The global generator set (genset) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising energy demands, increasing infrastructure development, and the need for reliable backup power across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. According to a 2024 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global genset market was valued at USD 20.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2024 to 2029, reaching an estimated USD 30.6 billion by 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research forecasts strong momentum, citing expanding construction activities, frequent power outages in emerging economies, and the growing adoption of containerized and smart gensets as key growth enablers. As demand surges across regions—from North America’s grid resilience initiatives to Asia-Pacific’s rapid urbanization—the competitive landscape has intensified among leading manufacturers pioneering efficiency, fuel flexibility, and IoT-enabled monitoring solutions. In this evolving market, identifying the top genset manufacturers is critical for businesses seeking reliable, scalable, and technologically advanced power solutions.
Top 9 Genset Generator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Stationary Generators
Domain Est. 1995
Website: generac.com
Key Highlights: Generac Industrial Energy delivers powerful, reliable stationary generators built to meet the demands of today’s evolving energy landscape….
#2 FG Wilson Generator Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fgwilson.com
Key Highlights: FG Wilson generators is a leading global provider and generator manufacturer of prime power and back up diesel power generators, built in modern facilities ……
#3 Genpower Generator: Generator
Domain Est. 1998
Website: genpower.com
Key Highlights: Genpower Generator is with you wherever you need it, with the production of industrial type diesel generators from 10 KVA to 3300 kVA and portable generators ……
#4 HIPOWER SYSTEMS a Yanmar Company, Generator Sets
Domain Est. 2008
Website: hipowersystems.com
Key Highlights: HIPOWER SYSTEMS manufacturer of Diesel and spark-ignited generator sets….
#5 Power Systems
Domain Est. 2024
Website: powersystems.rehlko.com
Key Highlights: Rehlko is one of the largest generator manufacturers in the world, with production facilities on four continents and vast global sales, services and ……
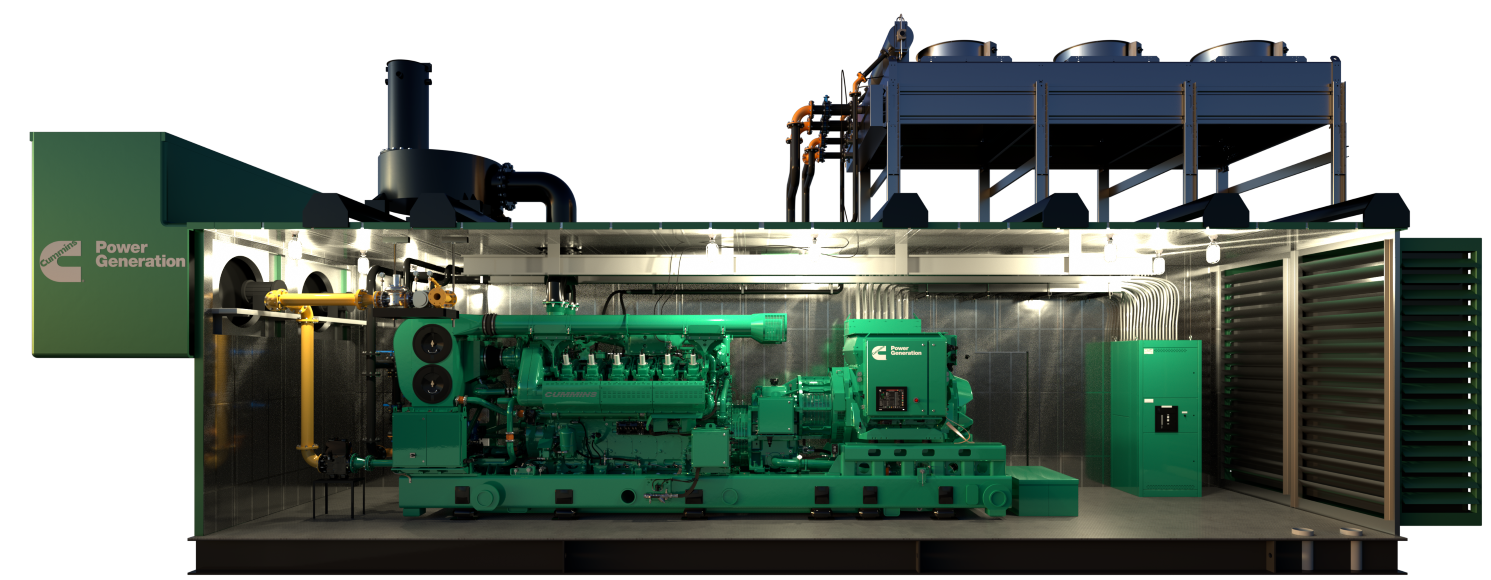
#6 Cummins Generator Sets
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cummins.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture, and test all major components of our generator sets – the engine, alternator, and control systems – so they work in harmony from the ……
#7 We Make Power Possible.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: genset.it
Key Highlights: A wide range of generator sets with diesel or patrol engines. The power of the engines ranges from 3KVA up to 2000kVA. Discover more ……
#8 WINCO Generators
Domain Est. 1999
Website: wincogen.com
Key Highlights: WINCO Generators ; Custom Bid Gen Sets. Complete Power Packaging Solutions ; Mobile EV Chargers. Recharge an EV Within Minutes ; Energy Storage Solutions….
