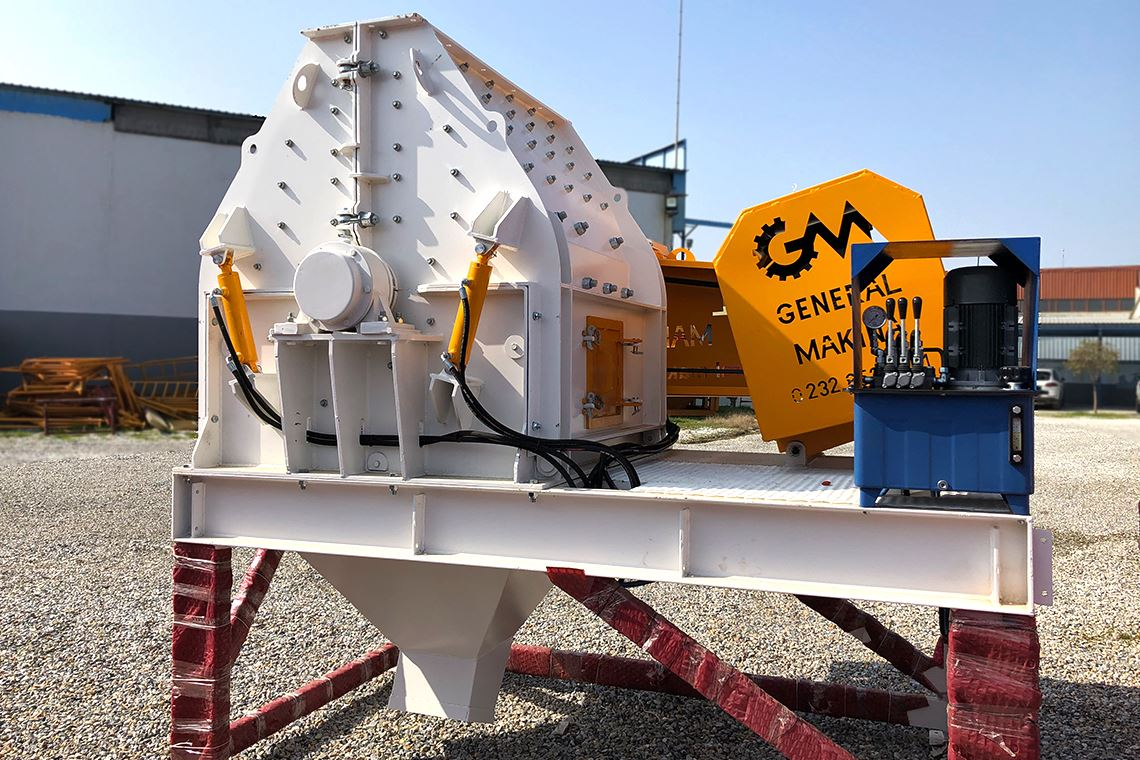
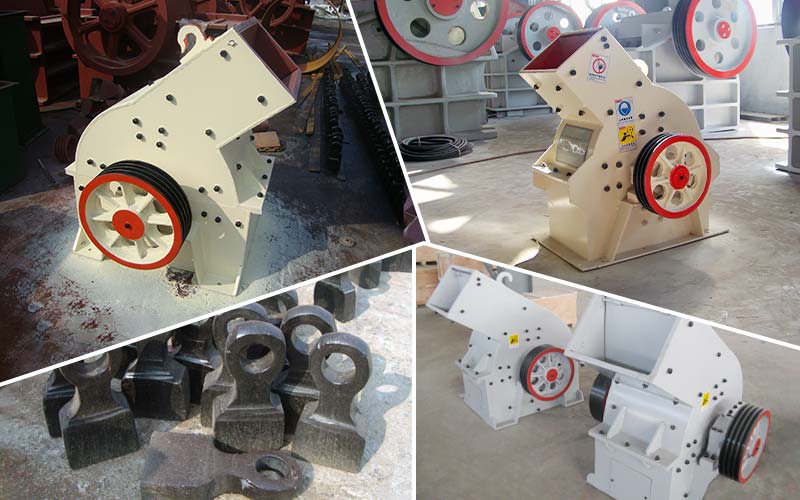
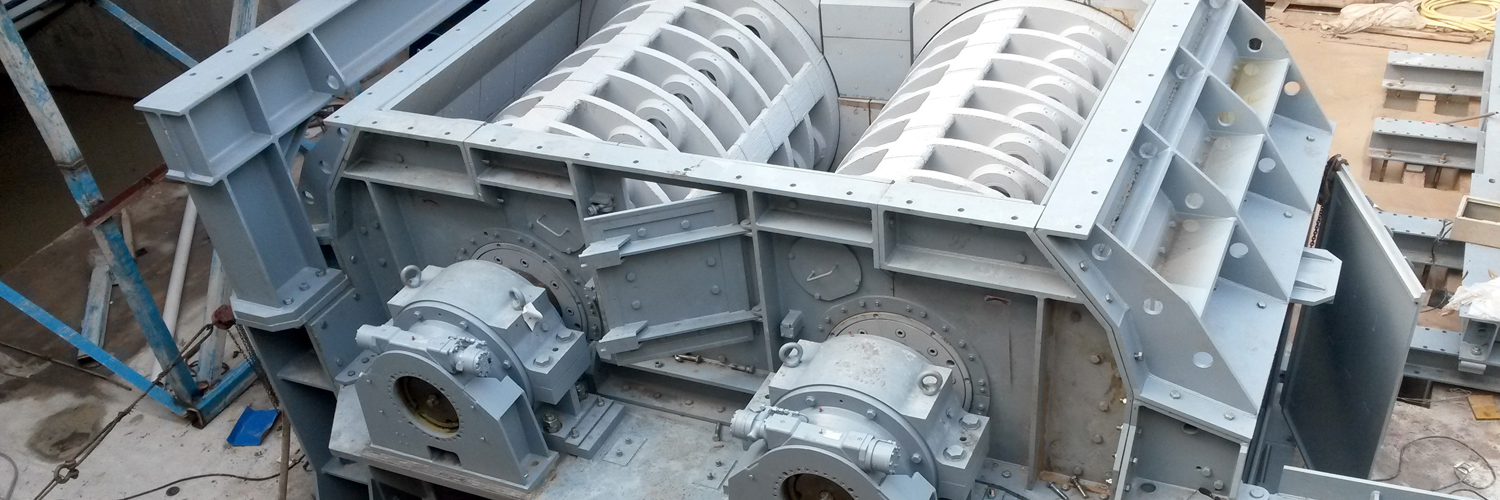
The global hammer crusher market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in mining, construction, and aggregate industries. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 4.2 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.1% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by increased infrastructure development in emerging economies, coupled with the need for efficient mineral processing technologies. As industries prioritize productivity and energy efficiency, manufacturers are innovating to deliver high-performance hammer crushers capable of handling diverse material types and operating conditions. The competitive landscape is led by established players with a strong global footprint, advanced R&D capabilities, and strategic partnerships. Based on market presence, technological innovation, production capacity, and customer feedback, we’ve compiled the top 10 hammer crusher manufacturers shaping the future of material crushing today.
Top 10 Hammer Crusher Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hammer Mills for Material Reduction
Domain Est. 1998
Website: williamscrusher.com
Key Highlights: Williams Patent Crusher is a leading hammer mill manufacturer. Our industrial size reduction machines can handle any material size reduction job….
#2 Industrial Hammer Mill Crushers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hammermills.com
Key Highlights: Our hammer mill crushers are perfect for efficient material size reduction while ensuring consistent performance and durability….
#3 Hammer Crushers Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2016
Website: minejxsc.com
Key Highlights: Hammer crusher is suitable for crushing limestone, bluestone, marl, sandstone, shale, gypsum, coal and other raw materials with compressive strength less than ……
#4 Hammermill Crushers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mclanahan.com
Key Highlights: The Centerfeed Hammermill is a secondary crusher designed to accept feed from a primary with controlled top size ranging from 3″ to 5″ (75mm to 125mm)….
#5 Crushers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metso.com
Key Highlights: All crusher types with 100+ years of experience. Metso crushers are fit for aggregates production, construction material recycling and mining operations….
