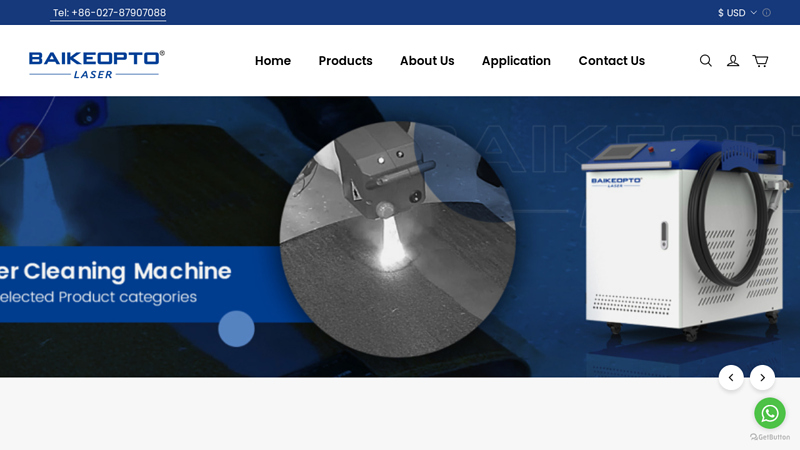
The global handheld laser cleaning machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, non-abrasive surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and precision manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the industrial laser cleaning equipment market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 18.5% from 2023 to 2028, with handheld systems gaining prominence due to their portability, precision, and ease of integration into existing workflows. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global laser cleaning market size was valued at over USD 500 million in 2022 and is expected to expand significantly by 2030, fueled by stricter environmental regulations and the phasing out of traditional cleaning methods like sandblasting and chemical solvents. As adoption accelerates, a competitive landscape of innovators has emerged, leading to rapid advancements in power efficiency, durability, and user safety. Here are the top 10 manufacturers leading this transformation with cutting-edge handheld laser cleaning solutions.
Top 10 Handheld Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturers
Founded: 2016
Website: fortunelaser.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 2016 and headquartered in Shenzhen city, Fortune Laser Technology Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer of industrial laser equipment, integrated ……
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#4 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL is an industrial pulsed laser cleaning machine series by PULSAR Laser with outputs from 100 W to 1000 W, air-cooled up to 500 W….
#5 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturer
Website: hantencnc.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide range of laser cleaners, from 100W to 3000W. Our lineup includes handheld, backpack, and trolley-type products to meet diverse cleaning needs….
#6 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#7 Hand Held Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturers, Suppliers
Website: hgtech-laser.com
Key Highlights: We’re professional hand held laser cleaning machine manufacturers and suppliers in China, specialized in providing high quality laser equipment….
#8 Handheld Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Handheld and portable laser cleaning machines designed for manual applications including rust removal, paint stripping, restoration, and more….
