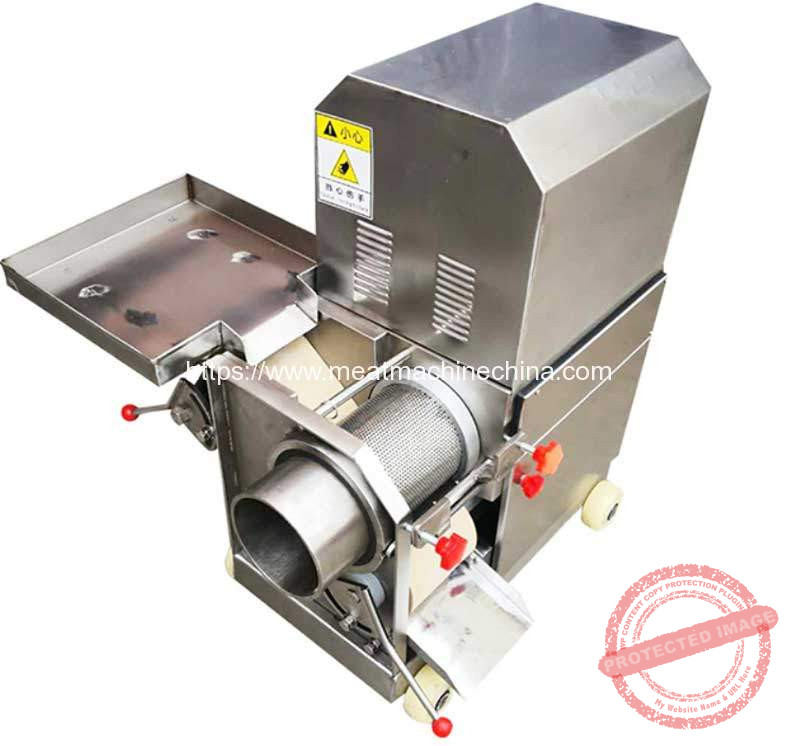
The global meat processing equipment market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for processed meat products, advancements in food processing technologies, and increasing automation in commercial and industrial meat production. According to Mordor Intelligence, the meat processing equipment market was valued at USD 28.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. A key segment within this market is heavy-duty grinders capable of processing both meat and bones—equipment essential for butcheries, meatpacking plants, and large-scale food manufacturers. These grinders combine robust motor power, durable construction, and precision engineering to handle high-volume, continuous operations. As demand for hygienic, efficient, and versatile meat grinding solutions grows, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and performance. Based on market presence, product capabilities, and technological advancements, the following eight manufacturers represent the top players in the meat and bone grinder industry.
Top 8 Grinder For Meat And Bones Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Heavy Duty Meat Mincer Grinders
Domain Est. 2016
Website: cmmachineservices.net
Key Highlights: CM Machine Services offers meat mincers, beef grinders also known as meat grinders, for the application of grinding up the raw material such as meat, fish, beef ……
#2 Meat Crushers
Domain Est. 2020
Website: tg-machines.com
Key Highlights: Industrial crushers are used for crushing fatty tissue, pork, sheep, beef, offal, and bones from meat and poultry slaughterhouses….
#3 Grinders
Domain Est. 1996
Website: marel.com
Key Highlights: Marel’s flexible, comprehensive range of grinders is manufactured to handle extremely high capacities of poultry meat….
#4 Speco
Domain Est. 1996
Website: speco.com
Key Highlights: From meat grinder plates and knives to bone collector systems and insert blades, we manufacture and supply the highest quality products in the industry….
#5 Commercial Meat Grinder
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mpbs.com
Key Highlights: Commercial Meat Grinder is a machine used to force meat or meat trimmings by means of a feeding worm (auger) under pressure through a horizontally mounted ……
#6 Weiler Commercial Food Grinders and Mixers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: provisur.com
Key Highlights: Our Weiler line includes a wide range of mixing, grinding and material handling solutions for meat, poultry, seafood, pet food and rendering….
#7 Meat Grinders for Kitchen & Food Prep
Domain Est. 2021
Website: hakkabros.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsHakka electric meat grinders for grinding meat, fillings, and food prep. Built for kitchens, restaurants, and sausage making….
