The global electrochemical instrumentation market, driven by rising demand in battery research, corrosion testing, and academic R&D, is experiencing robust growth. According to Grand View Research, the global battery testing equipment market size was valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is largely fueled by advancements in lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy storage sectors, where precise current control is critical. Galvanostats—essential tools that maintain a constant current in electrochemical cells—are at the heart of this evolution, used widely in cyclic voltammetry, electrodeposition, and battery cycling. With increasing investment in energy storage technologies and material science, the demand for high-precision galvanostats is escalating. In this competitive landscape, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, reliability, and advanced data acquisition capabilities. Based on market presence, product performance, and technical specifications, here are the top 9 galvanostat manufacturers shaping the future of electrochemical research and industrial testing.
Top 9 Galvanostat Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Galvanostat
Domain Est. 2003
Website: ivium.com
Key Highlights: Ivium Technologies is a leading manufacturer of Potentiostat/Galvanostat instruments, providing cutting-edge technology and solutions for the electrochemistry ……
#2 Electrochemical Instruments
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1989
Website: gamry.com
Key Highlights: Gamry the Leader in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy for Battery/Fuel Cell – Corrosion Testing. Potentiostat/Galvanostat Manufacturer since 1989….
#3 Electrochemical Instruments Manufacturer / BioLogic
Domain Est. 2001
Website: biologic.net
Key Highlights: Potentiostat Galvanostat. Modularity, performance, power and flexibility potentiostats for diverse applications, from single-channel to multichannel ……
#4 Wuhan Corrtest Instrument Co., Ltd
Domain Est. 2006 | Founded: 2007
Website: corrtest.com.cn
Key Highlights: … officially established in 2007. We specialize in R&D, manufacturing, and sales of potentiostat /galvanostat equipment. We have acquired ISO9001, CE ……
#5 Potentiostat / Galvanostat
Domain Est. 2009
Website: sciospec.com
Key Highlights: Our broad range of standard instruments and modules covers all types of application scenarios for research and development as well as industrial applications….
#6 Potentiostats & galvanostats
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metrohm.com
Key Highlights: Our portfolio of electrochemical measuring instruments includes compact to modular and single-channel to multi-channel potentiostats and galvanostats….
#7 PalmSens
Domain Est. 2000
Website: palmsens.com
Key Highlights: PalmSens develops instruments for electrochemical applications. We specialize in making ✓ small, ✓ portable, ✓ economical, potentiostats. View all types….
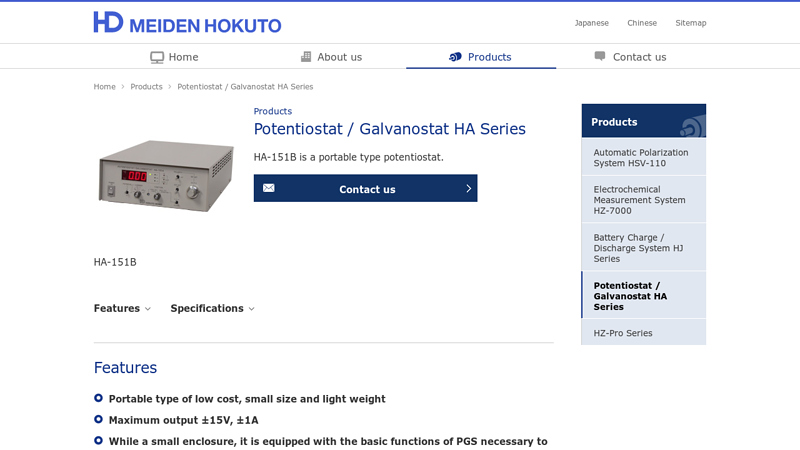
#8 Potentiostat / Galvanostat HA Series
Domain Est. 2010
Website: meidensha.com
Key Highlights: Features · Portable type of low cost, small size and light weight · Maximum output ±15V, ±1A · While a small enclosure, it is equipped with the basic functions of ……
#9 AMETEK SI
Domain Est. 2016
Website: ameteksi.com
Key Highlights: AMETEK SI – leader in manufacturing single, bipot and multichannel potentiostat galvanostat , battery analyzer and frequency response analyzer….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Galvanostat

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Galvanostats
The galvanostat market is poised for significant evolution in H2 2026, driven by advancements in energy storage, materials science, and automation. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends shaping the landscape:
1. Dominance of the Energy Storage & Battery R&D Sector:
* Primary Driver: Lithium-ion battery development remains the single largest application. H2 2026 will see intense focus on next-generation chemistries (Solid-State, Lithium-Sulfur, Sodium-Ion) requiring sophisticated galvanostatic cycling (charge/discharge) for performance, cycle life, and safety testing.
