The global heat exchanger market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy efficiency and thermal management across industries such as power generation, oil & gas, and HVAC. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 62.67 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 85.54 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.3% during the forecast period. This expansion underscores the critical role of key components like heat blocks, which are integral to the performance and reliability of modern thermal systems. As industries prioritize compact, high-efficiency solutions, the demand for advanced heat block manufacturing has intensified. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining engineering precision with scalable production to meet evolving technical requirements. Below, we explore the top 10 heat blocks manufacturers shaping the future of thermal management.
Top 10 Heat Blocks Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kelvion
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kelvion.com
Key Highlights: Kelvion, your manufacturer for heat exchangers & cooling & heating solutions: plate heat exchangers, cooling heat exchangers & more!…
#2 Leading Diesel heater & Engine Block Heater Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2017
Website: warmda.com
Key Highlights: Warmda LLC: Expert in diesel heater & engine block heaters. 27 years of innovation. Trusted globally. Explore our quality range for vehicles & boats….
#3 Dry Block Heater Heating / Cooling / Tempering
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ika.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryThese digital block heaters are ideal for melting and boiling point determination, enzyme reactions, incubation and activation of cultures….
#4 Innovative heating solutions from Webasto for all types of vehicles
Domain Est. 1997
Website: webasto.com
Key Highlights: Webasto offers versatile heating solutions for cars, buses, boats, motorhomes and more. Experience comfort and reliability wherever you are….
#5 Zerostart Block Heaters
Domain Est. 2001
Website: phillipsandtemro.com
Key Highlights: Engine block heaters designed and tested for each individual engine application. Manufactured under the Zerostart / Temro brands….
#6 Hydronic Baseboard Heating Systems
Domain Est. 2004
Website: haydoncorp.com
Key Highlights: Hydronic Baseboard Heating Systems · H-Block Rooftop Supports · Fittings and Accessories. Company. About Haydon · Haydon News · Join our Team · Contact Us….
