The global radiant heating systems market is experiencing robust growth, fueled by increasing demand for energy-efficient and cost-effective heating solutions in residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. According to Grand View Research, the global radiant heating market size was valued at USD 13.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by rising construction activities, evolving building codes favoring energy efficiency, and heightened consumer awareness of sustainable indoor climate solutions. Within this expanding market, garage-specific radiant heating systems are gaining traction due to their ability to deliver consistent warmth, reduce energy consumption, and prevent moisture-related damage in unconditioned spaces. As demand rises, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and performance—offering solutions tailored to the unique thermal challenges of garages. Based on market presence, product range, technological advancement, and customer feedback, the following nine manufacturers represent the top players in the garage radiant heating sector.
Top 9 Garage Radiant Heating Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Solaronics: Infrared Heaters Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: solaronicsusa.com
Key Highlights: Solaronics is a leading manufacturer of industrial radiant heaters with 60 years of expertise and personal experience in the industry….
#2 Uponor radiant heating and cooling
Domain Est. 1996
Website: uponor.com
Key Highlights: Uponor radiant floor heating and cooling systems provide superior indoor air quality and reduce energy use.Missing: garage manufacturer…
#3 Roberts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: robertsgordon.com
Key Highlights: Roberts Gordon Infrared Heating manufactures high quality, efficient radiant tube heaters for industrial and commercial applications….
#4 Radiant Heating & Snow Melting Solutions
Domain Est. 1995
Website: watts.com
Key Highlights: Watts radiant heating and snow melting solutions provide warm, energy-efficient floors to stand on and clear, snow-free surfaces to pull into….
#5 Superior Radiant Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: superiorradiant.com
Key Highlights: Superior Radiant Products (SRP®) is an industry leader in the design and manufacture of energy efficient commercial infrared heaters….
#6 Radiant Heating System
Domain Est. 1999
Website: radiantsystemsinc.com
Key Highlights: Radiant Systems, Inc’s Comfort Cove Radiant Heating system offers the best energy efficient heating for your home on the market, proudly built in the USA….
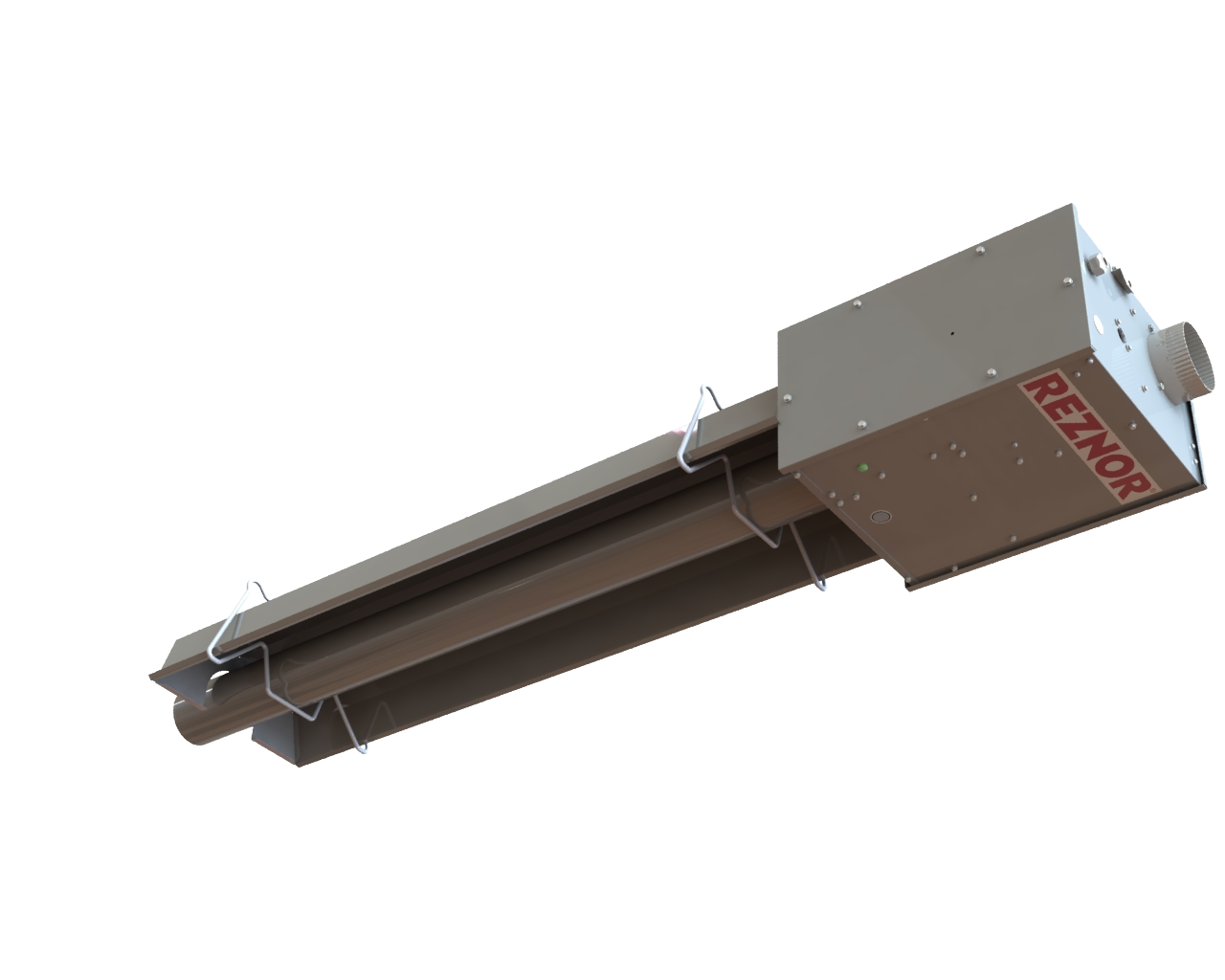
#7 Reznor HVAC
Domain Est. 1999
Website: reznorhvac.com
Key Highlights: For more than 90 years, we’ve delivered reliable, high-efficiency unit heaters to our customers. Our unit heaters feature attractive, high-gloss exteriors….
#8 ThermoSoft Electric Heating Systems
Domain Est. 2003
Website: us.thermosoft.com
Key Highlights: ThermoSoft electric radiant heat is dedicated to providing exceptional technical support and superior electric radiant heating. Priority 1: Making You Happy….
#9 Best Garage Heaters
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1949
Website: spaceray.com
Key Highlights: Looking for an infrared heater for your garage? At Space-Ray, we have been manufacturing gas-fired tube heating systems since 1949….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Garage Radiant Heating
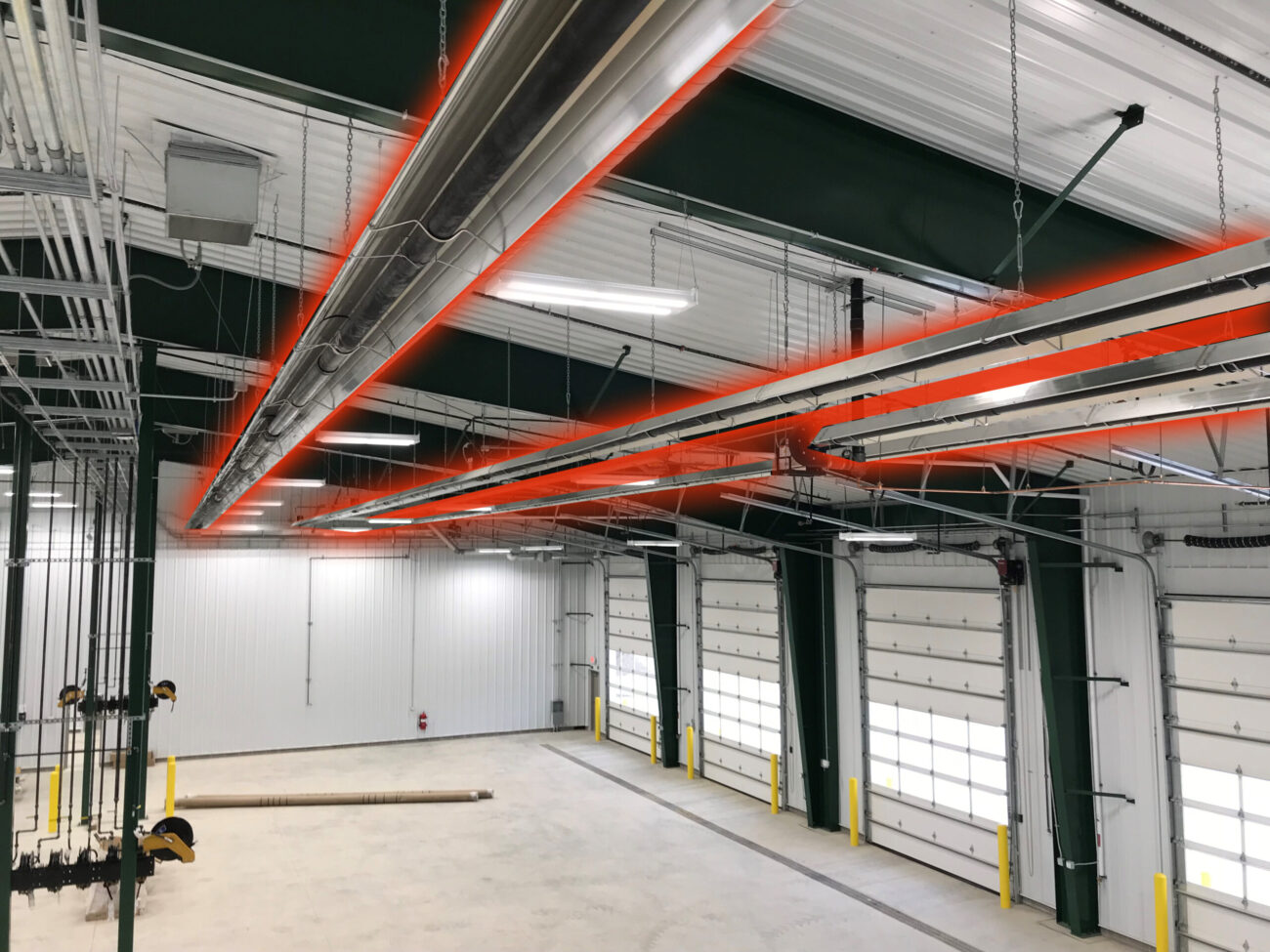

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Garage Radiant Heating
