The global stone processing machinery market, driven by rising construction and infrastructure development, continues to expand at a steady pace. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the granite sawing machine market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by increasing demand for precision-cut natural stone in residential and commercial applications. Complementing this, Grand View Research valued the global stone machinery market at USD 2.1 billion in 2022, with ongoing urbanization and architectural preferences for durable, aesthetically pleasing materials like granite serving as key growth accelerants. As the industry evolves with automation and CNC technology, manufacturers of granite saws are at the forefront of innovation, delivering high-efficiency solutions that meet stringent quality standards. In this data-backed landscape, the following nine companies have emerged as leaders, combining technological expertise, global reach, and proven performance to shape the future of stone cutting.
Top 9 Granite Saw Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
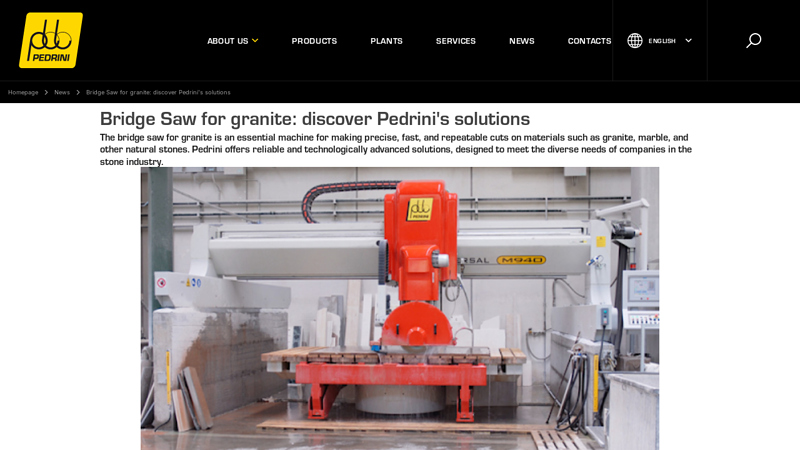
#1 Bridge Saw for granite
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pedrini.it
Key Highlights: Pedrini offers two models of bridge saws for granite, designed to ensure maximum precision and productivity: Universal M940 and Lux M920. Universal M940: ……
#2 Large Stone Fabrication Equipment: Bridge Saws …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: granquartz.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $350 90-day returnsGranQuartz offers a wide range of machinery and equipment solutions for stone fabricators. We’ve got you covered with bridge saws, miter saws,…
#3 Macchine CNC per Lavorazione e Taglio Pietra
Domain Est. 2000
Website: prussiani.com
Key Highlights: Prussiani Engineering designs and builds high quality numerical control machines for working marble, granite, stone, artificial quartz and porcelain….
#4 Saws
Domain Est. 2010
Website: poseidonmachinery.com
Key Highlights: Poseidon Industries manufactures industry-leading CNC bridge saws that perform hyper-precise sawing and profiling of granite and stone slabs….
#5 USA Granite Tools
Domain Est. 2014
Website: usagranitetools.com
Key Highlights: 4-day delivery 30-day returnsUSA Granite Tools is your trusted source for high-quality stone fabrication tools. Shop oremium equipment with fast shipping, expert support….
#6 SASSO USA
Domain Est. 2015
Website: sassousa.com
Key Highlights: SASSO USA builds 5-axis CNC bridge saws, sawjets and polishers for granite, quartz and porcelain. We help stone shops cut faster, reduce labor and grow ……
#7 Crownstone
Domain Est. 2019
Website: crownstoneusa.com
Key Highlights: Discover premium bridge saws, edge polishers & water recycling systems built by fabricators for fabricators. Made in USA with proven reliability….
