The global gold manufacturing industry continues to expand, driven by rising consumer demand for jewelry, increasing investment in bullion, and growing industrial applications in electronics and healthcare. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global gold market was valued at approximately USD 187 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is underpinned by expanding middle-class populations in Asia-Pacific, particularly in India and China, which remain the largest consumers of gold jewelry. Additionally, market volatility and geopolitical uncertainties have reinforced gold’s status as a safe-haven asset, boosting demand for refined gold products. As the industry evolves, top gold manufacturers are leveraging advanced refining technologies, sustainable sourcing practices, and digital distribution to strengthen their market positions. The following list highlights the ten leading gold manufacturing companies shaping this dynamic landscape through scale, innovation, and global reach.
Top 10 Gold Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Stuller: Fine Jewelry Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stuller.com
Key Highlights: Stuller, Inc. is the #1 supplier of fine jewelry, findings, mountings, tools, packaging, diamonds & gemstones for today’s retail jeweler….
#2 Nagosa Jewelry
Domain Est. 2020
Website: nagosajewelry.com
Key Highlights: Discover 925 silver jewelry wholesale, gold-plated jewelry manufacturing & wholesale supply at Nagosa Jewelry. OEM/ODM Service Available….
#3 Eldorado Gold
Domain Est. 1997
Website: eldoradogold.com
Key Highlights: Eldorado Gold is a gold and base metals producer with mining, development and exploration operations in Türkiye, Canada and Greece….
#4 A
Domain Est. 1996
Website: amark.com
Key Highlights: A-Mark’s Wholesale Sales division distributes and purchases precious metal products from sovereign and private mints….
#5 PAMP
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pamp.com
Key Highlights: Our brand, collections, craftsmanship, sustainability. Our collections: quality, innovation, artistry, sustainability….
#6 Italpreziosi
Domain Est. 1997
Website: italpreziosi.it
Key Highlights: Italpreziosi is a world leader across the precious-metals supply chain—especially gold and silver—providing always up-to-date, reliable price quotations….
#7 Wholesale Gold Jewelry Suppliers and Distributors
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rcjewelry.com
Key Highlights: RC Jewelry is a leading supplier of high-quality gold chains for retailers, boutique owners, and dropshippers. Our diverse selection includes elegant, durable, ……
#8 About the American Precious Metals Exchange
Domain Est. 2004
Website: apmex.com
Key Highlights: Not only does APMEX have a direct relationship to resell US Mint Gold and Silver, we offer a vast selection of Precious Metals with high quality and speedy ……
#9 U.S. Gold Bureau: Buy Gold Bars
Domain Est. 2005
Website: usgoldbureau.com
Key Highlights: Leading dealer of investment-quality gold bars and gold coins from the U.S. Mint and other suppliers on our website. Get free shipping & portfolio advice….
#10 YXPM Group
Domain Est. 2021
Website: yxgroup.com.my
Key Highlights: YXPM is a Malaysia-based investment holding company. The Company, through its subsidiaries, is involved in the wholesaling, design and manufacturing of gold ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Gold

H2 2026 Gold Market Outlook: Resilience Amid Shifting Fundamentals
As we look ahead to the second half of 2026, the gold market is expected to navigate a complex landscape shaped by evolving macroeconomic conditions, central bank policies, and geopolitical dynamics. While short-term volatility is likely, the underlying structural drivers point towards continued resilience and potential for price appreciation, albeit potentially at a more measured pace than seen in previous bull runs.
Key Drivers Shaping H2 2026:
-
Monetary Policy Pivot & Interest Rates:
- The Primary Catalyst: The trajectory of global monetary policy, particularly by the U.S. Federal Reserve, remains the dominant factor. By H2 2026, markets anticipate that major central banks (Fed, ECB) will likely be in a phase of holding rates steady or potentially initiating cautious cuts, assuming inflation has moderated closer to target levels (e.g., 2-2.5%).
- Impact on Gold: This environment is generally positive for gold. Lower real interest rates (nominal rates minus inflation) reduce the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding gold. Even expectations of future rate cuts can bolster gold prices. However, the pace and magnitude of any easing will be critical. A slower-than-expected easing cycle could cap gains, while aggressive cuts could provide a significant tailwind.