The garage radiant heating market is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by rising consumer demand for energy efficiency, comfort, and smart home integration. As homeowners increasingly convert garages into functional living or working spaces—such as home gyms, workshops, or guest suites—radiant floor heating systems are emerging as a preferred solution due to their consistent warmth, energy savings, and unobtrusive design.
One of the key drivers shaping the 2026 market is the integration of smart technology. Radiant heating systems are now commonly paired with Wi-Fi-enabled thermostats and home automation platforms, allowing users to schedule heating cycles, monitor energy usage, and control temperatures remotely via smartphones or voice assistants. This trend aligns with the broader movement toward connected homes and personalized climate control.
Energy efficiency regulations and sustainability initiatives are also influencing market dynamics. Governments and energy agencies are promoting low-carbon heating solutions, and radiant systems—particularly electric and hydronic models powered by renewable energy sources—are gaining favor over traditional forced-air systems. Advances in insulation materials and heat retention technologies are further improving the efficiency of radiant heating in garages, which often have poor insulation and high heat loss.
Another notable trend is the shift toward DIY and modular radiant heating kits. Manufacturers are responding to the growing number of homeowners undertaking garage conversions by offering easy-to-install, plug-and-play radiant systems that reduce labor costs and installation time. These kits often include pre-spaced heating mats, self-regulating cables, and detailed installation guides, making radiant heating more accessible to non-professionals.
