The global laser paint removal market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision surface treatment in aerospace, automotive, and industrial maintenance applications. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cleaning market—encompassing paint removal—was valued at USD 1.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.2% from 2023 to 2030. Factors such as the shift toward eco-friendly, non-abrasive cleaning methods and stringent environmental regulations are accelerating adoption. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, forecasting a CAGR of over 17% for the laser cleaning equipment market through 2028. With handheld systems emerging as a preferred solution for portability and ease of use, a new wave of manufacturers is innovating to meet rising demand. Below, we profile the top nine manufacturers leading advancements in handheld laser paint removal technology.
Top 9 Handheld Laser Paint Removal Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#3 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#4 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL is an industrial pulsed laser cleaning machine series by PULSAR Laser with outputs from 100 W to 1000 W, air-cooled up to 500 W….
#5 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: In stockXING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#6 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our Laser Ablation is the most cost-effective, efficient, and safest method of industrial cleaning, rust removal, paint removal, and surface preparation….
#7 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#8 Handheld Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Handheld and portable laser cleaning machines designed for manual applications including rust removal, paint stripping, restoration, and more….
#9 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Handheld Laser Paint Removal
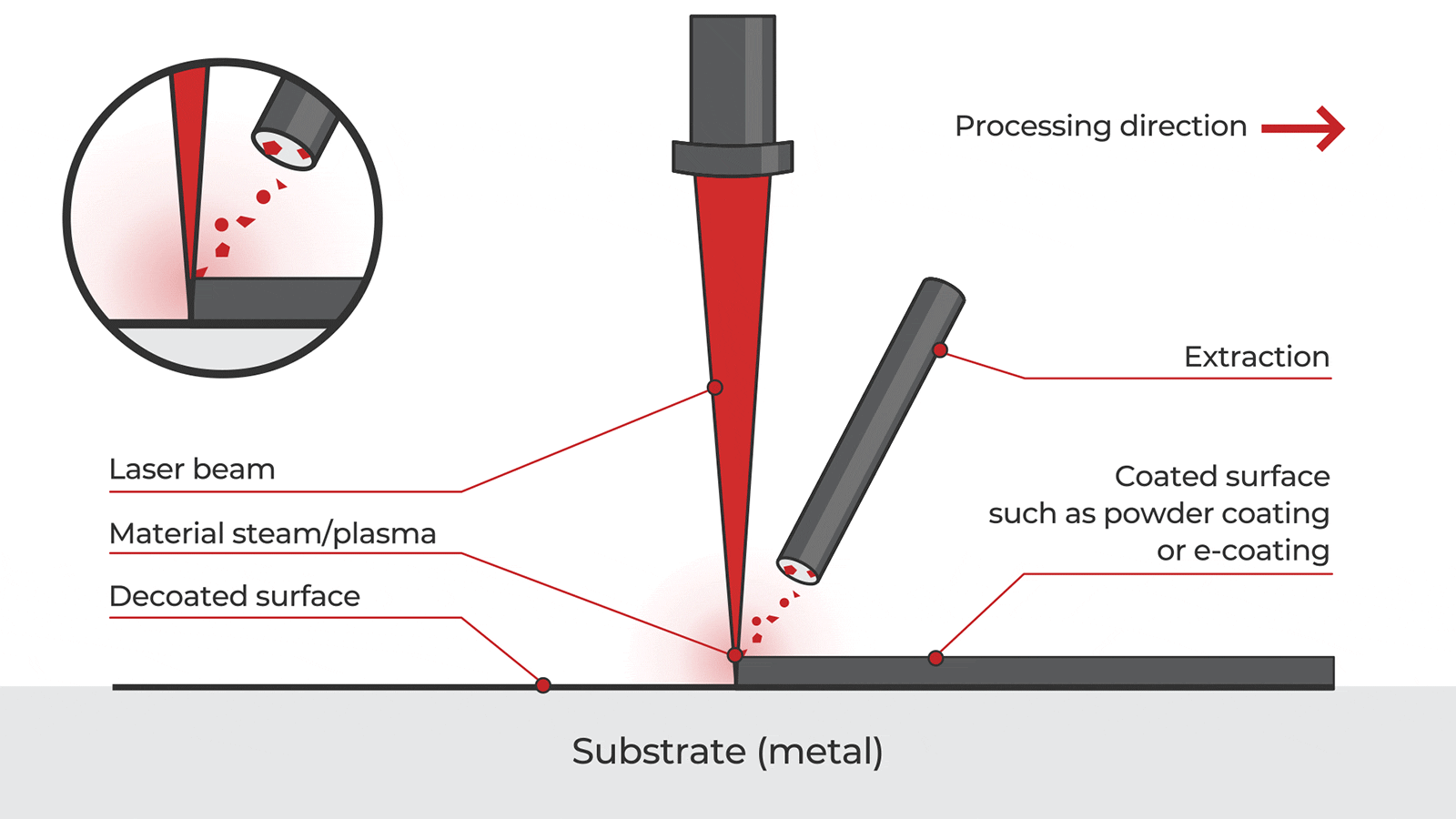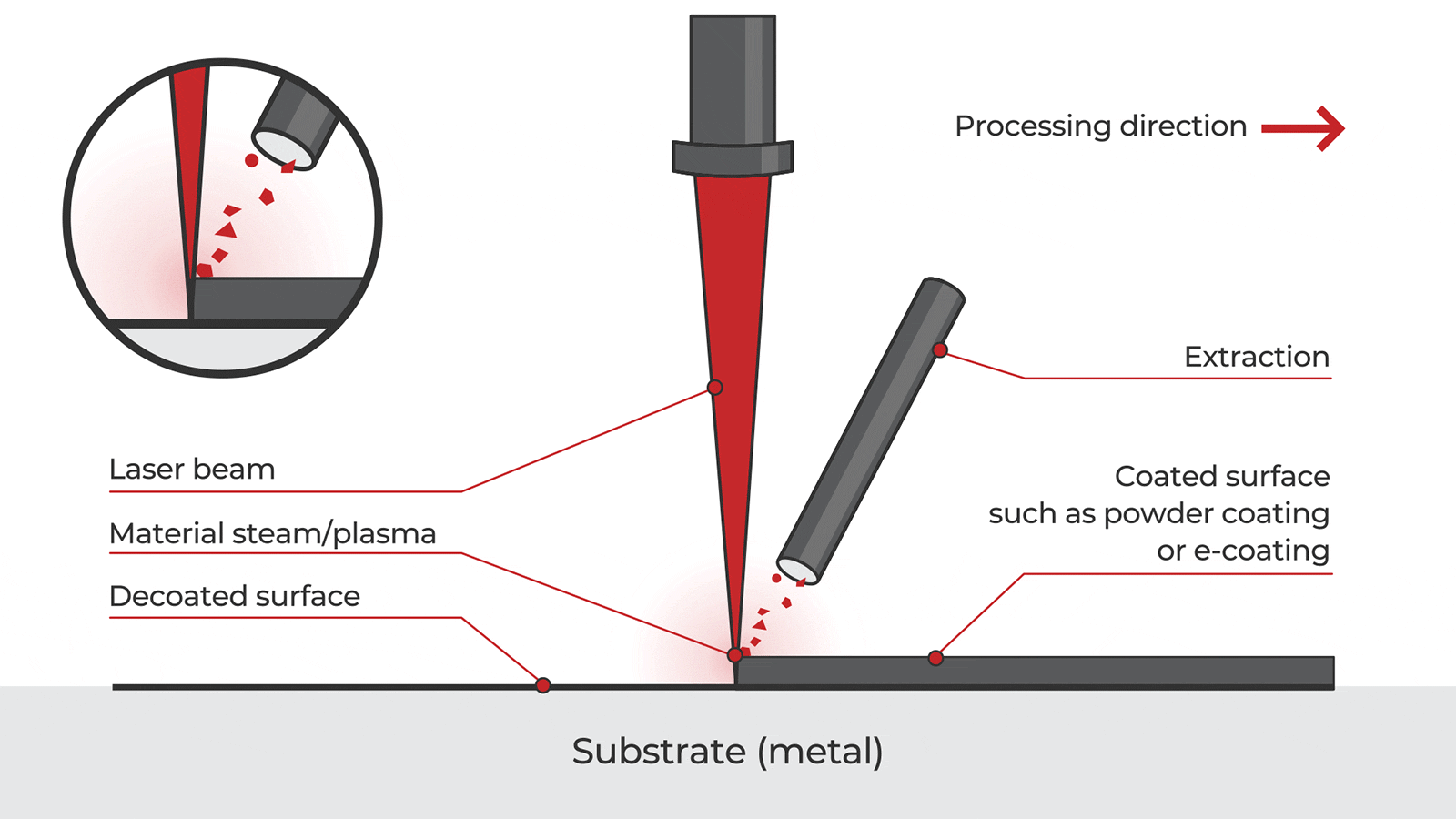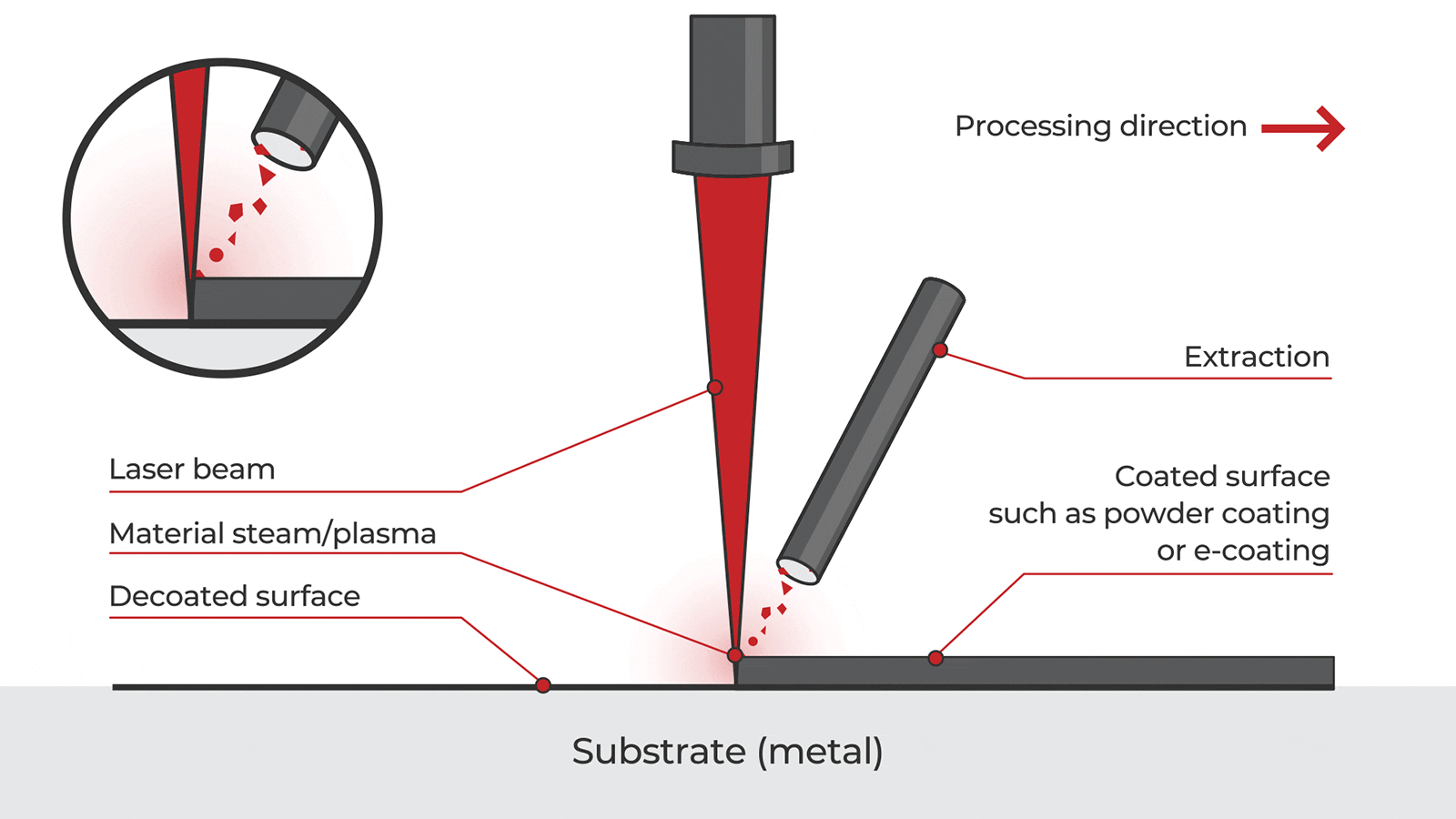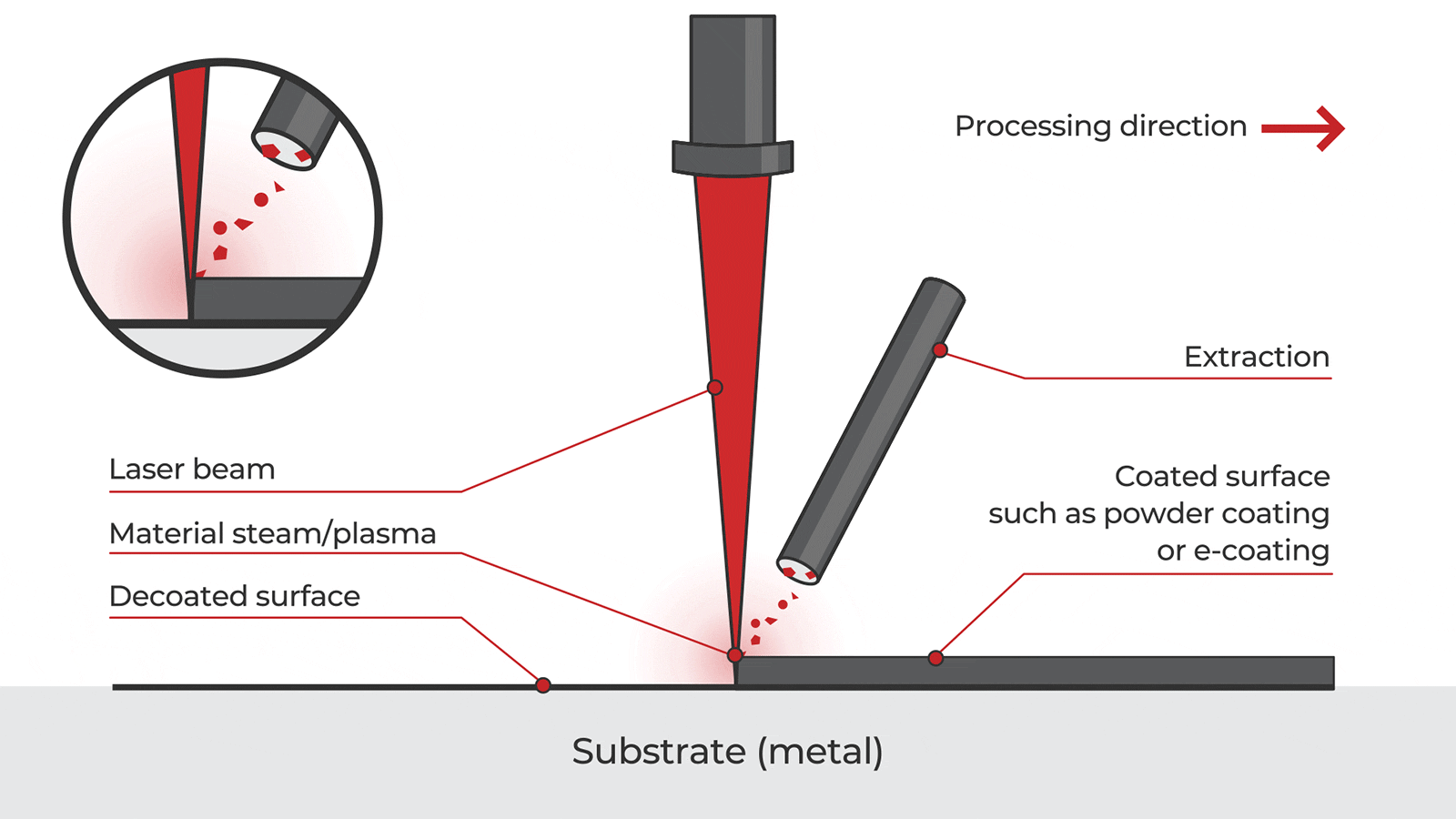
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Handheld Laser Paint Removal
The handheld laser paint removal market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing environmental awareness, and expanding industrial applications. Key trends shaping this dynamic sector include:
1. Accelerated Technological Advancements & Miniaturization:
Expect continued innovation in laser source efficiency (particularly fiber lasers), leading to smaller, lighter, and more ergonomic handheld units. Enhanced beam delivery systems and improved real-time monitoring (e.g., integrated sensors for surface temperature and ablation depth) will boost precision and automation, reducing operator skill requirements and minimizing substrate damage. Battery technology improvements will enable longer cordless operation, increasing mobility and safety on job sites.
2. Dominant Growth in Industrial & Maritime Sectors:
The aerospace, automotive (especially EV manufacturing and repair), and maritime industries will remain primary growth engines. Stringent regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous waste (like lead paint) are driving a shift away from sandblasting and chemical strippers. Handheld lasers offer a precise, non-abrasive, and environmentally compliant solution for maintaining and refurbishing high-value assets like aircraft fuselages, ship hulls, and composite parts.
3. Heightened Focus on Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance:
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) regulations will be a major market driver. Laser removal generates minimal secondary waste (only ablated paint particles captured by integrated filtration) and eliminates the need for toxic chemicals, aligning with global sustainability goals (ESG). Stricter enforcement of regulations like REACH, RoHS, and OSHA standards in North America and Europe will further incentivize adoption.
4. Expansion into New Application Verticals:
Beyond core industrial uses, the market will see growth in heritage restoration (delicate removal of paint from historic buildings and artifacts without damaging underlying materials) and infrastructure maintenance (bridges, pipelines, power plants). Increased affordability and ease of use will also make the technology more accessible to mid-sized contractors and specialized service providers.
5. Intensifying Competition and Market Consolidation:
As the market matures, competition will intensify between established industrial laser players and specialized startups. This will drive innovation, improve cost-effectiveness, and lead to potential consolidation. Key differentiators will include system reliability, ease of integration with robotics/automation, comprehensive safety features (especially Class 1 enclosures), and robust after-sales support and training.
6. Cost Reduction and Improved ROI:
While initial investment remains higher than traditional methods, total cost of ownership (TCO) is improving. Falling component costs, reduced consumables (no media or chemicals), lower waste disposal fees, and faster processing times contribute to a compelling ROI, particularly for high-value or regulated applications. This improved economics will broaden market adoption.
In conclusion, the 2026 handheld laser paint removal market will be characterized by smarter, smaller, and more efficient tools. Driven by environmental imperatives, technological progress, and expanding industrial needs, the sector is set for robust growth, moving beyond niche applications towards becoming a mainstream surface preparation technology across multiple high-value industries.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Handheld Laser Paint Removal Systems: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing handheld laser paint removal systems offers significant advantages for precision surface preparation, but it also presents specific challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial losses.
Quality Concerns in Sourcing
One of the primary pitfalls when sourcing handheld laser paint removal tools is inadequate attention to quality. Buyers may be tempted by lower prices or aggressive marketing claims without verifying the actual performance and durability of the equipment.