#9 Handheld Laser Cleaning Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: The CleanTech CF-1020 hand-held laser cleaning machine is compact and mobile, ready for in-field cleaning, finishing, and other surface preparation tasks. Learn ……
#10 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: baikeopto.com
Key Highlights: Backpack laser cleaning machine Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine. 01|Backpack cleaner. BK-FLC50SC Max 50W Backpack Pulse Laser ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Handheld Laser Cleaning Machine
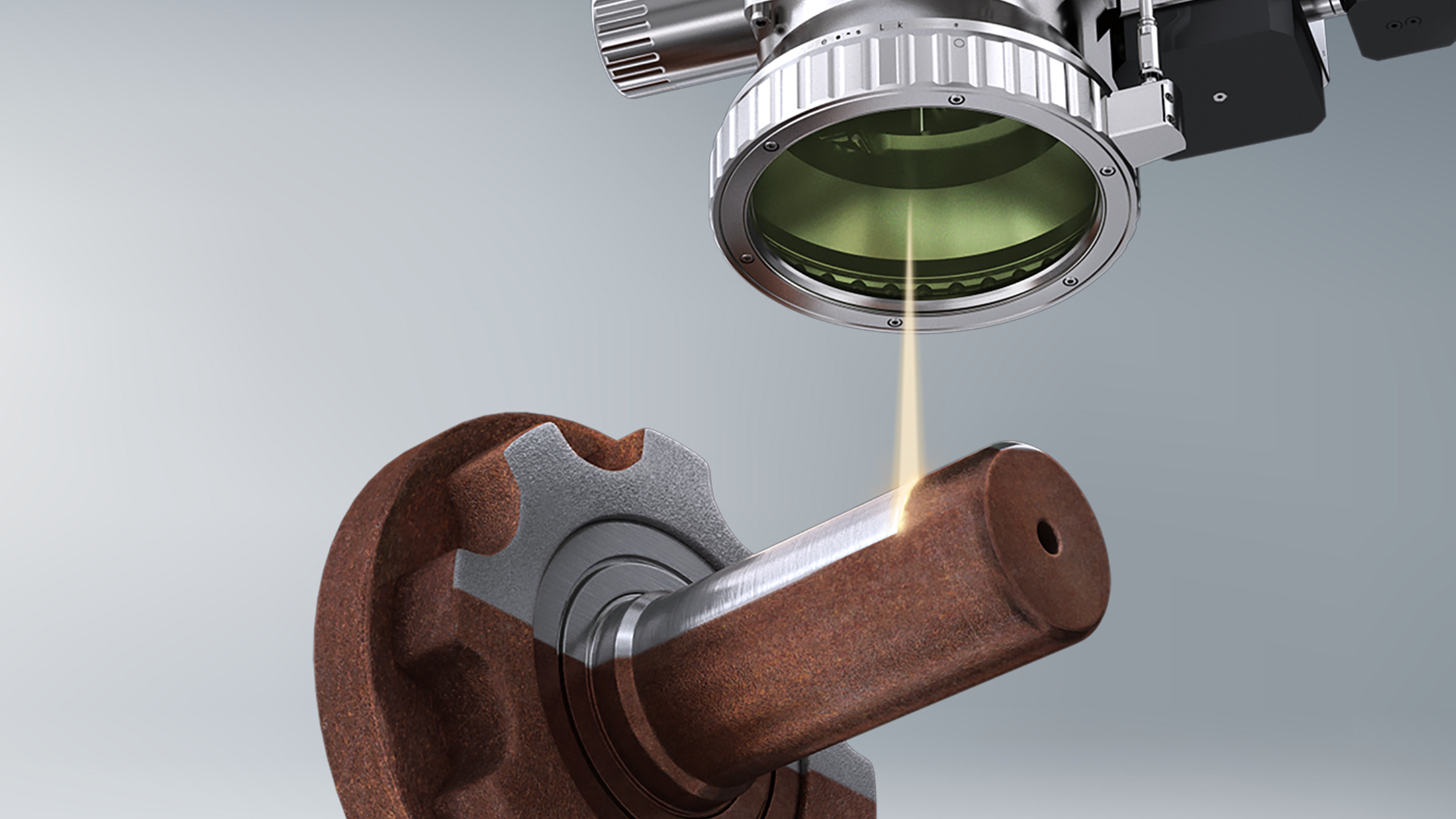

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Handheld Laser Cleaning Machines
The global market for handheld laser cleaning machines is poised for significant transformation and expansion by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing industrial automation, and increasing demand for eco-friendly cleaning solutions. Several key trends are shaping the trajectory of this market:
-
Rising Adoption Across Industrial Sectors
By 2026, handheld laser cleaning machines are expected to see widespread adoption in industries such as automotive, aerospace, precision manufacturing, and cultural heritage restoration. Their ability to remove rust, paint, oxides, and contaminants without damaging substrates makes them ideal for maintenance and surface preparation tasks. The shift toward non-abrasive, chemical-free cleaning methods is accelerating their integration into standard industrial workflows. -
