The global hand-held metal cutting laser market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for precision cutting solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication. According to Grand View Research, the global laser cutting equipment market was valued at USD 9.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, increasing automation in manufacturing, and the superior efficiency of hand-held systems over traditional cutting methods. As portability, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness become critical factors for industrial operations, hand-held metal cutting lasers are gaining traction worldwide. With China emerging as a dominant player in both production and technological innovation, a new wave of manufacturers is redefining performance benchmarks. Based on market presence, technological capability, customer reviews, and product reach, the following analysis identifies the top 10 hand-held metal cutting laser manufacturers shaping the future of industrial fabrication.
Top 10 Hand Held Metal Cutting Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Photonics
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics manufactures reliable, safe, and eco-friendly Laser Cleaning, Laser Cutting, Laser Engraving, Laser Marking, and Laser Welding solutions….
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Wattsan
Website: wattsan.com
Key Highlights: Wattsan is a manufacturer of laser and cnc milling machines of European quality at affordable prices with worldwide delivery….
#4 Bodor
Website: bodor.com
Key Highlights: Bodor laser is a fiber laser cutting machine manufacturer specialized in cnc fiber laser cutting machine equipment with integrating development, production, ……
#5 Full Spectrum Laser
#6 Fiber laser cutting machine
Website: hsglaser.com
Key Highlights: HSG LASER is an international company dedicated to R&D, production, sales of laser cutting, bending, welding machines, automatic loading & unloading and ……
#7 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#8 Laser Solutions
Website: lincolnelectric.com
Key Highlights: The easy-to-use Flex Lase handheld laser system puts power, speed, and precision at your fingertips. With 2kW of output power, operators can tackle high- ……
#9 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
#10 Handheld Laser Welding Machine, Handheld Laser Cleaning …
Website: kaihuanlaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser pipe cutting machines deliver precise cuts for complex shapes and tight tolerances. Fast cutting speeds improve production rates and reduce material waste ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hand Held Metal Cutting Laser
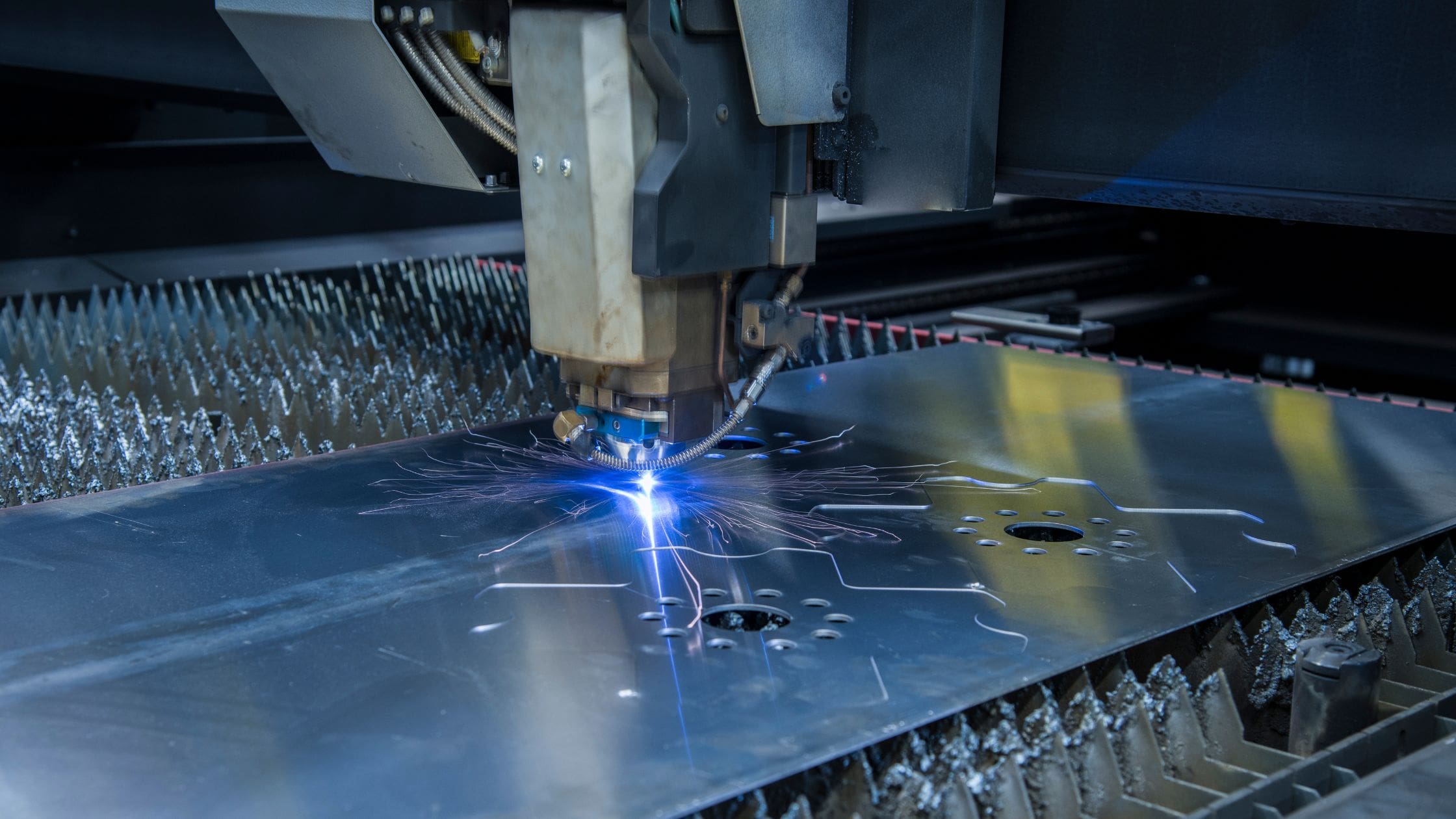

H2: Projected Market Trends for Hand-Held Metal Cutting Lasers in 2026
