The global handheld cleaning laser market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for non-contact, eco-friendly surface restoration solutions across heritage conservation, industrial maintenance, and aerospace sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global laser cleaning equipment market was valued at USD 452.3 million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 1.1 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 15.8% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by advancements in portable laser systems, rising awareness of precision cleaning benefits, and stricter environmental regulations limiting chemical and abrasive methods. With handheld units accounting for a significant share due to their mobility and ease of use, the competitive landscape is evolving rapidly. Here are the top 7 manufacturers leading innovation and market penetration in handheld laser cleaning technology.
Top 7 Handheld Cleaning Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#3 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#4 Handheld Laser Cleaning Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: How It Works. Laser cleaning effectively removes surface contaminants by directing a focused laser beam onto a targeted area to ablate unwanted material….
#5 Handheld Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Handheld and portable laser cleaning machines designed for manual applications including rust removal, paint stripping, restoration, and more….
#6 DefenseTech laser cleaning
Website: fonon.us
Key Highlights: The DTMF-1020 handheld laser system offers a non-abrasive cleaning process that is safe, easy to use, and eco-friendly. It minimizes chemical and abrasive usage ……
#7 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: strlaser-en.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning offers precise, controllable, and standardized operation, replacing manual labor to boost efficiency, enhance work quality….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Handheld Cleaning Laser

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Handheld Cleaning Lasers
The handheld cleaning laser market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding applications, and shifting industry demands. Key trends shaping this dynamic sector include:
1. Accelerated Adoption Across Diverse Industries:
Beyond traditional niches like heritage restoration and precision manufacturing, handheld lasers will gain traction in aerospace (rust/contamination removal on aircraft), automotive (paint stripping, weld prep), energy (cleaning turbines, solar panels), and electronics (delicate component cleaning). This diversification will be a primary growth driver.
2. Technological Advancements Driving Accessibility:
Expect continued innovation making devices smaller, lighter, more energy-efficient, and user-friendly. Improvements in diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) and fiber laser sources will enhance power efficiency and beam quality. Integration of AI-powered smart features (automatic parameter adjustment, defect detection) and IoT connectivity for performance monitoring and predictive maintenance will become more common, lowering the skill barrier.
3. Focus on Safety, Ergonomics, and Automation:
Enhanced safety features (improved beam shielding, real-time fume monitoring, intuitive interlocks) will be paramount for wider acceptance. Designs will prioritize ergonomics for reduced operator fatigue during prolonged use. Semi-automated solutions, such as robotic arms equipped with handheld-style laser heads or guided tracking systems, will emerge to improve consistency and efficiency in repetitive tasks.
4. Sustainability and Regulatory Push:
As industries prioritize eco-friendly processes, the chemical-free, waste-minimizing nature of laser cleaning will be a major advantage. Stricter environmental regulations on hazardous cleaning chemicals (solvents, abrasives) will further boost demand for laser alternatives, positioning them as a sustainable solution.
5. Cost Reduction and Market Expansion:
Economies of scale, component cost reductions (especially diodes), and increased competition will gradually lower device prices, making them accessible to smaller businesses and service providers. This will expand the market beyond large industrial players and specialized contractors.
6. Emergence of Service-Based Models:
Alongside hardware sales, “Laser Cleaning as a Service” (LCaaS) models will grow. Companies will offer on-site cleaning services using their own equipment, reducing the upfront investment barrier for end-users and accelerating technology adoption, particularly in maintenance and restoration sectors.
In summary, the 2026 handheld cleaning laser market will be characterized by broader industrial penetration, smarter and safer technology, strong sustainability drivers, and evolving business models, leading to robust growth and increased accessibility.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Handheld Cleaning Lasers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing handheld laser cleaning equipment involves navigating several critical challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Avoiding these pitfalls is essential for ensuring performance, safety, and legal compliance.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many budget handheld laser cleaners, especially those from less-reputable suppliers, use substandard materials and components to cut costs. This includes low-grade optical lenses, inadequate thermal management systems, and weak housing materials. These shortcomings lead to rapid degradation, inconsistent cleaning performance, and shorter device lifespans. Buyers may also face frequent maintenance issues or outright failure under regular use, undermining operational efficiency.
Inaccurate or Inflated Performance Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key performance metrics such as laser power output, cleaning speed, or effective working distance. For example, a device advertised as 1000W might actually deliver significantly less due to inefficient energy conversion or thermal throttling. Without independent verification or third-party test reports, buyers risk investing in equipment that fails to meet their operational requirements.