#8 Grinding & Separating
Website: vemag.de
Key Highlights: The Separation Grinder982 grinds the product to final particle size. The Separator 813 simultaneously separates bone particles, rinds, cartilage and sinews. The ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Grinder For Meat And Bones
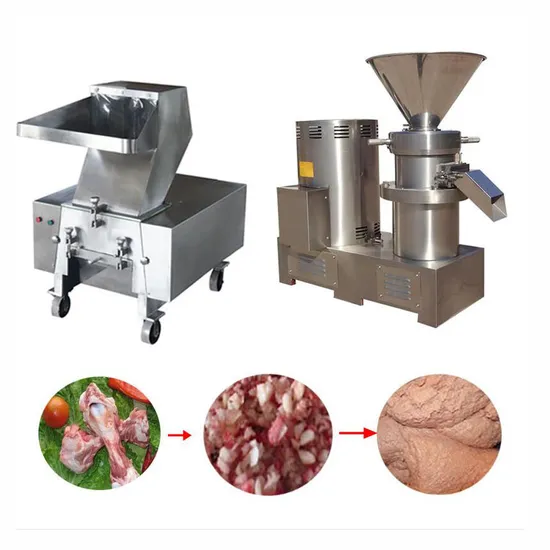

2026 Market Trends for Grinder for Meat and Bones
The market for grinders designed specifically for meat and bones is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by shifting consumer preferences, technological innovation, and expanding applications. Key trends shaping the industry include:
Rising Demand for Home Butchery and Whole-Animal Utilization
Growing consumer interest in sustainable food practices, nose-to-tail eating, and transparency in meat sourcing is fueling a surge in home meat processing. By 2026, more households are expected to invest in high-capacity, durable grinders capable of handling bones and connective tissue. This trend is supported by the popularity of farm-to-table movements, DIY food culture, and increased availability of whole animal shares from local farms.
Expansion of the Pet Food and Raw Feeding Market
The burgeoning demand for homemade and raw pet diets is a major driver for bone grinders. Pet owners seeking control over ingredients are using grinders to create custom raw meals incorporating ground bone for calcium and texture. As awareness of pet nutrition grows, manufacturers are responding with compact, pet-safe models designed for frequent residential use.
Advancements in Motor Power and Durability
By 2026, grinders are expected to feature more powerful motors (1,500+ watts), improved gear systems, and hardened steel components capable of efficiently processing dense bones like beef femurs and pork knuckles. Innovations in overheating protection and torque efficiency will enhance reliability, particularly for commercial and heavy-duty home users.
Commercial Adoption in Small-Scale Butcher Shops and Restaurants
Small-batch butchers, charcuterie producers, and farm-to-table restaurants are increasingly adopting bone grinders to create specialty products like bone broths, custom sausages, and house-ground meats. The trend supports waste reduction and product differentiation, positioning grinders as essential equipment in artisanal meat operations.
Integration of Smart Features and Ergonomic Design
Emerging models may incorporate smart technology such as variable speed control via app integration, automatic reverse functions to prevent jamming, and modular components for easier cleaning. Ergonomic improvements—lighter weight, quieter operation, and easy disassembly—will enhance user experience, particularly in residential kitchens.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction Focus
As food waste becomes a critical concern, grinders enable users to utilize animal by-products that would otherwise be discarded. This aligns with circular economy principles, especially in both home and commercial kitchens aiming to minimize environmental impact.
Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Europe lead in demand due to strong DIY and pet nutrition trends, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to grow by 2026. Urbanization, rising middle-class incomes, and increasing interest in Western-style meat preparation will drive adoption in these regions.
Overall, the grinder for meat and bones market in 2026 will reflect a convergence of health consciousness, sustainability, and technological progress—positioning these devices as essential tools across both home and professional culinary landscapes.
