The global gas steam boiler market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions and stringent environmental regulations favoring cleaner combustion technologies. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global industrial boiler market was valued at USD 16.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% from 2024 to 2030, with gas-fired boilers capturing a significant share due to their low emissions and operational efficiency. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a CAGR of over 4.5% during the forecast period 2024–2029, citing rising industrialization in emerging economies and the ongoing shift from coal to natural gas as key growth accelerators. As industries prioritize reliability, compliance, and sustainability, the competitive landscape has intensified among leading manufacturers innovating in high-efficiency combustion, smart controls, and ultra-low NOx emissions. In this evolving market, identifying the top gas steam boiler manufacturers becomes essential for businesses seeking performance-driven, future-ready thermal solutions.
Top 10 Gas Steam Boiler Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hurst Boiler
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hurstboiler.com
Key Highlights: Hurst Boiler, Inc. is the leading manufacturer of gas, oil, wood, coal, solid fuel, solid waste, biomass and hybrid fuel-fired steam and hot water boilers….
#2 Industrial Steam Boilers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: miuraboiler.com
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer of industrial steam boilers, Miura America specializes in high-efficiency, low NOx modular systems….
#3 Page ⋆ Burnham Commercial Boilers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: burnhamcommercial.com
Key Highlights: Burnham Commercial is a leading manufacturer of high-quality boilers and boiler control systems for commercial and industrial applications….
#4 U.S. Boiler Company
Domain Est. 2010
Website: usboiler.net
Key Highlights: US Boiler Company is a leading manufacturer of home heating equipment, water boilers, steam boilers, hot water heaters, radiators and boiler control systems….
#5 Fulton: High
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fulton.com
Key Highlights: Trusted globally, Fulton engineers high-efficiency steam and hydronic boilers, thermal fluid heaters, and custom heat transfer systems….
#6 All Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: weil-mclain.com
Key Highlights: 80 Series 1 Commercial Gas Oil Boiler. Fuel Type: · 88 High Efficiency Series 3 Commercial Gas Oil Boiler. Fuel Type: · 88 Series 2 Commercial Gas Oil Boiler ……
#7 Superior Boiler
Domain Est. 1997
Website: superiorboiler.com
Key Highlights: Superior Boiler solves your most complex boiler challenges so you can get down to business – sterilizing essential hospital equipment, heating large facilities….
#8 Cleaver
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cleaverbrooks.com
Key Highlights: Cleaver-Brooks is your total solution provider for boilers and boiler room systems, including rentals, maintenance programs, parts, and training….
#9 Smith Boilers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: smithboiler.com
Key Highlights: Smith Cast Iron Boilers are known throughout North America for their rugged reliability, operating efficiencies and longevity….
#10 Viessmann US
Domain Est. 2000
Website: viessmann-us.com
Key Highlights: Viessmann heating systems, including our wide range of condensing gas boilers, deliver comfort, convenience and efficiency. Whether you need residential ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Gas Steam Boiler
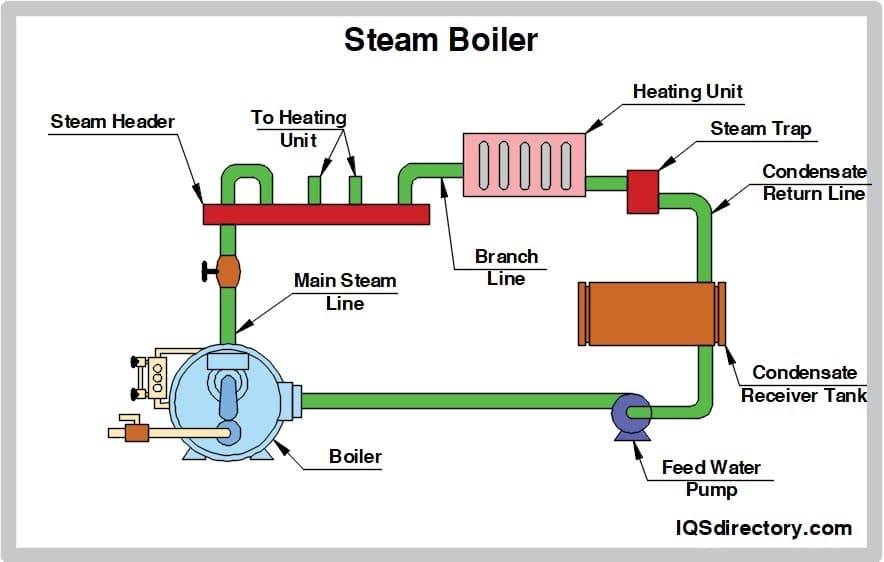
2026 Market Trends for Gas Steam Boilers
The global gas steam boiler market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving energy policies, technological innovation, and shifting industrial demands. As industries and governments worldwide intensify efforts to reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency, gas steam boilers are undergoing a strategic repositioning in the broader energy landscape. This analysis explores key market trends expected to shape the gas steam boiler industry through 2026.
