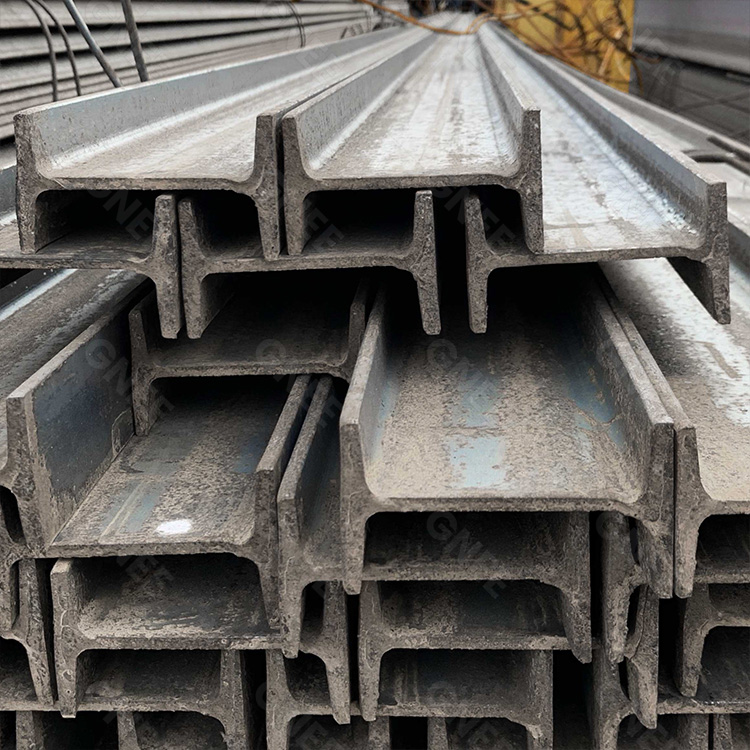
The global steel construction market is witnessing robust growth, driven by rising infrastructure development and increasing demand for durable, corrosion-resistant materials. According to Mordor Intelligence, the galvanized steel market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by expanding applications in construction, automotive, and industrial sectors. Galvanized I beams, known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and long-term durability due to zinc coating, are becoming a preferred choice in commercial and industrial building frameworks. With Asia-Pacific accounting for the largest share of production and consumption—led by China and India—manufacturers are scaling capacity and investing in advanced galvanization technologies to meet stringent quality standards and growing demand. This list highlights the top 10 galvanized I beam manufacturers leveraging innovation, production efficiency, and global distribution networks to lead a rapidly evolving market.
Top 10 Galvanised I Beam Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Algoma Steel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: algoma.com
Key Highlights: Algoma Steel Inc. is a steel producer of hot and cold-rolled steel sheet and plate products based in Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada. Land Acknowledgement….
#2 U.S. Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: We’re bringing industry-leading steelmaking talent and technology together to help customers solve, innovate and excel. Just one example: lighter, stronger ……
#3 Structural Steel Beams
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nssco.com
Key Highlights: As the premier supplier of structural and galvanized steel beams, we offer an extensive selection of beams in various standard sizes and finishes….
#4 Delta Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: deltasteel.com
Key Highlights: Delta Steel is your one-stop-shop for all your structural steel needs. We can guarantee customer satisfaction built with steel!…
#5 Chicago Tube & Iron
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1914
Website: chicagotube.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1914, CTI is one of the largest specialty steel service centers in the United States, with nine locations throughout the Midwest and in Monterrey, ……
#6 Steel Beams USA
Domain Est. 1998
Website: norfolkiron.com
Key Highlights: Norfolk Iron stocks three types of beams, including standard I beams, junior beams, and wide flange beams, in a wide range of sizes….
#7 Metwood
Domain Est. 1998
Website: metwood.com
Key Highlights: 6-day delivery 30-day returnsMetwood: Innovative cold-formed steel solutions for construction. Explore joist reinforcers, Ledger Brackets, ICF hangers, and more….
#8 Steel Dynamics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: lpg.steeldynamics.com
Key Highlights: A broad range of strong, durable wide-flange beams, I-beams, H-pile sections, M-beams, and structural merchant beams for steel buildings, bridges, and other ……
#9 Wheeling
Domain Est. 2020
Website: wheeling-nipponsteel.com
Key Highlights: WHEELING-NIPPON STEEL is the only steel coating mill in the United States that produces all major hot-dip coated products under one roof….
#10 Eagle National Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: eaglesteel.com
Key Highlights: Eagle National Steel provides quality steel products for all construction needs. Browse our selection for competitive pricing and reliable service….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Galvanised I Beam
H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Galvanised I-Beams
The global market for galvanised I-beams is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by rising demand in construction, infrastructure development, and industrial applications. As governments and private sectors invest heavily in sustainable and durable building materials, galvanised I-beams—known for their corrosion resistance, strength, and longevity—are becoming a preferred choice in structural engineering.
