The global heat exchanger tubes market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across key industries such as oil & gas, power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the heat exchanger market was valued at USD 17.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% through 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising energy consumption, stringent environmental regulations requiring efficient thermal systems, and the ongoing modernization of industrial infrastructure worldwide. As critical components in heat transfer systems, high-performance heat exchanger tubes are in growing demand for their reliability, corrosion resistance, and thermal efficiency. With Asia-Pacific emerging as a key growth region due to rapid industrialization and expanding power capacity—particularly in China and India—the competitive landscape among manufacturers is intensifying. In this dynamic environment, selecting the right supplier is crucial for ensuring system efficiency and longevity. Based on market presence, technological innovation, global reach, and product quality, we’ve identified the top 10 heat exchanger tubes manufacturers shaping the future of industrial thermal management.
Top 10 Heat Exchanger Tubes Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tranter: Responsive Heat Exchangers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: tranter.com
Key Highlights: At Tranter, we specialize in advanced gasketed and welded plate heat exchangers. As a global manufacturer, we are committed to precision and localized service….
#2 Heat Exchangers for Industrial & Mobile Applications
Domain Est. 1997
Website: thermaltransfer.com
Key Highlights: We offer the industry’s most complete lineup of air- and water-cooled heat exchangers; from brazed aluminum and copper tube designs to shell-and-tube and brazed ……
#3 Kelvion
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kelvion.com
Key Highlights: Kelvion, your manufacturer for heat exchangers & cooling & heating solutions: plate heat exchangers, cooling heat exchangers & more!…
#4 Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain Est. 2008
Website: braskinc.com
Key Highlights: Brask, Inc. is a leader in the design, manufacturing, and repair of Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers, Helixchangers, and related equipment….
#5 Heat Exchanger Repair & Fabrication
Domain Est. 2012
Website: altexinc.com
Key Highlights: Altex Industries designs and manufactures high-performance industrial heat exchangers for energy, chemical, and process industries with superior efficiency ……
#6 Curtiss
Domain Est. 2015
Website: cw-estgroup.com
Key Highlights: Our flagship product, Pop-A-Plug® Heat Exchanger Tube Plugs, are the industry’s leading technology for plugging leaking and degraded heat exchanger tubes….
#7 High Performance Tubes for Heat Exchangers (HX)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: superiortube.com
Key Highlights: Superior Tube manufactures high quality heat exchanger tubes for a range of industries such as nuclear and aerospace. Thin wall heat exchanger tubing in ……
#8 Southern Heat Exchanger
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sheco.com
Key Highlights: First Choice – Proven Experience. Customer Focused. ; Full Service Exchanger Manufacturing. Our design and project management team will make your life easier….
#9 Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain Est. 1999
Website: xylem.com
Key Highlights: Custom Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers, CPK – TEMA type AEW or BEW, removable bundle, packed floating tubesheet shell & tube heat exchanger….
#10 Heat Exchanger
Domain Est. 2006
Website: us.mersen.com
Key Highlights: Mersen is the global leader in designing and manufacturing graphite shell and tube heat exchangers, offering exceptional corrosion resistance, high thermal ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Heat Exchanger Tubes

H2: Projected Market Trends for Heat Exchanger Tubes in 2026
The global heat exchanger tubes market is anticipated to experience significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in materials, expanding industrial applications, and increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape during this period.