* Trend: Increased demand for high-current, high-precision galvanostats capable of testing large-format cells and battery packs under realistic conditions. Integration with thermal chambers for temperature-dependent studies will be standard.
* Impact: Major growth in sales to automotive OEMs, battery manufacturers, and research institutions. Expect consolidation of testing protocols requiring specific galvanostat capabilities.
2. Rise of Automation, Software, and Data Analytics:
* Primary Driver: The need for higher throughput, reproducibility, and data-driven insights in R&D and QC.
* Trend:
* Smart Galvanostats: Increased adoption of instruments with embedded intelligence, remote monitoring/control (IoT integration), and self-diagnostics.
* Advanced Software Suites: Demand for intuitive software with advanced data visualization, automated test sequencing, real-time analysis (e.g., dQ/dV), and seamless integration with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS).
* AI/ML Integration: Early adoption of AI for predictive maintenance, anomaly detection in test data, and optimizing test parameters based on historical results.
* Impact: Shift from selling hardware alone to offering integrated hardware-software-data solutions. Software subscription models may gain traction. Vendors emphasizing user experience and data management will gain market share.
3. Miniaturization and Integration for Specific Applications:
* Primary Driver: Demand for portable, cost-effective solutions for field testing, education, and specialized research.
* Trend:
* Compact Benchtop & Portable Units: Growth in smaller, USB-powered, or laptop-controlled galvanostats for corrosion monitoring (e.g., infrastructure, pipelines), fuel cell testing, and educational labs.
* Modular Systems: Increased use of modular potentiostat/galvanostat systems allowing users to scale channel counts and capabilities as needs grow, popular in battery testing labs.
* Impact: Expansion beyond traditional academic/research labs into industrial maintenance, field service, and smaller R&D facilities. Price competition in the lower-end segment.
4. Focus on High Precision, Stability, and Low Current Measurement:
* Primary Driver: Research into corrosion mechanisms, low-power devices, biosensors, and fundamental electrochemistry demands extreme sensitivity.
* Trend: Continued development and demand for galvanostats with ultra-low current measurement capabilities (picoamps to nanoamps), superior stability over long durations, and minimal noise. Emphasis on high accuracy and resolution.
* Impact: Premium segment growth. Differentiation through superior analog front-end design and shielding. Increased importance of specifications like compliance voltage range and bandwidth.
5. Sustainability and Green Chemistry Applications:
* Primary Driver: Global push towards sustainability and decarbonization.
* Trend: Growing use of galvanostats in R&D for:
* Electrochemical CO2 Reduction (eCO2R): Optimizing catalysts and processes for converting CO2 into valuable fuels/chemicals.
* Water Electrolysis (Green Hydrogen): Testing and developing efficient catalysts and membranes for PEM and alkaline electrolyzers.
* Advanced Recycling: Electrochemical recovery of critical materials from batteries and electronic waste.
* Impact: New market segments emerging, requiring galvanostats capable of handling complex, multi-step protocols and potentially harsh electrolytes. Collaboration between electrochemists and sustainability engineers will increase.
