The global galvanizing metals market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for corrosion-resistant materials across construction, automotive, and infrastructure industries. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 63.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, stringent regulatory standards for material durability, and the expanding use of galvanized steel in renewable energy infrastructure. As environmental conditions continue to accelerate metal degradation, the importance of high-performance galvanizing solutions has never been greater. Against this backdrop, leading manufacturers are scaling production, investing in advanced coating technologies, and broadening geographic reach to meet evolving industrial demands. Below is a data-driven look at the top 10 galvanizing metals manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Galvanizing Metals Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ZRC Worldwide
Domain Est. 1998
Website: zrcworldwide.com
Key Highlights: ZRC Worldwide has been worldwide industry leader providing unmatched, lasting solutions for cold galvanizing corrosion protection technology for over 70 ……
#2 ANDRITZ METALS
Domain Est. 1995
Website: andritz.com
Key Highlights: ANDRITZ METALS supplies complete lines for the production and processing of cold rolled carbon steel, stainless steel and non ferrous metal strip….
#3
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metalplate.com
Key Highlights: Metalplate is dedicated to providing the very best in hot-dip galvanizing. With seven modern plants located in steel and transportation centers across the ……
#4 AZZ
Domain Est. 1997
Website: azz.com
Key Highlights: North America’s leading provider of hot-dip galvanizing, metal coatings, and coil coating solutions to protect critical infrastructure….
#5 Hot
Domain Est. 1997
Website: galvanizeit.org
Key Highlights: The AGA serves the hot-dip galvanized steel industry by providing performance, specification, design, inspection and other resources for specifiers….
#6 Gregory Industries
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gregorycorp.com
Key Highlights: Gregory Industries leads with quality steel products, innovative processes, and expert people. See how our roll-formed solutions can support you….
#7 United States
Domain Est. 2003
Website: valmontcoatings.com
Key Highlights: Valmont Coatings is a leading provider of hot dip galvanizing and protective coating services. For years we have offered corrosion protection for metal….
#8 Commonwealth Galvanizing
Domain Est. 2012
Website: commonwealthgalv.com
Key Highlights: With decades of hot-dip galvanizing experience and expertise in everything from coating requirements to fabrication details, We can give you satisfaction….
#9 Sandvik Group
Domain Est. 2015
Website: home.sandvik
Key Highlights: Sandvik is an engineering group providing products and solutions for mining and rock excavation, rock processing and metal cutting based on innovation, ……
#10 Cold Galvanizing Products
Domain Est. 2015
Website: galv-pro.com
Key Highlights: For 20+ years, we’ve been supplying cold galvanizing products all around the USA. Our products are affordable & durable! Place an order with us today!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Galvanizing Metals
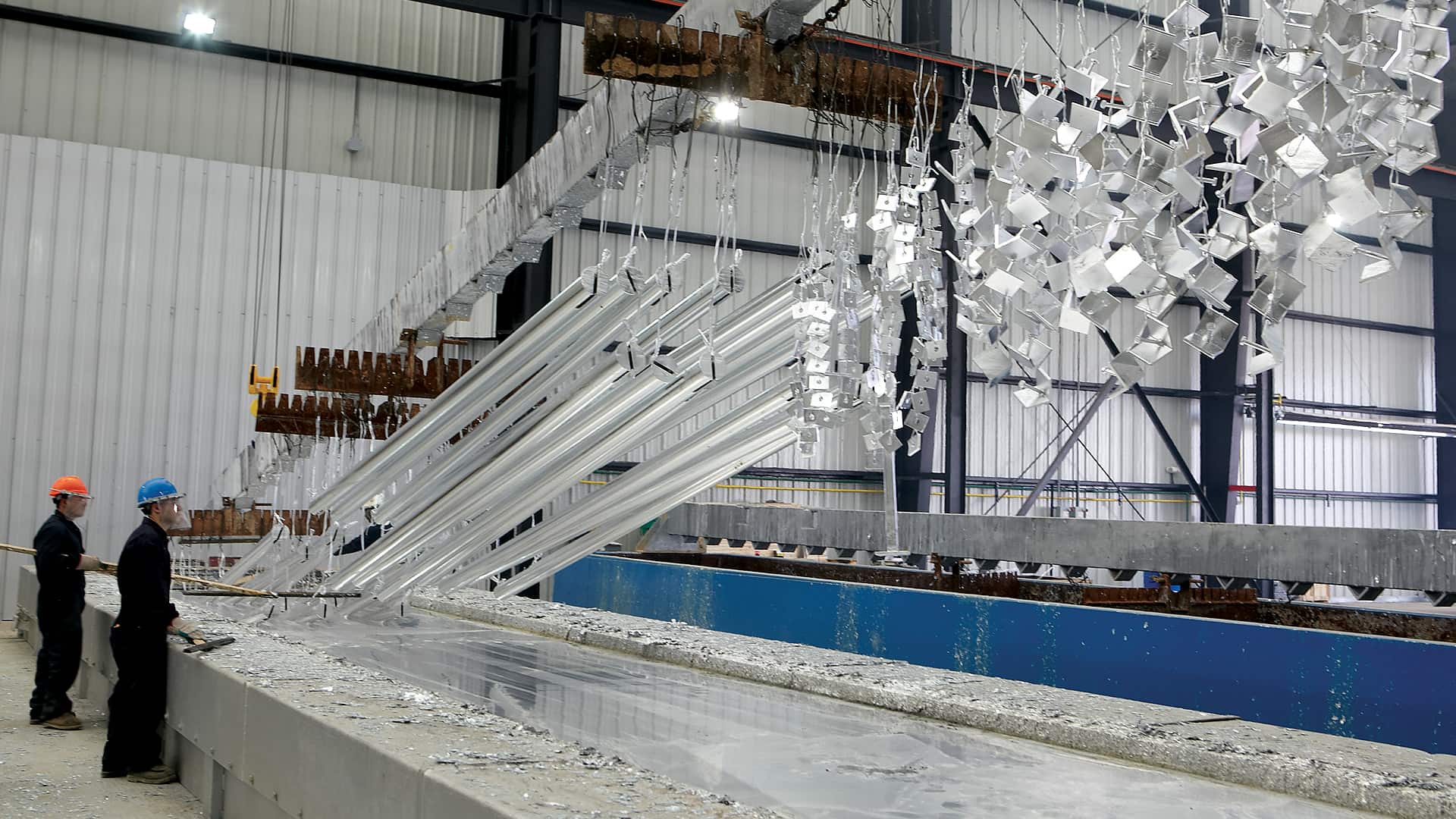

H2: Projected Market Trends in Galvanizing Metals for 2026
The galvanizing metals market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by infrastructure development, sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and fluctuating raw material dynamics. Hot-dip galvanizing, in particular, remains a dominant protective coating method for steel, with growing demand across construction, automotive, energy, and utility sectors. The following key trends are expected to shape the galvanizing metals market in 2026:
-
Increased Infrastructure Investment Driving Demand