#9 Power Generation Products
Domain Est. 2018
Website: mtu-solutions.com
Key Highlights: OUR mtu GAS GENSET MANUFACTURING SITE IN AUGSBURG Drawing on more than 45 years of experience, our competence center in Augsburg, Germany develops, assembles ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Genset Generator

2026 Market Trends for Genset Generators
The global genset (generator set) market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, energy transition initiatives, and evolving demand across both developed and emerging economies. As industries and infrastructures adapt to climate challenges and energy security concerns, genset generators are being redefined not only as backup power sources but also as integral components of hybrid and decentralized energy systems.
Rising Demand for Hybrid and Smart Gensets
By 2026, hybrid genset systems—integrating diesel or gas generators with battery storage and renewable sources like solar—are expected to dominate new installations. These systems enhance fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and lower operational costs, particularly in off-grid and remote areas. Smart gensets equipped with IoT-enabled monitoring, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance capabilities are gaining traction across commercial and industrial sectors. This trend is especially prominent in regions with unstable grid infrastructure, such as parts of Africa, South Asia, and Latin America.
Growth in Natural Gas and Dual-Fuel Gensets
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are accelerating the shift from diesel to cleaner alternatives. Natural gas gensets are projected to register the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) through 2026 due to their lower carbon footprint and abundant supply in key markets like North America and the Middle East. Dual-fuel gensets, capable of running on diesel and gas or biofuels, are also gaining popularity for their fuel flexibility and resilience in volatile fuel markets.
Expansion in Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific, particularly India, Indonesia, and Bangladesh, will remain the fastest-growing region for genset demand. Rapid urbanization, industrialization, and persistent power supply gaps are driving both residential and industrial procurement. In Africa, off-grid electrification projects supported by international development funds are creating new opportunities for containerized and modular gensets. Government initiatives promoting energy access and backup power in healthcare and telecom sectors further bolster market growth.
Impact of Electrification and Renewable Integration
While the long-term energy transition may reduce reliance on fossil-fuel gensets, the intermittent nature of solar and wind power ensures continued demand for gensets as balancing assets. By 2026, gensets are increasingly being deployed in microgrids and hybrid power parks, where they provide stability during low renewable output. This integration enhances the business case for gensets beyond emergency backup, positioning them as dynamic grid support tools.
Technological Advancements and Emission Regulations
Stricter emission norms, such as EU Stage V and U.S. EPA Tier 4 standards, are pushing manufacturers to innovate with cleaner combustion technologies, exhaust after-treatment systems, and low-emission engine designs. Additionally, advancements in digital twin modeling and AI-driven load management are optimizing genset performance and lifecycle costs. These developments are particularly influencing procurement decisions in Europe and North America, where compliance and sustainability are key purchasing criteria.
Conclusion
By 2026, the genset generator market will be characterized by a shift toward smarter, cleaner, and more integrated solutions. While traditional diesel gensets will remain relevant in certain applications, the future lies in hybrid systems, alternative fuels, and digital connectivity. Companies that invest in sustainable technologies and adapt to regional energy dynamics will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this evolving landscape.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Genset Generators: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing generator sets (gensets) from domestic or international suppliers can be cost-effective, but it comes with significant risks—especially regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for businesses aiming to ensure reliability, compliance, and long-term operational efficiency.
Poor Quality Control and Substandard Components
One of the most common issues when sourcing gensets—especially from low-cost manufacturers—is receiving units built with inferior materials and poor workmanship. Some suppliers may cut corners by using substandard alternators, engines, or control systems to reduce production costs. These gensets may fail prematurely, require frequent maintenance, or underperform under load, leading to costly downtime and safety hazards. Buyers often discover too late that the genset does not meet claimed specifications or international standards (e.g., ISO, CE, or UL).
Misrepresentation of Branding and Specifications
Many low-cost suppliers falsely claim that their gensets use engines or components from reputable brands (e.g., Cummins, Perkins, or Mitsubishi). In reality, they may use look-alike engines with similar names or branding, leading to confusion and misrepresentation. This not only affects performance but also voids warranties and service agreements. Buyers should verify component authenticity through documentation, serial number checks, and third-party inspections.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Sourcing gensets from certain regions—particularly where IP enforcement is weak—poses a risk of inadvertently purchasing counterfeit or cloned equipment. Some manufacturers copy the design, branding, and technical specifications of well-known genset models without licensing or authorization. Purchasing such equipment may expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in jurisdictions with strict IP laws. Additionally, using infringing equipment can damage a company’s reputation and complicate warranty and support arrangements.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
Many low-cost gensets lack proper certification for emissions, noise levels, or electrical safety. This becomes a problem when installing the units in regulated environments (e.g., urban areas, hospitals, or data centers). Non-compliant gensets may fail inspections, incur fines, or require costly retrofits. Always confirm that the genset meets local and international standards (e.g., EPA, EU Stage V, or IEC).