#6 Hammer Mill Crushers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stedman-machine.com
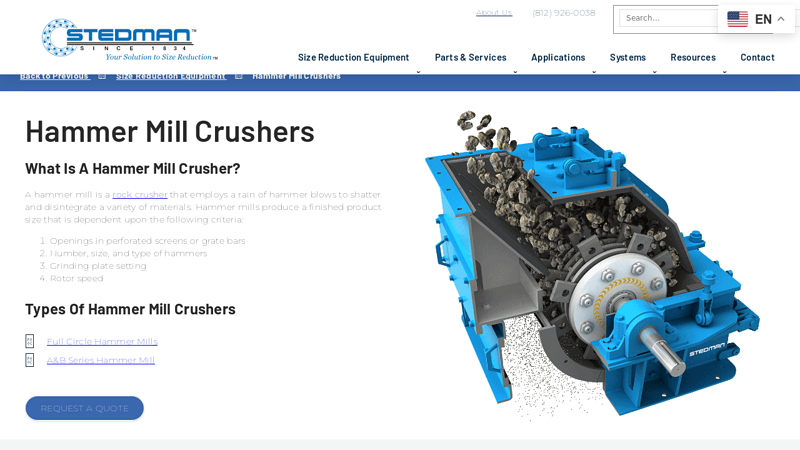
Key Highlights: Stedman offers Hammer Mills, a rock crusher that employs a rain of hammer blows to shatter and disintegrate a variety of materials. Contact us today for a ……
#7 HAMMER CRUSHER
Domain Est. 2000
Website: hazemag.com
Key Highlights: HAZEMAG Hammer Crushers used for primary crushing of soft to medium-hard rock with large feed size and high throughput rates….
#8 Hammer Crusher
Domain Est. 2014
Website: mekaglobal.com
Key Highlights: Hammer crushers are employed for the fine crushing of medium-hard to soft materials, such as anhydrite,quicklime, lignite, dolomite, gypsum,glass, potash, ……
#9 Portable Rock Crusher
Domain Est. 2016
Website: senyacrushers.com
Key Highlights: Senya Crushers specializes in manufacturing robust rock-crushing equipment for small to midsize organizations wanting to boost their business profitability….
#10 Hammer Crusher
Domain Est. 2022
Website: serviceportal.thyssenkrupp-polysius.com
Key Highlights: When the going gets tough, crushing systems from thyssenkrupp Polysius set standards worldwide in terms of performance, reliability and cost-effectiveness….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hammer Crusher

2026 Market Trends for Hammer Crusher
The global hammer crusher market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by shifting industrial demands, technological advancements, and sustainability imperatives. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Increasing Demand from Sustainable Construction and Recycling:
A major driver will be the surge in construction and demolition (C&D) waste recycling. As governments worldwide implement stricter waste disposal regulations and promote circular economy models, the need for efficient primary and secondary crushing of concrete, bricks, and asphalt will grow exponentially. Hammer crushers, valued for their ability to handle mixed, wet, or contaminated feed material effectively, are ideally suited for C&D recycling plants, positioning them for substantial market expansion in this sector.
2. Technological Advancements Focused on Efficiency and Intelligence:
Manufacturers will increasingly integrate smart technologies to enhance performance and reduce operational costs. Key developments by 2026 will include:
* Advanced Wear Parts: Widespread adoption of superior wear-resistant materials (e.g., specialized high-chrome cast iron, composite alloys) and optimized hammer designs (e.g., reversible, multi-edge hammers) to extend lifespan and reduce downtime.
* Predictive Maintenance and IoT Integration: Implementation of sensors monitoring vibration, temperature, and power consumption, feeding data to cloud-based platforms for predictive maintenance alerts, optimizing maintenance schedules and minimizing unplanned stoppages.
* Automated Control Systems: Enhanced PLC and SCADA systems enabling real-time optimization of rotor speed, feed rate, and gap settings based on material characteristics and desired output size, maximizing throughput and energy efficiency.
3. Rising Energy Efficiency and Emission Reduction Pressures:
Environmental regulations and operational cost concerns will push demand for more energy-efficient crushing solutions. Hammer crusher designs will focus on:
* Optimized Rotor Dynamics: Improved rotor balance, hammer trajectory, and chamber design to reduce energy consumption per ton crushed.