6. Competitive Landscape and Consolidation:
* Trend: The market remains competitive with established players (Bio-Logic, Metrohm Autolab, Gamry, Pine Research, Solartron/AMETEK) and a growing number of specialized or regional vendors. H2 2026 may see:
* Strategic Acquisitions: Larger players acquiring niche technology providers (e.g., specialized software, sensor integration).
* Partnerships: Increased collaboration between instrument manufacturers and software/AI companies.
* Price Pressure: In commoditized segments, while premium features command higher prices.
* Impact: Continued innovation but also potential for market consolidation. Value proposition will heavily rely on total solution (hardware + software + support).
Summary for H2 2026:
The galvanostat market in H2 2026 will be characterized by strong growth driven by battery R&D, a fundamental shift towards smarter, software-centric instruments, and expansion into new application areas like green chemistry. Success will depend on offering not just precise hardware, but integrated solutions with powerful data analytics, automation capabilities, and reliability tailored to the demanding needs of advanced energy storage, sustainability research, and high-throughput industrial testing. Vendors who excel in software, miniaturization for specific uses, and addressing the precision needs of emerging fields will lead the market.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Galvanostat (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a galvanostat, especially for research, development, or industrial applications involving electrochemistry (like battery testing, corrosion studies, or electroplating), requires careful consideration beyond just price and specifications. Overlooking critical aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to significant problems, including project delays, compromised data integrity, legal risks, and costly replacements.
Quality Pitfalls
-
Insufficient or Inaccurate Specifications:
- Pitfall: Relying solely on manufacturer-provided specs without independent verification or understanding tolerances. Key parameters like current accuracy, stability, resolution, compliance voltage, bandwidth, and noise levels might be overstated or measured under unrealistic conditions.
- Consequence: Poor experimental results, inability to replicate published work, or failure to meet process requirements due to unmet performance needs.
- Mitigation: Demand detailed datasheets with clear definitions of how specs are measured (e.g., over what time, temperature, load). Seek third-party reviews, user testimonials, or independent lab verification if possible. Test units rigorously upon receipt.
-
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection:
- Pitfall: Choosing devices built with low-cost, unreliable components or inadequate thermal management. This includes flimsy connectors, undersized heatsinks, or low-grade op-amps in critical signal paths.
- Consequence: Short operational lifespan, frequent failures (especially under continuous high-load operation), increased downtime, and potential safety hazards (overheating).
- Mitigation: Research the manufacturer’s reputation for durability. Examine build quality physically if possible. Inquire about component sourcing and thermal design. Consider industrial-grade vs. benchtop models for demanding applications.
-
Inadequate Software and Driver Support:
- Pitfall: Assuming software stability, ease of use, and long-term support. Poorly developed drivers (e.g., buggy DLLs, limited API functionality) or unstable, feature-limited control software can severely hamper usability.
- Consequence: Difficulties in automating experiments, data acquisition errors, compatibility issues with existing lab software (LabVIEW, Python), and reliance on vendor support for basic functionality.
- Mitigation: Evaluate the software thoroughly before purchase. Test the API with your intended programming environment. Check for active user forums, software update frequency, and the vendor’s commitment to support legacy hardware.
-
Lack of Calibration and Traceability:
- Pitfall: Sourcing instruments without proper factory calibration certificates or with calibration not traceable to recognized national standards (e.g., NIST, PTB).
- Consequence: Unreliable and non-comparable data, failure to meet quality standards (e.g., ISO 17025) in regulated environments, difficulty publishing results.
- Mitigation: Require a valid calibration certificate with traceability upon purchase. Establish a regular recalibration schedule with accredited labs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Unclear or Restrictive Licensing for Control Software/APIs:
- Pitfall: Failing to scrutinize the End User License Agreement (EULA) for the instrument’s control software or API. Licenses might prohibit modification, reverse engineering necessary for integration, redistribution in custom software, or commercial use of data/automation scripts.
- Consequence: Inability to develop custom automation solutions, potential legal action if IP rights are infringed, limitations on how research results or process data can be used or shared.