#7 Cubic graphite heat exchangers
Domain Est. 2006
Website: us.mersen.com
Key Highlights: The Graphite Cubic Block Heat Exchanger is adapted to the heating, cooling, condensation and absorption of highly corrosive liquid chemicals….
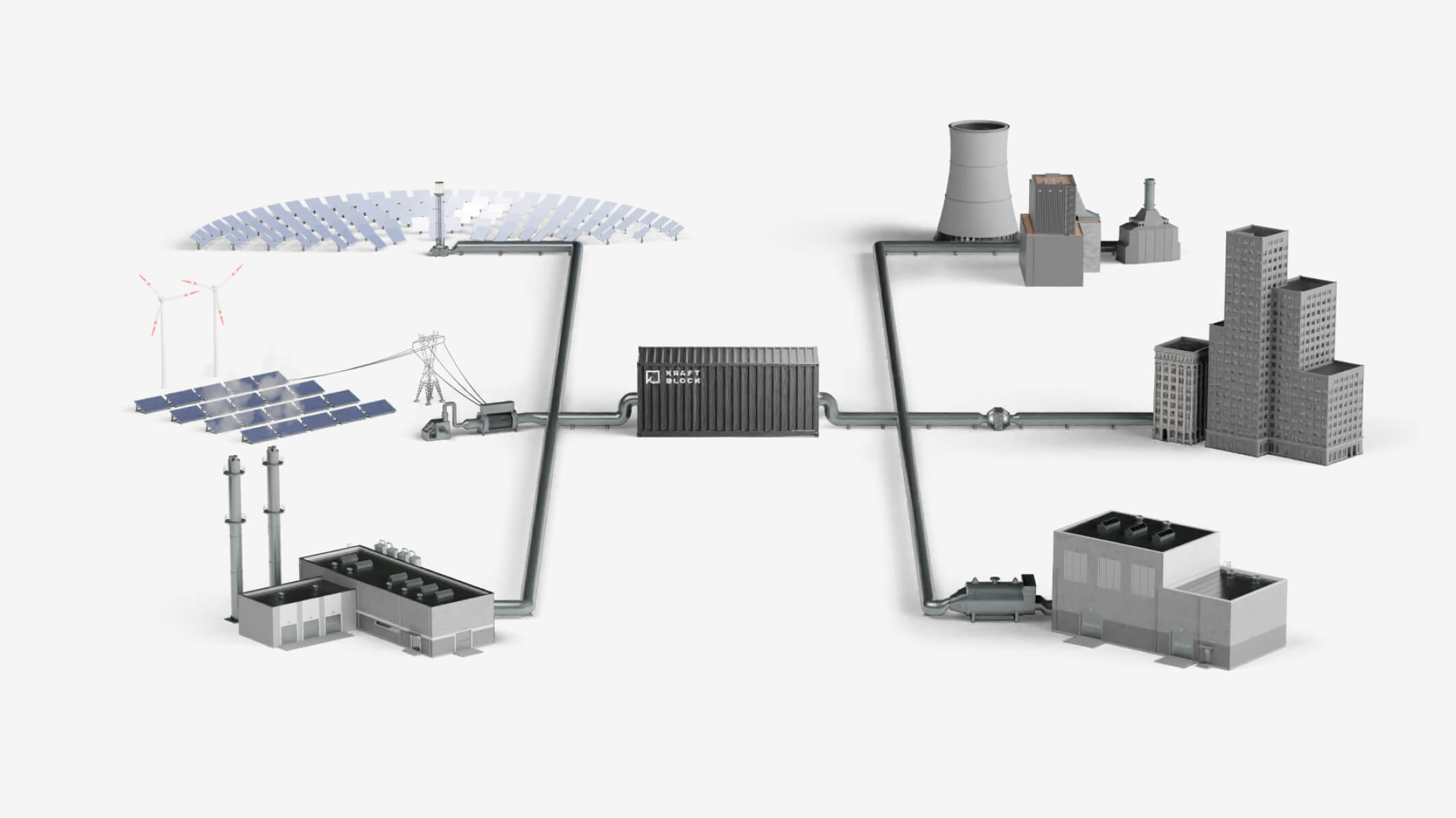
#8 Kraftblock
Domain Est. 2018
Website: kraftblock.com
Key Highlights: Kraftblock is a high-temperature thermal energy storage system for process heat from renewable energy and waste heat used in industries, district heating ……
#9 Mannok Aircrete Standard
Domain Est. 2020
Website: mannokbuild.com
Key Highlights: Mannok Aircrete Standard block combines optimum levels of thermal performance, strength and density to make it suitable for almost all on site applications….
#10 Sunfire Heating Blocks
Domain Est. 2021
Website: sunfireblocks.com
Key Highlights: Sunfire Blocks for woodstoves, fireplaces & campfires. Made from compressed kiln dried material, our Sunfire Heating Blocks are manufactured with 100% hardwood….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Heat Blocks

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Heat Blocks
As we approach 2026, the global market for heat blocks—precision heating devices used in laboratories, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and industrial processes—is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological innovation, rising demand for automation, and expanding applications in life sciences and diagnostics. Below is an analysis of the key market trends shaping the heat block industry in 2026 under the H2 (second half) outlook.
1. Increased Adoption in Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Heat blocks are becoming integral components in portable and rapid diagnostic devices, particularly in molecular testing (e.g., PCR, LAMP). With the continued emphasis on decentralized healthcare and rapid disease detection post-pandemic, demand for compact, energy-efficient heat blocks is surging. H2 2026 will likely see a spike in integration of smart heat blocks into handheld diagnostic tools, especially in emerging markets.
2. Advancements in Smart and Connected Heat Blocks
IoT-enabled heat blocks with real-time temperature monitoring, remote control via mobile apps, and data logging capabilities are gaining traction. By H2 2026, leading manufacturers are expected to offer cloud-connected systems that integrate with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), improving reproducibility and compliance in regulated environments.
3. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient heat blocks with lower thermal mass and faster ramp times. In H2 2026, expect to see more products featuring eco-friendly materials, reduced power consumption, and longer operational lifespans—aligning with green lab initiatives.
4. Customization and Modularity
The demand for application-specific heat blocks (e.g., for microtiter plates, PCR tubes, or unique sample formats) continues to grow. By mid-to-late 2026, modular heat block systems that allow quick interchangeability and 3D-printed custom inserts are anticipated to become standard, particularly in research and high-throughput screening environments.
5. Growth in Asia-Pacific Markets
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth engine due to rising investments in biotech infrastructure, expanding pharmaceutical R&D, and government support for healthcare innovation. In H2 2026, local manufacturing and partnerships with global suppliers are expected to accelerate market penetration in countries like China, India, and South Korea.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Following recent global disruptions, companies are reshoring or nearshoring production. By the second half of 2026, we anticipate increased regional production of heat blocks to reduce lead times and dependency on single-source suppliers, especially in North America and Europe.
7. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established players (e.g., Thermo Fisher, Eppendorf) and agile startups introducing innovations in temperature precision, heating uniformity, and user interface design. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic collaborations are expected to rise in H2 2026 as companies seek to expand their technological portfolios.
Conclusion:
The heat block market in H2 2026 is poised for robust growth, fueled by digitalization, healthcare advancements, and sustainability imperatives. Companies that prioritize smart integration, customization, and regional adaptability will be best positioned to capture market share. As automation and precision medicine continue to evolve, heat blocks will remain a critical, albeit often underappreciated, enabler of scientific progress.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Heat Blocks (Quality, IP)
Sourcing heat blocks—especially for high-performance applications like semiconductor manufacturing, power electronics, or precision thermal management—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly delays, performance failures, or legal exposure.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Properties
Heat blocks are often made from high-conductivity materials like copper, aluminum, or specialized alloys. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers may result in inconsistent purity, grain structure, or thermal conductivity, directly impacting thermal performance and reliability.
Poor Machining Tolerances and Surface Finish
Precision is critical for effective thermal contact. Poorly machined heat blocks with inadequate flatness, rough surface finishes, or dimensional inaccuracies can lead to air gaps, hotspots, and reduced heat transfer efficiency.
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Some suppliers may lack proper QA processes, such as thermal performance testing, dimensional inspection, or material certification. Without verified test data, there’s a risk of field failures under actual operating conditions.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Lack of material test reports (MTRs), RoHS compliance, or batch traceability can hinder quality assurance efforts and complicate root cause analysis in case of failure.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unintentional IP Infringement
Sourcing heat blocks with patented designs—such as proprietary fin structures, internal channel layouts, or mounting configurations—can expose your company to infringement claims, especially if the supplier is reproducing protected designs without authorization.
Lack of Design Ownership Clarity
When custom heat blocks are developed jointly with a supplier, unclear agreements may result in disputes over IP ownership. Without a written contract specifying that your organization retains full rights, the supplier may claim partial or full ownership of the design.
Reverse-Engineered or Copycat Components
Some suppliers, particularly in low-cost regions, may offer heat blocks that mimic branded or patented designs. Using such components—even unknowingly—can lead to legal liability and reputational damage.
Inadequate Protection of Custom Designs
Failing to secure non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or design confidentiality clauses before sharing custom specifications increases the risk of your proprietary designs being shared with competitors or replicated without consent.
Mitigation Strategies
- Vet suppliers thoroughly with audits and sample testing.
- Require detailed material and performance documentation.
- Establish clear IP ownership terms in contracts.
- Use NDAs and restrict distribution of sensitive design data.
