The global laser cleaning equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precise, and efficient surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the laser cleaning market was valued at USD 810.2 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1.56 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 11.4% during the forecast period. This surge is largely attributed to the rising adoption of handheld laser systems for rust removal, which offer non-abrasive, chemical-free alternatives to traditional cleaning methods. As industries prioritize sustainability and operational efficiency, handheld laser rust removal technology has emerged as a key innovation, prompting significant investment and competition among manufacturers. In this evolving landscape, nine companies have distinguished themselves through technological advancement, product reliability, and widespread industry application—setting the benchmark in performance and market reach.
Top 9 Handheld Laser That Removes Rust Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturer
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: Our laser technology efficiently removes rust, paint, oil, and more. Compact and Portable Design. The laser cleaning machines adopt compact and portable designs ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: LPC-100 Laserpack is a laser cleaning backpack. P-laser teambuilding. QF-2000 Laser removes almost any other kind of contamination, including grease, rust….
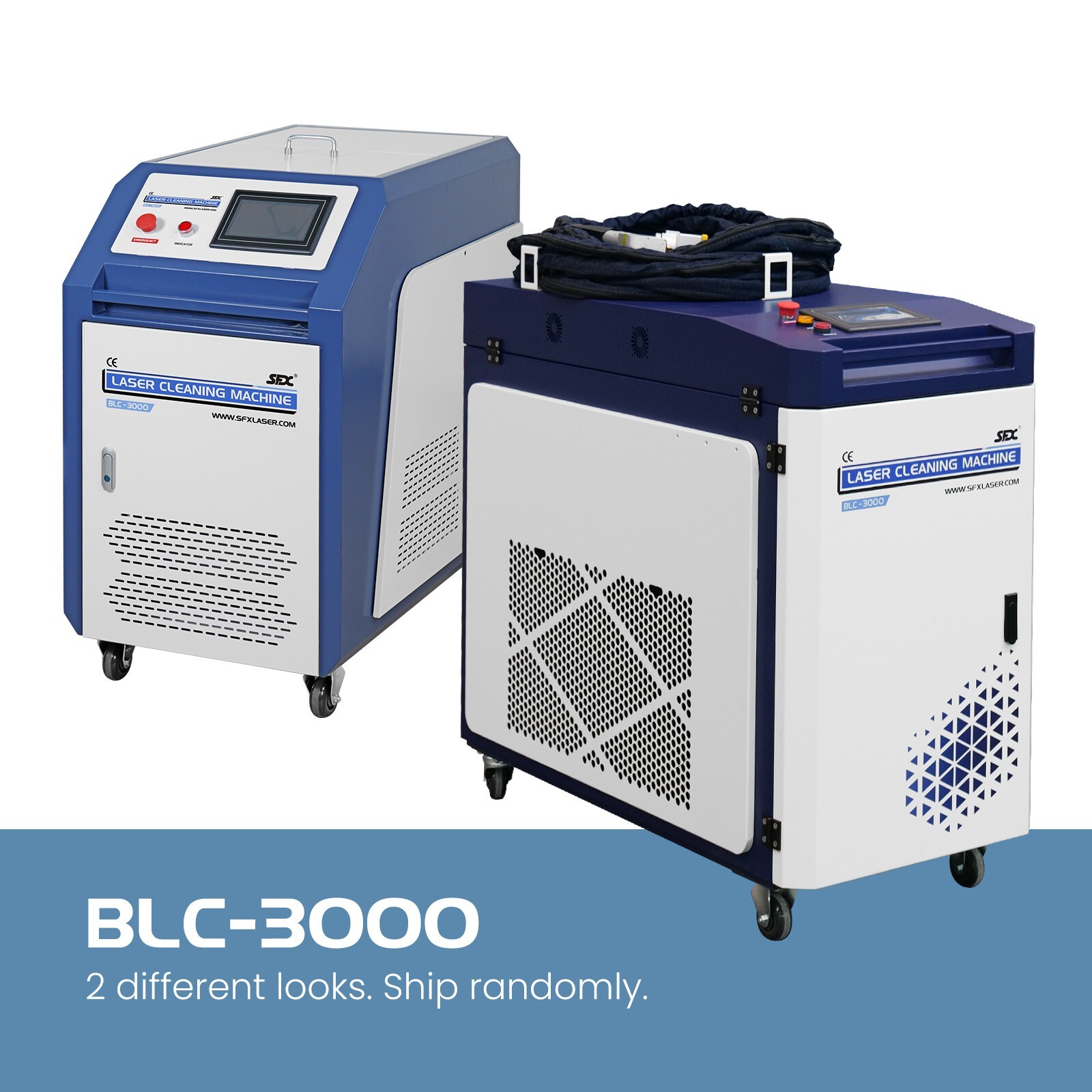
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#4 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#5 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: The SHARK P CL series is suitable for removing rust, paint, soot, carbon, mold, mildew, grease, weld residues, varnish, graffiti and other surface contaminants….