-
Persistent Inflation & Currency Debasement Fears:
- Despite expected moderation, structural inflationary pressures (supply chain reconfiguration, climate transition costs, demographics) are likely to persist. Gold’s role as a long-term hedge against currency debasement and loss of purchasing power will remain a core demand driver, particularly for institutional investors and central banks.
-
Central Bank Demand: Diversification Continues:
- The trend of central banks, especially in emerging markets (e.g., China, India, Middle East, Turkey), diversifying reserves away from the U.S. dollar is expected to continue into H2 2026. Geopolitical fragmentation and concerns about the weaponization of financial systems provide a strong rationale for official gold buying. This demand acts as a significant structural floor for prices.
-
Geopolitical Tensions & Safe-Haven Flows:
- Ongoing conflicts (e.g., Ukraine, Middle East), U.S.-China strategic competition, and potential election-related uncertainties in key regions could trigger risk-off sentiment. Gold remains a premier safe-haven asset during periods of heightened uncertainty, providing downside protection and potential upside spikes during crises.
-
Jewelry & Industrial Demand:
- Demand from traditional centers like India and China will be sensitive to local economic conditions and price levels. While high prices can dampen physical demand, cultural significance and wealth preservation motives often support consumption. Industrial and technological demand (electronics, dentistry) is expected to grow steadily but is a smaller component of overall demand.
-
Investor Sentiment & ETF Flows:
- Investor appetite, reflected in gold-backed ETF holdings, will be closely tied to the macro narrative. A shift towards risk-off sentiment or confirmation of a sustained rate-cutting cycle could see significant inflows. Conversely, strong risk-on markets and a lack of rate cuts could lead to outflows, creating headwinds.
H2 2026 Price Outlook & Risks:
- Base Case Scenario (Moderate Upside): Assuming a stable geopolitical environment, inflation trending towards target, and central banks beginning a gradual easing cycle, gold is likely to trade within a range of $2,200 to $2,500 per ounce by the end of 2026. This reflects a continuation of the bull market, supported by lower real rates and central bank buying, but tempered by potential profit-taking and competition from other assets if equities perform well.
- Upside Catalysts:
- Faster-than-expected central bank rate cuts.
- A significant resurgence in inflation (“sticky inflation” proving persistent).
- A major geopolitical shock or financial market stress event.
- Accelerated, coordinated central bank buying.
- A weaker U.S. dollar.
- Downside Risks:
- Central banks maintaining higher-for-longer rates due to stubborn inflation.
- A strong resurgence in risk-on sentiment (e.g., booming equities, strong economic growth).
- A significant strengthening of the U.S. dollar.
- Technical selling pressure if key support levels break.
- A sharp decline in physical demand due to very high prices.
Conclusion:
H2 2026 is poised to be a pivotal period for gold. The market is likely transitioning from a phase driven primarily by inflation and rate cut expectations to one influenced by the reality of monetary policy actions and the persistence of structural drivers. While volatility will persist, the confluence of anticipated lower real interest rates, sustained central bank demand, and ongoing geopolitical risks provides a strong foundation for gold’s resilience. Investors should expect a market sensitive to central bank communication but underpinned by long-term themes of currency diversification and financial uncertainty. Gold is expected to remain a core component of diversified portfolios, potentially achieving new nominal highs by year-end under favorable conditions, but facing headwinds if the economic outlook shifts decisively towards robust growth and sustained high rates.