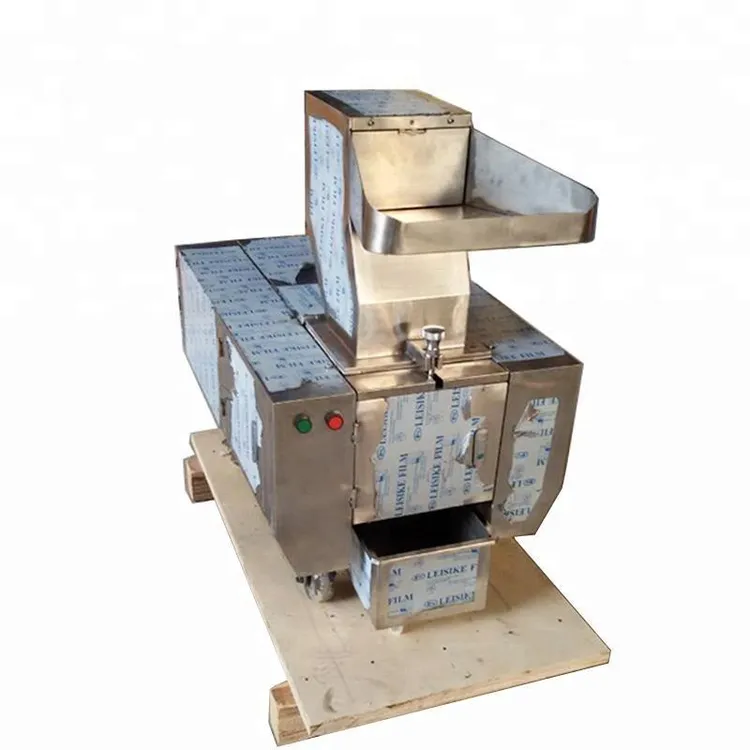

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Grinder for Meat and Bones (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing a grinder for meat and bones—especially for industrial or commercial use—requires careful evaluation to ensure both product quality and protection of intellectual property (IP). Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Build Quality
Choosing a low-cost grinder without assessing material durability can lead to frequent breakdowns. Grinders must handle tough materials like bones, which require hardened steel components and robust motors. Inadequate build quality results in contamination risks, downtime, and higher long-term costs.
2. Ignoring Motor Power and Duty Cycle
Underpowered motors or those not rated for continuous operation can overheat or fail under heavy loads. For bone grinding, motors should be industrial-grade with sufficient torque and thermal protection. Verify the duty cycle to ensure it matches your operational demands.
3. Overlooking Certification and Food Safety Standards
Grinders must comply with food safety regulations (e.g., FDA, CE, or ISO 22000). Equipment lacking proper certifications may introduce contamination risks or fail health inspections, impacting business operations and compliance.
4. Failing to Verify IP and Design Authenticity
Some suppliers offer “replica” or reverse-engineered grinders that infringe on patented designs. Using such equipment may expose your business to legal liability. Always confirm that the manufacturer holds valid IP rights or licenses for the design and technology used.
5. Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality grinders require maintenance. Sourcing from suppliers without reliable technical support or spare parts availability leads to prolonged downtime. Ensure the supplier offers service networks and component longevity.
6. Not Assessing Customization and Scalability
Off-the-shelf models may not meet specific throughput or hygiene requirements. Avoid vendors who cannot provide customizable solutions or scalable designs. This limits future expansion and process optimization.
7. Overlooking Noise, Safety, and Ergonomic Features
Industrial grinders can be hazardous if not properly designed. Missing safety interlocks, excessive noise levels, or poor ergonomics increase workplace risks and may violate OSHA or local safety standards.
8. Neglecting Supplier Transparency on IP and Manufacturing Origin
Some manufacturers obscure the origin of components or use third-party designs without disclosure. Request documentation on IP ownership, manufacturing location, and component sourcing to mitigate legal and quality risks.
By addressing these pitfalls, businesses can source reliable, compliant, and legally sound meat and bone grinders that support efficient and sustainable operations.
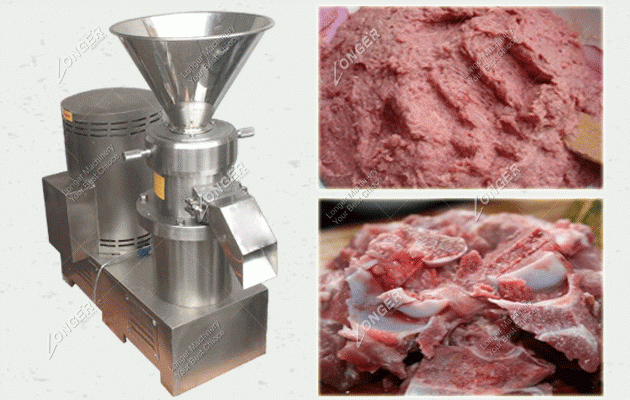
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Grinder For Meat And Bones
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations when importing, exporting, distributing, or selling a Grinder For Meat And Bones. Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, product safety, and smooth supply chain operations.
Regulatory Compliance
Food-Grade Equipment Standards
Grinders used for meat and bones must meet food safety standards to prevent contamination. In the United States, equipment should comply with FDA 21 CFR regulations for food-contact surfaces. Materials like stainless steel (typically 304 or 316 grade) must be corrosion-resistant and non-toxic.
CE Marking (European Union)
For sale in the EU, the grinder must carry the CE mark, indicating compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and the EU’s Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on materials and articles intended to come into contact with food.
