The global epoxy resin market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, construction, aerospace, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global epoxy resin market size was valued at USD 11.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the material’s superior adhesive strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making epoxy resins a preferred choice for high-performance applications. Additionally, increasing investments in infrastructure development and the growing adoption of lightweight materials in vehicle manufacturing are further accelerating market expansion. As demand rises, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, production capacity, and product reliability. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and global reach, the following list highlights the top 10 glue epoxy resin manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Glue Epoxy Resin Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 EpoxySet, Inc.
Domain Est. 2014
Website: epoxysetinc.com
Key Highlights: Epoxyset is a trusted manufacturer of epoxy, urethane, and silicone compounds for electronics, medical, and industrial applications. · Engineered Adhesives….
#2 Wholesale Epoxy Resin Adhesive Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2013
Website: atcepoxy.com
Key Highlights: Adhesives Technology Corporation is a top manufacturer of wholesale epoxy resin adhesives and more. Learn more about our wholesale adhesives….
#3 • Gougeon Brothers, Inc.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: gougeon.com
Key Highlights: Gougeon Brothers, Inc. is the employee-owned, family-run company that manufactures Entropy Resins®, PRO-SET® Epoxy, and WEST SYSTEM® Epoxy….
#4 Epoxy.com Chemical Resistant Floors Coatings Bonding Resins …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: epoxy.com
Key Highlights: We offer time proven epoxy resin and other similar 2-component resin systems. We offer the latest materials, with the most advanced technology….
#5 Cotronics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cotronics.com
Key Highlights: Cotronics manufactures and distributes high temp adhesives, epoxies, ceramics, putties, sealants, conductive and insulating adhesives, insulation materials….
#6 E
Domain Est. 2012
Website: e-chem.net
Key Highlights: E-Chem is an adhesives manufacturer specializing in the design, development, marketing and supply of epoxy polymer products. Call now: (505) 832-3667….
#7 Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: westsystem.com
Key Highlights: WEST SYSTEM Epoxy is a versatile, high-quality, two-part epoxy that is easily modified for a wide range of coating and adhesive applications….
#8 Advanced Materials
Domain Est. 1997
Website: huntsman.com
Key Highlights: Huntsman has more than 50 years’ experience of combining design materials, composite resins and adhesives in a variety of applications for sports and leisure….
#9 Powerful Liquid Epoxy Resins
Domain Est. 2015
Website: olinepoxy.com
Key Highlights: Explore our line of High-Performance Coatings Resins and Curing Agents that offer the performance you need, backed by the local customer support Only Olin ……
#10 Frontpage
Domain Est. 2022
Website: westlakeepoxy.com
Key Highlights: Coatings & Composites. We have been enabling progress through development of innovative epoxy resin systems for more than 75 years….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Glue Epoxy Resin
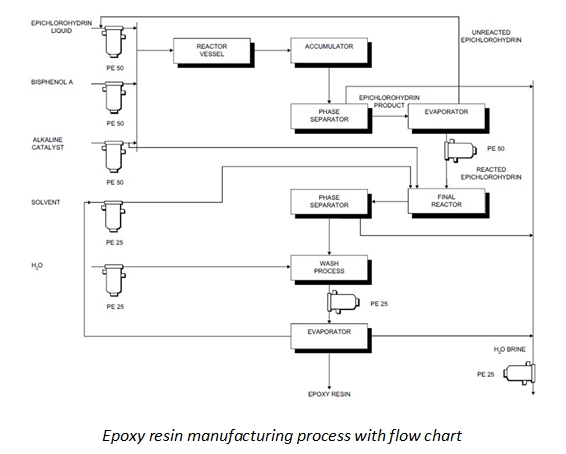
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Epoxy Resin: Growth, Innovation, and Strategic Shifts
The global epoxy resin market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and increasing regulatory and environmental pressures. Here’s a comprehensive analysis of the key trends shaping the market:
1. Sustained Market Growth Driven by Key End-Use Industries:
* Wind Energy Boom: The dominant driver. Global push for renewable energy, particularly offshore wind farms requiring longer, more durable turbine blades, will massively increase demand for high-performance epoxy resins (especially in infusion processes). This sector alone is expected to account for a substantial portion of market growth.
* Electronics & Electrical Insulation: Miniaturization of electronics, growth in electric vehicles (EVs), and expansion of 5G infrastructure will fuel demand for epoxies used in encapsulants, underfills, printed circuit boards (PCBs), and insulating coatings due to their excellent electrical properties and reliability.
* Automotive Lightweighting: While competition from polyurethanes and polyesters exists, epoxy resins remain crucial for high-strength composite parts (e.g., structural components, battery enclosures in EVs) and high-performance adhesives enabling the use of mixed materials (aluminum, composites, steel).
* Construction & Infrastructure: Growing infrastructure development, especially in emerging economies, and the need for durable, corrosion-resistant repair materials (e.g., flooring, concrete protection, rebar coatings) will sustain demand for epoxy systems.