Lack of IP Protection and Risk of Infringement
A major concern when sourcing from certain regions—particularly China—is the potential for IP infringement. Some manufacturers may copy patented designs, control systems, or software interfaces from established brands without authorization. Purchasing such products can expose buyers to legal risks, especially if the equipment is imported into jurisdictions with strict IP enforcement. Additionally, using cloned technology may result in poor technical support and lack of firmware updates.
Inadequate Safety Features and Non-Compliance
Reputable handheld laser cleaners include critical safety mechanisms such as key switches, emergency stop buttons, and laser emission indicators. Lower-quality units often lack these features or implement them poorly, increasing the risk of accidental exposure. Furthermore, many budget devices fail to meet international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825), making them unsuitable for regulated environments and potentially uninsurable.
Insufficient IP (Ingress Protection) Rating for Industrial Use
While “IP” commonly refers to intellectual property, in hardware contexts it also denotes Ingress Protection—resistance to dust and moisture. Many handheld lasers are marketed for industrial use but lack a certified IP rating (e.g., IP54 or higher). Without proper sealing, internal components are vulnerable to contamination from dust, rust, and cleaning byproducts, leading to malfunctions and increased downtime in harsh environments.
Limited or No After-Sales Support and Warranty Enforcement
Even if a product appears reliable initially, the absence of responsive technical support, spare parts availability, or enforceable warranty terms can be a major drawback. Some suppliers disappear after sale or refuse warranty claims due to vague terms. This leaves buyers without recourse when issues arise, increasing total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence: request verifiable test data, confirm IP ownership through legal documentation, verify compliance certifications, and assess