- Mitigation: Review the EULA before purchase. Negotiate licensing terms if necessary, especially for commercial R&D. Prefer vendors offering open APIs or permissive licensing (e.g., MIT, BSD) for software components.
-
Proprietary Data Formats and Lock-in:
- Pitfall: Vendors using closed, undocumented data file formats that can only be read by their specific software.
- Consequence: Vendor lock-in, inability to analyze data with preferred third-party software (e.g., Python, Origin, MATLAB), loss of access to data if the vendor software becomes obsolete or unsupported.
- Mitigation: Demand open, well-documented data formats (e.g., CSV, HDF5, .mpt for Bio-Logic) or ensure robust export functions to standard formats. Verify long-term data accessibility plans.
-
Ambiguity in Ownership of Developed Software/Protocols:
- Pitfall: Assuming that custom control software, automation scripts, or experimental protocols developed using the galvanostat automatically belong to the user, without considering if they incorporate significant elements of the vendor’s proprietary IP.
- Consequence: Disputes over ownership, inability to patent or freely commercialize processes developed using the instrument, or restrictions on publishing methods.
- Mitigation: Consult legal counsel. Clearly define IP ownership in contracts, especially for custom development work. Document the separation between vendor IP and user-developed IP.
-
Counterfeit or Gray Market Instruments:
- Pitfall: Sourcing from unauthorized distributors or markets where counterfeit instruments or stolen/reconditioned units are sold.
- Consequence: Significant quality and reliability issues, lack of warranty, potential safety risks, no access to legitimate software updates or support, and potential IP infringement by the manufacturer of the counterfeit device.
- Mitigation: Purchase only from authorized distributors or directly from the manufacturer. Verify authenticity through serial numbers and official channels.
By proactively addressing these common quality and IP pitfalls during the sourcing process, organizations and researchers can ensure they acquire a reliable, capable galvanostat that supports their work effectively and avoids costly downstream problems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Galvanostat
Overview
A galvanostat is an electronic instrument used primarily in electrochemical research and industrial applications to maintain a constant current through an electrochemical cell. Proper logistics handling and compliance with international, national, and institutional regulations are essential due to the device’s electronic components, potential battery content, and use in regulated environments.
Shipping & Handling
Packaging Requirements
- Use original manufacturer packaging whenever possible to ensure shock and moisture protection.
- If original packaging is unavailable, use a double-boxing method with anti-static foam or cushioning material to prevent internal movement.
- Clearly label the package as “Fragile,” “Electronic Equipment,” and “This Side Up.”
- Include desiccant packs if shipping to high-humidity environments to prevent condensation.
Transportation Modes
- Air Freight: Acceptable if devices contain no restricted batteries. Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if lithium batteries (e.g., internal backup) are present.
- Ground Freight: Preferred for domestic shipments; standard commercial carriers (e.g., FedEx, UPS) are suitable with proper labeling.
- Sea Freight: Use for large or bulk shipments; ensure packaging is moisture-resistant and palletized with waterproof wrapping.
Temperature & Environmental Conditions
- Store and transport within 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F).
- Avoid condensation, excessive vibration, and direct sunlight.
- Relative humidity should not exceed 80% (non-condensing).
Regulatory Compliance
International Regulations
- CE Marking: Required for entry into the European Economic Area (EEA). Confirms compliance with EU directives on electromagnetic compatibility (EMC Directive 2014/30/EU) and electrical safety (Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU).
- RoHS Compliance: Ensure the device complies with Restriction of Hazardous Substances (EU Directive 2011/65/EU), limiting lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials.
- REACH: Confirm no restricted substances above threshold levels are used in construction materials.
North American Standards
- FCC Certification: Required for sale in the U.S. Ensures electromagnetic interference does not disrupt other devices (47 CFR Part 15).
- UL/CSA Certification: Recommended for electrical safety compliance in both U.S. and Canada. Look for UL 61010-1 or CSA C22.2 No. 61010-1 certification.
