The global heat pump market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising energy efficiency demands and increasing adoption of HVAC systems across residential and commercial sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the heat pump market was valued at USD 68.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 107.8 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period. This sustained growth is directly fueling demand for critical heat pump components, including expansion valves—essential for regulating refrigerant flow and optimizing system performance. As heat pump installations rise worldwide, particularly across Europe and North America due to decarbonization policies and incentives, the need for high-precision, reliable expansion valves has intensified. In this competitive environment, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, quality, and market reach. Below are the top 9 expansion valve manufacturers playing a pivotal role in enabling the next generation of efficient heat pump systems.
Top 9 Heat Pump Expansion Valve Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
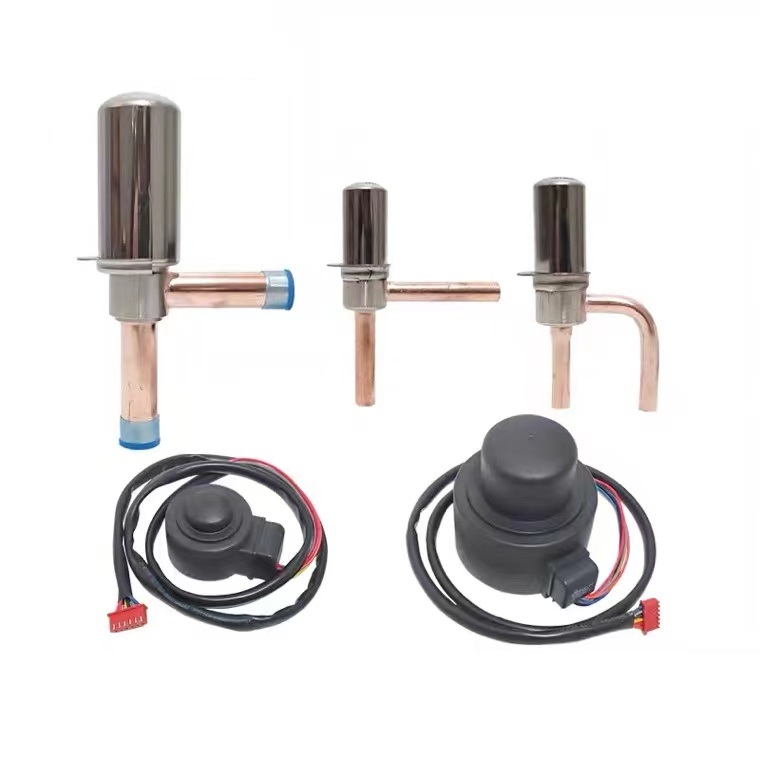
#1 Thermostatic expansion valve customized for industrial companies
Domain Est. 2007
Website: sanhuaeurope.com
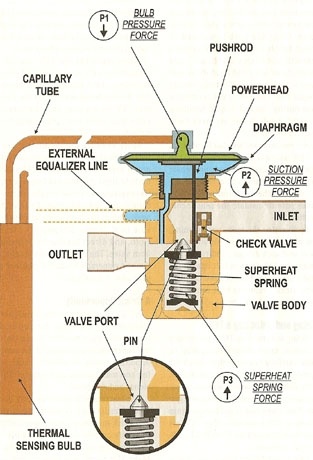
Key Highlights: Sanhua valves for refrigeration systems prevent the overheating and adjust the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. Knows its advanteges!…
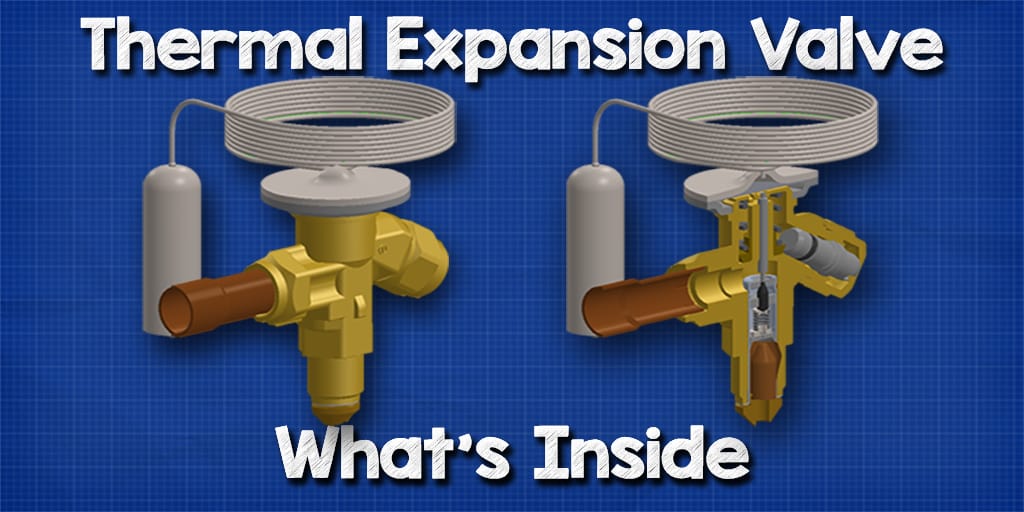
#2 Thermal Expansion Valve
Domain Est. 1995
Website: emerson.com
Key Highlights: Emerson’s Thermostatic and Electronic Expansion Valves are designed for a wide range of air conditioning, refrigeration, heat pump, and chiller applications….
