The global hawthorn powder market has experienced steady expansion in recent years, driven by rising consumer interest in natural health supplements and plant-based extracts. According to Grand View Research, the global herbal supplements market—under which hawthorn powder falls—was valued at USD 9.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increased awareness of cardiovascular health benefits associated with hawthorn berry extracts, traditionally used to support heart function and circulation. Mordor Intelligence further highlights a rising demand for functional food ingredients in North America and Europe, where regulatory support and consumer preference for clean-label products are accelerating product innovation. Amid this expanding landscape, several manufacturers have emerged as key players, consistently delivering high-quality hawthorn powder with standardized bioactive compounds such as flavonoids and oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs). The following is a data-informed overview of the top nine hawthorn powder manufacturers shaping the industry through production capacity, certification standards, global distribution, and R&D investment.
Top 9 Hawthorn Powder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hawthorn Berry Extract Powder
Domain Est. 2014
Website: medikonda.com
Key Highlights: Medikonda Nutrients is the Largest Manufacturer, Wholesale Supplier, Bulk Distributor, Exporter of USDA organic Hawthorn Berry Extract Powder….
#2 Hawthorn Berry Powder
Domain Est. 2017
#3 Hawthorn Berry Extract Powder
Domain Est. 2021
Website: kintai-bio.com
Key Highlights: As one of the most professional hawthorn berry extract powder manufacturers and suppliers in China, we’re featured by quality products and competitive price ……
#4 Wholesale Organic Hawthorn Powder Manufacturer and Supplier …
Domain Est. 2023
Website: xindaobiotech.com
Key Highlights: Our organic hawthorn powder is carefully processed to retain the maximum nutritional value of the berries, preserving their natural flavor, color, and aroma….
#5 Penn Herb Co. Ltd.
Domain Est. 1996
#6 Frontier Co
Domain Est. 1997
#7 Hawthorn Berry Powder
Domain Est. 2000
Website: lhasakarnak.com
Key Highlights: Hawthorn berry powder is made from finely ground dried berries of Crataegus monogyna, prepared for teas and herbal blends. … Tart, fruity, and slightly sweet….
#8 Wholesale Bulk Hawthorn Berry Powder
Domain Est. 2001
Website: intotherainforest.com
Key Highlights: Out of stockHawthorn Berry Powder at Ecuadorian Rainforest. Wholesale Bulk Hawthorn Berry Powder In Stock And Ready To Ship. Get A Quote And Free Sample Today!…
#9 Organic Hawthorn Berry Powder
Domain Est. 2011
Website: bulksupplements.com
Key Highlights: A vibrant, finely-ground botanical supplement sourced from premium hawthorn berries. Our powder has been meticulously harvested to ensure only the highest ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hawthorn Powder

H2: Analysis of Hawthorn Powder Market Trends in 2026
The global hawthorn powder market is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by rising consumer interest in natural health supplements, preventive healthcare, and plant-based wellness solutions. As a concentrated form of Crataegus species—traditionally used in both Western and Chinese herbal medicine—hawthorn powder is gaining traction across dietary, nutraceutical, and functional food sectors.
- Market Expansion and Demand Drivers
By 2026, the hawthorn powder market is projected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.5–7.8%, with North America and Asia-Pacific leading in market share. Key demand drivers include: - Increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and consumer preference for natural remedies to support heart health.
- Growing integration of herbal extracts into functional foods and beverages, such as energy bars, smoothie mixes, and herbal teas.
-
Rising awareness of hawthorn’s antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and vasodilatory properties among health-conscious consumers.
-
Product Innovation and Formulation Trends
Manufacturers are focusing on product differentiation through: - Organic and non-GMO certifications to appeal to clean-label consumers.
- Synergistic blends combining hawthorn powder with other heart-supportive ingredients like CoQ10, magnesium, and garlic extract.
-
Water-soluble and micronized powder forms to enhance bioavailability and ease of incorporation into ready-to-drink formulations.