#6 Laser Machine – Laser Equipment Manufacturer
Website: dplaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning machine often use to remove contaminants, such as rust, paint, oil, and coatings from the surface of a material. Laser cleaning is a non-contact, ……
#7 Handheld Laser Cleaning Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Utilize this laser cleaning machine for rust removal and coating removal, decontamination, degreasing, pre- and post-weld surface preparation, and texturing….
#8 Laser Rust Removal
Website: powerlase-limited.com
Key Highlights: Watch this super fast rust removal from carbon steel panel with the new ultra-lightweight Vulcan handheld from Powerlase. The nature of laser cleaning ……
#9 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: sltl.com
Key Highlights: This futuristic laser cleaning solution can capably remove rust, oil, paint, grease, colour and other particles from the surface of the metals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Handheld Laser That Removes Rust

2026 Market Trends for Handheld Laser Rust Removal Devices
Rising Demand Across Industrial Sectors
The global market for handheld laser rust removal devices is projected to experience significant growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across key industrial sectors including automotive, marine, aerospace, and infrastructure maintenance. As industries shift toward eco-friendly and precision-based maintenance solutions, traditional rust removal methods such as sandblasting and chemical treatments are being phased out due to environmental and safety concerns. Handheld laser systems offer a non-abrasive, chemical-free alternative, making them ideal for sensitive components and environmentally regulated environments. This transition is expected to accelerate adoption rates, particularly in developed markets such as North America, Western Europe, and parts of East Asia.
Advancements in Laser Technology and Portability
By 2026, technological advancements will have significantly enhanced the performance, efficiency, and portability of handheld laser rust removal tools. Manufacturers are investing in more compact, lightweight designs powered by high-efficiency fiber lasers, enabling longer operation times and improved ergonomics for field technicians. Innovations such as smart targeting systems, real-time monitoring, and AI-assisted rust detection are being integrated into next-generation devices, increasing precision and reducing operator fatigue. These improvements are broadening the user base beyond specialized contractors to include maintenance teams in manufacturing and public infrastructure sectors.
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Environmental regulations are playing a pivotal role in shaping the 2026 market landscape. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are enforcing stricter controls on emissions, waste disposal, and worker safety, particularly concerning hazardous substances used in traditional rust removal. Laser-based cleaning methods generate no secondary waste or airborne pollutants, aligning with sustainability goals and compliance requirements. In regions like the European Union and North America, incentives for green technologies and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) commitments are further boosting investment in laser cleaning equipment.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
While mature markets lead in adoption, emerging economies in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and parts of Africa are expected to see rapid growth in demand by 2026. This expansion is fueled by infrastructure development, aging industrial assets, and increasing awareness of advanced maintenance technologies. Local and regional manufacturers are beginning to produce cost-competitive handheld laser systems, reducing entry barriers for small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, training programs and government-backed industrial modernization initiatives are supporting wider deployment across diverse applications.
