The global glassware polisher market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for precision-finished glass products in industries such as optics, semiconductors, automotive, and consumer electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global glass machining and polishing market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in manufacturing technologies, increased automation, and the need for high-surface-quality glass in emerging applications like augmented reality (AR) devices and electric vehicle displays. With the Asia Pacific region leading in both production and consumption due to rapid industrialization and expanding electronics manufacturing, the competitive landscape has seen a surge in innovation among glassware polisher manufacturers. In this evolving market, identifying the top players who combine engineering excellence, technological innovation, and global reach becomes essential for businesses seeking reliable and high-performance polishing solutions.
Top 10 Glassware Polisher Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CMS Glass Machinery
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cmsmachine.com
Key Highlights: We are glass machine manufacturer with 30 years of experience producing glass cutting machines, glass washing machines, glass washing lines, insulated glass ……
#2 Manufacturer machinery maintenance glass moulds plungers neck …
Domain Est. 2002
Website: sonicam.com
Key Highlights: SONICAM offers a complete range of top-of-the-range professional machines and equipment for cleaning and polishing moulds and glass accessories….
#3 Bar Maid
Domain Est. 2009
Website: bestinthebar.com
Key Highlights: Bar Maid Corporation is America’s leading manufacturer of 5-brush portable electric glass washers as well as glass washer detergent, sanitizers and test strips….
#4 Industrial Glass Polishing Machines Supplier
Domain Est. 2021
Website: matodigroup.com
Key Highlights: Discover top-quality glass polishing machines at Matodi. We offer tailored solutions and comprehensive support for all your flat glass edging needs….
#5 Sanding and polishing glass and other transparent surfaces
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mirka.com
Key Highlights: Glass sanding and glass polishing is a cost-effective alternative to glass replacement. Instead of replacing damaged glass and other transparent surfaces ……
#6 Samuel’s Glass Company: Glass Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: samuelsglass.com
Key Highlights: For all your commercial, home, and auto glass needs contact Samuel’s Glass Company in San Antonio, TX. Call (210) 227-2481….
#7 SV1000 Glass Polishers
Domain Est. 2000
Website: frucosol.com
Key Highlights: A machine for drying and polishing glasses and cups that will finish with the hard job of the manual drying….
#8 Campus Products Inc
Domain Est. 2006
Website: cpishine.com
Key Highlights: Discover our Essential Equipment Collection, featuring SilverShine Cutlery Dryers and StemShine Glass Polishers. Designed to enhance efficiency and reduce labor ……
#9 Glass Polishers Information
Domain Est. 2018
Website: glasspolishersglobal.com
Key Highlights: Our Global Range of Glass Polishing Systems are effective, safe and simple to operate. Our polishers are fitted with either 5 or 8 polishing brushes….
#10 About Us
Domain Est. 2020
Website: theclear360.com
Key Highlights: This group of entrepreneurs developed and perfected the Clear360° and built a rock-solid company to support global demand….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Glassware Polisher
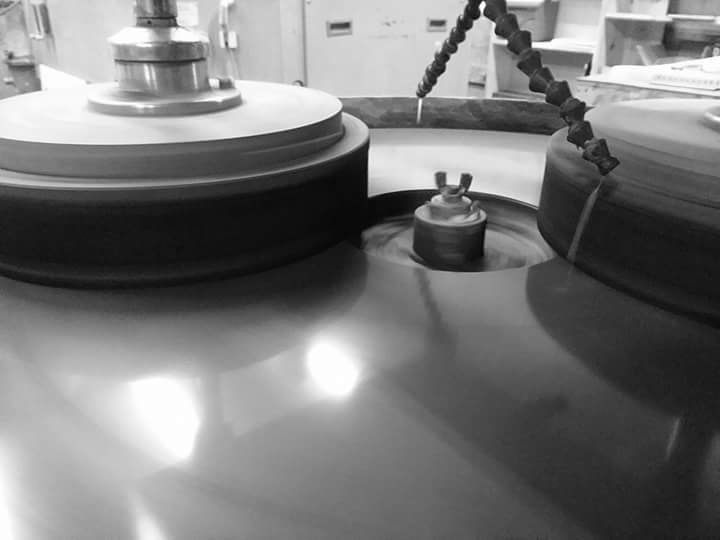

2026 Market Trends for Glassware Polisher: Key Developments and Insights
Rising Demand for Premium Glassware in Hospitality and Retail
By 2026, the global glassware polisher market is expected to experience steady growth, primarily driven by the expanding premium hospitality and retail sectors. Upscale hotels, fine dining restaurants, and luxury bars are increasingly focused on presentation and guest experience, necessitating the use of spotless, high-clarity glassware. This trend is particularly strong in emerging markets across Asia-Pacific and the Middle East, where luxury tourism is on the rise. As a result, commercial glassware polishers are becoming essential equipment to maintain brand standards and reduce labor costs associated with manual polishing.