Technological Advancements and Miniaturization
Ongoing innovations in fiber laser technology are leading to more compact, energy-efficient, and user-friendly handheld devices. Enhanced beam quality, improved cooling systems, and longer operational lifespans are increasing reliability and performance. Additionally, integration with smart features—such as IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, and AI-assisted diagnostics—is expected to enhance usability and productivity. -
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
With increasing global emphasis on sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations, traditional cleaning methods involving chemicals and abrasive blasting are being phased out. Handheld laser cleaning offers a green alternative by eliminating secondary waste and reducing hazardous emissions. Regulatory support in regions like the EU and North America is expected to boost market penetration. -
Cost Reduction and Improved Accessibility
As production scales and component costs decline—particularly in diode and fiber lasers—the price of handheld laser cleaners is becoming more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). By 2026, competitive pricing and flexible financing options are anticipated to broaden market reach beyond large industrial players. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Rapid industrialization in Asia-Pacific (especially China, India, and Southeast Asia), coupled with government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing, is fueling demand. Local manufacturing of laser components is reducing dependency on imports and enabling faster service and customization, further stimulating regional growth. -
Safety and Training Standardization
With growing usage comes the need for standardized safety protocols and operator training. By 2026, industry stakeholders are expected to collaborate on certification programs and safety guidelines, particularly concerning laser class compliance (e.g., IEC 60825) and personal protective equipment (PPE), to ensure safe deployment across diverse work environments. -
Integration with Robotics and Automation
While handheld units remain popular for flexibility, hybrid models that can be mounted on robotic arms or collaborative robots (cobots) are emerging. This trend supports semi-automated cleaning processes, enhancing precision and repeatability in high-volume applications.