Electrical Safety Certifications
If the grinder is electric-powered, it must meet electrical safety standards such as UL (USA), CSA (Canada), or IEC/EN 60335 (international). These certifications ensure safe operation and protection against electrical hazards.
Sanitation and Cleanability Requirements
Equipment must be designed for easy disassembly and cleaning to prevent bacterial growth. Compliance with 3-A Sanitary Standards (common in dairy and meat processing) may be required for commercial use.
Import/Export Regulations
Harmonized System (HS) Code Classification
Correctly classify the product using the HS Code for accurate customs declaration. Typical codes include:
– 8437.80 – Machinery for cleaning, sorting, or grading seed, grain, or dried leguminous vegetables (may apply if grinder is multi-use)
– 8438.20 – Machinery for mincing, homogenizing, or mixing foodstuffs (often used for meat grinders)
Confirm with local customs authorities for precise classification.
Import Duties and Tariffs
Import duties vary by country. Check with the destination country’s customs authority for applicable tariffs. Some countries may offer reduced rates under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU free trade deals).
Documentation Requirements
Ensure all shipments include:
– Commercial invoice
– Packing list
– Bill of lading or air waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Product compliance certificates (e.g., CE, FDA, UL)
– Sanitation or food-safety compliance statement (if required)
Product Labeling and Packaging
Mandatory Labeling
Labels must include:
– Manufacturer name and address
– Model and serial number
– Voltage and power requirements
– Safety warnings and usage instructions
– Compliance marks (e.g., CE, UL, EAC)
Language Requirements
In non-English markets (e.g., France, Germany, Japan), user manuals and safety labels must be provided in the local language.
Packaging Standards
Use durable, tamper-evident packaging suitable for international shipping. Include protective materials to prevent damage during transit. Clearly mark packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Invert”).
Transportation and Handling
Shipping Methods
Choose shipping mode based on urgency and volume:
– Air freight: Faster but more expensive; ideal for samples or urgent orders
– Sea freight: Cost-effective for bulk shipments; requires longer lead times
– Ground transport: Suitable for domestic or regional distribution
Temperature and Environmental Controls
While the grinder itself is not temperature-sensitive, ensure storage and transport avoid extreme humidity or corrosive environments, especially for long-term warehousing.
Handling and Storage
Store grinders in dry, clean areas to prevent rust or contamination. Use pallets and stretch wrap for secure stacking. Follow first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory practices.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Pre-Shipment Inspection
Conduct quality checks before dispatch to verify:
– Correct model and accessories included
– Functionality and safety compliance
– Absence of manufacturing defects
Serial Number Tracking
Maintain a traceability system using serial numbers to track units through the supply chain. This supports warranty claims, recalls, and compliance audits.
Recalls and Non-Compliance Response
Establish a recall protocol in case of safety issues or regulatory non-compliance. Notify relevant authorities (e.g., FDA, EU Rapid Alert System) and customers promptly.
After-Sales Support and Warranty
Warranty Compliance
Offer a warranty that meets regional legal requirements (e.g., 2 years in the EU under consumer law). Clearly state warranty terms in local language.
Spare Parts and Service Network
Ensure availability of spare parts (e.g., blades, augers, gaskets) and access to repair services in target markets. Partner with local distributors or service centers if necessary.
Conclusion
Adhering to logistics and compliance standards for a Grinder For Meat And Bones ensures market access, consumer safety, and legal protection. Always consult local regulatory bodies and customs experts to stay updated on evolving requirements.
Conclusion:
After evaluating various options for sourcing a grinder capable of processing both meat and bones, it is clear that durability, power, and ease of cleaning are critical factors in making the right choice. Industrial-grade grinders with high horsepower, stainless steel construction, and interchangeable plates offer the best performance for heavy-duty applications. Models specifically designed to handle bones—such as those with augers and blades built to withstand hard materials—ensure consistent results and longer equipment life.
Considering cost, availability, and maintenance requirements, it is recommended to source from reputable suppliers with proven track records in food processing equipment. Whether opting for a commercial standalone unit or a heavy-duty attachment for existing machinery, investing in a high-quality grinder will enhance efficiency, ensure food safety, and reduce long-term operational costs.
Ultimately, the selected grinder should align with the scale of production, types of ingredients processed, and hygiene standards required. Proper training for operators and routine maintenance will further maximize performance and longevity. Based on these criteria, a well-informed sourcing decision will support consistent product quality and operational success in meat and bone processing.