Governments worldwide—especially in emerging economies and through initiatives like the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act—are allocating substantial funds toward transportation, water systems, and renewable energy infrastructure. These projects require corrosion-resistant materials, boosting demand for galvanized steel in bridges, pipelines, and transmission towers. By 2026, infrastructure expansion in Asia-Pacific (particularly India and Southeast Asia) and Africa is expected to be a primary growth driver. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals will intensify focus on sustainable production methods. Galvanizing is increasingly favored for its long service life (50+ years with minimal maintenance) and recyclability. Zinc, a key component in galvanizing, is 100% recyclable without degradation. By 2026, producers will likely adopt more energy-efficient furnaces, closed-loop water systems, and recycled zinc to meet green building standards and reduce carbon footprints. -
Advancements in Galvanizing Technology
Innovation in alloy development, such as zinc-aluminum-magnesium (ZAM) coatings, will gain traction by 2026 due to enhanced corrosion resistance and reduced zinc consumption. These high-performance coatings are especially valuable in harsh environments (coastal, industrial). Automation and digital monitoring in galvanizing lines—using IoT and AI for process control—will improve coating consistency and reduce operational costs. -
Fluctuating Zinc Prices and Supply Chain Dynamics
Zinc, the core material in galvanizing, faces price volatility due to geopolitical tensions, mining disruptions, and demand from battery technologies (e.g., zinc-air and zinc-ion batteries). By 2026, supply chain resilience will be critical. Producers may diversify sourcing, increase recycling efforts, or enter long-term contracts with miners to stabilize input costs. -
Growth in Renewable Energy Applications
The global push toward clean energy will expand the use of galvanized steel in wind turbine towers, solar panel mounting structures, and grid infrastructure. Offshore wind projects, in particular, demand high-grade galvanized or duplex-coated (galvanized + paint) steel due to extreme marine corrosion. This sector is expected to be a high-growth niche by 2026. -
Regional Market Shifts
While China remains the largest producer and consumer of galvanized steel, environmental crackdowns may shift some production to Southeast Asia and India. North America will see steady growth due to reshoring of manufacturing and infrastructure renewal. Europe’s strict environmental standards will promote premium galvanizing solutions and recycled content usage. -
Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The galvanizing industry may experience consolidation as smaller players struggle with regulatory and cost pressures. Larger firms with vertical integration—from steel production to coating services—will gain market share. Strategic partnerships between galvanizers and construction firms are likely to increase for turnkey corrosion protection solutions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the galvanizing metals market will be shaped by a confluence of regulatory, technological, and macroeconomic forces. Demand will remain robust, particularly in infrastructure and renewable energy, while innovation and sustainability will differentiate market leaders. Companies that invest in advanced coatings, circular practices, and supply chain resilience are best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Galvanizing Metals: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing galvanizing metals, whether for hot-dip galvanizing, electro-galvanizing, or as finished galvanized products, involves navigating complex quality and intellectual property (IP) challenges. Overlooking these areas can lead to project delays, increased costs, safety risks, and legal liabilities. Here are the key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate or Non-Standard Material Specifications