Automation and Efficiency Driving Product Innovation
Technological advancements are shaping the 2026 glassware polisher landscape, with manufacturers prioritizing automation, energy efficiency, and compact design. Modern polishers are integrating smart sensors, programmable cleaning cycles, and water-recycling systems to reduce operational waste. These features appeal to businesses seeking to lower utility costs and meet sustainability goals. Additionally, IoT-enabled polishers allow remote monitoring and maintenance, minimizing downtime—especially beneficial for large hotel chains and banquet facilities.
Sustainability Regulations Influencing Equipment Design
Environmental regulations are tightening globally, prompting shifts in glassware polisher design and operation. By 2026, compliance with water conservation standards and reduced chemical usage is becoming mandatory in many regions, including the EU and parts of North America. This has led to increased adoption of eco-friendly polishers that use minimal water and biodegradable polishing compounds. Manufacturers are responding by developing closed-loop systems that filter and reuse water, aligning with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) commitments.
Growth in Residential and Specialty Applications
While commercial use dominates, the residential segment is emerging as a niche growth area. High-net-worth individuals and collectors of crystal glassware are investing in compact, high-performance polishers for home use. Moreover, specialty applications—such as museum conservation, antiques restoration, and lab glassware maintenance—are creating new market opportunities. These applications require precision polishing without surface damage, pushing innovation in gentler polishing technologies like ultrasonic and soft-abrasive methods.
Regional Market Expansion and Competitive Landscape
The Asia-Pacific region is projected to be the fastest-growing market for glassware polishers by 2026, fueled by urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and a booming hospitality industry in countries like India, China, and Vietnam. Meanwhile, North America and Europe remain mature markets with steady demand, characterized by product upgrades and replacements. The competitive landscape is consolidating, with key players focusing on R&D, strategic partnerships, and after-sales service to differentiate themselves in an increasingly quality-conscious market.
In summary, the 2026 glassware polisher market is defined by technological sophistication, sustainability mandates, and expanding end-user applications. Businesses that adapt to these trends—particularly in automation, eco-efficiency, and regional customization—are likely to gain a competitive edge.
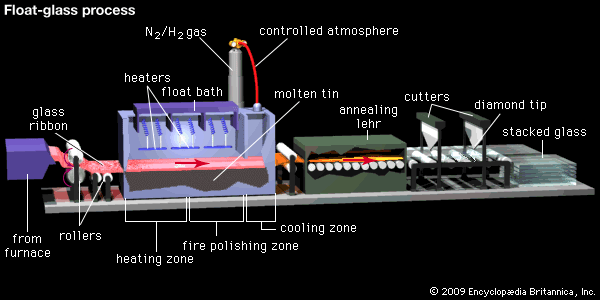
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Glassware Polisher: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing a glassware polisher—especially for industrial or high-precision applications—can present several challenges, particularly in ensuring product quality and avoiding intellectual property (IP) risks. Buyers and manufacturers often encounter pitfalls that can lead to subpar performance, legal complications, or reputational damage. Below are the most common issues related to quality and IP when sourcing glassware polishers.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material and Build Standards
One of the most frequent quality issues is receiving polishers made from substandard materials. Components such as polishing wheels, motors, and housing must meet specific durability and precision requirements. Sourcing from suppliers without proper quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of premature wear, inconsistent polishing results, and safety hazards.