By 2026, the global market for hand-held metal cutting lasers is expected to undergo significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, expanding industrial automation, and growing demand for precision tools across manufacturing, construction, and metal fabrication sectors. Several key trends are anticipated to shape the industry:
-
Increased Adoption in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs):
The affordability and portability of hand-held laser systems are making them accessible to SMEs. As equipment costs decline due to advancements in diode and fiber laser technology, more small workshops and on-site contractors are expected to adopt these tools for cutting, beveling, and shaping metal components. -
Integration with Smart Manufacturing and IoT:
The rise of Industry 4.0 is pushing hand-held laser tools toward greater connectivity. By 2026, leading manufacturers are likely to offer laser cutters with real-time data monitoring, remote diagnostics, and compatibility with digital work management platforms. This integration enhances precision, reduces errors, and improves workflow efficiency. -
Advancements in Laser Power and Portability:
Ongoing improvements in battery technology and compact fiber laser sources are expected to result in higher-powered hand-held systems without sacrificing portability. Lasers capable of cutting thicker metals (up to 25–30 mm) with improved cutting speeds and edge quality will become more common, expanding their use in heavy-duty applications. -
Growth in Construction and On-Site Fabrication:
The construction, shipbuilding, and pipeline industries are increasingly adopting hand-held lasers for field applications. Their ability to perform precise cuts in constrained or remote environments offers significant advantages over traditional plasma or oxy-fuel torches. This trend is expected to accelerate through 2026, particularly in infrastructure development projects across Asia-Pacific and emerging markets. -
Focus on Safety and Ergonomics:
As hand-held lasers become more powerful, safety features such as real-time beam shielding, motion sensors, and anti-backfire mechanisms will become standard. Manufacturers are also expected to prioritize ergonomic design to reduce operator fatigue during prolonged use. -
Regional Market Expansion:
While North America and Europe remain key markets due to advanced manufacturing ecosystems, the Asia-Pacific region—led by China, India, and Southeast Asia—is projected to register the highest growth. Government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing and infrastructure development are key drivers. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
The environmental benefits of laser cutting over traditional methods—such as reduced material waste, lower emissions, and no need for consumable gases in some models—are gaining attention. By 2026, energy-efficient and eco-friendly hand-held laser systems are expected to be a competitive differentiator.