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The handheld laser rust removal market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established laser technology firms and new entrants vying for market share. By 2026, market consolidation is anticipated through strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions as companies aim to expand their product portfolios and geographic reach. Key players are focusing on after-sales services, training, and rental models to lower upfront costs and increase accessibility. Price competition is expected to intensify, particularly in mid-range performance segments, driving innovation and affordability.
Challenges and Adoption Barriers
Despite positive momentum, several challenges remain. High initial equipment costs, limited battery life, and the need for operator training continue to hinder widespread adoption, particularly among smaller operators. Safety concerns related to laser exposure require strict compliance with protective protocols, which can slow deployment in unregulated environments. However, ongoing advancements in safety features, automation, and leasing/financing options are expected to mitigate these barriers by 2026.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for handheld laser rust removal devices is poised for robust growth, supported by technological innovation, environmental regulations, and expanding industrial applications. As the technology becomes more accessible and user-friendly, it is set to redefine surface preparation and maintenance practices across multiple industries, establishing laser cleaning as a standard in sustainable industrial maintenance.

H2. Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Handheld Laser Rust Removal Equipment (Quality and Intellectual Property)
-
Overlooking Build Quality and Durability
Many suppliers offer handheld laser rust removal devices at competitive prices, but often compromise on build quality. Low-quality materials, poor thermal management, and inadequate sealing can lead to premature failure, especially in industrial environments. Buyers should verify the device’s construction standards, including IP ratings for dust and moisture resistance, and ensure components like cooling systems and laser sources are from reputable manufacturers. -
Inadequate or Misrepresented IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
Some suppliers may claim high IP ratings (e.g., IP54 or IP65) without third-party certification. Without proper protection, dust and moisture can damage sensitive laser optics and electronics. Always request test reports or certification documents to confirm the stated IP rating, and consider real-world testing under operating conditions. -
Substandard or Counterfeit Laser Components
A major risk is sourcing devices that use low-quality or counterfeit laser modules (e.g., fiber lasers). These may underperform, fail prematurely, or pose safety hazards. Verify the origin and specifications of the laser source—preferably from known brands like IPG, Raycus, or nLight—and request component datasheets. -
Lack of Intellectual Property Compliance
Some manufacturers, especially in regions with lax IP enforcement, may produce devices that infringe on patented technologies (e.g., beam delivery systems, control software, or safety features). Sourcing such products can expose buyers to legal risks, especially in markets like the EU or U.S. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio and ensure they can provide proof of legitimate design rights or licensing agreements. -
Insufficient Safety Features and Certifications
Handheld laser devices must comply with international laser safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825). Some low-cost models lack essential safety interlocks, proper labeling, or emission controls. Avoid devices without CE, FDA, or other relevant certifications, as they may not meet regulatory requirements in your target market. -
Inconsistent Performance Claims
Suppliers may exaggerate cleaning speed, rust removal depth, or energy efficiency. Without standardized testing protocols, these claims can be misleading. Request real-world demo videos, third-party performance reports, or trial units to validate advertised capabilities. -
Poor After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality devices require maintenance and occasional repairs. Sourcing from suppliers without reliable technical support, training, or spare parts access can lead to extended downtime. Confirm service network coverage and warranty terms before purchase. -
Hidden Costs from Non-Compliant Designs
Devices that don’t meet regional regulatory standards may require costly modifications or fail customs inspections. Ensure the product complies with electrical, laser safety, and environmental regulations (e.g., RoHS, REACH) in your country to avoid delays and additional expenses.
By addressing these pitfalls early, buyers can mitigate risks and select a reliable, compliant, and high-performance handheld laser rust removal solution.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Handheld Laser Rust Removal Devices
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Handheld laser rust removal devices are classified as industrial laser systems and are subject to strict international and regional regulations due to their use of high-powered lasers. These devices typically fall under Class 4 laser products, meaning they pose significant risks of eye and skin injury, fire, and fumes. Understanding the product classification is essential for compliance across supply chains, customs clearance, and end-user safety.