-
Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific: China and India remain dominant producers and consumers, with strong integration of hawthorn in traditional medicine systems (e.g., Traditional Chinese Medicine). Local demand is further bolstered by aging populations and government support for herbal industries.
- North America and Europe: Regulatory clarity from agencies like the EFSA and FDA on health claims related to cardiovascular support is expected to boost market legitimacy and consumer trust.
-
Latin America and Middle East: Emerging markets show increasing interest due to rising disposable income and digital health education.
-
Supply Chain and Sustainability Considerations
By 2026, sustainability and traceability are becoming critical competitive advantages. Leading suppliers are investing in: - Vertical integration of hawthorn farming and processing to ensure quality control.
- Eco-friendly drying and milling technologies (e.g., freeze-drying, low-temperature processing) to preserve active compounds like flavonoids and oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs).
-
Certification from bodies like USDA Organic, FairWild, and ISO to meet export standards.
-
Regulatory and Safety Outlook
Regulatory scrutiny is increasing, particularly regarding standardized extract concentrations and accurate labeling of active constituents. In the EU, compliance with the Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products Directive (THMPD) will influence market access. Meanwhile, the U.S. FDA is expected to enhance oversight on adulteration and heavy metal contamination, pushing producers toward rigorous third-party testing. -
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges include fluctuating raw material supply due to climate variability and competition from synthetic alternatives. However, opportunities lie in: - Digital marketing and e-commerce expansion, especially through direct-to-consumer platforms.
- Clinical research investments to validate health claims and support premium pricing.
- Expansion into pet health supplements, where hawthorn is increasingly used for canine cardiac support.
Conclusion
By 2026, the hawthorn powder market will be shaped by scientific validation, consumer demand for holistic wellness, and innovation in delivery formats. Companies that prioritize quality, transparency, and clinical backing will be best positioned to capture value in this evolving landscape.
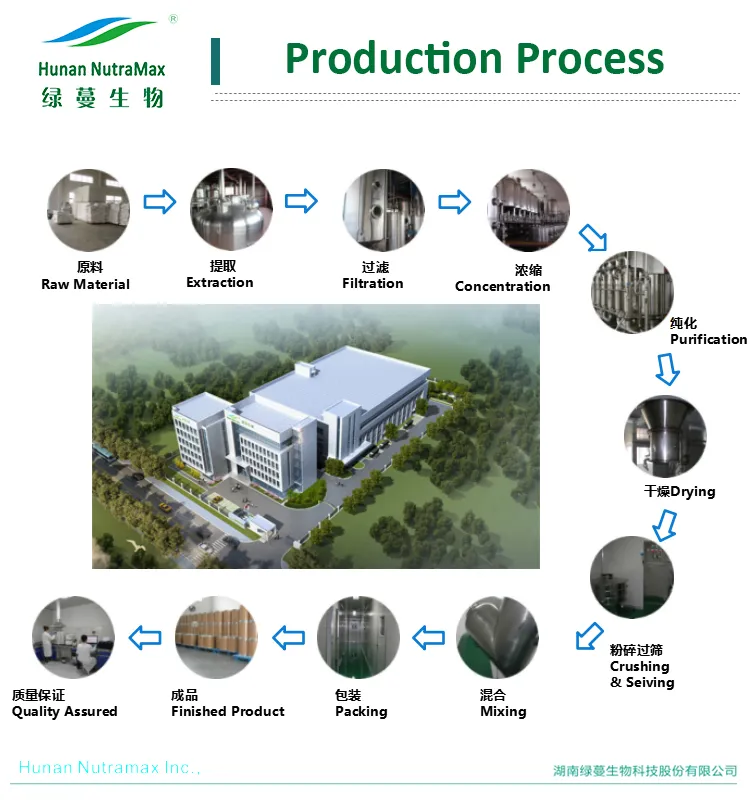
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Hawthorn Powder (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing hawthorn powder for use in dietary supplements, herbal formulations, or functional foods presents several challenges related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Being aware of these pitfalls can help ensure product safety, efficacy, and legal compliance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Botanical Identification
One of the most critical quality issues is misidentification of the plant species. Hawthorn refers primarily to Crataegus monogyna or Crataegus laevigata, but suppliers may provide powders from unrelated or less effective species. Without proper authentication—such as DNA barcoding or chromatographic fingerprinting—there’s a risk of adulteration or substitution.