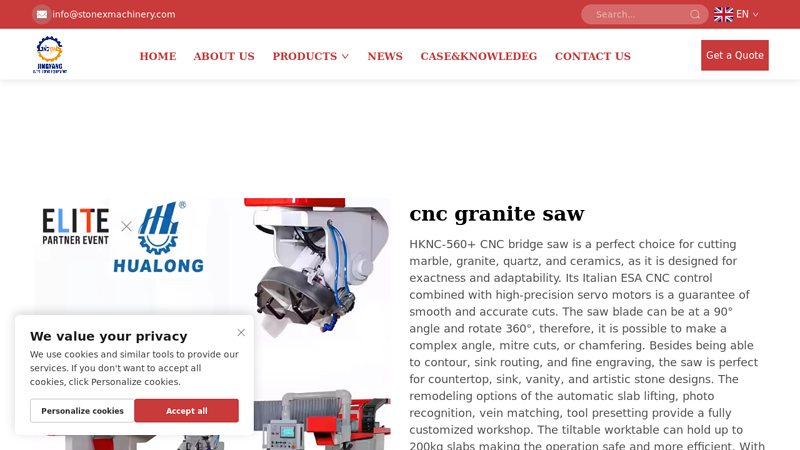
#8 cnc granite saw
Website: stonemachinerypro.com
Key Highlights: HKNC-560+ CNC bridge saw is a perfect choice for cutting marble, granite, quartz, and ceramics, as it is designed for exactness and ……
#9 A Guide to BACA’s Granite Cutting Machines
Domain Est. 2013
Website: bacasystems.com
Key Highlights: Explore the features of BACA Systems’ granite saw machines to see how you can increase productivity, reduce labor, and increase material yield….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Granite Saw
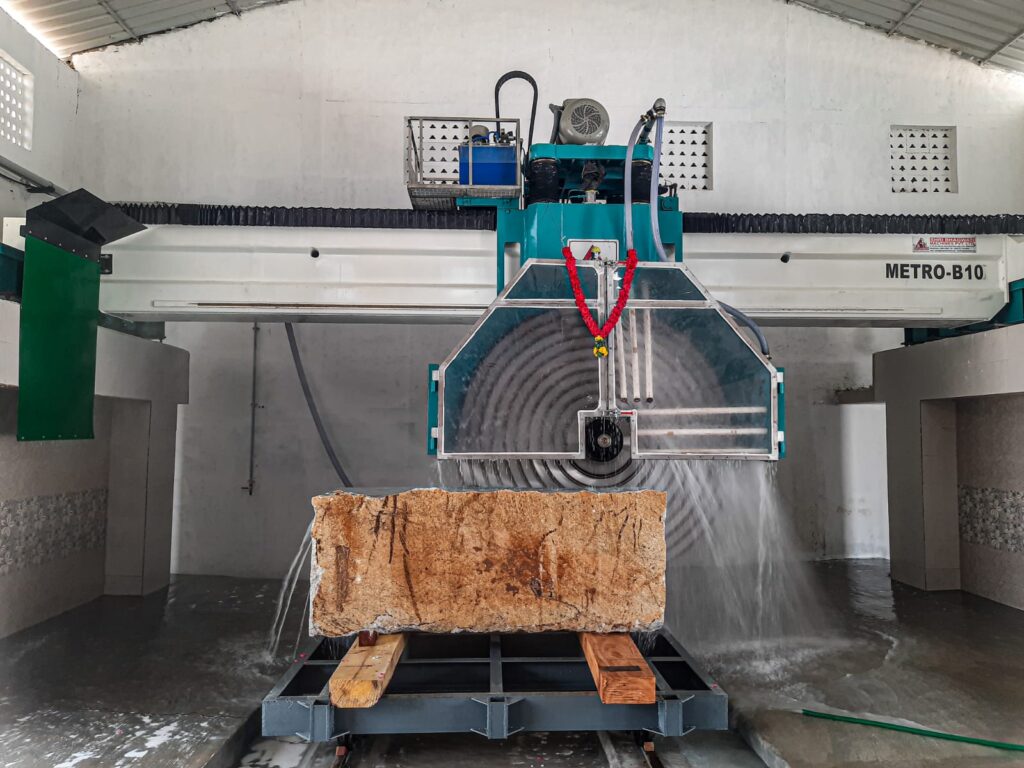

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Granite Saws
As the global construction and stone fabrication industries evolve, the granite saw market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and shifting regional dynamics, several key trends are expected to shape the landscape for granite saws in the mid-term future.
1. Technological Advancements and Automation Integration
By 2026, automation and smart manufacturing will play a central role in the granite saw industry. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, AI-driven diagnostics, and CNC-controlled cutting systems into saws to improve precision, reduce waste, and increase operational efficiency. Automated loading/unloading systems paired with robotic arms are likely to become standard in mid- to high-end granite processing facilities, especially in Europe and North America.