Rising Demand for Energy Efficiency and Emissions Reduction
One of the most influential drivers shaping the gas steam boiler market in 2026 is the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Natural gas, while still a fossil fuel, emits significantly less CO₂ than coal or oil when burned. As a result, gas steam boilers are increasingly viewed as a transitional solution in the move toward decarbonization.
Regulatory frameworks such as the European Green Deal, the U.S. Clean Air Act amendments, and China’s dual carbon goals (carbon peak by 2030, carbon neutrality by 2060) are pushing industries to upgrade outdated boiler systems. By 2026, high-efficiency condensing gas boilers are expected to dominate new installations, particularly in commercial and light industrial sectors. These boilers can achieve thermal efficiencies exceeding 90%, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs.
Technological Advancements and Smart Integration
In 2026, the integration of digital technologies into gas steam boiler systems is expected to accelerate. The rise of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has paved the way for IoT-enabled boilers equipped with real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics.
Key technological trends include:
- AI-driven optimization: Machine learning algorithms analyze operational data to optimize combustion efficiency, minimize fuel waste, and extend equipment life.
- Modular and scalable designs: Compact, modular gas boilers allow for flexible capacity adjustments, making them ideal for facilities with fluctuating steam demands.
- Hybrid systems: Some manufacturers are developing hybrid boilers that integrate gas combustion with electric or renewable heat sources, improving overall system flexibility and sustainability.
These innovations not only enhance performance but also align with corporate sustainability goals, making smart gas boilers more attractive to facility managers and plant operators.
Regional Market Dynamics
The adoption and growth of gas steam boilers vary significantly by region, influenced by energy infrastructure, fuel availability, and policy environments.
- Asia-Pacific: China, India, and Southeast Asian countries are expected to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization and urban development. However, increasing air quality regulations are steering new projects toward cleaner gas-based systems over coal.
- North America: The U.S. and Canada continue to replace aging coal and oil boilers with natural gas alternatives, supported by abundant domestic shale gas and favorable pricing. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the U.S. also incentivizes clean energy upgrades, indirectly benefiting efficient gas boiler installations.
- Europe: Stricter emissions standards and carbon pricing mechanisms are limiting the long-term role of gas boilers. However, in the short to medium term, gas remains a critical bridge fuel, especially in countries transitioning from coal. By 2026, hybrid and hydrogen-ready boilers are gaining traction in markets like Germany and the UK.
Shift Toward Hydrogen-Ready and Low-Carbon Fuels
A defining trend by 2026 is the emergence of hydrogen-compatible gas steam boilers. With many countries investing in green hydrogen infrastructure, boiler manufacturers are adapting designs to handle hydrogen-natural gas blends (up to 20–30% H₂), with the goal of eventually operating on 100% hydrogen.
Leading companies such as Bosch, Viessmann, and BDR Thermea have already launched pilot hydrogen-ready models. Regulatory support, including updated building codes and boiler standards, is expected to expand in 2026, facilitating the adoption of these future-proof systems.
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The gas steam boiler market is becoming increasingly competitive, with major players focusing on innovation, sustainability, and global expansion. By 2026, market consolidation is likely as larger manufacturers acquire niche technology firms specializing in controls, emissions reduction, or digital integration.
Key strategic moves include:
- Partnerships with energy service companies (ESCOs) to offer performance-based boiler-as-a-service models.
- Expansion into emerging markets with tailored, cost-effective boiler solutions.
- Investment in R&D for low-NOx burners and carbon capture-readiness.
Conclusion
By 2026, the gas steam boiler market will be characterized by a strong shift toward efficiency, digitalization, and decarbonization. While long-term sustainability goals may eventually reduce reliance on fossil fuels, natural gas boilers will remain a vital component of the global energy mix—particularly as transitional and hybrid solutions. Manufacturers and end-users who embrace innovation, regulatory compliance, and low-carbon pathways will be best positioned to succeed in this evolving landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Gas Steam Boilers (Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns)
Sourcing gas steam boilers, especially from international suppliers, involves several critical risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure a reliable, efficient, and legally compliant acquisition.
1. Compromised Quality Standards
- Substandard Materials and Manufacturing: Some suppliers—particularly those offering significantly lower prices—may use inferior materials (e.g., low-grade steel, poor welding) that reduce boiler efficiency, safety, and lifespan.
- Lack of Certifications: Reputable gas steam boilers should comply with international standards such as ASME, CE, ISO, or local pressure vessel codes. Sourcing from vendors without verifiable certifications increases the risk of non-compliance and operational hazards.