In conclusion, the 2026 outlook for the handheld laser cleaning machine market is highly positive, characterized by technological maturity, environmental alignment, and expanding application horizons. Companies that invest in innovation, user safety, and market education are likely to gain a competitive edge in this rapidly evolving landscape.
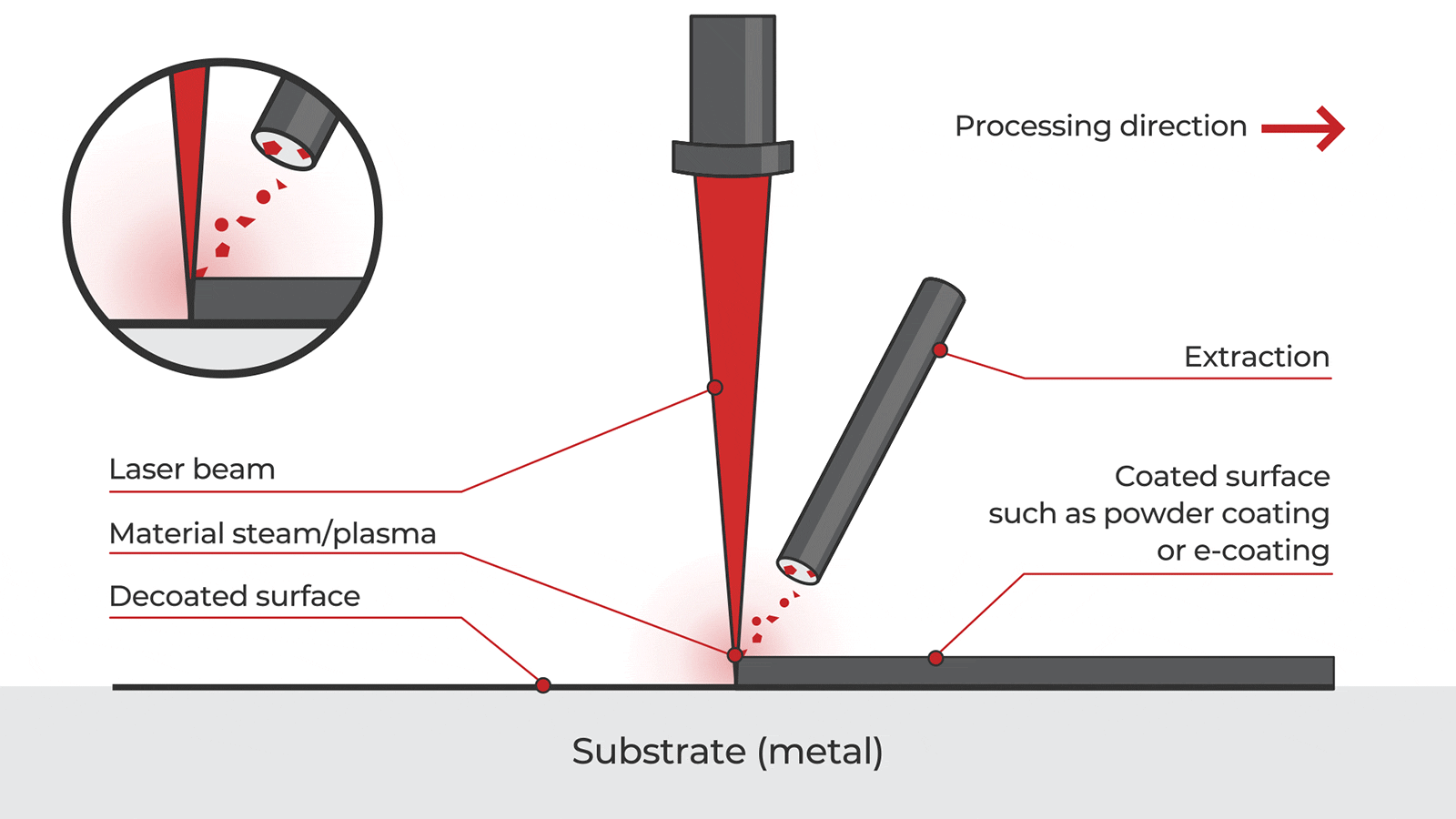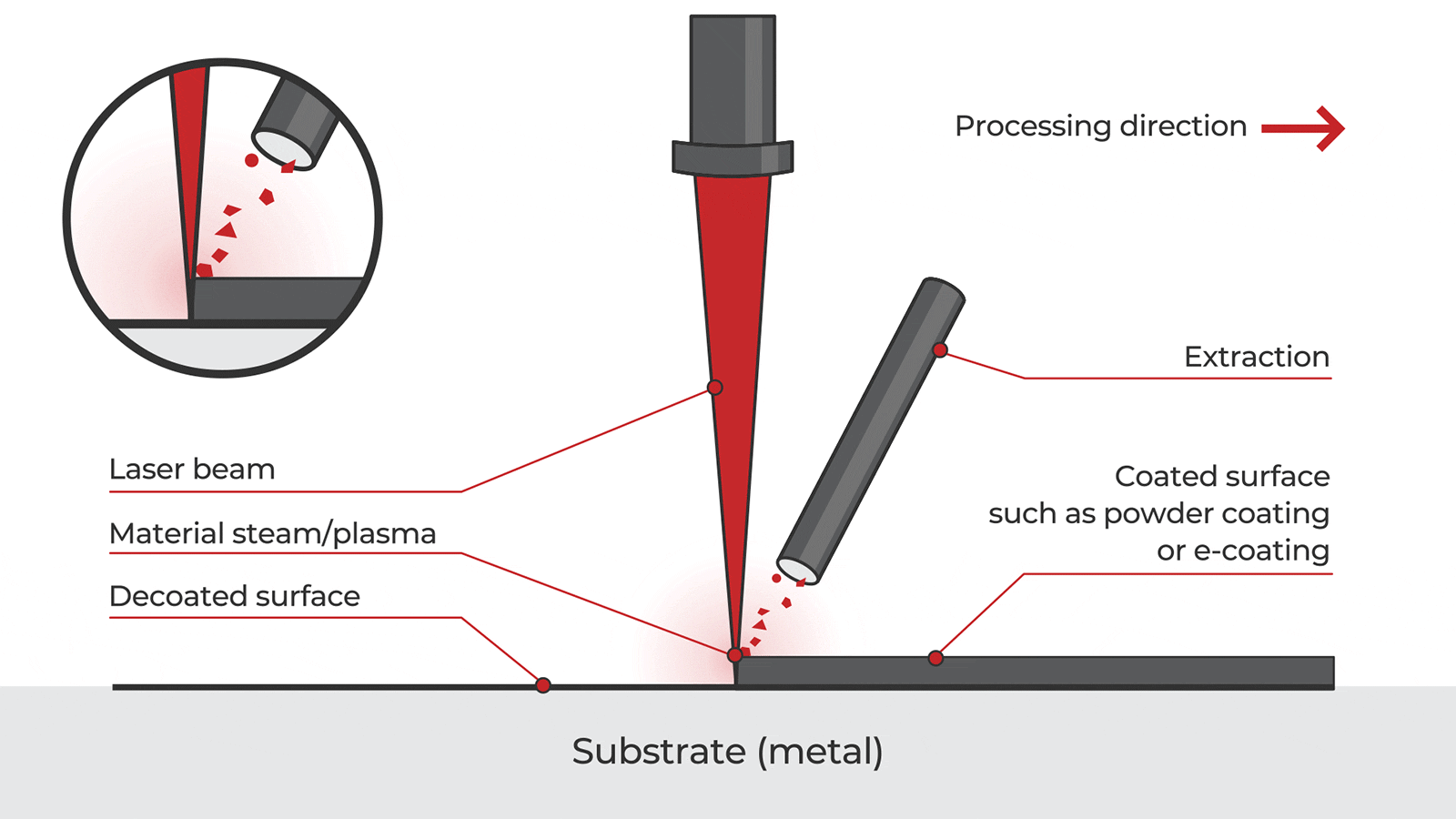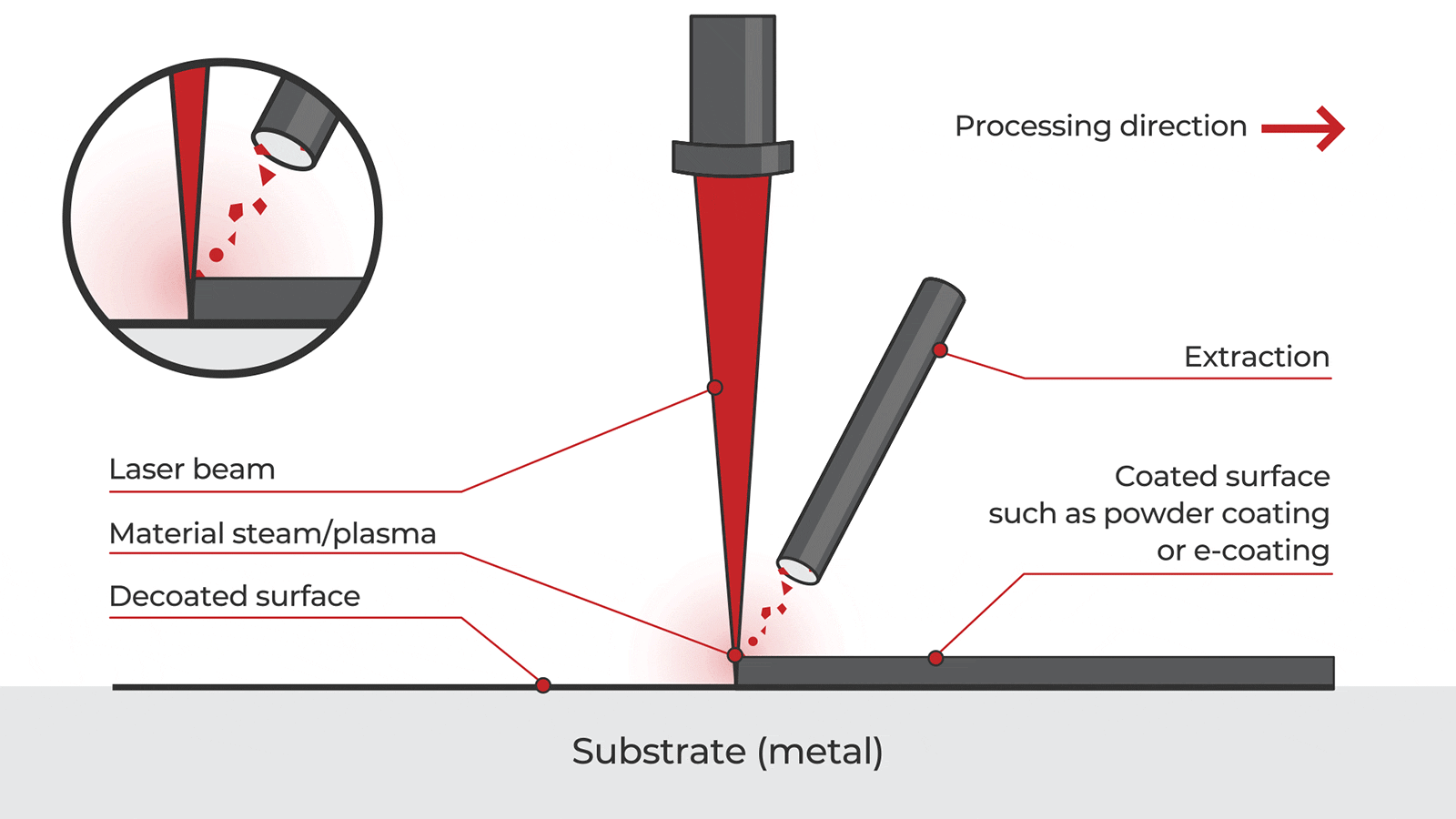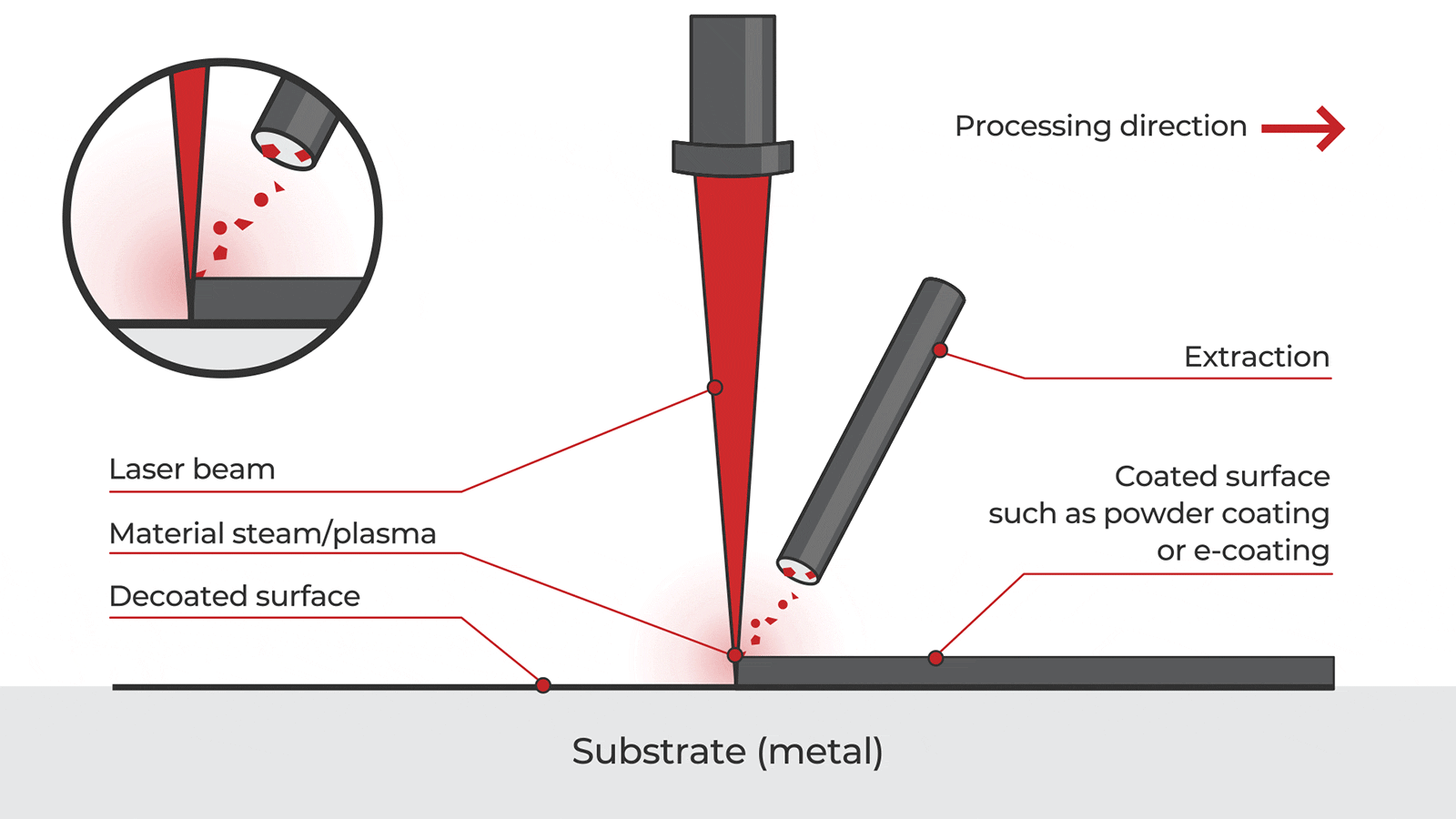
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Handheld Laser Cleaning Machines (Quality & IP)
Sourcing handheld laser cleaning machines from international suppliers, particularly in regions like China, presents significant opportunities but also notable risks. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to subpar equipment, legal complications, and operational failures.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Inadequate Safety Standards
Many suppliers prioritize low cost over reliability, resulting in machines built with inferior components. Critical issues include unstable laser output, poor beam quality, and inconsistent cleaning performance. Additionally, some units lack proper safety certifications (such as CE, FDA, or IEC 60825), exposing users to health hazards and potential legal liability. Inadequate cooling systems and weak mechanical construction further reduce machine lifespan and increase downtime.