Variable Active Compound Levels
The therapeutic value of hawthorn powder lies in its flavonoids (e.g., vitexin, rutin) and oligomeric procyanidins (OPCs). However, concentrations can vary widely based on plant part used (flower, leaf, berry), growing conditions, harvest time, and processing methods. Sourcing without standardized potency specifications may result in inconsistent product performance.
Contamination Risks
Poor agricultural or manufacturing practices can lead to contamination with heavy metals, pesticides, microbial pathogens (e.g., Salmonella, E. coli), or mycotoxins. Suppliers from regions with lax regulatory oversight may not conduct adequate testing, increasing safety risks.
Improper Processing and Storage
Excessive heat or prolonged exposure to light and moisture during drying, milling, or storage can degrade bioactive compounds. Hawthorn powder that is improperly processed may lose potency before it even reaches the end user.
Lack of Third-Party Testing and Certifications
Relying solely on supplier-provided certificates of analysis (CoAs) without independent verification is risky. Reputable sourcing requires third-party testing for identity, purity, potency, and safety, along with certifications such as GMP, organic, or ISO.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Extracts or Formulations
Some hawthorn extracts (e.g., standardized to specific OPC levels or combined with other ingredients) are protected by patents. Sourcing a powder that mimics a patented formulation—even unintentionally—can lead to legal disputes. It’s essential to conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses before commercializing products.
Misuse of Brand Names or Trademarks
Using branded names like “LI 132” (a well-known hawthorn extract) without authorization infringes on trademark rights. Suppliers may market generic powders using suggestive naming, leading buyers into unintentional IP violations.
Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain
Some suppliers may source material from manufacturers that use proprietary processes or licensed technologies. Without clear disclosure, buyers risk indirect infringement or supply chain disruptions due to IP litigation involving upstream partners.
Inadequate Documentation for Regulatory and IP Defense
In the event of a quality or IP dispute, having comprehensive documentation—such as botanical authentication reports, chain of custody records, and supplier agreements—is critical. Omitting these can weaken legal standing and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, companies should vet suppliers rigorously, require transparent documentation, invest in independent quality testing, and conduct thorough IP due diligence. Establishing strong supplier agreements and staying informed about relevant patents and trademarks are essential steps in responsible hawthorn powder sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hawthorn Powder
Overview of Hawthorn Powder
Hawthorn powder, derived from the dried berries, leaves, or flowers of the Crataegus species, is commonly used in dietary supplements and herbal products due to its potential cardiovascular benefits. As a botanical ingredient, it is subject to specific regulatory and logistical requirements across international markets. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling of hawthorn powder during transportation, storage, and distribution.
Regulatory Classification and Compliance
Hawthorn powder is typically classified as a dietary supplement ingredient in jurisdictions such as the United States (regulated by the FDA under DSHEA) and as a herbal medicinal product or food supplement in the European Union (regulated by EFSA and EMA). Suppliers and importers must ensure compliance with local regulations, including:
– Verification of ingredient safety and permissible use levels
– Adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for botanicals
– Compliance with labeling requirements (e.g., ingredient list, allergen statements)
– Registration with relevant authorities where required (e.g., FDA facility registration, EU Responsible Person designation)
Products intended for sale must not make unapproved health claims, and all documentation should support the product’s status as a supplement or food ingredient.