- Inconsistent Performance: Low-quality systems often fail to deliver consistent power output and beam focus, resulting in uneven paint removal, incomplete stripping, or damage to the underlying substrate (e.g., metal pitting). This inconsistency necessitates rework and increases labor costs.
- Poor Build Quality and Reliability: Substandard materials and manufacturing processes can lead to frequent breakdowns, shortened component lifespan (especially optics and cooling systems), and unplanned downtime. Handheld units must withstand demanding industrial environments—cheap alternatives often lack the necessary robustness.
- Inadequate Safety Features: Reputable systems incorporate multiple safety mechanisms such as key switches, emission indicators, and interlocks. Sourcing from unverified suppliers may result in systems with insufficient or non-compliant safety features, exposing operators to laser radiation and increasing liability risks.
- Lack of Certification and Standards Compliance: Genuine quality systems are typically certified to relevant international standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety). Sourced units from questionable origins may lack proper certification, making them non-compliant with workplace safety regulations and uninsurable in some jurisdictions.
Intellectual Property and Legal Risks
Another critical pitfall involves intellectual property (IP) infringement, which can arise when sourcing from manufacturers who replicate patented technologies or use proprietary designs without authorization.
- Patent Infringement: Leading laser paint removal technologies often involve patented beam delivery systems, cooling mechanisms, or control software. Sourcing from suppliers who copy these innovations exposes the buyer to potential legal action, seizure of equipment at customs, or mandatory recall—even if the buyer was unaware of the infringement.
- Counterfeit or “Clone” Equipment: Some suppliers market systems that are near-identical copies of established brands but lack licensing. These clones may use inferior components, offer no technical support, and void any IP-related warranties. Purchasing such equipment supports unethical practices and risks reputational damage.
- Unclear IP Ownership and Support: When IP rights are ambiguous, buyers may find themselves without access to software updates, spare parts, or technical support. This lack of post-purchase support can render the system obsolete or unusable over time.
- Exposure to Legal Liability: Companies found using equipment that infringes on third-party IP may face litigation, fines, and injunctions. This risk is particularly high in regulated industries such as aerospace or automotive, where compliance with technology sourcing laws is strictly enforced.
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence—verifying supplier credentials, requesting proof of certifications, reviewing patent documentation, and sourcing from reputable manufacturers with transparent IP practices. Investing in quality and legally compliant systems ultimately ensures safer operations, better performance, and long-term cost savings.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Handheld Laser Paint Removal Equipment
Overview of Handheld Laser Paint Removal Technology
Handheld laser paint removal systems use focused laser energy to ablate paint, coatings, and surface contaminants from substrates such as metal, concrete, and composites without damaging the underlying material. These portable systems offer advantages over traditional methods (e.g., sandblasting, chemical stripping), including reduced waste, improved safety, and precision control. However, their deployment involves complex logistics and regulatory compliance due to laser safety, hazardous materials, and transportation regulations.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser Safety Standards (IEC 60825 & FDA/CDRH)
Handheld laser systems must comply with international and national laser safety standards:
– IEC 60825-1: International standard for laser product safety, classifying lasers by hazard level (typically Class 4 for paint removal).
– FDA/CDRH (U.S.): Requires manufacturers to file a product report and comply with performance standards under 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11.
– Compliance includes proper labeling, safety interlocks, key-controlled operation, and user training. Operators must wear appropriate laser protective eyewear rated for the laser’s wavelength and power.
Workplace Safety and OSHA Regulations
- Hazard Communication (HazCom): Operators must be trained on chemical hazards from vaporized paint (e.g., lead, chromium, VOCs).
- Respiratory Protection: Use of NIOSH-approved respirators when working with hazardous coatings.
- Controlled Access Zones: Establish laser-controlled areas with warning signs and barriers to prevent accidental exposure.
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction: Local exhaust ventilation or integrated fume extraction systems are required to capture airborne particulates and fumes.