2. Rising Demand in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies in Southeast Asia, India, and the Middle East are expected to drive market growth. Rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and an expanding middle class are fueling demand for natural stone in residential and commercial construction. Countries like Vietnam, Turkey, and Egypt—already major players in granite processing—are investing in modern sawing equipment, boosting demand for advanced granite saws.
3. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient granite saws with reduced water and diamond blade consumption. By 2026, water recycling systems and dry-cutting technologies are expected to gain traction, particularly in water-scarce regions. Additionally, blade longevity and recyclability will become key selling points, aligning with circular economy principles.
4. Shift Toward Multi-Material Capability
Granite saws are increasingly being designed to cut a variety of materials—including quartz, marble, and engineered stone—allowing fabricators to diversify offerings without investing in multiple machines. This trend toward versatility is particularly relevant as consumer preferences shift toward hybrid and engineered surfaces.
5. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The market is likely to see increased consolidation among equipment manufacturers, with larger firms acquiring niche technology providers to enhance their product portfolios. Strategic partnerships between saw manufacturers and software developers will also grow, enabling seamless integration of design-to-production workflows through cloud-based platforms.
6. Impact of Alternative Materials and Market Saturation
Despite growth, the granite saw market may face headwinds due to competition from engineered stone and composite materials, which are easier to cut and require less maintenance. In mature markets like Western Europe and North America, slower construction growth and market saturation could limit expansion, pushing companies to focus on retrofitting and after-sales service.
Conclusion
By 2026, the granite saw market will be characterized by smarter, more efficient, and environmentally conscious machinery. While growth will be strongest in developing regions, innovation and service differentiation will be critical in mature markets. Companies that invest in automation, sustainability, and multifunctional capabilities will be best positioned to capture value in the evolving stone fabrication ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Granite Saw (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a granite saw—especially from international or unfamiliar suppliers—can present several challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure a reliable, legal, and cost-effective procurement process.
Poor Build Quality and Material Standards
One of the most frequent issues is receiving granite saws constructed with substandard materials or poor workmanship. Low-cost manufacturers may use inferior steel, weak motors, or inadequate safety features, leading to premature breakdowns, inconsistent cutting performance, and potential safety hazards. This can result in higher long-term costs due to downtime, repairs, and replacement.
Inaccurate Performance Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key performance metrics such as cutting depth, blade speed, or power efficiency. Without independent verification or third-party testing reports, buyers risk acquiring equipment that fails to meet project requirements. This misalignment can disrupt production timelines and increase operational inefficiencies.
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Environmental Regulations
Granite saws must comply with regional safety standards (e.g., CE in Europe, OSHA in the U.S.). Some imported models may not meet these requirements, putting buyers at legal and operational risk. Non-compliant equipment could be seized at customs, banned from use on job sites, or lead to liability in the event of injury.
Counterfeit or Clone Equipment
Some suppliers offer granite saws that closely mimic well-known branded models but are unauthorized copies. These clones may infringe on patents, trademarks, or design rights. Purchasing such equipment can expose the buyer to legal complications, especially if the product is later found to violate intellectual property laws in their jurisdiction.
Infringement of Intellectual Property (IP)
Using or importing a granite saw that incorporates patented technologies—such as unique blade cooling systems, dust extraction mechanisms, or motor designs—without proper licensing can lead to IP infringement claims. Buyers may face lawsuits, product recalls, or fines, particularly if the equipment is sold or used commercially in IP-sensitive markets.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Low-cost suppliers, especially those based overseas, may offer limited technical support, training, or spare parts access. When a critical component fails, the delay in obtaining replacements can halt operations for days or weeks, undermining the initial cost savings.
Misleading Warranty Terms
Warranties offered with cheaper granite saws may appear comprehensive but contain restrictive clauses—such as voiding coverage for use with certain blade types or requiring service by certified technicians who are unavailable locally. This can render the warranty effectively useless when needed most.
Solutions and Best Practices
To mitigate these risks:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site visits or third-party audits.
– Request certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, UL) and verify technical specifications.
– Consult legal experts to assess IP risks, particularly when sourcing from regions with lax enforcement.
– Prioritize suppliers with established service networks and transparent warranty policies.