* Dust Suppression Integration: More sophisticated and effective dust collection systems (e.g., integrated spray bars, advanced baghouse filters) will become standard to comply with stringent air quality standards, particularly in urban recycling and mining operations.
* Noise Reduction: Enhanced enclosure designs and sound-dampening materials to mitigate operational noise, crucial for operations near residential areas.
4. Growth in Mining and Industrial Minerals Processing:
Beyond recycling, demand will be sustained by mining operations (particularly for softer ores like limestone, gypsum, coal, and phosphate) and industrial minerals processing. The need for cost-effective primary and secondary crushing in these sectors, especially in emerging economies with expanding infrastructure, will support market growth. Portable and mobile hammer crusher units will gain traction for their flexibility in remote or temporary mining sites.
5. Regional Market Diversification and Competitive Landscape:
* Asia-Pacific Dominance: The region, led by China, India, and Southeast Asian nations, will remain the largest market due to massive construction activities, urbanization, and industrial growth.
* Growth in Emerging Markets: Increased infrastructure investment in Africa, Latin America, and parts of Eastern Europe will create significant opportunities.
* Consolidation and Innovation: The competitive landscape will see consolidation among established players, while specialized manufacturers focusing on niche applications (e.g., biomass, specific waste streams) or advanced technology will gain market share through innovation.
In conclusion, the 2026 hammer crusher market will be characterized by a strong emphasis on sustainability (driven by recycling), technological sophistication (smart features, efficiency), and adaptation to diverse global demands, particularly in construction, mining, and waste management sectors. Manufacturers who invest in innovation, energy efficiency, and specialized solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these trends.
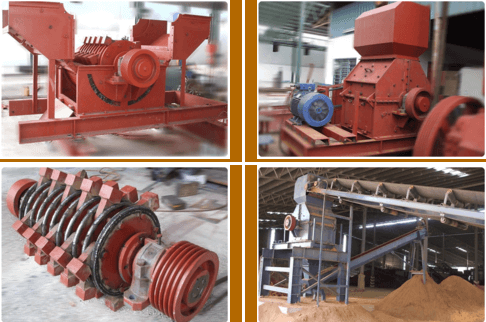
Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Hammer Crusher: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing a hammer crusher, especially from international suppliers, involves several risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Businesses must be vigilant to avoid these common pitfalls that can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal complications, and financial losses.
Poor Quality Control and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing hammer crushers is the variability in build quality. Some suppliers may use inferior materials for critical components such as hammers, rotors, and liners to reduce costs. This leads to premature wear, frequent breakdowns, and higher maintenance expenses. Buyers often discover discrepancies only after installation, when performance fails to meet specifications.
- Inadequate Testing: Suppliers may skip rigorous factory acceptance tests (FAT), resulting in undetected flaws.
- Lack of Certification: Absence of ISO, CE, or other quality certifications is a red flag.
- Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards: Especially with OEMs in regions with lax regulatory oversight.
Buyers should insist on material test reports (MTRs), third-party inspections, and pilot runs before full-scale procurement.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate crusher capacity, throughput, or energy efficiency to win contracts. This misleading information can result in mismatched equipment that underperforms in real-world conditions.
- Verify claims with independent engineering assessments.
- Request performance data from existing installations.
- Include penalty clauses for non-compliance in contracts.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
When sourcing hammer crushers, particularly from manufacturers in certain regions, there is a risk of inadvertently purchasing equipment that infringes on patented designs or technologies.
- Reverse-Engineered Designs: Some manufacturers replicate proprietary crusher mechanisms without licensing, exposing buyers to legal risks.
- Use of Counterfeit Components: Critical parts such as bearings or hydraulic systems may be counterfeit, voiding warranties and affecting reliability.
- Lack of IP Due Diligence: Buyers may unknowingly support or become liable for IP violations if the equipment uses protected technology.
To mitigate IP risks:
– Conduct supplier audits and request proof of design ownership or licensing agreements.
– Work with legal counsel to include IP indemnity clauses in procurement contracts.
– Prefer suppliers with a transparent innovation history and registered patents.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if the initial crusher meets quality standards, poor after-sales service can undermine long-term performance. Many low-cost suppliers fail to provide timely technical support or genuine spare parts.