#3 Thermostatic expansion valves
Domain Est. 1995
Website: danfoss.com
Key Highlights: The thermostatic expansion valve allows you to keep a constant superheat (or refrigerant level) at varying load situations in the refrigeration system to save ……
#4 Thermostatic Valves
Domain Est. 1995
Website: copeland.com
Key Highlights: Thermostatic Expansion valves control the superheat of refrigerant vapor to ensure the rate of refrigerant flow….
#5 Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ph.parker.com
Key Highlights: Parker HX/HXC Series thermostatic expansion valves are designed for use on air conditioning and heat pump systems. HXC valves contain an internal check valve….
#6 Thermal Expansion Valves
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parts.ruud.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsUse the search bar above to find: Search by Part Number; Search by Description; Search by HVAC Model Number Search by HVAC Model or Serial Number; Search by WH ……
#7 Electronic Expansion Valve
Domain Est. 1998
Website: apac.sanhuagroup.com
Key Highlights: Stainless Steel 4-Way Valve SHF-G Series · 4-Way Valve SHF Series · 3-way Switching Valve · EEV DPF-TS/S Series · EEV VPF Series · EEV LPF Series · TXV RFKH Series….
#8 Products
Domain Est. 2003
Website: sanhuausa.com
Key Highlights: Explore the extensive catalog of electronic controls, solenoid valves, pressure sensors, expansion valves and all Sanhua products….
#9 TXV
Domain Est. 2015
Website: lennoxpros.com
Key Highlights: Lennox Heat Pump Check Valve Kit for ELA240 & EL240XA 16G33. Sale Clearance. Lennox Heat Pump Check Valve Kit for ELA240 & EL240XA 16G33. Cat #: 16G33 Model ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Heat Pump Expansion Valve
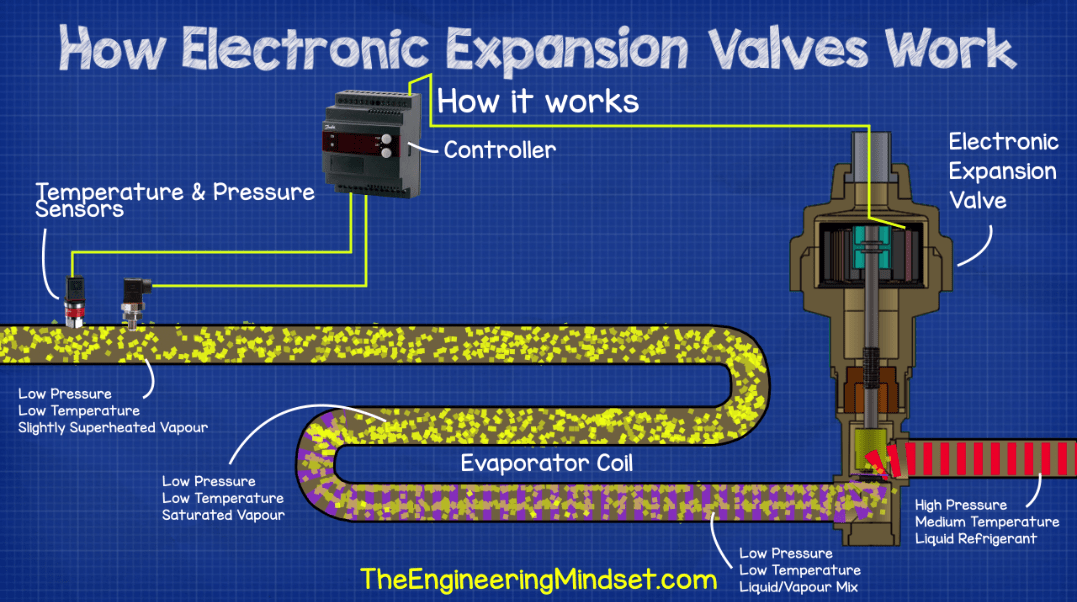
2026 Market Trends for Heat Pump Expansion Valves
The global market for heat pump expansion valves is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by escalating demand for energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions, stringent environmental regulations, and technological innovation. Expansion valves, critical components for regulating refrigerant flow and optimizing system efficiency, are at the heart of these advancements.