Regionally, North America and Europe are leading the adoption, supported by colder climates and higher disposable incomes. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific are expected to see accelerated growth due to urbanization and rising interest in premium home amenities.
By 2026, the garage radiant heating market is projected to benefit from continued innovation, declining costs of components, and increased awareness of indoor air quality benefits—radiant systems do not circulate dust or allergens, making them ideal for health-conscious consumers. As a result, the market is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 7–9% through 2026, with hydronic systems maintaining dominance in high-end applications and electric systems gaining traction in retrofit and compact installations.
In summary, the 2026 garage radiant heating market will be defined by smart integration, sustainability, ease of installation, and expanding use cases beyond traditional heating—positioning it as a critical component in modern garage design and home energy management.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Garage Radiant Heating (Quality and IP)
Sourcing a garage radiant heating system involves more than just selecting a product—it requires careful attention to quality standards and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to poor performance, safety risks, legal issues, and costly replacements. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Low Cost Over Quality Components
One of the most frequent mistakes is choosing the cheapest available system to cut upfront costs. Low-cost radiant heating kits often use substandard materials such as thin-gauge heating cables, inferior insulation, or non-durable thermostats. These components are more prone to premature failure, inconsistent heating, and potential fire hazards. Always verify material specifications, certifications (e.g., UL, ETL), and warranty terms to ensure long-term reliability.
2. Ignoring System Compatibility and Design Mismatch
Garage environments vary significantly in size, insulation levels, and usage (e.g., workshop vs. vehicle storage). A common pitfall is selecting a one-size-fits-all system that doesn’t match the actual thermal load requirements. Underpowered systems will struggle to maintain temperature, while oversized systems waste energy and increase installation complexity. Always perform a proper heat loss calculation and choose a system engineered for your specific garage conditions.
3. Overlooking IP Protection and Using Unlicensed Products
Using radiant heating systems or components that infringe on existing patents or trademarks can expose you to legal liabilities. Some suppliers—especially offshore or unbranded vendors—may offer “clone” versions of patented technologies (e.g., specific heating cable designs, thermostat algorithms, or control systems). Sourcing such products can result in cease-and-desist orders, shipment seizures, or litigation. Always verify that the supplier holds appropriate IP rights or licenses for the technology they’re offering.
4. Failing to Verify Third-Party Testing and Certifications
Not all radiant heating systems undergo rigorous third-party testing. Some manufacturers may claim performance metrics without independent validation. Always confirm that the system is certified by recognized bodies such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CSA (Canadian Standards Association), or CE (European Conformity), especially for electrical safety and performance in damp or cold environments typical of garages.
5. Poor Attention to Installation and Support Documentation
Even high-quality systems can underperform if installation instructions are unclear or incomplete. A major pitfall is sourcing from suppliers who provide inadequate technical documentation, lack English-language manuals, or offer limited customer support. This can lead to improper installation, voided warranties, and inefficient operation. Ensure the supplier provides detailed installation guides, layout templates, and responsive technical assistance.
6. Neglecting Future Maintenance and Spare Parts Availability
Some radiant heating systems, particularly niche or proprietary models, may become difficult to service over time. A critical oversight is not considering the long-term availability of replacement thermostats, sensors, or heating elements. Choose systems from reputable brands with established supply chains and accessible spare parts to avoid obsolescence.
By avoiding these pitfalls—focusing on quality assurance, verifying IP legitimacy, and ensuring proper certifications and support—you can source a durable, efficient, and legally compliant radiant heating solution for your garage.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Garage Radiant Heating
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations when installing radiant heating in a garage. Proper planning ensures safety, efficiency, and adherence to local regulations.