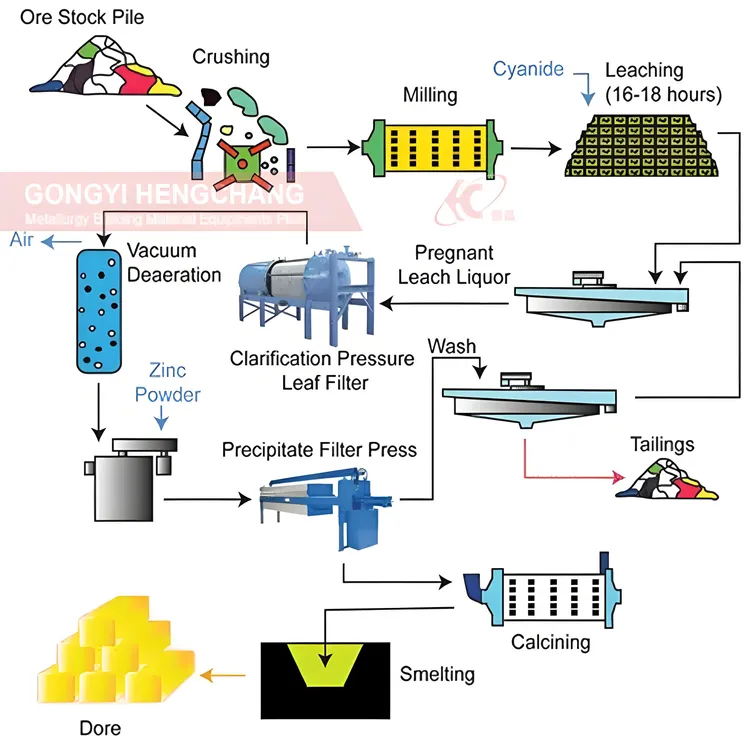
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Gold: Quality and Intellectual Property Issues
Sourcing gold, whether for jewelry, electronics, or investment, involves navigating a complex supply chain fraught with risks related to both material quality and intellectual property (IP). Failure to address these pitfalls can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, legal disputes, and regulatory non-compliance. Below are key challenges to be aware of in each category.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Purity Misrepresentation
One of the most common issues is receiving gold that does not meet the stated purity (e.g., advertised as 24K but actually 18K or lower). Unscrupulous suppliers may provide falsified assay certificates or mix lower-grade metals into the final product.
2. Counterfeit or Tainted Materials
Fake gold bars or plated items can enter the supply chain, especially when dealing with intermediaries or informal markets. Additionally, gold may be contaminated with other metals during refining, compromising its integrity for high-precision applications like electronics.
3. Inconsistent Refining Standards
Suppliers may use different refining processes that result in variable quality. Without adherence to international standards (e.g., LBMA accreditation), buyers risk receiving gold with impurities or inconsistent characteristics.
4. Lack of Traceability and Certification
Without proper documentation—such as Certificates of Authenticity, assay reports, or chain-of-custody records—verifying the origin and quality of gold becomes difficult. This increases the risk of receiving substandard or conflict-sourced material.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Trademarks or Hallmarks
Some suppliers may counterfeit well-known hallmarks (e.g., “999.9” or brand-specific stamps) to falsely indicate quality or origin. Using such materials can expose buyers to legal liability for trademark infringement.
2. Copying of Design Elements in Jewelry
When sourcing custom gold jewelry, designs may be based on or directly copied from protected IP. Buyers risk infringement claims if the manufacturer reproduces copyrighted or patented designs without proper licensing.
3. Third-Party IP in Manufacturing Processes
Advanced refining or fabrication techniques may be protected by patents. Sourcing gold processed using such methods without authorization can lead to indirect IP violations, especially in industrial applications.
4. Misappropriation of Trade Secrets
Sharing proprietary specifications or designs with suppliers increases the risk of trade secret exposure, especially if proper non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are not in place or enforced.
Mitigation Strategies
- Verify Supplier Credentials: Work only with certified, reputable suppliers (e.g., LBMA-accredited refiners).
- Demand Independent Assay Testing: Conduct third-party verification of gold purity and composition.
- Audit the Supply Chain: Ensure traceability from mine to final product, particularly for ethical and quality compliance.
- Conduct IP Due Diligence: Review design rights, trademarks, and patents before production; require suppliers to warrant IP compliance.
- Use Legal Safeguards: Implement strong contracts, NDAs, and IP indemnification clauses with suppliers.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP risks, businesses can protect their interests, maintain product integrity, and avoid costly legal and operational setbacks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Gold
Moving gold across borders or within supply chains involves complex logistics and stringent compliance requirements due to its high value, susceptibility to theft, and regulatory scrutiny. This guide outlines key considerations for the secure and legal transportation and handling of gold.
Regulatory Compliance
Gold is subject to numerous international, national, and regional regulations designed to prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and illegal trade. Compliance is essential at every stage of the supply chain.
-
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations: Most jurisdictions require businesses dealing in gold (dealers, refiners, importers/exporters) to register with financial intelligence units and implement AML programs. This includes customer due diligence (CDD), beneficial ownership verification, and reporting of suspicious transactions.