Rising Demand for High-Efficiency and Variable-Capacity Systems
The 2026 landscape will be dominated by the shift towards high-efficiency heat pump systems, particularly variable refrigerant flow (VRF) and inverter-driven units. This trend directly boosts demand for thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs) and, more significantly, electronic expansion valves (EEVs). EEVs offer superior precision in superheat control, enabling heat pumps to operate efficiently across a wider range of outdoor temperatures and load conditions. As manufacturers strive to meet higher SEER2 and HSPF2 standards in North America and Ecodesign requirements in Europe, the adoption of EEVs as the standard over traditional TXVs will accelerate, especially in residential and light commercial applications.
Growth Fueled by Regulatory Push and Energy Transition
Stringent government regulations targeting carbon emissions and energy consumption are primary drivers. Policies like the EU’s F-Gas Regulation (phasing down high-GWP refrigerants) and the US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) providing substantial consumer tax credits for heat pump installations will massively increase heat pump deployment. This directly translates to higher demand for expansion valves. Furthermore, the global push towards electrification of heating and decarbonization of buildings makes heat pumps a cornerstone technology, ensuring sustained market growth for their key components, including expansion valves.
Technological Advancements: Smart Valves and Digital Integration
By 2026, expansion valves will become smarter and more integrated. Expect increased adoption of EEVs with enhanced digital capabilities, featuring improved sensor integration (pressure, temperature, flow), advanced control algorithms, and compatibility with building management systems (BMS) and IoT platforms. This enables predictive maintenance, real-time performance optimization, and remote diagnostics. Development will focus on valves offering wider modulation ranges, faster response times, and improved reliability with next-generation low-GWP refrigerants like R32 and A2Ls (e.g., R454B, R290).
Supply Chain Optimization and Regional Diversification
The market will see continued efforts to optimize supply chains, particularly in response to past disruptions. While Asia-Pacific (especially China) remains the dominant manufacturing hub due to established HVAC production, there will be a noticeable trend towards regional diversification and “nearshoring,” particularly in North America and Europe, driven by geopolitical factors, logistics costs, and policy incentives (like those in the IRA). This may lead to increased local assembly or partnerships, but core component manufacturing may remain concentrated.
Competitive Landscape and Material Innovation
The competitive landscape will be characterized by consolidation among major HVAC component suppliers and increased competition from specialized valve manufacturers. Key players will focus on R&D for valves compatible with flammable (A2L, A3) refrigerants, requiring enhanced safety features and materials. Material innovation will be crucial, with development of components resistant to the higher pressures and potential oil incompatibilities associated with new refrigerants. Cost-effectiveness while maintaining performance and reliability will remain a key competitive differentiator.
Conclusion
By 2026, the heat pump expansion valve market will be defined by a shift towards electronic, intelligent, and highly efficient components. Driven by regulatory mandates, energy transition goals, and technological progress, the demand for advanced EEVs will surge. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate with smart features, ensure compatibility with evolving refrigerants, optimize supply chains, and meet the growing global demand for high-performance heat pump systems.