A frequent issue is sourcing metals without clearly defined, industry-standard specifications (e.g., ASTM A1008/A1008M for sheet, ASTM A53/A53M for pipe, or ISO 1461 for galvanized coatings). Relying on vague descriptions or supplier promises without documented specs can result in receiving subpar materials that fail to meet performance requirements such as corrosion resistance, tensile strength, or coating thickness.
2. Inconsistent Coating Thickness and Adherence
Galvanized coatings must meet minimum thickness standards (e.g., specified in ASTM A123 for structural steel) to ensure long-term durability. Pitfalls arise when suppliers deliver materials with uneven, too-thin, or poorly bonded coatings. This compromises corrosion protection, leading to premature rusting and structural degradation—especially in harsh environments.
3. Poor Base Metal Quality
The quality of the underlying steel significantly impacts the galvanizing process and final product. Sourcing steel with high silicon or phosphorus content (e.g., reactive steel) can lead to excessively thick, brittle, or non-uniform zinc-iron alloy layers. Additionally, surface contaminants like paint, oil, or mill scale can inhibit proper zinc adhesion, resulting in bare spots or peeling.
4. Lack of Certification and Traceability
Failing to require certified material test reports (MTRs) or mill certificates is a major risk. Without documentation verifying chemical composition, mechanical properties, and conformity to standards, traceability is lost. This becomes critical during audits, failure investigations, or compliance checks (e.g., for construction or infrastructure projects).
5. Inadequate Inspection and Testing Protocols
Many organizations source galvanizing metals without implementing incoming inspection procedures. Skipping checks for coating thickness (using magnetic gauges), visual defects (bare spots, drips, roughness), or mechanical damage during transit can allow defective materials into the production or construction phase, leading to costly rework.
Intellectual Property (IP) Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Patented Alloys or Processes
Some advanced galvanizing processes or alloy formulations (e.g., Galfan, Galvalume, or proprietary Zn-Al-Mg coatings) are protected by patents. Sourcing metals using these technologies without proper licensing can expose the buyer to IP infringement claims, especially in international markets with strong IP enforcement.
2. Reverse Engineering and Design Replication
When custom-fabricated galvanized components are outsourced, there’s a risk that suppliers may reverse-engineer the design and produce or sell similar products without authorization. This is particularly dangerous when working with non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are weak or absent, leading to loss of competitive advantage.
3. Lack of IP Clauses in Supplier Contracts
Many procurement agreements fail to explicitly define ownership of designs, molds, or process improvements developed during the sourcing relationship. Without clear IP clauses, disputes may arise over who owns tooling or technical data—especially if the supplier uses your design to serve other clients.
4. Sourcing from Suppliers with Questionable IP Practices
Engaging suppliers known for copying branded or patented products (e.g., imitation galvanized roofing sheets or fasteners) can indirectly implicate your organization in IP violations. This not only risks legal action but also damages brand reputation and customer trust.
5. Insufficient Due Diligence on Supplier IP Compliance
Failing to vet suppliers for IP compliance—such as requesting proof of licensing for patented materials or processes—can result in downstream liability. This is particularly critical in regulated industries like automotive or aerospace, where traceability and IP integrity are rigorously audited.
