlook the importance of integrity testing (IP), which verifies that a HEPA filter is free from leaks or defects. Filters should undergo testing via methods such as DOP (Di-Octyl Phthalate) or PAO (Poly-Alpha-Olefin) aerosol testing. Sourcing filters without documented integrity test results increases the risk of undetected leaks, undermining air quality and compliance with ISO 14644 or GMP standards.
Poor Sealing and Frame Integrity
Even high-efficiency filters can fail if the frame or sealing mechanism is substandard. Poor gasket design or fragile frames can lead to air bypass during installation or operation. Always ensure the filter housing and gasket materials (e.g., silicone, neoprene) are compatible with environmental conditions (humidity, temperature, chemicals) and support a secure seal.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable suppliers provide full traceability, including batch numbers, test reports, and compliance with international standards (e.g., EN 1822, IEST, FDA, USP ). Sourcing from vendors without proper documentation exposes users to counterfeit or non-compliant products. Always request a Certificate of Conformance (CoC) and independent test data.
Mismatched Application Requirements
HEPA filters perform differently based on airflow, resistance, and environmental conditions. Selecting a filter without matching it to the specific HVAC system or containment requirement (e.g., laminar flow hoods, isolation rooms) can lead to premature clogging, excessive energy consumption, or insufficient air changes. Consider factors such as face velocity, pressure drop, and filter longevity.
Overlooking Supplier Reliability and Long-Term Support
Choosing vendors based solely on price often leads to poor quality or unreliable supply chains. Evaluate suppliers on their manufacturing consistency, technical support, and ability to provide replacement filters on demand. Lack of long-term support can disrupt operations, especially in critical environments.
Failure to Verify Real-World Performance Data
Lab-tested performance does not always reflect real-world conditions. Ensure that the supplier provides data on actual field performance, especially regarding dust-holding capacity and long-term efficiency. Filters that degrade rapidly under load reduce system reliability and increase maintenance frequency.
By avoiding these pitfalls—focusing on correct efficiency ratings, integrity testing, proper sealing, certification, application fit, and supplier credibility—organizations can ensure they source HEPA filters that deliver reliable, high-performance air filtration.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) Filters
Handling, transporting, and installing HEPA filters requires strict adherence to logistical best practices and regulatory compliance due to their critical role in maintaining air quality—especially in healthcare, pharmaceutical, cleanroom, and nuclear environments. This guide outlines key considerations for safe and compliant HEPA filter management.
H3: Storage and Handling
- Environmental Conditions: Store HEPA filters in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment. Avoid exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures (>60°C or <0°C), and direct sunlight, which can degrade filter media or adhesive seals.
- Positioning: Always store filters upright in their original packaging. Laying filters flat or stacking them improperly may damage pleats or cause deformation.
- Contamination Prevention: Keep filters sealed until ready for installation. Handle only by the frame to avoid touching the media. Use clean gloves to prevent oil or debris transfer.
- Shelf Life: While HEPA filters have no strict expiration, prolonged storage (typically beyond 5 years) should be assessed for integrity before use, especially in critical applications.
H4: Transportation
- Packaging: Use manufacturer-supplied packaging, which includes protective corner guards, moisture barriers, and rigid outer cartons. Never transport unpackaged or loosely handled filters.
- Securement: During transit, secure filters to prevent shifting, vibration, or impact. Use pallets and straps; avoid placing heavy items on top.
- Orientation: Maintain upright orientation (as marked) during transport. Clearly label “This Side Up” and “Fragile.”
- Documentation: Maintain shipping manifests, certificates of compliance (e.g., EN 1822, IEST-RP-CC001), and chain-of-custody records for traceability.
H5: Regulatory & Industry Standards
- Testing & Certification:
- Filters must meet recognized standards (e.g., EN 1822 in Europe, IEST-RP-CC001 in the U.S., ISO 29463 internationally).
- Classifications: HEPA H13 (99.95% efficient at 0.3 µm), H14 (99.995%); ULPA (beyond HEPA) may apply in ultra-sensitive settings.
- Require DOP/PAO aerosol testing to verify integrity before and after installation.
- Compliance Requirements:
- OSHA (29 CFR 1910.1000): General air quality standards in workplaces.
- CDC/NIOSH Guidelines: For healthcare settings (e.g., TB isolation rooms, operating theaters).
- FDA cGMP: Mandatory for pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturing (21 CFR Part 211).
- EPA Regulations: Relevant for hazardous material containment (e.g., asbestos, radionuclides).
- ASHRAE Standard 52.2: For HVAC filter performance evaluation.
H6: Installation & Integrity Testing
- Qualified Personnel: Installation must be performed by trained technicians using cleanroom protocols (e.g., gowning, tool sterilization).
- Sealing: Ensure gasket integrity and proper sealing (e.g., silicone sealant or compression gaskets) to prevent bypass leakage.
- Post-Installation Testing:
- Conduct scan testing using photometers or particle counters to detect leaks.
- Acceptable leakage: ≤0.01% for H13/H14 filters per EN 1822.
- Document test results and retain for audit purposes.
H7: Disposal & Decommissioning
- Contaminated Filters: If used in biohazardous, radioactive, or toxic environments, follow hazardous waste protocols (e.g., EPA RCRA, DOT 49 CFR for transport).
- Decontamination: Autoclaving or fumigation may be required prior to handling (per institutional biosafety protocols).
- Documentation: Maintain logs of filter removal, decontamination method, disposal route, and certifications.
- Recycling: Some components (metal frames, cardboard) may be recyclable if media is uncontaminated—verify with local regulations.
H8: Recordkeeping and Audits
- Maintain complete lifecycle records including:
- Manufacturer certification and test reports
- Installation date, location, and technician
- Periodic inspection and retesting results (typically every 6–12 months)
- Maintenance, replacement, and disposal logs
- Ensure records are accessible for regulatory audits (e.g., FDA inspections, Joint Commission reviews).
Adherence to this logistics and compliance framework ensures HEPA filters perform as designed, protecting personnel, products, and processes from airborne contaminants. Always consult site-specific safety and regulatory requirements for full compliance.
Conclusion on Sourcing HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) Filters
Sourcing HEPA filters requires careful consideration of quality, certification, application requirements, and supplier reliability. True HEPA filters, particularly those meeting standards such as HEPA H13, H14, or MIL-STD, are essential for environments demanding high air purity—such as healthcare facilities, laboratories, cleanrooms, and HVAC systems in sensitive settings. When procuring HEPA filters, it is crucial to verify compliance with recognized standards (e.g., EN 1822, IEST, or DOE-STD-3020) to ensure filtration efficiency of at least 99.97% for particles 0.3 microns in size.
Cost should not be the sole determining factor, as substandard or counterfeit “HEPA-type” filters may compromise air quality and system performance. Building relationships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers, requesting test certificates (such as DOP/PAO test results), and considering factors like filter lifespan, airflow resistance, and compatibility with existing systems are key to effective sourcing.
In conclusion, a strategic, standards-driven approach to sourcing HEPA filters ensures optimal air quality, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational efficiency—protecting both human health and sensitive processes.