supplier reputation through customer references. Investing in quality and legitimacy from the outset avoids costly setbacks and ensures safe, effective laser cleaning operations.
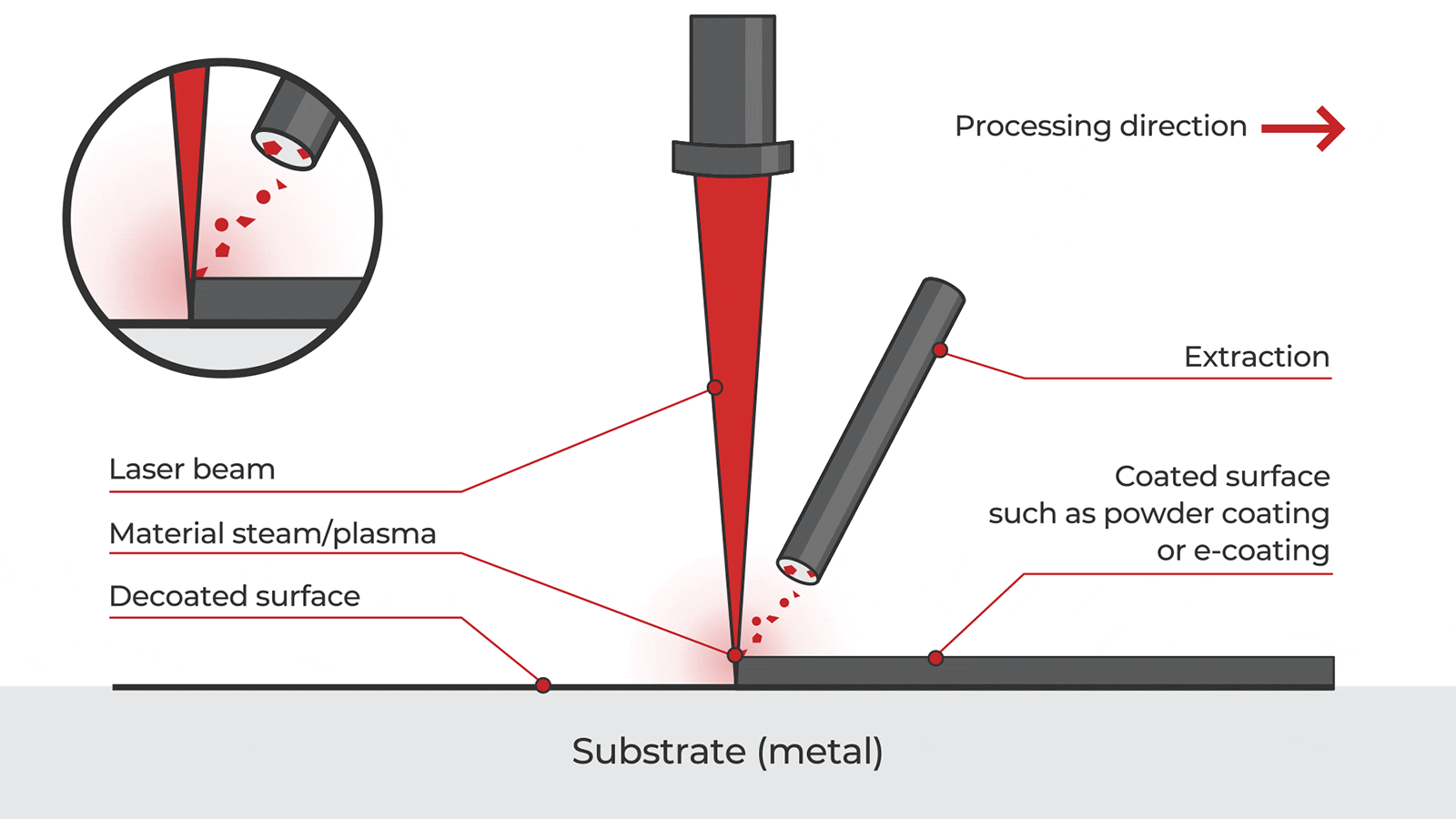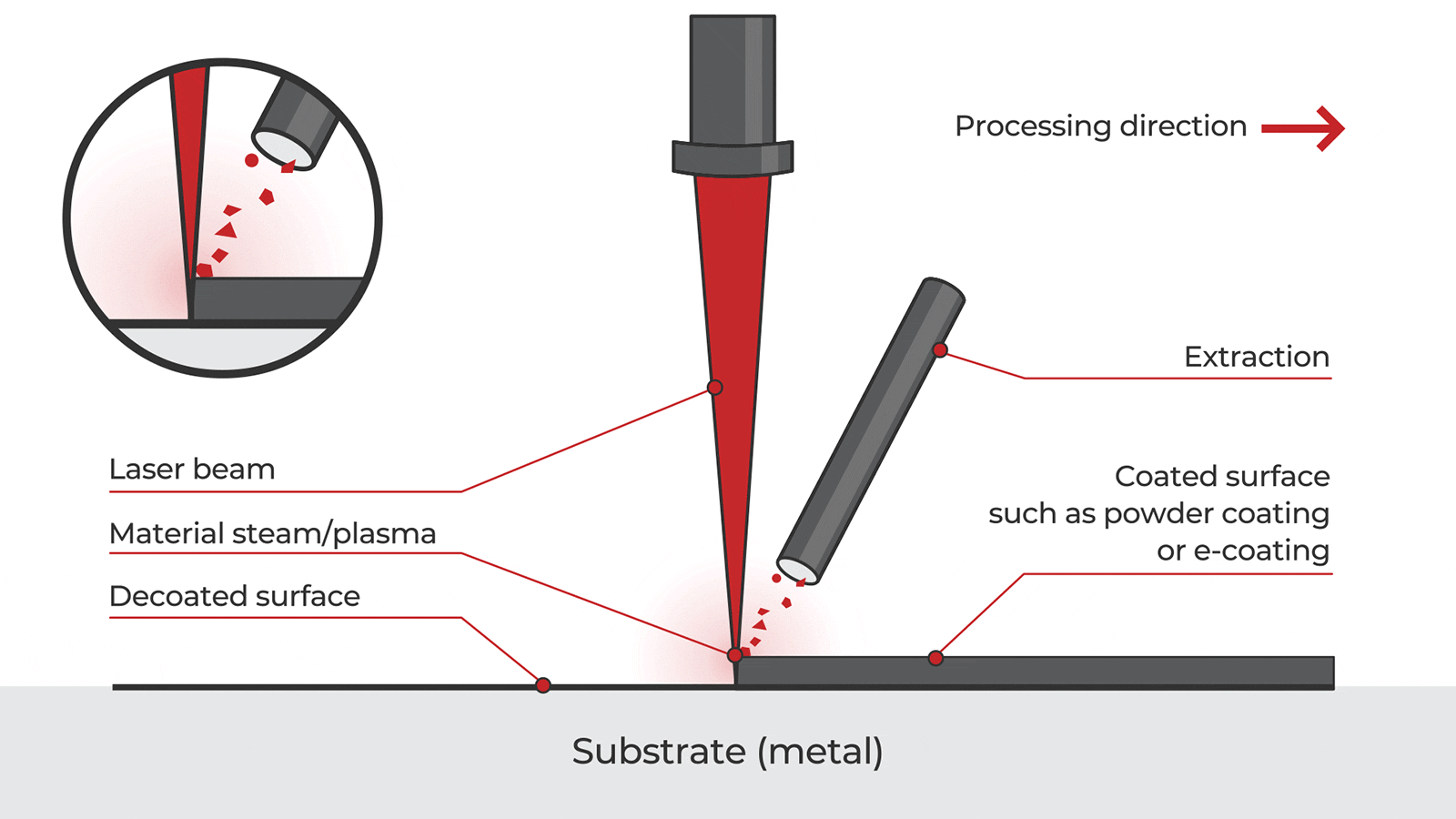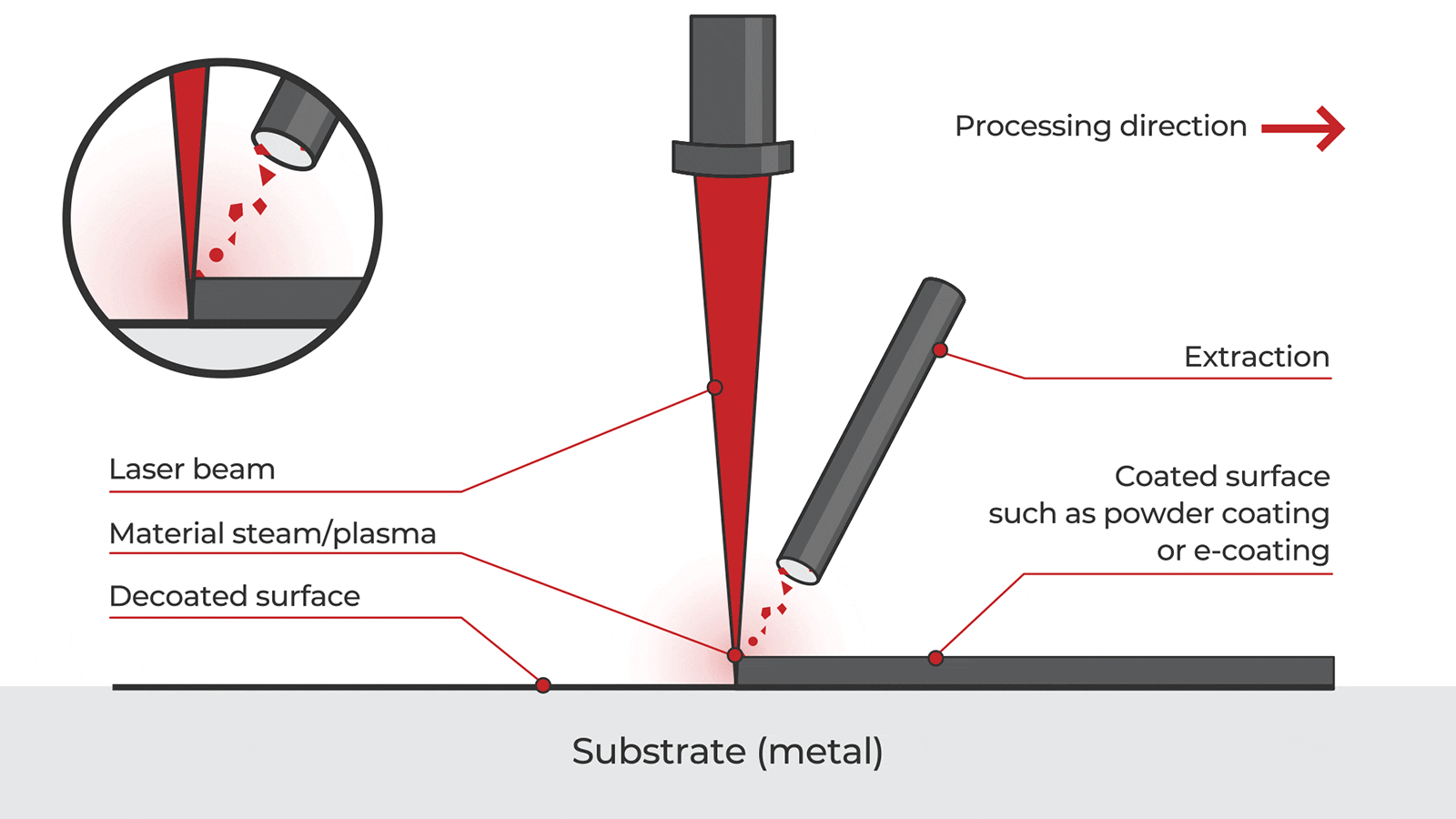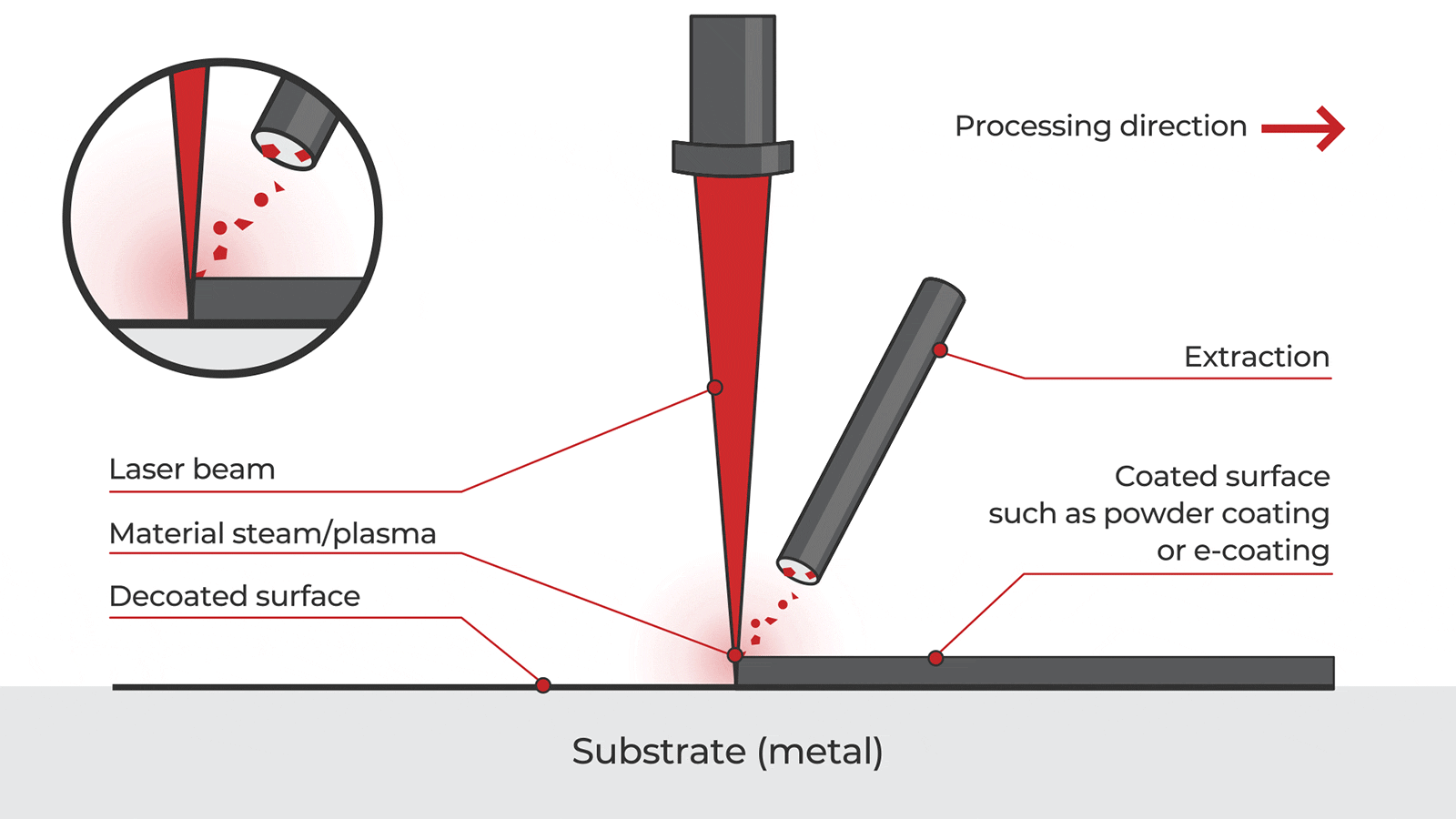
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Handheld Cleaning Laser
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe transportation, handling, and regulatory adherence of Handheld Cleaning Lasers. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational safety, legal compliance, and smooth international and domestic movement of the equipment.