- Inadequate Testing and Documentation: Poorly documented hydrostatic, efficiency, and emissions testing can mask performance issues and safety flaws.
2. Misrepresentation of Performance Specifications
- Suppliers may exaggerate efficiency ratings, steam output, or emissions compliance to win contracts. Without third-party validation, these claims can lead to underperforming systems and higher operational costs.
3. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
- Counterfeit or Clone Designs: Some manufacturers replicate patented boiler technologies (e.g., burner designs, control systems, heat exchangers) without authorization. Purchasing such equipment exposes the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated markets.
- Use of Unauthorized Software or Controls: Modern boilers often include proprietary control systems. Cloned or pirated software can compromise safety, serviceability, and warranty coverage.
4. Weak or Unclear Warranty and Support
- Poorly defined warranty terms or lack of local service networks can leave buyers stranded when maintenance or repairs are needed. This is especially problematic with IP-protected components that require certified technicians.
5. Supply Chain Transparency Issues
- Opaque supply chains make it difficult to trace component origins or verify whether subcomponents (e.g., valves, sensors) are genuine or counterfeit, increasing the risk of IP violations and reliability issues.
6. Regulatory and Compliance Risks
- Using boilers that infringe on IP or fail to meet local safety and environmental regulations can result in fines, operational shutdowns, or import bans—particularly in regions with strict enforcement (e.g., EU, North America).
Mitigation Strategies:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and reference checks.
– Require certification documentation (ASME, CE, etc.) and performance test reports.
– Verify IP ownership through patents, trademarks, and licensing agreements.
– Partner with legal and technical experts during procurement.
– Use contracts that specify quality requirements, warranty terms, and IP indemnification clauses.
By addressing both quality and IP concerns proactively, organizations can avoid costly downtime, legal exposure, and safety incidents when sourcing gas steam boilers.
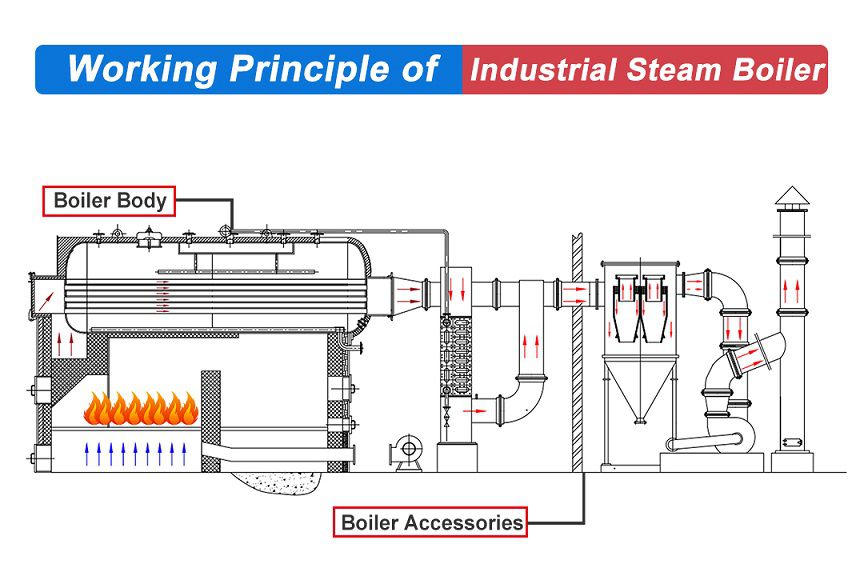
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Gas Steam Boilers
Transporting, installing, and operating gas steam boilers requires strict adherence to logistical protocols and regulatory compliance standards to ensure safety, efficiency, and legal conformity. This guide outlines key considerations under the H2 classification framework for gas steam boilers, focusing on international and regional logistics, safety compliance, environmental regulations, and documentation.
- Classification & Regulatory Framework (H2 Context)
While “H2” typically refers to hydrogen fuel or hazardous materials in some regulatory systems (e.g., UN Class 2 for gases), in the context of gas steam boilers, it may imply:
– Use of hydrogen (H₂) as a fuel source (emerging trend for low-carbon operations).
– Compliance with pressure equipment directives where H2 could denote a hazard classification.
Important Standards:
– ASME BPV Code (Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code), Section I – Power Boilers
– European Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU
– ISO 16812:2022 – Safety requirements for steam boilers
– NFPA 85 – Boiler and Combustion Systems Hazards Code
– Local gas codes (e.g., National Fuel Gas Code – NFPA 54 in the U.S.)
If hydrogen (H₂) is used as fuel:
– Comply with ISO 19880 (gaseous hydrogen fueling stations) and CGA H-7 for hydrogen handling.