Environmental Regulations (EPA, REACH, RoHS)
- Toxic Materials Handling: Paint removal may release regulated substances (e.g., lead-based paint). Comply with EPA’s Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) Rule if lead is present.
- Waste Disposal: Collected debris and filter waste may be classified as hazardous. Follow RCRA guidelines for testing, labeling, storage, and disposal.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure equipment materials and coatings comply with substance restrictions.
Transportation and Logistics
Domestic and International Shipping
- Battery Safety (if applicable): If the device includes lithium-ion batteries, comply with UN 38.3 testing and IATA/IMDG/ICAO regulations for air, sea, or ground transport.
- Hazard Classification: Classify equipment under proper shipping names and hazard classes. Most handheld laser systems are non-hazardous unless containing batteries or hazardous components.
- Packaging Requirements: Use shock-resistant, protective packaging with clear labeling, including laser warning symbols and battery handling instructions (if applicable).
Import/Export Controls
- Export Administration Regulations (EAR): Some high-power laser systems may be subject to dual-use export controls under the U.S. Department of Commerce. Verify if the system requires an export license.
- Customs Documentation: Provide detailed technical specifications, end-use statements, and certificates of conformity to facilitate customs clearance.
- CE Marking (EU): Required for sale in the European Economic Area, demonstrating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Operational Deployment and On-Site Logistics
Equipment Setup and Calibration
- Ensure the laser system is properly calibrated before use.
- Verify power supply compatibility (voltage, frequency) at the job site.
- Use grounding and surge protection to prevent electrical hazards.
Personnel Training and Documentation
- Operators must complete laser safety training (ANSI Z136.1 recommended).
- Maintain logs for equipment maintenance, laser usage, and safety incidents.
- Provide multilingual user manuals and safety warnings where applicable.
Maintenance and Spare Parts Logistics
- Establish a supply chain for consumables (e.g., filters, lenses) and spare parts.
- Schedule routine maintenance per manufacturer guidelines to ensure performance and safety.
- Track calibration and service history to support compliance audits.
Incident Response and Emergency Procedures
Laser Exposure Protocols
- In case of accidental exposure, immediately cease operations and seek medical evaluation.
- Maintain an emergency eyewash station and first aid supplies on-site.
Fire and Fume Response
- Laser operations can ignite flammable materials. Keep fire extinguishers (Class C for electrical fires) accessible.
- In case of smoke or fumes, evacuate the area and activate ventilation systems.
Reporting and Recordkeeping
- Document all incidents, near-misses, and safety violations.
- Retain records for a minimum of five years (or per local regulation) for compliance audits.
Conclusion
Handheld laser paint removal systems offer efficient, eco-friendly surface preparation but require strict adherence to safety, environmental, and transportation regulations. A comprehensive logistics and compliance strategy—encompassing operator training, regulatory documentation, proper shipping, and emergency planning—is essential for legal and safe operation across domestic and international markets.
Conclusion: Sourcing Handheld Laser Paint Removal Systems
Sourcing handheld laser paint removal systems presents a promising opportunity for industries seeking efficient, environmentally friendly, and precise surface preparation solutions. As advancements in laser technology continue, these portable systems offer significant advantages over traditional methods—such as sandblasting or chemical stripping—including reduced material damage, minimal waste generation, improved worker safety, and compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
When sourcing such equipment, key considerations include laser power, wavelength, portability, cooling mechanisms, safety certifications, and after-sales support. It is essential to evaluate reputable suppliers offering reliable technology, proven performance across targeted substrates (e.g., metal, composites, or historical structures), and compliance with international safety standards such as CE or FDA regulations.
While the initial investment may be higher than conventional methods, the long-term operational savings, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced precision make handheld laser paint removal a cost-effective and sustainable choice, especially for aerospace, automotive restoration, maritime, and heritage conservation applications.
In conclusion, organizations should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting a supplier, prioritize systems with robust technical support and training, and consider pilot testing to validate performance in real-world conditions. With the right sourcing strategy, handheld laser paint removal can significantly enhance productivity, safety, and sustainability in surface treatment operations.