Mitigation Strategies
- Define clear technical specifications aligned with international standards.
- Require full material certification and maintain a traceability system.
- Conduct pre-qualification audits of suppliers, including quality systems and IP compliance.
- Include robust IP clauses in contracts covering design ownership, confidentiality, and infringement indemnity.
- Perform regular incoming inspections and third-party testing when necessary.
- Engage legal counsel to review sourcing agreements, especially for proprietary or patented materials.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally sound sourcing of galvanizing metals.
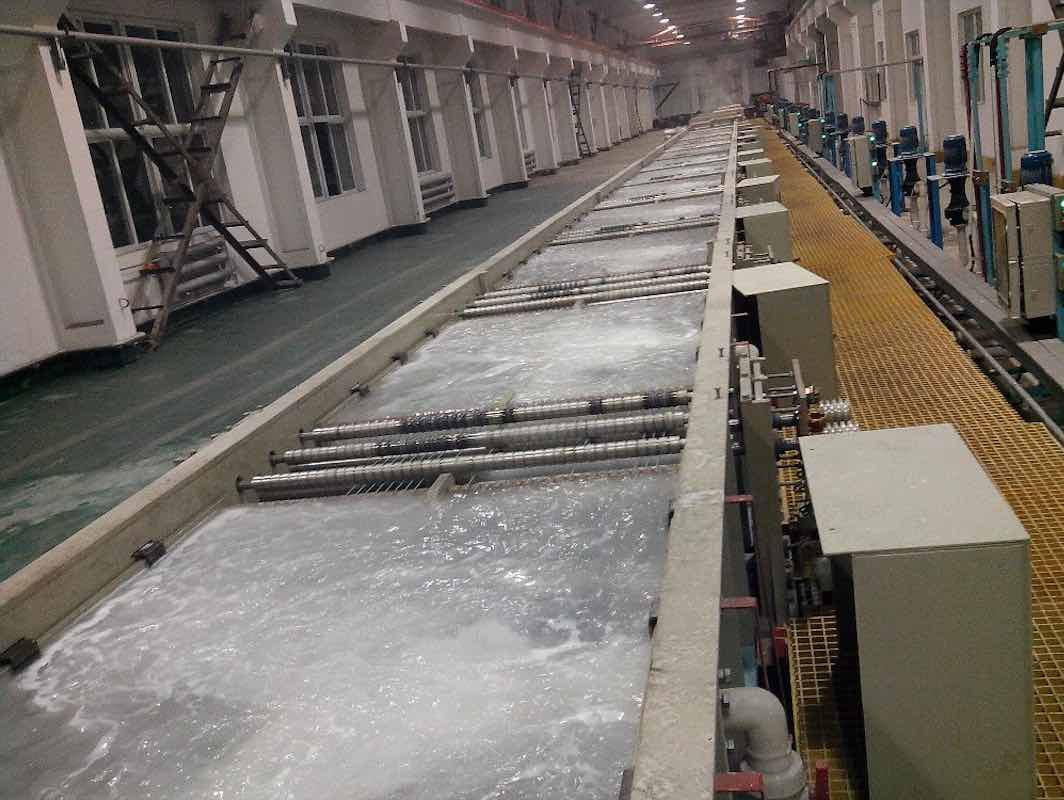

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Galvanizing Metals
Overview of Metal Galvanizing Processes
Galvanizing is a critical process used to protect metals, primarily steel and iron, from corrosion by applying a protective zinc coating. The most common method is hot-dip galvanizing, where the metal is immersed in molten zinc. Other techniques include electrogalvanizing, sherardizing, and zinc spraying. Each method has specific logistical and compliance implications related to handling, transportation, storage, and environmental safety.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Environmental Protection Standards
Galvanizing operations are subject to stringent environmental regulations due to the use of hazardous materials such as zinc, hydrochloric acid (for pickling), and caustic soda. Compliance with agencies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), European Union REACH, and local environmental authorities is mandatory. Facilities must:
- Obtain air emissions permits for zinc fumes and acid mists.
- Implement wastewater treatment systems to manage spent pickling solutions and rinse waters.
- Follow Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) guidelines for managing hazardous waste byproducts.
Occupational Health and Safety (OSHA/NIOSH)
Worker safety is paramount in galvanizing operations. High temperatures, chemical exposure, and heavy lifting require strict adherence to OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards, including:
- Providing personal protective equipment (PPE) such as heat-resistant gloves, face shields, and respirators.