– Ensure compatibility of boiler materials with hydrogen (avoid embrittlement).
- Logistics Planning
A. Transportation
– Mode: Road (most common), rail, or sea depending on size and destination.
– Packaging: Secure anchoring on flatbeds; crated components for modular units.
– Labeling: Mark with “Heavy Equipment,” “Fragile,” and “This Side Up.” If hydrogen components are involved, apply UN 1049 (Hydrogen, compressed) labels if applicable.
– Permits: Oversize/overweight permits for large boiler units.
– Environmental Controls: Protect from moisture and extreme temperatures during transit.
B. Site Delivery & Handling
– Access routes must support weight (boilers can exceed 10+ tons).
– Use cranes or forklifts with adequate load capacity; follow rigging safety protocols.
– Unloading must occur on stable, level ground near foundation points.
- Import/Export Compliance
A. Customs Documentation
– Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill
– Certificate of Conformity (e.g., CE mark for EU)
– ASME Product Manufacturer’s Data Report (PPD) for pressure vessels
– Material Test Reports (MTRs)
– Energy efficiency certification (e.g., ERP Directive in EU)
B. Tariff Classification
– HS Code Example: 8402.11 (Steam boilers for central heating) or 8402.90 (other steam generators)
– Country-specific duties and trade agreements may apply.
- Installation & Site Compliance
A. Location Requirements
– Adequate ventilation and clearance (per NFPA 54/ANSI Z223.1)
– Fire-rated walls if near combustible materials
– Drainage provisions for condensate (especially with condensing boilers)
B. Gas Supply & Piping
– Natural gas or hydrogen pipelines must meet local code (e.g., CSA B149.3 in Canada, IGEM/UP/1 in UK)
– Leak testing required post-installation (e.g., pressure decay test)
– Use of certified welders and licensed gas fitters
C. Electrical & Controls
– Compliance with NEC (NFPA 70) or IEC 60364
– Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS) if applicable
- Safety & Environmental Compliance
A. Emissions Standards
– Adhere to EPA (U.S.) or EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED)
– NOx, CO, and particulate limits; use low-NOx burners
– For H₂-fueled boilers: near-zero CO₂ emissions, but ensure monitoring of NOx formation due to high flame temperatures
B. Pressure Relief & Safety Devices
– Certified safety valves (ASME CSD-1 compliance)
– High-limit controls and flame safeguard systems
C. Operator Training & Certification
– Certified boiler operators (jurisdiction-dependent, e.g., NYC requires 1A, 2B licenses)
– Training on emergency shutdown and H₂-specific risks (e.g., flammability range: 4–75% in air)
- Inspection & Certification
A. Pre-Startup Inspections
– Third-party inspection (e.g., NBIC – National Board Inspection Code)
– Registration with local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ)
B. Ongoing Compliance
– Annual internal and external inspections
– Water quality testing (prevent scaling/corrosion)
– Emission testing (quarterly or as required)
-
Decommissioning & Disposal
-
Follow environmental regulations for refractory materials, insulation (e.g., asbestos check), and metals.
- Proper purging of gas lines (especially H₂) before dismantling.
- Recycle boiler components per WEEE or local recycling programs.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for gas steam boilers—especially those utilizing or compatible with hydrogen (H2)—require a multidisciplinary approach integrating engineering, regulatory knowledge, and safety management. Always consult local authorities, certified engineers, and regulatory bodies to ensure full compliance throughout the boiler’s lifecycle.
Note: If “H2” refers to a specific classification code in your region (e.g., customs or safety category), consult the relevant regulatory database for precise interpretation.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Gas Steam Boiler
Sourcing a gas steam boiler is a critical investment that significantly impacts the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of industrial or commercial operations. After thorough evaluation of technical specifications, fuel efficiency, emissions compliance, lifecycle costs, and supplier reputation, it becomes evident that selecting the right boiler system requires a balanced approach that considers both immediate needs and long-term operational goals.
Natural gas boilers offer numerous advantages, including lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to oil or coal-fired systems, high thermal efficiency, and stable fuel supply in many regions. Modern condensing boilers, in particular, provide enhanced energy savings and environmental benefits, making them ideal for organizations striving to meet sustainability targets.
When sourcing, it is essential to partner with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who offer robust after-sales support, warranty coverage, and compliance with safety standards such as ASME, CE, or local regulatory requirements. Additionally, incorporating energy audits, future load projections, and maintenance planning into the decision-making process ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness over the boiler’s lifespan.
In conclusion, a well-researched and strategically implemented gas steam boiler procurement process not only improves operational efficiency but also contributes to environmental stewardship and long-term cost savings. Prioritizing quality, efficiency, and service support will lead to a resilient and future-ready steam generation system.