Sourcing and Quality Assurance
Ensure hawthorn powder is sourced from reputable suppliers who provide:
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA) confirming identity, potency, microbial load, heavy metals, and pesticide residues
– Proof of Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GACP) compliance
– Non-GMO and organic certifications (if applicable)
– Full traceability from raw material to finished product
Regular third-party testing is recommended to verify consistency and safety.
Packaging Requirements
Hawthorn powder should be packaged to prevent contamination, moisture absorption, and degradation:
– Use food-grade, airtight containers (e.g., HDPE bags with moisture barriers or foil-lined pouches)
– Include desiccants if necessary to control humidity
– Label packages with batch number, production date, expiration date, storage instructions, and handling warnings
– Ensure outer shipping containers are sturdy and protect against physical damage
Packaging must comply with international shipping standards and any specific requirements of the destination country.
Storage Conditions
Store hawthorn powder in a cool, dry, and dark environment to maintain stability:
– Ideal temperature range: 15–25°C (59–77°F)
– Relative humidity: below 60%
– Protect from direct sunlight and strong odors
– Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management to prevent expiration
Regular inspections should be conducted for signs of clumping, discoloration, or contamination.
Transportation and Shipping
When shipping hawthorn powder:
– Use temperature-controlled transport if exposed to extreme climates
– Prevent cross-contamination by segregating from hazardous or strongly scented materials
– Comply with IATA, IMDG, or other relevant transport regulations (note: hawthorn powder is generally non-hazardous but may require phytosanitary documentation)
– Maintain a cold chain only if specified by stability studies
For international shipments, ensure all export and import documentation is complete, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Import/Export Documentation and Restrictions
Key documentation for cross-border movement includes:
– Phytosanitary certificate (required by many countries to certify plant material is pest-free)
– Certificate of Free Sale (if required by the importing country)
– FDA Prior Notice (for U.S. imports)
– EU Health Certificate (for certain herbal imports)
Check destination-specific restrictions—some countries regulate hawthorn due to its pharmacological activity (e.g., Saudi Arabia, Australia require pre-approval).
Labeling and Traceability
Final product labels must comply with destination market laws and include:
– Product name
– List of ingredients (scientific name Crataegus spp.)
– Net weight
– Manufacturer/distributor information
– Batch number and expiry date
– Storage instructions
– Any required disclaimers (e.g., “These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA…”)
Maintain full traceability through batch records and supply chain documentation for recall readiness.
Handling and Worker Safety
While hawthorn powder is generally safe, standard precautions include:
– Use of PPE (gloves, masks) during handling to prevent inhalation or skin contact
– Adequate ventilation in processing and packing areas
– Training staff on allergen control and hygiene practices
Ensure Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are available, even for non-hazardous botanicals, per GHS guidelines.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Dispose of expired or contaminated hawthorn powder in accordance with local waste regulations. As an organic botanical material, it may be compostable, but verify compliance with municipal or industrial waste policies. Minimize packaging waste through recyclable materials.
Audits and Recordkeeping
Maintain records for a minimum of 3–5 years, including:
– Supplier qualifications and CoAs
– Batch production and testing records
– Shipping and import documentation
– GMP or ISO audit reports
Regular internal audits help ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory and quality standards.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for hawthorn powder require attention to regulatory details, quality control, proper storage, and accurate documentation. By adhering to this guide, businesses can ensure the safe and lawful distribution of hawthorn powder while minimizing risk and maximizing product integrity. Always consult local regulatory authorities or legal experts when entering new markets.
In conclusion, sourcing high-quality hawthorn powder requires careful consideration of several key factors, including botanical authenticity, processing methods, supplier reliability, and compliance with safety and regulatory standards. Opting for organic, non-GMO, and third-party tested products ensures purity, potency, and consumer safety. Establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers, preferably those with transparent sourcing and sustainable practices, contributes to consistent product quality and long-term supply chain stability. Whether for use in dietary supplements, functional foods, or herbal remedies, investing time in due diligence during the sourcing process ultimately supports product efficacy, brand reputation, and consumer trust.