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key performance metrics such as laser power (e.g., listing peak power instead of average power), cleaning speed, or effective working distance. Without independent verification or third-party testing reports, buyers may receive equipment that falls significantly short of promised capabilities. This misalignment can disrupt production schedules and compromise cleaning results.
Lack of Intellectual Property Protection and Risk of Infringement
Sourcing from regions with lax IP enforcement increases the risk of purchasing machines that infringe on patented technologies. Some manufacturers reverse-engineer or copy designs from reputable brands, exposing buyers to potential legal action, especially if the equipment is imported into jurisdictions with strong IP laws. Conducting due diligence on the supplier’s IP compliance and requesting proof of legitimate design rights is essential.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many overseas suppliers offer limited technical support, extended response times, and poor documentation. Access to replacement parts can be slow and costly, leading to prolonged machine downtime. A lack of local service centers or trained technicians further complicates maintenance and troubleshooting, undermining operational efficiency.
Failure to Verify Real-World Performance and Supplier Credibility
Relying solely on marketing materials or lab demonstrations can be misleading. Without on-site testing, customer references, or verifiable case studies, buyers may not assess the machine’s true performance under actual working conditions. Additionally, some suppliers operate through shell companies or trade intermediaries, making accountability difficult if quality or contractual issues arise.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Handheld Laser Cleaning Machine
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Handheld laser cleaning machines are classified as industrial laser systems and are subject to international and regional regulations concerning safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and transportation. These devices typically fall under Class 4 lasers due to their high power, capable of causing skin and eye injuries, as well as fire hazards. Key regulatory frameworks include the U.S. FDA/CDRH (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11), the EU’s IEC 60825-1 standard for laser safety, the Radio Equipment Directive (RED) for EMC compliance, and the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC where applicable. Manufacturers and distributors must ensure compliance with these standards prior to market access.