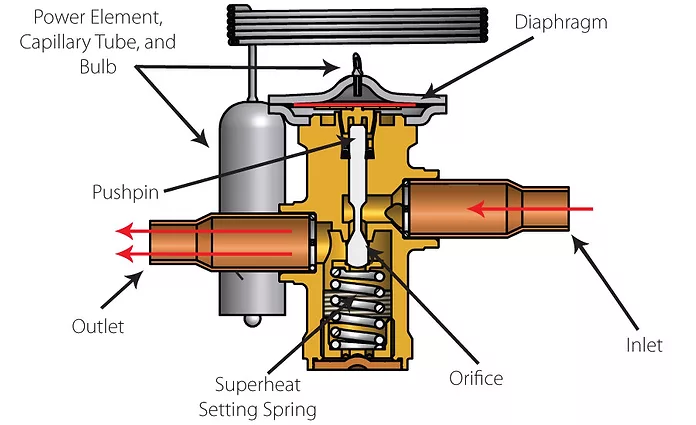
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Heat Pump Expansion Valves: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing heat pump expansion valves—especially for high-efficiency or next-generation systems using refrigerants like H2 (hydrogen) or other low-GWP alternatives—requires careful attention to both component quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
- Compromised Quality Due to Substandard Materials
- Pitfall: Selecting expansion valves made from low-grade materials that are incompatible with hydrogen (H2) environments. H2 can cause hydrogen embrittlement in certain metals, leading to valve failure.
- Risk: Premature wear, leaks, or catastrophic system failure under high-pressure or cryogenic conditions common in H2-based heat pumps.
-
Prevention: Source valves specifically rated for hydrogen service, with materials such as austenitic stainless steel or specialized alloys resistant to embrittlement.
-
Inadequate Flow Control Precision
- Pitfall: Using generic or off-the-shelf expansion valves not optimized for the dynamic operating conditions of H2 heat pumps.
- Risk: Poor superheat control, reduced efficiency, and unstable system performance due to inaccurate refrigerant metering.
-
Prevention: Choose electronically controlled thermal expansion valves (EEVs) with precise modulation capabilities validated for H2 applications.
-
Lack of Certification and Testing for H2 Use
- Pitfall: Assuming standard HVAC expansion valves are suitable for H2 without proper certification.
- Risk: Non-compliance with safety standards (e.g., ISO 19880, ASME BPVC, or ADR regulations), leading to liability and safety hazards.
-
Prevention: Verify valves carry certifications for hydrogen service and have undergone rigorous testing for leak-tightness, cycle life, and pressure cycling.
-
Intellectual Property Infringement
- Pitfall: Sourcing from suppliers offering “compatible” or “equivalent” valves that mimic patented designs (e.g., specialized valve geometries or control algorithms).
- Risk: Legal exposure, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation due to IP litigation.
-
Prevention: Conduct IP due diligence—review patent landscapes and ensure suppliers provide freedom-to-operate assurances or licensed technology.
-
OEM Clones and Counterfeit Components
- Pitfall: Purchasing low-cost alternatives that appear identical to original equipment manufacturer (OEM) valves but lack performance validation.
- Risk: Poor reliability, mismatched performance curves, and voided system warranties.
-
Prevention: Procure only from authorized distributors or manufacturers with traceable supply chains and quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
-
Insufficient Technical Support and Documentation
- Pitfall: Working with suppliers who do not provide comprehensive data for H2-specific performance (e.g., pressure drop curves, compatibility charts).
- Risk: Design errors during system integration and difficulty troubleshooting in the field.
-
Prevention: Require full technical documentation, including test reports under H2 conditions and compatibility with system controls.
-
Overlooking Long-Term Supply Chain Stability
- Pitfall: Relying on niche suppliers without proven scalability or sustainability in H2 component manufacturing.
- Risk: Production delays or obsolescence if the supplier cannot meet volume or innovation demands.
- Prevention: Evaluate supplier track record, R&D investment, and roadmap for hydrogen-compatible components.
Conclusion:
When sourcing expansion valves for H2 heat pumps, prioritize suppliers with proven expertise in hydrogen systems, robust quality assurance, and clear IP compliance. Cutting corners on valve selection can compromise system safety, efficiency, and legal integrity—especially in emerging H2 applications where performance and reliability are critical.