– Use contracts that clearly define quality standards, delivery terms, and IP indemnification clauses.
Avoiding these common pitfalls ensures you source a granite saw that is not only high-performing and durable but also legally compliant and protected from IP exposure.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Granite Saw
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations when transporting, handling, and operating granite saws, whether for import/export, domestic distribution, or on-site usage. Adhering to these standards ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance
International Trade Regulations
When shipping granite saws across borders, compliance with international trade laws is critical. This includes adherence to export control regulations such as the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) in the U.S. or equivalent frameworks in other countries. Verify if the equipment falls under controlled categories due to motor power, automation features, or dual-use potential.
Customs Documentation
Ensure accurate preparation of shipping documents including commercial invoices, packing lists, bill of lading/airway bill, and certificates of origin. Classify the granite saw correctly under the Harmonized System (HS Code)—typically under 8467.21 or similar codes for powered saws.
Safety and Electrical Standards
Granite saws must comply with regional safety standards such as:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliant with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Low Voltage Directive.
– UL/CSA Certification (North America): Required for electrical safety.
– CCC Mark (China): Mandatory for electrical products entering China.
Verify compliance before shipment to avoid customs delays or rejection.
Transportation & Handling
Packaging Requirements
Granite saws must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use wooden crates or reinforced pallets with corner protectors and waterproof wrapping. Include shock and tilt indicators for high-value or sensitive models.
Freight Mode Selection
Choose the appropriate transportation mode based on distance, urgency, and equipment size:
– Air Freight: Suitable for urgent, high-value, or smaller units.
– Sea Freight: Cost-effective for bulk shipments; use FCL (Full Container Load) or LCL (Less than Container Load).
– Road Transport: Ideal for domestic or regional delivery; ensure proper securing in flatbed or enclosed trailers.
Load Securing and Weight Distribution
Ensure the saw is firmly anchored during transit using straps, braces, or blocking. Confirm that weight limits for vehicles and containers are not exceeded, especially with heavy industrial models.
Import & Export Procedures
Import Duties and Taxes
Calculate applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on the destination country’s tariff schedule. Leverage free trade agreements if eligible to reduce duty costs.
Restricted Components
Check for restrictions on components such as blades (especially diamond-tipped), coolants, or motors with high power ratings. Some countries regulate or tax these items separately.
Environmental Compliance
Ensure the granite saw and its accessories comply with environmental regulations, including:
– REACH and RoHS (EU): Restriction of hazardous substances.
– Proposition 65 (California): Warning requirements for equipment emitting dust or chemicals.
On-Site Compliance and Safety
Workplace Safety Standards
Follow OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent local regulations for operating granite saws. Required measures include:
– Use of personal protective equipment (PPE): goggles, gloves, hearing protection, and respirators.
– Dust control systems to minimize silica exposure.
– Emergency stop mechanisms and machine guarding.
Equipment Registration and Inspection
Some jurisdictions require industrial machinery to be registered or inspected before operation. Maintain logs for routine maintenance and safety checks.
Training and Certification
Operators must be trained in safe handling, emergency procedures, and machine-specific protocols. Certification may be required in certain regions or job sites.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records including:
– Equipment manuals and safety data sheets (SDS) for coolants.
– Proof of compliance with electrical and safety standards.
– Maintenance logs and inspection reports.
– Import/export licenses and customs clearance documents.
Retain these documents for audits, warranty claims, or incident investigations.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and compliance management are essential for the safe and legal distribution and operation of granite saws. By following international regulations, ensuring proper handling, and maintaining accurate documentation, businesses can mitigate risks, avoid penalties, and ensure smooth operations across the supply chain.
In conclusion, sourcing a granite saw requires careful consideration of factors such as cutting capacity, blade quality, power source (electric, pneumatic, or manual), durability, and intended application—whether for industrial quarrying, fabrication, or on-site construction work. Evaluating suppliers based on reputation, certifications, warranty offerings, and after-sales support ensures reliability and long-term performance. Additionally, prioritizing safety features and compliance with industry standards is essential for operational efficiency and worker protection. By conducting thorough research and comparing options based on technical specifications and cost-effectiveness, businesses can source a granite saw that meets their production needs while ensuring precision, durability, and return on investment.