Planning and Permitting
Before beginning any installation, confirm whether local building codes require permits for radiant heating systems in garages. Most jurisdictions mandate permits for electrical or hydronic modifications, especially when altering garage structures. Contact your local building department to determine specific requirements. Submit detailed plans including system type (electric or hydronic), layout, insulation specifications, and thermostat placement. Approval must be obtained prior to installation to avoid costly delays or failed inspections.
System Selection and Compatibility
Choose between electric or hydronic radiant heating based on your garage’s usage, insulation level, and energy sources. Electric systems are easier to install in small or retrofit garages but may have higher operating costs. Hydronic systems, though more complex to install, offer greater energy efficiency for larger or frequently used spaces. Ensure the selected system is rated for garage environments, including resistance to moisture, oil, and temperature fluctuations. Verify compatibility with existing power supplies or boiler systems.
Insulation and Subfloor Preparation
Proper insulation is critical for efficient radiant heating performance. Install insulation beneath the slab or subfloor to direct heat upward into the garage space rather than dissipating into the ground. Use rigid foam insulation boards with appropriate R-values as specified by local energy codes. For slab installations, ensure the concrete is fully cured and moisture barriers are in place. For retrofit applications, assess subfloor integrity and make repairs as needed before installing heating elements or tubing.
Electrical and Plumbing Code Compliance
All electrical components must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC), including GFCI protection for electric radiant systems, especially in potentially damp garage environments. Wiring must be properly sized and installed by a licensed electrician. For hydronic systems, plumbing must adhere to local codes for piping materials, pressure ratings, and antifreeze use (if applicable). PEX tubing should be installed per manufacturer guidelines and protected from physical damage. Thermostats must be garage-rated and installed at proper height and location.
Safety and Fire Code Requirements
Radiant heating systems must not compromise fire safety. Maintain required clearances around heating elements, boilers, or electrical panels. Avoid placing heating components under flammable storage or vehicles with leaking fluids. In some jurisdictions, garages with radiant heat may be considered “conditioned spaces,” affecting requirements for carbon monoxide detectors, fire separation from living areas, and door insulation ratings. Ensure compliance with NFPA 850 or local fire codes.
Ventilation and Indoor Air Quality
While radiant heating does not rely on air circulation, proper ventilation is still necessary in garages to manage fumes from vehicles or stored chemicals. Ensure garage ventilation systems (exhaust fans, passive vents) remain functional and are not obstructed by new flooring or insulation. For hydronic systems using boilers, confirm adequate combustion air and venting to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Installation and Professional Certification
Installation should be performed by qualified professionals—licensed electricians for electric systems and certified plumbers or HVAC technicians for hydronic systems. All work must follow manufacturer instructions and local code requirements. Keep detailed records of materials, permits, inspections, and certifications for future reference, resale, or insurance purposes.
Inspection and Testing
Schedule mandatory inspections at key stages: rough-in (before pouring concrete or covering subfloors) and final inspection after completion. The system should undergo pressure testing (hydronic) or continuity and resistance testing (electric) to verify integrity. Thermostats and controls must be calibrated and operational. Obtain official sign-off from the local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ).
Maintenance and Compliance Documentation
After installation, maintain a log of system maintenance, including annual checks for leaks, thermostat calibration, and pump functionality (hydronic). Retain all compliance documentation, including permits, inspection reports, and equipment warranties. This ensures ongoing code adherence and facilitates future repairs or upgrades.
By following this logistics and compliance guide, you ensure a safe, efficient, and code-compliant radiant heating system in your garage.
In conclusion, sourcing a garage radiant heating system is a worthwhile investment for enhancing comfort, energy efficiency, and functionality in your workspace. By carefully evaluating key factors such as heating type (electric vs. hydronic), insulation quality, installation costs, and long-term energy savings, you can select a solution that meets both your performance needs and budget. Additionally, working with reputable suppliers and certified installers ensures reliable equipment and proper system integration. Whether for occasional use or as a year-round workshop, radiant heating provides even, consistent warmth—eliminating cold spots and improving overall usability. With proper planning and sourcing, a radiant heating system can transform your garage into a comfortable and efficient extension of your home.