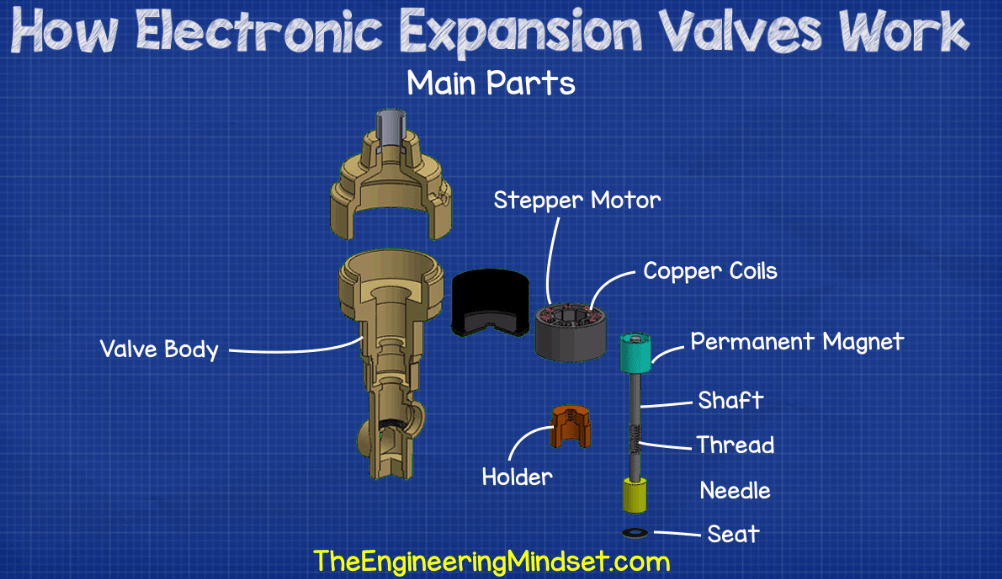
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Heat Pump Expansion Valve
This guide provides essential information for the safe and compliant handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence related to Heat Pump Expansion Valves throughout the supply chain.
Logistics Considerations
Ensure proper packaging to prevent physical damage during transit. Expansion valves are precision components sensitive to impact, vibration, and contamination. Use manufacturer-recommended packaging with protective caps on ports and secure internal cushioning.
Label all packages clearly with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “Do Not Drop,” and “Protect from Moisture.” Maintain upright orientation during transport to avoid internal component displacement or lubricant migration.
Store valves in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 5°C to 40°C) away from direct sunlight, corrosive substances, and excessive humidity. Avoid long-term storage beyond manufacturer recommendations to prevent seal degradation or contamination.
Use reliable carriers experienced in handling HVACR components, and verify that shipping documentation includes accurate product descriptions, part numbers, and any relevant safety data.
Compliance Requirements
Ensure all expansion valves comply with applicable international and regional standards, including ISO 5151 (hermetic refrigerant flow control devices), EN 13313 (HVAC product safety), and UL 60335-2-40 (safety for heat pump controls).
Verify that valves are certified for use with specific refrigerants (e.g., R32, R410A, R290) and meet pressure, temperature, and material compatibility standards under regulations such as the EU F-Gas Regulation (No. 517/2014) or the U.S. EPA SNAP Program.
Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) as required by OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) and align with GHS classification, especially if valves contain residual refrigerants or lubricants.
Ensure compliance with customs regulations including correct HS codes (e.g., 8481.80 for valves for refrigerating or air conditioning machinery) and country-specific import requirements for HVAC components.
Maintain traceability through batch/lot numbers and retain certificates of conformity, test reports, and RoHS/REACH declarations where applicable, particularly for shipments into the European Union.
Conclusion for Sourcing Heat Pump Expansion Valve:
Sourcing the appropriate expansion valve for a heat pump system is a critical step that directly impacts system efficiency, reliability, and performance. After evaluating technical specifications, compatibility with refrigerants, capacity requirements, and operating conditions, it is clear that selecting a high-quality, precisely matched expansion valve—whether thermostatic (TXV), electronic (EEV), or fixed orifice—is essential for optimal refrigerant flow control and system stability across varying loads and climates.
Key considerations such as brand reputation, availability of technical support, cost-effectiveness, and supply chain reliability should guide procurement decisions. Sourcing from reputable suppliers or manufacturers with proven experience in HVAC components ensures product quality, compliance with industry standards, and long-term serviceability.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing strategy—balancing performance needs, cost, and supplier reliability—will enhance the overall efficiency and durability of the heat pump system, supporting sustainable operation and reducing maintenance issues over its lifecycle.