Inconsistent Performance Across Units
Low-cost suppliers may lack rigorous quality control, leading to inconsistencies between units. This variability affects production efficiency and product uniformity, especially in high-volume manufacturing environments where repeatability is critical.
Insufficient Technical Documentation and Support
Many sourced polishers come with poor or incomplete technical documentation, making installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting difficult. A lack of ongoing technical support can result in extended downtime and increased operational costs.
Overstated Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate performance metrics such as polishing speed, surface finish quality, or compatibility with glass types. Without third-party validation or sample testing, buyers may end up with equipment that fails to meet operational requirements.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Use of Counterfeit or Copycat Designs
A significant IP concern is sourcing equipment that mimics patented designs or branded machinery without authorization. Some manufacturers, particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement, produce “look-alike” polishers that infringe on existing patents. Purchasing such equipment may expose the buyer to legal liability, especially if used in regulated markets.
Lack of IP Due Diligence from Suppliers
Many suppliers do not provide proof of ownership or licensing for their designs. Without proper documentation, buyers cannot verify whether the equipment legally incorporates proprietary technologies, such as specialized polishing mechanisms or control systems.
Hidden Use of Proprietary Software or Components
Modern glassware polishers often include embedded software or automation systems. Sourcing equipment with unauthorized or pirated software not only creates compliance risks but may also lead to cybersecurity vulnerabilities or system failures.
Exposure to Infringement Claims in Target Markets
Even if a polisher is legally produced in the country of origin, using it in markets with strong IP protections (e.g., the U.S. or EU) can trigger infringement claims. Buyers may be held responsible for using equipment that violates existing patents, especially if due diligence was not performed during procurement.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and request quality certifications.
– Test sample units under real-world conditions before bulk ordering.
– Require IP warranties and documentation from suppliers.
– Consult legal experts to assess potential IP risks in target markets.
– Work with reputable manufacturers who respect IP rights and offer transparent supply chains.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, businesses can ensure reliable performance and legal compliance when sourcing glassware polishers.
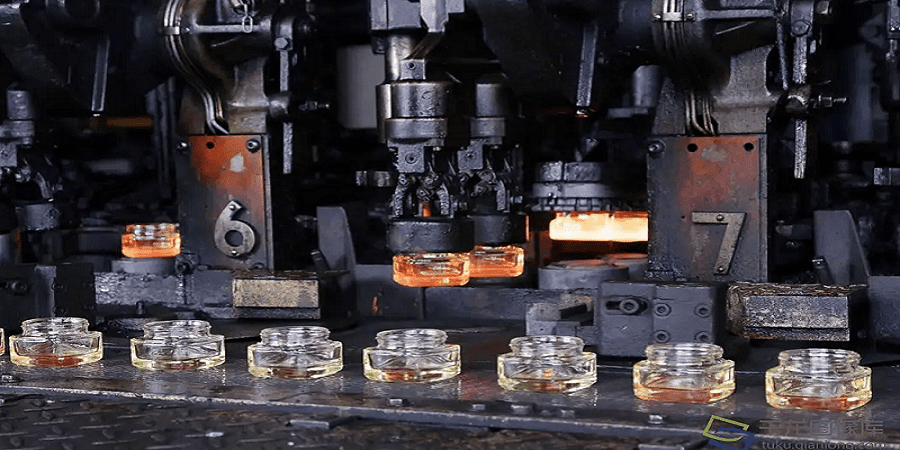
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Glassware Polisher
Product Overview and Classification
A Glassware Polisher is a machine used to clean, shine, and restore glass items such as drinking glasses, laboratory glassware, or decorative glass. It typically uses abrasive pads, polishing compounds, and controlled rotation or vibration to remove scratches and restore clarity. Proper classification under international trade codes (e.g., HS Code) is essential for customs clearance. It may fall under HS Code 8479.89 (Machines of a kind used in industrial or laboratory processes, not elsewhere specified), but classification should be verified with local customs authorities based on technical specifications.