2. Intensifying Focus on Sustainability and Bio-based Alternatives:
* Regulatory Pressure: Stricter global regulations (e.g., REACH, EPA guidelines) targeting BPA (Bisphenol A) and reducing VOC emissions will accelerate the shift towards BPA-free epoxy resins and low-VOC/high-solids formulations.
* Bio-based Resins: Development and commercialization of epoxies derived from renewable resources (e.g., plant oils like linseed or soy, lignin, cardanol) will gain significant traction. While performance parity and cost remain challenges, demand from eco-conscious industries (especially consumer goods, some automotive, and construction) will push innovation and scale, improving economics by 2026.
* Recyclability & Circular Economy: Growing R&D focus on recyclable thermoset epoxies (e.g., vitrimers, chemically recyclable networks) and improved recycling methods for epoxy composites (e.g., solvolysis, pyrolysis) will emerge as critical areas, driven by end-of-life concerns, particularly in wind turbine blades.
3. Technological Advancements and Performance Enhancement:
* Toughened & Flexible Epoxies: Demand for epoxies with improved impact resistance, flexibility, and crack resistance without sacrificing adhesion or thermal stability will grow, especially for automotive, aerospace, and demanding electronic applications.
* Faster Curing Systems: Development of epoxies with faster cure times (e.g., via novel catalysts, photoinitiation) will be crucial for high-volume manufacturing processes (e.g., automotive, electronics assembly) to improve efficiency.
* Nanotechnology Integration: Incorporation of nanomaterials (e.g., graphene, carbon nanotubes, nano-silica) to create epoxies with enhanced mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, electrical properties, or barrier performance for specialized applications.
* Smart/Functional Epoxies: Increased R&D into epoxies with self-healing capabilities, sensing properties, or stimuli-responsiveness for next-generation applications.
4. Supply Chain Dynamics and Geopolitical Factors:
* Raw Material Volatility: The market will remain sensitive to fluctuations in the prices of key feedstocks like epichlorohydrin and BPA (or their bio-based equivalents), influenced by crude oil prices, production capacity, and geopolitical events (e.g., in major producing regions like Asia).
* Regional Shifts: Asia-Pacific (especially China, India, and Southeast Asia) will remain the largest market and production hub, driven by manufacturing growth. However, nearshoring/reshoring trends in North America and Europe for critical supply chains (e.g., electronics, aerospace, wind energy) may lead to increased regional production capacity investments.
* Consolidation & Vertical Integration: Continued consolidation among major producers and increased vertical integration (e.g., resin producers sourcing bio-based feedstocks) are likely to shape the competitive landscape.
5. Competitive Landscape and Innovation:
* Innovation as Key Differentiator: Competition will intensify, with companies differentiating through proprietary formulations (bio-based, BPA-free, high-performance), technical service, and application expertise.
* Focus on Niche Applications: Growth will be particularly strong in high-value, specialized segments like aerospace composites, semiconductor packaging, and advanced adhesives for EVs, requiring tailored solutions.
* Digitalization: Increased use of digital tools for formulation design, process optimization, and predictive maintenance in production.
Conclusion for 2026:
By 2026, the epoxy resin market will be characterized by robust growth, primarily fueled by wind energy and electronics, but fundamentally transformed by the imperative for sustainability. Success will depend on a company’s ability to innovate rapidly, particularly in developing high-performance, environmentally friendly resins (bio-based, BPA-free, recyclable). While traditional applications remain vital, the future lies in advanced materials enabling renewable energy, electrification, and sustainable manufacturing. Companies that proactively address raw material challenges, navigate geopolitical complexities, and invest in next-generation technologies will be best positioned to thrive.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Glue Epoxy Resin (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing glue epoxy resin requires careful evaluation to avoid compromising on performance, compliance, and legal integrity. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to production failures, safety risks, and legal exposure. Below are the most common pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Batch Performance
One of the most frequent issues is inconsistent resin quality across batches. Low-cost or unverified suppliers may lack rigorous quality assurance processes, leading to variations in viscosity, curing time, strength, and thermal resistance. This inconsistency can disrupt manufacturing, compromise product reliability, and increase waste. Always request material test reports (MTRs) and conduct incoming quality inspections to verify specifications.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate or falsify performance data—such as tensile strength, glass transition temperature (Tg), or pot life—to win business. Relying on unverified datasheets without third-party testing can result in resin that fails under real-world conditions. Validate claims through independent testing or trusted certifications (e.g., UL, ISO, REACH).
Use of Substandard or Recycled Raw Materials
To cut costs, certain manufacturers dilute epoxy formulations with fillers or use recycled or off-spec epichlorohydrin and bisphenol-A. These substitutions degrade adhesive performance and long-term durability. Ensure suppliers disclose raw material sources and adhere to industry-grade standards.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Inadequate batch traceability increases risk during quality audits or failure investigations. Suppliers should provide full documentation, including Certificates of Conformance (CoC), Safety Data Sheets (SDS), and batch-specific test results. Missing or vague documentation is a red flag for poor quality systems.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing epoxy resin from unauthorized or counterfeit suppliers may expose your company to IP violations. Some manufacturers reverse-engineer patented formulations or falsely brand generic resins as equivalent to proprietary products (e.g., mimicking知名品牌 like Hexion or Huntsman). Using such resins can lead to legal disputes, product recalls, or reputational damage.