-
Rising Demand from Key Industries
By 2026, the oil & gas, power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC sectors are projected to remain the primary consumers of heat exchanger tubes. The ongoing modernization of aging infrastructure, particularly in North America and Europe, coupled with new energy projects in Asia-Pacific—especially in China, India, and Southeast Asia—will drive sustained demand. Additionally, the growing deployment of LNG (liquefied natural gas) terminals and offshore drilling platforms will amplify the need for corrosion-resistant and high-performance tubing solutions. -
Shift Toward Advanced Materials
There will be an accelerated shift from traditional carbon steel tubes to high-performance alloys such as stainless steel, titanium, duplex stainless steel, and nickel-based alloys (e.g., Inconel). These materials offer enhanced resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and pressure—critical for harsh operating environments. Innovations in manufacturing techniques, such as precision welding and seamless tube drawing, will further improve product reliability and lifespan, supporting their adoption in critical applications. -
Growth in Renewable Energy and Hybrid Systems
The expansion of renewable energy infrastructure, including concentrated solar power (CSP) and geothermal plants, will create new opportunities for specialized heat exchanger tubes. These applications require materials capable of withstanding thermal cycling and high-temperature differentials. Additionally, hybrid power systems integrating fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies will demand advanced heat transfer solutions to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the market by 2026, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and government investments in energy and infrastructure. China and India will be key growth engines, supported by domestic manufacturing initiatives and foreign direct investment. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will focus on retrofitting and upgrading existing facilities to meet stricter environmental regulations, favoring high-efficiency and low-maintenance tube solutions. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations aimed at reducing industrial emissions and improving energy efficiency will play a pivotal role in shaping product development. Manufacturers will increasingly adopt eco-friendly production processes and promote recyclable materials. Compliance with international standards (e.g., ASME, ASTM, PED) will remain critical, especially for export-oriented suppliers. -
Technological Innovation and Digital Integration
The integration of predictive maintenance technologies, such as IoT-enabled sensors and AI-driven analytics, will enhance the monitoring of heat exchanger tube performance. This will allow for real-time detection of fouling, corrosion, or leaks, minimizing downtime and extending equipment life. Digital twins and simulation tools will also become more prevalent in the design and optimization phase. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Geopolitical uncertainties and past supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to diversify sourcing and increase regional production. By 2026, localized manufacturing hubs are expected to emerge in strategic markets to reduce lead times, lower logistics costs, and mitigate trade risks.
In summary, the heat exchanger tubes market in 2026 will be characterized by technological innovation, material advancements, and a strong focus on sustainability. Companies that invest in R&D, adapt to regulatory changes, and align with global energy transition trends will be best positioned for growth in this evolving landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Heat Exchanger Tubes (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing heat exchanger tubes involves critical technical and commercial considerations. Overlooking key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to catastrophic failures, safety hazards, financial losses, and legal disputes. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Material Specification & Certification:
- Pitfall: Relying solely on generic material grades (e.g., “316L SS”) without defining critical parameters like exact alloy composition (trace elements), mechanical properties (yield/tensile strength, hardness), grain size, and manufacturing process (e.g., seamless vs. welded, cold-worked vs. annealed).
- Consequence: Tubes may meet nominal specs but fail prematurely due to stress corrosion cracking (SCC), pitting, erosion, or insufficient strength under operating conditions (pressure, temperature, vibration). Lack of full traceability (mill test certs – MTCs) prevents root cause analysis.
- Mitigation: Specify exact ASTM/ASME/EN/other standards (e.g., ASTM B444 UNS N06625 for Inconel 625), require detailed MTCs with full chemical analysis and mechanical test results, mandate positive material identification (PMI) upon receipt.
-
Compromised Manufacturing Quality & Process Control:
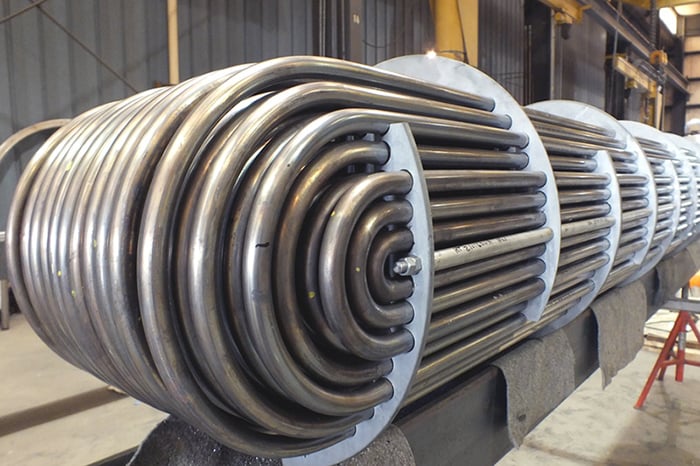
- Pitfall: Selecting low-cost suppliers with poor quality management systems (lack of ISO 9001:2015 certification), inadequate process controls, or substandard equipment. Overlooking critical steps like heat treatment, straightening, cleaning, and non-destructive testing (NDT).