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if a genset appears reliable at purchase, long-term operation depends on access to spare parts, technical support, and qualified service technicians. Some suppliers offering attractive upfront pricing provide little or no after-sales support. This is particularly problematic with counterfeit or cloned units, where genuine spare parts are unavailable, and local technicians may not be trained to service them.
How to Mitigate These Risks
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and reference checks.
- Request proof of component authenticity and original manufacturer documentation.
- Use independent third-party inspection services before shipment.
- Ensure contracts include quality guarantees, IP indemnification clauses, and warranty terms.
- Prioritize suppliers with established reputations, verifiable certifications, and global service networks.
By addressing quality and IP concerns proactively, businesses can avoid costly failures and ensure reliable, compliant power generation solutions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Genset Generators
Transporting and deploying generator sets (gensets) involves navigating complex logistics and regulatory requirements. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure safe, efficient, and compliant operations.
Classification and Documentation
Gensets are classified as heavy machinery and often contain hazardous components such as fuel, oil, and batteries. Accurate classification under international shipping codes (e.g., UN numbers) is critical. Key documentation includes:
– Commercial invoice and packing list
– Bill of lading (air, sea, or land)
– Certificate of origin
– Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for fuels and lubricants
– Dangerous Goods Declaration (if applicable)
Ensure all paperwork reflects accurate technical specifications, weight, dimensions, and hazardous materials content.
Transport Mode Considerations
Choose the appropriate transport method based on genset size, weight, and destination:
– Road: Ideal for regional delivery; verify axle weight limits and route restrictions.
– Sea: Common for international shipments; use standard ISO containers (20’ or 40’) with proper securing to prevent shifting.
– Air: Reserved for urgent, lightweight units; subject to strict IATA regulations for hazardous components (e.g., fuel residue, batteries).
Secure gensets using load bars, straps, or cradles, and block wheels to prevent movement during transit.
Hazardous Materials & Battery Handling
Gensets often contain:
– Residual fuel (flammable liquid – UN 1202 or 1203)
– Lead-acid or lithium batteries (Class 8 corrosive or Class 9 hazardous)
Compliance requirements:
– Drain fuel below 25% capacity or fully remove for air transport.
– Batteries must be disconnected, terminals protected against short circuits, and labeled per IATA/IMDG regulations.
– Declare all hazardous items and package in accordance with ADR (road), IMDG (sea), or IATA (air) codes.
Import/Export Regulations
Comply with destination country requirements:
– Obtain import permits or licenses if required.
– Verify customs tariff codes (HS codes) for gensets (typically 8502.11 or 8502.12).
– Check for emissions standards (e.g., EPA, EU Stage V) compliance for diesel gensets.
– Be aware of sanctions or trade restrictions affecting certain regions.
Partner with a licensed customs broker to facilitate clearance.
Environmental and Safety Standards
Ensure gensets meet:
– Emissions standards: EPA Tier 4, EU Stage V, or local equivalents.
– Noise regulations: Verify sound pressure levels comply with site or municipal codes.
– Electrical safety: Certification marks such as CE, UL, or CSA as required by destination.
Non-compliant units may be rejected at borders or face fines upon deployment.
On-Site Compliance and Installation
After delivery:
– Verify stable, level foundation and proper ventilation.
– Follow local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S.) for wiring and grounding.
– Install exhaust systems to safely vent emissions.
– Equip with fire suppression and emergency shutoff mechanisms.
– Conduct routine maintenance per manufacturer guidelines to maintain compliance.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Maintain comprehensive records:
– Shipping and customs documentation
– Maintenance logs
– Emissions and safety certifications
– Training records for operators
These records support compliance audits and simplify future transport or regulatory inspections.
Adhering to this guide ensures genset logistics are efficient, legal, and safe across global supply chains. Always consult local authorities and regulatory bodies for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Generator (Genset):
In conclusion, sourcing a generator (genset) requires a comprehensive evaluation of power requirements, operational environment, fuel availability, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance needs. Selecting the right genset involves balancing initial investment with reliability, fuel efficiency, and total cost of ownership. It is crucial to partner with reputable suppliers or manufacturers that offer quality products, after-sales support, and warranty coverage to ensure continuous and dependable performance. Additionally, considering future scalability and adherence to environmental and regulatory standards will contribute to a sustainable and resilient power solution. A well-informed sourcing decision ultimately ensures uninterrupted power supply, operational efficiency, and peace of mind across critical applications.