Import/Export Regulations
Import and export of a Glassware Polisher are subject to national and international trade regulations. Exporters must comply with the export control laws of the country of origin, such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or EU Dual-Use Regulations, if the machine contains controlled technology. Importers must verify compliance with local machinery safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Some countries may require import permits, especially if the equipment includes motors or electrical components exceeding certain power thresholds.
Shipping and Transportation
Glassware polishers are typically heavy and fragile, requiring secure packaging and proper handling. Use wooden crates or reinforced pallets with anti-vibration materials to prevent damage during transit. Clearly label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Heavy.” Coordinate with freight forwarders to ensure compliance with IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations if shipping internationally. For air freight, ensure compliance with lithium battery rules if the unit includes rechargeable components.
Customs Documentation
Accurate documentation is critical for smooth customs clearance. Required documents typically include:
– Commercial Invoice (detailing product description, value, quantity, and Incoterms)
– Packing List (itemizing contents and weights per package)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (if claiming preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Technical Specifications or User Manual (to support HS code classification)
Ensure all documents reflect consistent information to avoid delays or penalties.
Safety and Compliance Standards
The Glassware Polisher must meet relevant safety standards in the destination market. Key certifications may include:
– CE Marking (for EU markets, indicating compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMC Directive 2014/30/EU)
– UKCA Marking (for the United Kingdom)
– UL/CSA Certification (for North America, under standards such as UL 197)
– RoHS Compliance (restriction of hazardous substances in electrical equipment)
Provide test reports and conformity declarations as required by local authorities.
Electrical and Environmental Compliance
Verify voltage, frequency, and plug compatibility with the destination country (e.g., 120V/60Hz in North America, 230V/50Hz in Europe). Include appropriate power adapters or internal transformers if needed. The machine must comply with environmental regulations such as WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) in the EU, requiring proper labeling and end-of-life recycling plans. Packaging should minimize plastic use and comply with local recyclability standards.
After-Sales and Warranty Considerations
Include multilingual user manuals and safety warnings. Clearly define warranty terms, including duration, coverage, and service procedures. For international sales, partner with local service providers or distributors to support installation, maintenance, and repairs. Maintain records of serial numbers and customer locations for compliance with product recall protocols if necessary.
Restricted Destinations and Sanctions
Check international sanctions lists (e.g., OFAC, UN, EU) to ensure the Glassware Polisher is not being shipped to embargoed countries or restricted entities. Some nations may restrict import of industrial machinery based on economic or political conditions. Conduct due diligence on end-users to prevent diversion to unauthorized applications.
Recordkeeping and Audit Preparedness
Maintain detailed records of all transactions, compliance certifications, shipping documents, and correspondence with regulatory bodies for a minimum of five years. This supports audit readiness and facilitates resolution of customs or compliance inquiries. Implement a documented compliance program to regularly review and update procedures in line with changing regulations.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Glassware Polisher
After a thorough evaluation of available options, it is evident that sourcing a reliable and efficient glassware polisher is essential for maintaining high-quality standards in glass production or restoration. Key considerations such as polishing precision, automation level, compatibility with glass types, energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, and total cost of ownership have guided the selection process.
The preferred supplier demonstrates proven expertise in glass finishing technology, offers customizable solutions, and provides strong after-sales support. Ultimately, investing in a high-performance glassware polisher not only enhances product quality and consistency but also improves operational efficiency and reduces long-term costs. This strategic sourcing decision supports ongoing goals of quality excellence and customer satisfaction in the glass manufacturing or processing workflow.