- Consequence: Defects like seams, laps, inclusions, inconsistent wall thickness, poor surface finish (affecting heat transfer and fouling), residual stresses, or improper heat treatment leading to susceptibility to corrosion or embrittlement.
- Mitigation: Audit potential suppliers’ facilities and QMS. Specify required manufacturing routes (e.g., cold-drawn seamless), mandatory heat treatment procedures, and stringent surface finish requirements. Define NDT scope clearly (e.g., 100% Eddy Current Testing to ASTM E215/E309, hydrostatic testing, dimensional checks).
-
Insufficient or Inappropriate Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
- Pitfall: Accepting minimal or non-standard NDT, or using the wrong method for the material/application (e.g., relying only on visual inspection for critical alloys). Not verifying NDT personnel certification (e.g., ASNT Level II/III).
- Consequence: Undetected internal flaws (laminations, voids), surface cracks, or wall thinning can lead to tube leaks, tube rupture, or accelerated degradation once in service.
- Mitigation: Mandate comprehensive, standardized NDT protocols (Eddy Current, Ultrasonic, Hydrostatic) appropriate for the material and service. Require certified NDT reports (including calibration records) and specify acceptance criteria per relevant standards (e.g., ASTM, API).
-
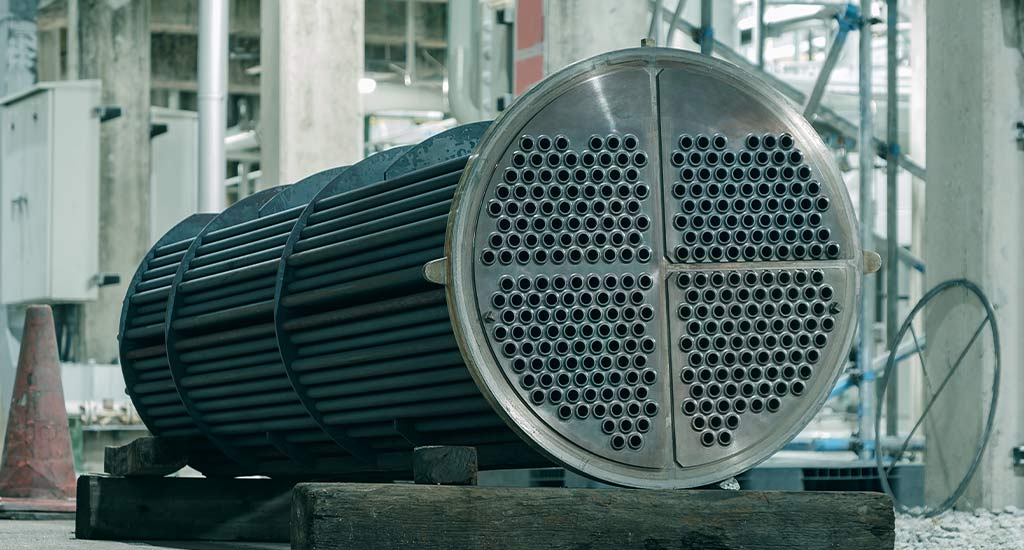
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Integrity:
- Pitfall: Tolerating tubes outside specified dimensional tolerances (OD, ID, wall thickness, straightness, roundness) or with poor surface quality (scratches, scale, pits, roughness).
- Consequence: Difficult or impossible tube installation in tube sheets, uneven heat transfer, accelerated fouling, initiation points for corrosion (pitting), vibration issues leading to fretting wear or fatigue failure.
- Mitigation: Define tight dimensional tolerances (e.g., per ASTM A213/A269) and precise surface finish requirements (e.g., Ra value). Specify inspection methods and sampling plans. Rejection criteria must be clear.
-
Inadequate Corrosion Resistance Verification:
- Pitfall: Assuming material specifications guarantee performance in the specific service environment without validating it. Not requiring or performing corrosion testing (e.g., pitting resistance equivalent number – PREN calculation, ferric chloride testing, actual service simulation if critical).
- Consequence: Unexpected corrosion modes (pitting, crevice, galvanic, SCC, microbiologically influenced corrosion – MIC) leading to rapid tube failure, product contamination, and unplanned shutdowns.