- Conducting regular training on handling molten zinc and chemical safety.
- Ensuring proper ventilation in pickling and galvanizing areas to control fume exposure.
International Standards and Certifications
Compliance with ISO standards such as ISO 1461 (hot-dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles) and ISO 9001 (quality management) ensures product consistency and operational reliability. For export, adherence to ASTM A123 (U.S. standard) or EN ISO 1461 (European standard) may be required depending on the destination market.
Logistics Management
Raw Material Handling and Storage
Proper storage and handling of raw materials are essential to maintain process efficiency and safety.
- Steel components: Must be clean, dry, and free of contaminants such as oil, paint, or rust before galvanizing.
- Zinc ingots: Stored in dry, ventilated areas to prevent moisture contact, which can lead to oxidation.
- Acids and alkalis: Stored in corrosion-resistant containers, segregated from other materials, with secondary containment to prevent spills.
Transportation of Galvanized Products
Transporting galvanized metal requires protection against mechanical damage and environmental exposure.
- Use padded straps and protective wraps to prevent coating damage during loading and transit.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to saltwater or high-humidity environments to prevent white rust (zinc oxide formation).
- Comply with DOT (Department of Transportation) or ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road) regulations when shipping chemicals used in the process.
In-Plant Material Flow
Efficient workflow minimizes delays and safety risks.
- Implement a linear process flow: degreasing → rinsing → pickling → fluxing → galvanizing → cooling → inspection.
- Use automated handling systems where possible to reduce worker exposure to high-temperature areas.
- Schedule production to minimize idle time between stages, especially after pickling, to avoid re-oxidation.
Waste Management and Environmental Compliance
Spent Acid and Sludge Disposal
Spent hydrochloric or sulfuric acid from pickling baths must be neutralized and treated before disposal. Zinc-iron sludge generated during the process is often classified as hazardous waste and must be:
- Collected in sealed containers.
- Labeled and stored in designated hazardous waste areas.
- Transported by licensed waste handlers with proper manifests.
Air Emission Controls
Galvanizing furnaces emit zinc oxide fumes, which must be controlled using:
- Fume extraction systems with baghouses or wet scrubbers.
- Regular monitoring and reporting to environmental agencies.
- Routine maintenance of pollution control equipment.
Recycling and Sustainability Practices
- Recycle zinc ash and skimmings back into the galvanizing bath where feasible.
- Reuse rinse water through closed-loop water treatment systems to reduce consumption and wastewater discharge.
- Partner with certified recyclers for scrap metal and spent chemical containers.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Accurate documentation supports compliance and traceability:
- Maintain logs of chemical inventories, usage, and disposal.
- Keep calibration and maintenance records for pollution control and safety equipment.
- Retain material test reports (MTRs) and coating thickness certifications for each batch.
- Document employee training on safety and environmental procedures.
Import/Export Considerations
When shipping galvanized metal products internationally:
- Verify destination country regulations for zinc-coated materials (e.g., RoHS compliance in the EU).
- Prepare proper shipping manifests, safety data sheets (SDS), and export documentation.
- Account for customs classifications under HS Code 7306 (iron or steel products, galvanized).
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance in metal galvanizing require a holistic approach integrating safety, environmental stewardship, and regulatory adherence. By following established standards and maintaining rigorous operational controls, galvanizing facilities can ensure product quality, worker safety, and legal compliance across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Galvanizing Metals:
Sourcing galvanizing metals requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, supply chain reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Hot-dip galvanized steel remains a preferred material for its superior corrosion resistance, longevity, and low maintenance, especially in demanding environments such as construction, automotive, and infrastructure projects. When selecting suppliers, it is essential to partner with reputable providers who adhere to recognized galvanizing standards (e.g., ASTM A123, ISO 1461) and maintain consistent quality control processes.
Key considerations include zinc coating thickness, material grade, lead times, geographic proximity, and environmental practices. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who offer technical support and traceability can enhance project efficiency and reduce risks. Additionally, monitoring fluctuations in raw material prices and global zinc markets allows for better cost management and procurement planning.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of galvanizing metals hinges on a comprehensive evaluation of supplier capabilities, material specifications, and sustainability factors. A well-structured procurement strategy ensures the delivery of high-performance galvanized products that contribute to durable, safe, and cost-effective end applications.