Classification & Regulatory Framework
Handheld Cleaning Lasers are classified as Class 4 lasers under international laser safety standards (IEC 60825-1). This classification indicates high-power lasers capable of causing skin and eye injuries, as well as posing fire hazards. Key regulatory bodies include:
- IEC 60825-1: International standard for laser product safety.
- FDA/CDRH (U.S.): Regulates laser products under 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11.
- Health Canada (Canada): Controlled under the Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA).
- CE Marking (EU): Requires compliance with the EU Laser Product Standard EN 60825-1 and the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) or Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), depending on configuration.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Restrictions on hazardous substances and chemical safety.
Ensure all devices are labeled with appropriate laser warning symbols, class designation, and manufacturer information per local requirements.
Packaging & Transportation Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage and unauthorized operation during transit.
- Secure Enclosure: Use rigid, shock-absorbent packaging designed to immobilize the laser unit and accessories (e.g., power supplies, protective eyewear).
- Laser Safety Interlocks: Confirm safety mechanisms (e.g., key switch, safety interlock) are engaged or disabled prior to shipping.
- Battery Handling: If the unit contains lithium-ion batteries:
- Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) for air transport.
- Pack batteries to prevent short circuits (insulated terminals, individual packaging).
- Declare batteries according to UN 3480 (lithium-ion) or UN 3090 (lithium metal), as applicable.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packaging with:
- “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators.
- Laser warning labels.
- Appropriate hazardous material labels if batteries are installed or shipped separately.
Import/Export Compliance
Cross-border shipments require strict adherence to export control and customs regulations.
- Export Controls:
- Verify if the laser falls under export control lists (e.g., U.S. Commerce Control List – ECCN 6A003.b.4, or Wassenaar Arrangement).
- Obtain necessary export licenses for restricted destinations or end-uses.
- Customs Documentation:
- Provide accurate commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin.
- Include technical specifications (wavelength, output power, pulse duration) for customs classification.
- Declare compliance with relevant standards (e.g., CE, FDA).
- Restricted Countries: Be aware of trade embargoes or restrictions on laser equipment for certain countries.
Safety & Handling Protocols
Ensure end-users and logistics personnel are trained in laser safety.
- Training Requirements:
- Provide user manuals and safety documentation with each unit.
- Mandate laser safety training (e.g., ANSI Z136.1) for operators.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Ship with appropriate laser safety goggles rated for the specific wavelength and power of the device.
- Include skin protection guidance if applicable.
- Operational Environment:
- Recommend use in controlled environments with restricted access during operation.
- Implement beam containment and warning signage as per safety standards.
Maintenance & Documentation
Maintain compliance throughout the product lifecycle.
- Service Records: Keep logs of calibration, maintenance, and repairs.
- Software/Firmware Updates: Ensure updates do not alter safety features without re-certification.
- Regulatory Updates: Monitor changes in laser safety or transportation regulations and update documentation and procedures accordingly.
Adherence to this logistics and compliance framework minimizes risk, ensures regulatory conformity, and supports the safe deployment of Handheld Cleaning Lasers worldwide.
Conclusion for Sourcing Handheld Cleaning Laser
In conclusion, sourcing a handheld laser cleaning system requires a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, supplier reliability, and total cost of ownership. Handheld laser cleaners offer significant advantages over traditional cleaning methods, including precision, environmental friendliness, reduced secondary waste, and minimal substrate damage. When selecting a supplier, it is critical to consider factors such as laser power, pulse rate, portability, safety features, after-sales support, and compliance with international safety standards.
Prioritizing reputable manufacturers with proven track records in industrial laser solutions ensures the acquisition of a durable, efficient, and safe system. Additionally, requesting product demonstrations, customer references, and service agreements can further mitigate procurement risks. As laser cleaning technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, investing in a high-quality handheld system can deliver long-term operational benefits, improve workplace safety, and support sustainability goals across industries such as automotive, aerospace, heritage restoration, and manufacturing.
Therefore, a well-researched sourcing strategy—aligned with specific cleaning needs and future scalability—will enable organizations to leverage the full potential of laser cleaning technology and achieve a strong return on investment.