- Mitigation: Perform detailed corrosion assessment based on actual process fluids, temperatures, pressures, and flow rates. Specify required PREN or other corrosion indices. Consider requiring specific corrosion test reports from the supplier for critical applications.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Unlicensed Use of Patented Designs or Processes:
- Pitfall: Sourcing tubes manufactured using a patented manufacturing process (e.g., a specific cold-working or heat treatment technique) or incorporating a patented tube design feature (e.g., enhanced surface geometry, specific fin configuration) without securing the necessary license.
- Consequence: The end-user (or potentially the buyer) can be sued for patent infringement by the IP holder, leading to injunctions (halting operation), significant damages, and reputational damage. The supplier might be liable, but enforcement often targets the user.
- Mitigation: Conduct thorough due diligence on the supplier’s manufacturing processes and the design of the tube. Require suppliers to warrant they hold necessary licenses or that their product does not infringe valid patents. Obtain indemnification clauses in contracts.
-
Sourcing “Copycat” or “Knock-off” Tubes:
- Pitfall: Unknowingly purchasing tubes that mimic the appearance or name of a proprietary, high-performance product (e.g., a specific branded alloy or enhanced tube) but are made using inferior materials or processes, potentially infringing on trademarks or trade dress.
- Consequence: Poor performance, premature failure, safety risks, and potential liability for trademark infringement. Loss of expected efficiency gains (e.g., from enhanced surfaces).
- Mitigation: Source directly from authorized distributors or the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) for critical or proprietary products. Verify supplier authenticity and authorization. Be wary of prices significantly below market for branded items.
-
Ambiguous or Absent IP Clauses in Contracts:
- Pitfall: Failing to include clear contractual terms regarding IP ownership, infringement indemnification, and warranty against IP infringement in the purchase agreement.
- Consequence: No legal recourse against the supplier if an IP infringement claim arises. The buyer bears the full cost and risk of defending lawsuits and potential damages.
- Mitigation: Include robust IP clauses in contracts requiring the supplier to:
- Warrant they own or have licensed all necessary IP.
- Indemnify the buyer against any third-party IP infringement claims related to the supplied tubes.
- Defend the buyer in such claims.
-
Reverse Engineering Without Proper Authorization:
- Pitfall: Attempting to replicate a competitor’s tube design (especially enhanced surfaces) or process based on sample analysis without understanding if patents or trade secrets are protected.
- Consequence: Direct infringement of patents or misappropriation of trade secrets, leading to costly litigation.
- Mitigation: Conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses before developing or sourcing replicas. Consult IP legal counsel. Focus on designing around existing IP if possible.
By proactively addressing these common quality and IP pitfalls through rigorous specification, supplier vetting, clear contracts, and due diligence, organizations can ensure the reliability, safety, and legal compliance of their heat exchanger tube sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Heat Exchanger Tubes
Overview
Heat Exchanger Tubes are critical components used across industries such as oil & gas, power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems. Due to their specialized nature, stringent material specifications, and international usage, proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure timely delivery, product integrity, and adherence to legal and safety standards.
H2: Material Specifications and Standards Compliance
Heat Exchanger Tubes must comply with recognized international material and performance standards to ensure reliability and safety. Key standards include:
- ASTM Standards:
- ASTM B161 (Nickel and Nickel Alloy Seamless Tubes)
- ASTM B163 (Seamless Nickel and Nickel Alloy Condenser and Heat-Exchanger Tubes)
- ASTM B466 (Copper-Nickel Tubes)
-
ASTM A213/A213M (Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy-Steel Boiler, Superheater, and Heat-Exchanger Tubes)
-
ASME and PED Compliance:
- ASME Section II and Section VIII for pressure vessel applications
-
Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU for products shipped to the European Union
-
NACE MR0175/ISO 15156: Required for sour service environments (e.g., oil & gas) to resist sulfide stress cracking.
Ensure all material test reports (MTRs), mill certifications, and compliance documentation (e.g., 3.1 or 3.2 EN 10204) are provided and verified before shipment.
H2: Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents mechanical damage, corrosion, and contamination during transit. Key practices include:
- End Protection: Use plastic or metal caps on tube ends to prevent dents and contamination.
- Bundling: Secure tubes in tightly strapped bundles on wooden or metal skids. Use separator materials (e.g., paper or foam) to avoid surface abrasion.