- Conduct IP clearance searches for critical components.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures not only reliable thermal performance but also protects your organization from legal and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Heat Blocks
Overview of Heat Blocks
Heat blocks are temperature-controlled devices used in laboratories, medical settings, and industrial processes to maintain precise heating for samples, reagents, or materials. Due to their electrical components and thermal properties, specific logistics and compliance considerations must be followed to ensure safe handling, transportation, and regulatory adherence.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Heat blocks are typically classified as laboratory equipment or electrical devices under international trade and safety standards. Documentation required includes:
– Technical specifications (voltage, wattage, dimensions)
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, UKCA, or other regional markings)
– Safety data sheets (if applicable, e.g., for materials in contact with samples)
– Commercial invoice and packing list detailing quantity, weight, and value
– Export control classification number (ECCN), if subject to trade restrictions
Ensure compliance with IEC 61010-1 (safety requirements for electrical laboratory equipment) and local electrical safety regulations.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit:
– Use anti-static or static-dissipative materials if components are sensitive
– Secure internal components to prevent movement (e.g., foam inserts)
– Seal units in moisture-resistant bags if shipping to humid environments
– Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators
– Include user manuals and power adapters (if shipped together) in sealed compartments
For international shipments, ensure packaging meets ISTA 3A or similar standards for parcel delivery.
Transportation and Shipping
Heat blocks may be shipped via air, ground, or sea freight, subject to the following guidelines:
– Air Transport: Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if lithium batteries are included (rare, but possible in portable models). Most standard heat blocks without batteries are not classified as dangerous goods.
– Ground/Sea Transport: Follow ADR (Europe), 49 CFR (USA), or IMDG Code (maritime) as applicable.
– Voltage compatibility: Confirm regional voltage (110V vs. 220–240V) and include appropriate plug adapters if required.
– Use carriers experienced in handling scientific equipment to ensure climate-controlled or secure handling options when necessary.
Import/Export Compliance
When shipping across borders:
– Verify tariff codes (HS Code: typically 9027.80 or 8543.70 for laboratory heating equipment)
– Comply with import regulations in destination country (e.g., FDA registration for medical use in the U.S., RoHS and REACH in the EU)
– Provide proof of conformity with local electrical safety certifications (e.g., UL, CSA, TÜV)
– Declare dual-use potential if applicable (e.g., for biological or chemical processing)
End-User Certification and Restrictions
Certain destinations or applications may require end-user statements, especially if heat blocks are used in regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, forensics). Verify:
– No embargoed end-users or destinations (check U.S. OFAC, EU Sanctions Lists)
– Compliance with anti-bribery and corruption laws (e.g., FCPA, UK Bribery Act)
– Proper licensing for controlled technologies (if applicable)
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
At end-of-life, heat blocks must be disposed of in accordance with:
– WEEE Directive (EU): Requires recycling of electrical and electronic equipment
– Local e-waste regulations (e.g., EPA guidelines in the U.S.)
– Remove and dispose of any hazardous components (e.g., mercury switches in older models) per hazardous waste protocols
Encourage customers to return units through certified e-waste recyclers.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure smooth logistics and compliance for heat blocks:
– Maintain up-to-date technical and compliance documentation
– Use certified packaging and experienced freight partners
– Verify destination-specific regulations before shipping
– Train staff on export controls and labeling requirements
– Monitor changes in international trade policies affecting scientific equipment
Adhering to this guide minimizes delays, avoids penalties, and ensures safe, compliant delivery of heat blocks worldwide.
Conclusion on Sourcing Heat Blocks
In conclusion, sourcing heat blocks requires a careful evaluation of several key factors including material quality, thermal conductivity, precision manufacturing, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Depending on the application—whether in electronics cooling, industrial machinery, or scientific instrumentation—selecting the appropriate material (such as aluminum, copper, or specialized alloys) and ensuring tight tolerances are critical for optimal thermal performance and system efficiency.
Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers, conducting thorough technical assessments, and considering long-term maintenance and scalability will ultimately lead to a successful sourcing strategy. Additionally, prioritizing sustainability and supply chain resilience can further enhance operational reliability and reduce downtime. By aligning technical requirements with strategic procurement practices, organizations can ensure the consistent availability of high-performance heat blocks that meet both current and future thermal management needs.