1. Growth Drivers in 2026
Urbanization and infrastructure expansion, particularly in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America, are key catalysts. Countries such as India, Indonesia, and Nigeria are launching large-scale public infrastructure projects, including bridges, railways, and commercial buildings, which significantly boost demand for galvanised steel products. Additionally, the push for green building certifications (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) encourages the use of corrosion-resistant materials like galvanised I-beams, reducing maintenance costs and environmental impact over a structure’s lifecycle.
2. Technological and Manufacturing Advancements
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to adopt advanced galvanising techniques such as continuous galvanising lines (CGL) and improved zinc alloy coatings (e.g., Galfan, Galvalume) to enhance product performance. Automation and digitalization in steel production will improve precision, reduce waste, and support just-in-time delivery—critical factors in meeting large project timelines.
3. Regional Market Outlook
– Asia-Pacific: Dominates the market due to rapid industrialization and government-backed construction initiatives. China and India remain top consumers, with growing emphasis on high-quality, pre-treated structural steel.
– North America: Sustained demand from infrastructure modernization programs (e.g., U.S. Bipartisan Infrastructure Law) and commercial construction supports market growth.
– Europe: Focus on sustainable construction and stringent environmental regulations favor galvanised over painted or untreated steel components.
– Middle East & Africa: Mega-projects (e.g., NEOM in Saudi Arabia, infrastructure upgrades in Egypt) are driving demand for durable structural materials.
4. Challenges and Constraints
Fluctuating raw material prices, especially zinc and iron ore, pose cost volatility risks. Trade policies, carbon emission regulations, and supply chain disruptions (e.g., shipping delays, energy costs) may affect production and distribution. However, recycling initiatives and closed-loop manufacturing systems are helping companies mitigate environmental and cost pressures.
5. Competitive Landscape
The market is moderately consolidated, with key players including ArcelorMittal, Nippon Steel, JSW Steel, and Tata Steel investing in capacity expansion and R&D. Strategic partnerships with construction firms and prefabrication companies are becoming common to secure long-term contracts.
6. Price and Demand Forecast
The global galvanised I-beam market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.5% from 2023 to 2026. Prices are expected to remain stable or increase slightly due to energy costs and environmental compliance requirements, but demand will remain resilient due to the product’s long-term value proposition.
Conclusion
By 2026, the galvanised I-beam market will be shaped by infrastructure development, sustainability mandates, and technological innovation. Companies that prioritize product quality, environmental compliance, and supply chain resilience are likely to capture significant market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Galvanised I Beams (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing galvanised I beams requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to structural failures, project delays, legal disputes, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Galvanising Quality
One of the most frequent issues is receiving galvanised I beams with substandard coating quality. This includes insufficient zinc coating thickness, uneven coverage, bare spots, or poor adhesion. Such defects compromise corrosion protection, significantly reducing the beam’s lifespan, especially in harsh environments. Always verify compliance with relevant standards (e.g., ASTM A123 or ISO 1461) and request coating thickness reports from certified laboratories.
Inadequate Base Steel Quality
The performance of the galvanised coating depends heavily on the underlying steel. Beams made from low-grade or improperly processed steel may contain impurities (e.g., excessive silicon or phosphorus), leading to overly thick, brittle zinc coatings or premature coating failure. Ensure the supplier provides mill test certificates (MTCs) confirming the steel meets required mechanical and chemical specifications (e.g., ASTM A36, A572, or S355).
Non-Compliance with Design Standards
Suppliers may offer I beams that do not conform to the required dimensional tolerances or load-bearing specifications. Using non-compliant beams can compromise structural integrity. Always confirm that beams meet regional or project-specific standards (e.g., ASTM, BS, or EN) and cross-check dimensions and load ratings with engineering drawings.
Incomplete or Missing Documentation
Lack of proper documentation—such as mill test reports, galvanising certificates, or third-party inspection records—raises red flags about traceability and quality assurance. Insist on full documentation packages to verify compliance and support quality audits.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Sourcing beams from unauthorized manufacturers or those replicating patented designs (e.g., proprietary I beam profiles or connection systems) can expose your project to legal risks. Using counterfeit or imitation products may void warranties and lead to liability in case of failure. Always purchase from licensed, reputable suppliers and verify the legitimacy of the product design and branding.
Misrepresentation of Origin or Certification
Some suppliers may falsely claim that beams originate from certified mills or are produced under specific quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001). This misrepresentation can mask poor manufacturing practices. Conduct supplier audits or work with third-party inspection agencies to validate claims and inspect materials before shipment.
Inconsistent Coating After Transportation or Handling
Even high-quality galvanised beams can suffer coating damage during transport or on-site handling. Scratches, dents, or abrasions expose the steel to corrosion. Specify protective packaging and proper handling procedures in procurement contracts to minimise damage risks.