- Moisture Protection: Apply vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI) and seal bundles in moisture-resistant wrapping or shrink film. For marine shipments, use desiccants inside sealed packaging.
- Labeling: Clearly label each bundle with:
- Material grade
- Dimensions (OD, wall thickness, length)
- Heat number
- Customer PO and part number
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack”, “Protect from Moisture”)
Avoid direct ground contact; store and transport on skids only.
H2: Transportation and Logistics Planning
Due to the length and fragility of heat exchanger tubes, transportation logistics require careful coordination.
- Mode of Transport:
- Road: Standard for regional deliveries. Use flatbed or enclosed trailers with proper load securing.
- Rail: Suitable for long domestic hauls; ensure secure bracing to prevent movement.
- Sea: Primary mode for international shipments. Use 20’ or 40’ dry containers or open-top containers for longer tubes. Consider flat-rack containers for oversized lengths.
-
Air: Rare due to cost and size limitations; only for urgent, small-diameter, short-length tubes.
-
Loading and Securing:
- Distribute load weight evenly
- Use dunnage and edge protectors to prevent damage
- Secure bundles with ratchet straps or chains
-
Avoid overhang beyond vehicle edges (comply with local transport regulations)
-
Temperature and Humidity Control: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures and high humidity, especially for corrosion-prone alloys (e.g., stainless steel, copper-nickel).
H2: Import/Export Regulations and Documentation
International shipments require strict adherence to customs and trade regulations.
- Harmonized System (HS) Codes:
-
Example: 7304.59 (Stainless steel tubes), 7411.10 (Copper-nickel tubes) – verify based on material and application.
-
Required Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice (with full product description, value, origin)
- Packing List (itemized per bundle/skid)
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
- Certificate of Origin (for preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
- Material Test Reports (MTRs) and compliance certificates
-
Export License (if applicable, e.g., dual-use items or strategic materials)
-
Regulatory Compliance:
- ITAR/EAR (U.S.): Check if tubes fall under export control based on material or end-use.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Confirm compliance for hazardous substances.
- Customs Inspections: Be prepared for potential inspection of tube dimensions and material verification.
Engage a freight forwarder experienced in industrial metal products to manage documentation and customs clearance.
H2: Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain full traceability from manufacturing to delivery:
- Assign unique batch/heat numbers to each tube or bundle.
- Retain MTRs and inspection records for minimum 10 years (as per ASME and industry norms).
- Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) for large orders, especially for offshore or critical applications.
- Use barcode or RFID tagging for inventory and logistics tracking where feasible.
H2: Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Anticipate and prepare for common logistics risks:
- Delays: Monitor port congestion, weather, and geopolitical factors. Build buffer time into delivery schedules.
- Damage Claims: Photograph packaging and load condition before and after transit. Use carriers with proven experience in handling long metal products.
- Non-Compliance Penalties: Audit documentation and labeling prior to shipment. Consult legal or compliance experts for high-risk markets.
- Alternative Routes: Identify backup ports or transport corridors in case of disruptions.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for Heat Exchanger Tubes ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. By following standardized practices in packaging, transport, documentation, and quality control, companies can minimize risks and support seamless global operations. Regular training for logistics and procurement teams on evolving regulations (e.g., customs updates, environmental standards) is recommended to maintain continuous compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Heat Exchanger Tubes
In conclusion, sourcing heat exchanger tubes requires a comprehensive evaluation of material compatibility, performance requirements, cost efficiency, and supplier reliability. The selection of appropriate tube materials—such as stainless steel, copper alloys, titanium, or specialty alloys—must align with the operating conditions, including temperature, pressure, and exposure to corrosive media, to ensure long-term durability and optimal heat transfer efficiency.
Engaging qualified suppliers with proven manufacturing standards, quality certifications (e.g., ASME, ASTM, ISO), and consistent track records is critical to maintaining system integrity and minimizing downtime. Additionally, considerations such as lead times, total cost of ownership, and availability of inventory play a significant role in supply chain resilience.
By adopting a strategic sourcing approach that balances technical specifications with commercial factors, organizations can secure high-quality heat exchanger tubes that enhance operational performance, extend equipment lifespan, and support overall project success. Ongoing collaboration with trusted vendors and periodic reassessment of sourcing strategies will further ensure adaptability to evolving industrial demands and technological advancements.