Insufficient Regulatory Compliance
Epoxy resins must comply with regional regulations (e.g., FDA for food contact, RoHS/REACH for electronics, TSCA in the U.S.). Non-compliant resins may contain restricted substances like BPA (in certain applications) or hazardous solvents. Verify that the supplier provides compliance documentation relevant to your end-use.
Inadequate Technical Support and Transparency
Reliable suppliers offer technical data, application guidance, and troubleshooting support. Choosing a supplier with limited technical engagement can lead to improper handling, curing issues, or adhesion failures. Transparent communication about formulation changes is also essential to maintain process consistency.
Overlooking Supply Chain Stability
Dependence on a single or geopolitically vulnerable supplier can disrupt production. Assess the supplier’s production capacity, raw material sourcing, and contingency planning. Sudden changes in supply can force rushed qualification of alternative resins, increasing quality risks.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: audit suppliers, validate technical claims, ensure IP legitimacy, and prioritize long-term reliability over initial cost savings.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Glue Epoxy Resin
Classification and Hazard Identification
Glue epoxy resin is typically classified as a hazardous material due to its chemical composition. It often falls under UN 1866, “Resin solution, flammable,” or similar classifications depending on formulation. Most epoxy resins are classified as flammable liquids (Class 3) under the UN Globally Harmonized System (GHS), with potential health hazards including skin and eye irritation, respiratory sensitization, and possible long-term toxicity. Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the specific product to determine accurate classification.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Packages must be compatible with epoxy resin and securely sealed to prevent leaks. Use UN-certified packaging rated for flammable liquids. Outer packaging should be rigid and protect inner containers during transit. Proper labeling is mandatory: include the UN number, proper shipping name, hazard class (e.g., Class 3 Flammable Liquid), GHS pictograms (flame, health hazard, exclamation mark), hazard statements (e.g., H226, H317), and supplier information. Ensure labels are durable and affixed clearly on all sides of the package.
Transport Regulations (Air, Sea, and Land)
For air transport (IATA DGR), epoxy resin may be restricted or require special provisions depending on flash point and quantity. Most formulations are forbidden on passenger aircraft and limited on cargo aircraft. For sea freight (IMDG Code), classify according to packing group (usually II or III) and follow stowage and segregation rules. On land (ADR for Europe, 49 CFR for USA), drivers must have appropriate training, vehicles may require placarding, and documentation must accompany shipments. Always verify regulations based on transport mode and region.
Storage Conditions and Handling
Store epoxy resin in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and ignition hazards. Keep containers tightly closed when not in use. Use only non-sparking tools and grounded equipment during handling to prevent static discharge. Avoid contact with skin and eyes; use appropriate PPE including gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection if vapor exposure is possible. Segregate from oxidizers, acids, and amines.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and Documentation
Ensure a current, jurisdiction-compliant SDS is available for each epoxy resin product. The SDS must accompany shipments and be accessible to handlers, emergency responders, and receiving personnel. Required shipping documents include a dangerous goods declaration (for regulated shipments), packing list, and commercial invoice with accurate product description and hazard classification. Maintain records for traceability and regulatory audits.
Emergency Response and Spill Management
In case of spill or leak, evacuate non-essential personnel and eliminate ignition sources. Use absorbent materials (e.g., spill kits with inert absorbents) to contain and collect spilled resin. Do not use sawdust or combustible materials if the resin is flammable. Wear full PPE during cleanup. For skin contact, wash with soap and water; for eye exposure, flush with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention. Report spills per local environmental regulations. Keep spill kits and fire extinguishers (e.g., CO2 or dry chemical) accessible in storage and handling areas.
Regulatory Compliance and Training
Ensure compliance with relevant regulations such as OSHA (USA), REACH and CLP (EU), WHMIS (Canada), and other local chemical safety laws. Personnel involved in handling, packaging, or transporting epoxy resin must receive hazardous materials training specific to the product and transport mode, updated regularly (typically every 1–3 years). Maintain training records and conduct periodic compliance audits to verify adherence to safety and legal requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Epoxy Resin Adhesive:
Sourcing epoxy resin adhesive requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and technical compatibility with specific application requirements. After evaluating potential suppliers, assessing product specifications, and considering factors such as curing time, viscosity, temperature resistance, and environmental impact, it is clear that selecting the right epoxy resin goes beyond price alone. Establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers who provide consistent quality, technical support, and compliance with industry standards ensures long-term performance and reliability in end-use applications.
Additionally, considering supply chain resilience, lead times, and scalability is essential to avoid production delays and to support future growth. By conducting thorough due diligence and prioritizing both performance and supplier reliability, organizations can secure a dependable source of epoxy resin that meets technical needs while optimizing cost-efficiency and operational continuity. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy enhances product quality, reduces risk, and supports sustainable manufacturing practices.