- Spare parts may be unavailable or incompatible, leading to extended downtime.
- Lack of local service technicians increases reliance on costly international support.
Ensure service-level agreements (SLAs) are clearly defined and include spare parts inventory commitments.
Conclusion
Sourcing a hammer crusher requires more than just comparing prices. Due diligence on quality assurance processes and intellectual property compliance is essential to avoid costly setbacks. Engaging third-party inspectors, verifying technical documentation, and securing legal protections can safeguard both operational performance and legal integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hammer Crusher
Overview of Hammer Crusher Transport Requirements
Hammer crushers are heavy-duty industrial machines used in mining, quarrying, and recycling operations. Due to their weight, size, and mechanical components, transporting and installing them requires careful planning, adherence to international and local regulations, and strict compliance with safety standards. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements to ensure safe and legal shipment and deployment.
Packaging and Handling Specifications
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit. Hammer crushers should be secured on wooden skids or steel bases with anti-vibration mounts. All exposed surfaces, especially the rotor, hammers, and bearings, must be protected with corrosion-resistant coatings and waterproof wrapping. Moving parts should be immobilized using bracing or locking mechanisms. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators, and include handling instructions (e.g., forklift points, crane lifting zones).
Transportation Modes and Route Planning
Select the appropriate transportation method based on the crusher’s dimensions and weight:
– Road Transport: Use low-bed trailers or modular extendable trailers for oversized loads. Obtain special permits for overweight or over-dimensional cargo. Conduct route surveys to ensure bridges, tunnels, and roads can accommodate the load.
– Rail Transport: Suitable for long-distance domestic shipments. Confirm railcar weight and dimension limits and secure the unit to prevent shifting.
– Sea Freight: For international shipments, use flat-rack or open-top containers. Ensure compliance with IMDG (International Maritime Dangerous Goods) Code if lubricants or hydraulic fluids are present. Waterproof and salt-resistant packaging is essential.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Comply with all applicable regulations across origin, transit, and destination countries:
– Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and equipment conformity certificates (e.g., CE, ISO).
– Import/Export Controls: Verify if the hammer crusher or its components are subject to export restrictions or require licenses (e.g., under EAR or ITAR, if applicable).
– Safety Standards: Ensure the crusher meets regional safety directives such as OSHA (USA), Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC (EU), or local workplace safety regulations. Include safety guards, emergency stops, and warning labels as required.
Installation and Site Compliance
Upon arrival, verify site readiness:
– Ensure the foundation meets manufacturer specifications for load-bearing capacity and alignment.
– Confirm availability of required utilities (power supply, dust extraction, water cooling if applicable).
– Conduct a site risk assessment and implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during installation.
– Perform initial safety checks and operator training in accordance with local occupational health and safety laws.
Environmental and Waste Management Considerations
During transport and installation:
– Prevent oil or lubricant leaks by sealing hydraulic and lubrication systems.
– Dispose of packaging materials (wood, plastic, metal) in compliance with local environmental regulations.
– If decommissioning an old crusher, follow hazardous waste protocols for disposal of worn hammers, liners, or contaminated components.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain comprehensive records throughout the logistics chain:
– Equipment manuals, warranty documents, and compliance certificates.
– Transport logs, customs clearance records, and inspection reports.
– Proof of insurance coverage for transit and installation risks.
By adhering to this guide, stakeholders can ensure the safe, compliant, and efficient delivery and deployment of hammer crushers, minimizing delays, regulatory penalties, and safety incidents.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Hammer Crusher:
Sourcing a hammer crusher requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, supplier reliability, and total cost of ownership. It is essential to select a crusher that aligns with the material characteristics, desired output size, and production capacity to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Prioritizing reputable manufacturers with proven track records, strong after-sales support, and compliance with industry standards enhances equipment durability and minimizes operational downtime. Additionally, considering factors such as energy consumption, maintenance requirements, and spare parts availability contributes to long-term cost savings and process sustainability. By conducting thorough due diligence and engaging in strategic supplier partnerships, organizations can secure a hammer crusher that delivers consistent performance, operational reliability, and a strong return on investment.