Export Documentation and Customs Clearance
Proper export documentation is essential for international shipments. Required documents include a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or air waybill, and a Certificate of Origin. For laser products, an FDA Laser Product Report (U.S.) or EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) must accompany the shipment. Some countries may require additional certifications, such as the Chinese CCC mark or Russian EAC certification. Accurate product classification using the Harmonized System (HS) Code—typically 8543.70 for laser systems—is critical to avoid customs delays and ensure correct duty assessment.
Transportation and Packaging Requirements
Handheld laser cleaning machines must be shipped in robust, shock-resistant packaging to prevent damage during transit. Internal components, especially optical elements, are sensitive to vibration and moisture. Use anti-static materials and foam inserts to secure the unit. When transporting by air, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations. Although most laser devices are not classified as hazardous, batteries (if included) may fall under UN 3480 (lithium-ion) or UN 3090 (lithium metal) and require appropriate labeling, packaging, and documentation. Ground and sea shipments must also follow IMDG or ADR regulations where applicable.
Import Compliance and Market-Specific Regulations
Each destination country has unique import requirements for laser equipment. In the United States, the FDA requires prior notification and product registration through the FDA’s CDRH portal. The EU mandates CE marking with technical documentation demonstrating compliance with relevant directives. In Canada, lasers are regulated by Health Canada under the Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA). Australia requires conformity with the Radiation Protection Standard (RPS No. 11) and registration with the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) if used in medical applications. Always verify local requirements before shipment to avoid seizure or rejection at customs.
Safety and User Training Compliance
Due to the inherent risks of Class 4 lasers, end users must receive comprehensive safety training. Suppliers should provide multilingual user manuals, safety labels, and laser protective eyewear. Compliance with ANSI Z136.1 (U.S.) or EN 60825-1 (EU) includes implementing safety interlocks, emergency shut-offs, and clear warning labels. Employers using these machines must conduct workplace risk assessments and provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Documentation of user training and safety protocols may be required during regulatory audits or inspections.
Warranty, Service, and After-Sales Logistics
Establish a clear warranty policy that complies with local consumer protection laws (e.g., 2 years in the EU under the Consumer Rights Directive). Plan for spare parts distribution and technical support in target markets. If software updates or remote diagnostics are offered, ensure compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR. Repair shipments may require temporary import/export documentation (e.g., ATA Carnet) to avoid duties on returned equipment. Maintain records of all service activities for compliance and traceability purposes.
In conclusion, sourcing a handheld laser cleaning machine requires careful evaluation of several key factors to ensure optimal performance, safety, and return on investment. It is essential to assess the machine’s technical specifications—such as laser power, pulse frequency, beam quality, and cleaning speed—against your specific application requirements, including the type of contaminants and materials involved. Additionally, portability, ergonomics, cooling system efficiency, and ease of maintenance play a significant role in long-term usability.
Safety features, such as built-in fume extraction compatibility, protective enclosures, and compliance with international laser safety standards (e.g., FDA, CE, IEC), must not be overlooked. Equally important is selecting a reliable supplier with proven technical support, post-sales service, training, and warranty coverage.
After comparing various suppliers and models based on performance, durability, cost-effectiveness, and user feedback, it is recommended to choose a machine that strikes the right balance between power, precision, portability, and safety. Investing in a high-quality handheld laser cleaning solution not only enhances operational efficiency and cleaning precision but also reduces environmental impact by eliminating the need for chemical solvents or abrasive media. With the right sourcing strategy, a handheld laser cleaner can be a valuable asset across industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and heritage restoration.