-
Know Your Customer (KYC) Requirements: Gold traders must verify the identity of their customers and maintain records of transactions, especially for high-value purchases (often above $10,000 or local equivalent).
-
Export/Import Controls: Many countries regulate the export and import of gold. Exporters may need licenses or permits, and declarations must accurately state the quantity, purity, and value of gold. Non-compliance can result in seizure and penalties.
-
Customs Declarations: Accurate Harmonized System (HS) code classification (e.g., 7108 for unwrought gold) is crucial. Misdeclaration can lead to delays, fines, or confiscation.
-
Conflict Minerals & Due Diligence: While gold is not always classified under conflict minerals frameworks like the Dodd-Frank Act (which focuses on 3TG), responsible sourcing standards (e.g., OECD Due Diligence Guidance) apply. Companies must ensure gold is not sourced from conflict-affected or high-risk areas.
Transportation & Logistics
The physical movement of gold requires specialized handling to ensure security, integrity, and traceability.
-
Secure Packaging: Gold should be sealed in tamper-evident containers, often with unique serial numbers and barcodes. Weight, purity, and assay certificates should accompany each shipment.
-
Insured Transport: All gold shipments must be fully insured against loss, theft, or damage. Insurance policies should cover the full replacement value and specify coverage during transit and storage.
-
Armored Transport & Courier Services: Use only vetted, professional logistics providers experienced in high-value goods. Armored vehicles and GPS-tracked, monitored shipments are standard.
-
Chain of Custody: Maintain a documented chain of custody from origin to destination. Each handover should be recorded with timestamps, signatures, and verification of contents.
-
Storage Security: During transit layovers or final storage, gold must be held in high-security vaults compliant with standards such as ISO 22301 (Business Continuity) or local regulatory requirements (e.g., LBMA Good Delivery vault standards).
Reporting & Documentation
Proper documentation ensures compliance and traceability.
-
Commercial Invoice: Must include seller/buyer details, description of goods, weight, fineness, value, and terms of sale (e.g., Incoterms®).
-
Packing List: Details packaging, container numbers, and gross/net weights.
-
Certificate of Origin: May be required by customs authorities to determine tariff eligibility.
-
Assay Certificate: Provides proof of gold purity and is essential for LBMA-approved bars.
-
Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Serves as a contract of carriage and receipt of goods.
-
Regulatory Filings: Submit required reports (e.g., FinCEN Form 8300 in the U.S. for cash transactions over $10,000) and electronic export information (EEI) via systems like AES (Automated Export System).
Industry Standards & Best Practices
-
LBMA Good Delivery List: For wholesale transactions, use only bars produced by refiners on the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) Good Delivery List. These meet strict quality and integrity standards.
-
Responsible Gold Guidance: Follow the Responsible Gold Guidance (RGG) by the LBMA, which sets environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria for gold sourcing and refining.
-
Audits & Record Retention: Maintain records for a minimum of 5–7 years (depending on jurisdiction). Regular internal and external audits help ensure ongoing compliance.
Risk Mitigation
-
Due Diligence on Partners: Vet all suppliers, buyers, and logistics providers for compliance history and reputational risk.
-
Cybersecurity: Protect digital records and transaction systems from breaches, especially when handling sensitive financial and customer data.
-
Contingency Planning: Have emergency protocols for theft, natural disasters, or geopolitical disruptions affecting supply chains.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, businesses can ensure the lawful, secure, and efficient handling of gold while minimizing regulatory and operational risks.
In conclusion, sourcing gold suppliers requires a strategic and diligent approach that balances quality, reliability, cost, and ethical considerations. It is essential to conduct thorough due diligence by verifying supplier credentials, certifications (such as LBMA or Fairmined), and traceability of the gold supply chain to ensure compliance with international standards. Building strong relationships with reputable suppliers, assessing geographic and logistical factors, and regularly evaluating performance contribute to long-term supply chain stability. Additionally, prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing not only mitigates reputational and regulatory risks but also aligns with growing consumer and investor demands for responsible practices. Ultimately, a well-vetted and diversified supplier base enhances operational efficiency, supports business integrity, and strengthens competitive advantage in the gold market.