In summary, the hand-held metal cutting laser market in 2026 will be characterized by greater accessibility, smarter technology, and expanded industrial applications. Companies that prioritize innovation in power, safety, and integration are likely to lead this dynamic and rapidly evolving market.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Hand Held Metal Cutting Lasers (Quality, IP)
When sourcing hand-held metal cutting lasers, businesses often encounter challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Understanding and mitigating these pitfalls is critical to securing reliable, legally compliant, and high-performance equipment.
1. Inadequate Quality Control from Suppliers
Many suppliers, especially those in low-cost manufacturing regions, may lack robust quality control processes. This can result in inconsistent laser performance, substandard components (e.g., optics, cooling systems), and reduced machine lifespan. Buyers may receive units that fail to meet advertised specifications, such as cutting thickness, precision, or duty cycle. Verifying certifications (e.g., CE, ISO 9001), requesting third-party inspection reports, and conducting on-site factory audits can help mitigate this risk.
2. Misrepresentation of IP Ownership
A significant concern when sourcing from certain regions—particularly in Asia—is the misrepresentation of intellectual property. Some suppliers may claim to be original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or hold proprietary technology when, in reality, they are reverse-engineering or copying designs protected by patents in other jurisdictions. Purchasing such equipment may expose buyers to legal liability, especially if the product is imported into countries with strict IP enforcement.
3. Lack of Genuine Technical Support and Documentation
Hand-held laser systems require proper installation, maintenance, and operator training. Suppliers offering inferior or counterfeit systems often provide incomplete or poorly translated technical documentation and limited after-sales support. This can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, and difficulty troubleshooting issues. Ensure the supplier offers comprehensive support, including software updates, spare parts availability, and accessible technical experts.
4. Non-Compliance with International Safety and Emission Standards
Many low-cost hand-held laser cutters fail to meet international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety or EMC regulations). Units lacking proper IP (Ingress Protection) ratings may also be unsuitable for industrial environments with dust or moisture. Using non-compliant equipment can result in workplace safety violations, insurance issues, or import bans. Always verify compliance with local regulatory requirements before purchase.
5. Hidden IP Infringement in Software and Control Systems
Beyond hardware, the embedded software and control systems (e.g., CNC interfaces, motion control algorithms) may infringe on third-party IP. Open-source code used without proper licensing or proprietary software cloned from competitors can lead to legal disputes. Buyers should request software licensing documentation and consider legal review when integrating systems into their operations.
6. Supply Chain Opacity and Component Traceability
Many suppliers source critical components (e.g., laser sources from IPG or Raycus) but do not disclose their origin. In some cases, counterfeit or used components are installed to reduce costs. This lack of transparency undermines system reliability and voids warranties. Demand full component traceability and verify authenticity through supplier documentation and serial number checks.
By addressing these common pitfalls—focusing on verifiable quality assurance and legitimate IP status—buyers can reduce risks and ensure a more reliable, compliant, and efficient integration of hand-held metal cutting lasers into their operations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hand Held Metal Cutting Laser
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
Hand Held Metal Cutting Lasers are high-powered industrial tools classified under laser radiation safety and electrical equipment regulations. They typically fall under Class 4 laser products due to their ability to cut metal, posing significant risks including fire, eye/skin injury, and electrical hazards. Compliance with international, regional, and national standards is essential for legal distribution and safe operation.
International Laser Safety Standards (IEC)
Compliance with IEC 60825-1 (“Safety of laser products – Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements”) is mandatory. Hand Held Metal Cutting Lasers are designated as Class 4 lasers, requiring strict safety measures such as emergency stop functions, key-controlled operation, beam shielding (where applicable), and clear warning labels. IEC 60825-14 (“Safety of laser products – Part 14: User’s guide”) provides operational safety guidance, including training and protective equipment protocols.
Regional Compliance Requirements
European Union (CE Marking)
Products sold in the EU must comply with the following directives:
– Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2014/35/EU: Ensures electrical safety.
– Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU: Prevents interference with other devices.
– Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC: Applies due to moving parts and laser integration; requires risk assessment and technical documentation.
– Laser Product Standard EN 60825-1: Harmonized standard under the Radio Equipment Directive (RED) and LVD.
CE marking requires a Declaration of Conformity, technical file, and involvement of a Notified Body if applicable.
United States (FDA/CDRH & OSHA)
- FDA/CDRH (Center for Devices and Radiological Health): Regulates lasers under 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11. Class 4 lasers must be registered, include proper labeling (e.g., “Danger – Invisible Laser Radiation”), have safety interlocks, and ship with an operational manual.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Enforces workplace safety under 29 CFR 1910.133 (eye protection) and 1910.97 (non-ionizing radiation). Employers must implement laser safety programs, provide training, and use engineering controls.
Other Regions
- Canada: Complies with ICES-001 (EMC) and the Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA); requires compliance with CSA C851.
- China: Requires CCC (China Compulsory Certification) for electrical safety and compliance with GB 7247.1 (laser safety).
- Australia/New Zealand: Must meet AS/NZS IEC 60825.1 and obtain RCM (Regulatory Compliance Mark).
Packaging, Labeling & Shipping Regulations
- Hazard Communication: Packages must display Class 4 laser warning labels, directional arrows, fragile handling symbols, and compliance marks (CE, FDA, etc.).
- UN/DOT Shipping Classification: Hand Held Metal Cutting Lasers may contain lithium batteries (if portable) or laser components regulated under UN 3481 (lithium batteries) or UN 2032 (internal combustion engines, if applicable). Proper documentation (SDS, Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods) is required for air and sea freight.
- Export Controls: Subject to dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation, U.S. EAR). Check if the laser’s power output exceeds thresholds requiring export licenses (e.g., >500W may trigger controls).
Import & Customs Clearance
- Provide accurate HS (Harmonized System) codes. Typical codes include:
- 8515.21: Laser welding, cutting or soldering machines.
- 9013.20: Other optical appliances and instruments (laser-based).
- Submit documentation: Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and conformity certificates (CE, FDA, etc.).
- Be aware of import duties and potential customs delays due to laser classification.
Operational Compliance & End-User Responsibilities
End users must:
– Conduct a site-specific laser safety assessment.
– Appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) where required (e.g., ANSI Z136.1 in the U.S.).
– Implement engineering controls (e.g., beam enclosures, interlocks) and administrative controls (e.g., restricted access, training).
– Provide appropriate PPE: Laser protective eyewear (OD-rated for specific wavelength), flame-resistant clothing, and face shields.
– Maintain service records and perform regular safety inspections.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive in the EU for end-of-life disposal.
- Laser optics and electronic components may contain hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium); dispose of per local environmental regulations.
- Return programs or certified recyclers should be used for responsible decommissioning.
Summary & Best Practices
Ensure compliance by:
– Verifying product conformity with IEC 60825-1 and regional standards.
– Preparing complete technical documentation and Declarations of Conformity.
– Training logistics partners on hazardous material handling (if applicable).
– Regularly monitoring regulatory updates in target markets.
– Providing end users with multilingual safety manuals and compliance certificates.
Conclusion:
Sourcing a handheld metal cutting laser requires careful evaluation of several key factors, including cutting power, precision, portability, safety features, ease of use, and after-sales support. As this technology continues to advance, handheld laser cutters offer increasing efficiency and flexibility for on-site and industrial applications, providing a strong alternative to traditional cutting methods. However, it is essential to select a reputable supplier offering reliable equipment that meets industry standards and safety regulations.
When making a decision, consider the specific needs of your operations—such as material thickness, desired cut quality, and working environment—while balancing upfront investment with long-term productivity gains. Proper training and maintenance are also critical to ensuring operational safety and maximizing the lifespan of the equipment.
Ultimately, sourcing a high-quality handheld metal cutting laser from a trusted provider can significantly enhance workflow efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve cutting accuracy, making it a valuable addition to modern metal fabrication processes.