International Standards and Certifications
Compliance with international standards is mandatory for global distribution. Key certifications include:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
– IEC 62471: Photobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems.
– CE Marking (EU): Required for sale in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– FDA/CDRH (USA): Compliance with 21 CFR Part 1040.10 and 1040.11 for laser products; registration with the Center for Devices and Radiological Health is required.
– RoHS and REACH (EU): Restrictions on hazardous substances and chemical safety.
– FCC Part 18 (USA): Electromagnetic compatibility and radio frequency interference.
Manufacturers must obtain and maintain documentation proving compliance with these standards before shipping.
Import and Export Regulations
Shipping handheld laser devices across borders requires adherence to export control and customs regulations:
– Export Controls: Devices may be subject to national export control regimes such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or the EU Dual-Use Regulation. Lasers above certain power thresholds may require export licenses.
– Harmonized System (HS) Code: Typical HS codes for handheld laser rust removers include 8515.21 (laser soldering, welding, cutting machines) or 8543.70 (other electrical machines with specific functions). Accurate classification ensures correct duty assessment and customs compliance.
– End-Use Documentation: Importers may be required to provide end-user statements confirming the device will be used for industrial purposes only.
Consult national customs authorities and freight forwarders to ensure proper documentation and licensing.
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Due to the sensitive and hazardous nature of laser equipment, proper packaging is critical:
– Shock-Resistant Packaging: Use custom foam inserts and rigid outer containers to prevent damage during transit.
– Laser Safety Labels: Clearly display Class 4 laser warning labels, including the laser radiation symbol and safety instructions.
– Moisture and Dust Protection: Include desiccants and sealed packaging to protect optical components.
– Battery Shipping (if applicable): If the device includes lithium-ion batteries, comply with IATA/ICAO regulations for air transport (e.g., UN38.3 testing, state-of-charge limits, and proper packaging).
Use carriers experienced in handling industrial laser equipment and hazardous materials.
Safety and Handling Instructions
End-users must be trained in safe operation and compliance:
– Provide multilingual user manuals with safety warnings, operating procedures, maintenance guidelines, and emergency protocols.
– Include required personal protective equipment (PPE) such as laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) ratings.
– Mandate installation of fume extraction systems to manage hazardous particulates generated during rust removal.
– Recommend restricted access zones and interlocks where applicable to prevent unauthorized use.
Ensure training materials comply with OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent workplace safety regulations.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Laser rust removal generates metal particulates and potential airborne contaminants:
– Advise users to comply with local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S., EEA in Europe) for handling and disposal of waste materials.
– Devices may contain electronic components subject to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU.
– Recommend recycling programs for end-of-life units and batteries.
Include disposal guidance in product documentation.
Post-Sale Compliance and Recordkeeping
Maintain compliance throughout the product lifecycle:
– Keep records of certifications, import/export licenses, and customer declarations for at least five years.
– Report adverse events or malfunctions to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EU RAPEX).
– Provide software/firmware updates that maintain compliance with evolving standards.
Regular audits of compliance documentation are recommended for distributors and importers.
By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure safe, legal, and efficient logistics and compliance management for handheld laser rust removal devices globally.
In conclusion, sourcing a handheld laser for rust removal requires careful consideration of several key factors, including laser power, wavelength, portability, safety features, and overall cost-effectiveness. While laser rust removal offers significant advantages—such as precision, minimal substrate damage, environmental friendliness, and reduced maintenance downtime—it represents a higher initial investment compared to traditional methods like sandblasting or chemical treatments.
When evaluating suppliers, prioritize manufacturers with proven experience, reliable technical support, and compliance with international safety standards (e.g., CE, FDA). It is also important to verify compatibility with your specific materials and rust conditions through product demonstrations or pilot testing.
Ultimately, a well-sourced handheld laser rust removal system can deliver long-term efficiency, improved worker safety, and sustainable maintenance operations—making it a valuable addition to industrial, automotive, marine, and heritage restoration applications. Proper training and ongoing maintenance will further ensure optimal performance and return on investment.