Battery Considerations
- If the galvanostat contains a built-in lithium battery:
- Comply with UN 38.3 testing certification for lithium cells/batteries.
- Follow IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (Section II or Section IB, depending on battery size) for air transport.
- Mark packages with proper Class 9 Lithium Battery Hazard Label and include a Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods when required.
Import & Export Requirements
Export Controls
- Galvanostats may fall under dual-use export control lists due to potential applications in materials research or defense-related electrochemistry.
- Check EAR (Export Administration Regulations – U.S. Department of Commerce): Most galvanostats are classified under ECCN 3A999 (No License Required – NLR), but verify based on specifications (e.g., current accuracy, frequency response).
- For EU exports, consult EU Dual-Use Regulation (EC) No 428/2009 and check if the device requires an export license.
Import Documentation
- Provide a detailed commercial invoice including:
- Full product description (“Galvanostat for Electrochemical Testing”)
- Model and serial number
- Harmonized System (HS) Code – typically 9027.80 (instruments and apparatus for physical or chemical analysis)
- Country of origin
- Value in USD or local currency
- Include packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of compliance (CE, FCC, etc.) when required.
Customs & Duties
HS Code Classification
- HS 9027.80: Instruments and apparatus for physical or chemical analysis (e.g., galvanostats, potentiostats).
- Confirm local tariff classification; some countries may apply specific subcategories.
Duty Exemptions
- ATA Carnet: Recommended for temporary exports (e.g., for trade shows or collaborative research). Allows duty-free, temporary importation in over 80 countries.
- Scientific Equipment Programs: Some countries (e.g., U.S. under HTSUS 9810.00.60) offer duty-free entry for equipment used in research or educational institutions.
End-Use & Institutional Compliance
Laboratory Safety
- Comply with OSHA (29 CFR 1910) or equivalent local regulations for electrical safety in workplaces.
- Ensure grounding and surge protection are used during operation.
- Train personnel on proper handling and emergency shutdown procedures.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
- At end-of-life, dispose of the galvanostat according to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive 2012/19/EU) in Europe.
- In the U.S., follow EPA guidelines for electronic waste; recycle through certified e-waste handlers.
- Remove and recycle batteries separately per local regulations (e.g., under Part 273 of RCRA for U.S. generators).
Summary Checklist
| Category | Action Required |
|—————————|———————————————————————————|
| Packaging | Use anti-static, shock-absorbing materials; label as fragile |
| Shipping | Comply with IATA if lithium battery present; avoid extreme temperatures |
| Certifications | Verify CE, FCC, RoHS, and UL/CSA as applicable |
| Export Controls | Confirm ECCN under EAR or EU dual-use status; obtain license if required |
| Import Documentation | Provide commercial invoice, HS code (9027.80), and compliance certificates |
| End-of-Life | Recycle via WEEE or certified e-waste program; handle batteries separately |
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient logistics for galvanostats across global supply chains. Always consult local regulations and involve compliance officers for high-value or sensitive shipments.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Galvanostat
After evaluating technical specifications, performance requirements, cost considerations, and supplier reliability, sourcing a galvanostat requires a balanced approach that aligns the instrument’s capabilities with the intended electrochemical applications—such as battery testing, corrosion studies, or electrodeposition. Both in-house procurement and outsourcing options were considered, with an emphasis on accuracy, stability, current range, and compatibility with existing systems.
Ultimately, selecting a galvanostat from a reputable supplier with strong technical support, calibration services, and scalability ensures long-term reliability and data integrity. For high-precision or research-intensive applications, investing in a higher-end model with modular features may offer better value over time. Conversely, for routine or educational use, cost-effective alternatives without compromising essential functionality should be prioritized.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing decision—based on application needs, budget constraints, and future scalability—will optimize performance, ensure experimental reproducibility, and support the advancement of electrochemical research or industrial processes.