Failure to Specify Galvanising Method
Hot-dip galvanising is the standard for structural steel, but some suppliers may offer inferior alternatives like electrogalvanising or zinc spraying. These methods do not provide the same level of protection. Clearly specify hot-dip galvanising in procurement documents to ensure durability.
By being aware of these pitfalls and implementing rigorous sourcing protocols—including vetting suppliers, demanding documentation, and conducting inspections—you can ensure the quality and IP compliance of galvanised I beams for your project.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Galvanised I Beams
Overview
Galvanised I Beams are structural steel beams coated with a protective layer of zinc to enhance corrosion resistance. Due to their weight, dimensions, and material properties, their transportation, handling, and regulatory compliance require careful planning. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and efficient movement of galvanised I beams from manufacturer to end-user.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging and handling are essential to maintain the integrity of the galvanised coating and ensure worker safety.
- Bundle Securing: I beams should be bundled together using steel strapping or binding wire, with protective padding (e.g., timber dunnage) between layers to prevent coating damage.
- Lifting Procedures: Use slings or lifting clamps designed for structural steel. Avoid direct contact between lifting equipment and the galvanised surface to prevent scratches or zinc damage.
- Storage: Store beams off the ground on level platforms with adequate support to avoid warping. Cover if stored outdoors to reduce exposure to moisture and contaminants that may compromise the galvanised layer.
Transportation Requirements
Transporting galvanised I beams requires adherence to load securement standards and dimensional regulations.
- Load Securing: Use chains, binders, or tension straps to secure beams to flatbed trailers. Ensure even weight distribution and prevent shifting during transit.
- Over-Dimensional Loads: Beams exceeding standard road dimensions (e.g., length > 12 meters) may require special permits, pilot vehicles, and route planning. Check local transport authority regulations.
- Corrosion Protection During Transit: Cover loads with waterproof tarpaulins if exposed to rain or sea spray to prevent white rust (wet storage stain) formation on the galvanised surface.
International Shipping Considerations
When shipping galvanised I beams internationally, additional compliance and documentation are required.
- Export Documentation: Include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and material test reports (e.g., EN 10204 3.1).
- Customs Compliance: Ensure Harmonized System (HS) code accuracy (typically 7301.10 for structural sections). Declare zinc-coated steel beams correctly to avoid delays.
- Marine Transport: Protect beams from saltwater exposure. Use vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI) or desiccants in containers if shipping by sea.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Adherence to international and regional standards ensures structural integrity and worker safety.
- Material Standards: Galvanised I beams must comply with relevant standards such as:
- ASTM A123 (Standard for Zinc Coating on Iron and Steel Products)
- EN ISO 1461 (Hot-Dip Galvanized Coatings on Fabricated Iron and Steel Articles)
- AS/NZS 4680 (Hot-Dip Galvanized Coatings on Fabricated Ferrous Articles)
- Structural Codes: Beams should conform to structural design standards (e.g., AISC, Eurocode 3) based on project location.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: Confirm zinc and steel composition meets EU chemical regulations, particularly for construction projects in Europe.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Galvanised steel is recyclable, but environmental considerations apply during handling and end-of-life.
- Recycling: Galvanised steel is 100% recyclable. Coordinate with certified metal recyclers to ensure proper processing.
- Waste Handling: Cut-offs or damaged beams should be collected and disposed of in accordance with local waste management regulations. Avoid open burning, which can release zinc oxide fumes.
Quality Assurance and Inspection
Ensure compliance and product integrity through routine checks.
- Coating Thickness Testing: Use magnetic gauges to verify zinc coating thickness meets specification (e.g., 85–100 µm for heavy-duty applications).
- Visual Inspection: Check for coating defects such as bare spots, excessive drips, or damage from handling.
- Certification: Require mill test certificates and galvanising certificates from suppliers to confirm compliance with applicable standards.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for galvanised I beams minimizes risks, prevents material degradation, and ensures regulatory alignment. By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure safe handling, efficient transportation, and adherence to quality and environmental standards throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Galvanised I-Beams
In conclusion, sourcing galvanised I-beams is a strategic decision that balances structural integrity, durability, and long-term cost-efficiency. The hot-dip galvanisation process provides superior corrosion resistance, making these beams ideal for outdoor, marine, or high-moisture environments where longevity and minimal maintenance are critical. When sourcing, it is essential to work with reputable suppliers who adhere to international standards such as ASTM A123 or AS/NZS 4680 to ensure coating quality and structural performance.
Factors such as lead times, availability of required dimensions, logistical considerations, and total cost (including transportation and handling) should be carefully evaluated. Additionally, verifying certification and conducting periodic quality inspections can mitigate risks associated with substandard materials.
Overall, investing in high-quality galvanised I-beams not only enhances the safety and lifespan of construction projects but also reduces lifecycle costs, making it a prudent choice for infrastructure, industrial, and commercial applications. A well-planned sourcing strategy ensures that project timelines are met while maintaining the highest standards of quality and performance.