The global base oils market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-performance lubricants across automotive, industrial, and manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 44.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2024 to 2030. With this upward trajectory, the production of Group I, II, and III (G13) base oils—particularly Group III due to its superior oxidation stability and low volatility—has become increasingly strategic. As refiners shift toward advanced hydroprocessing technologies to meet stringent environmental and performance standards, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in G13 base oil supply. This analysis identifies the top six G13 base oil manufacturers based on production capacity, technological advancement, global footprint, and market influence, reflecting their critical role in shaping the future of high-quality lubricant supply chains.
Top 6 G13 Base Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
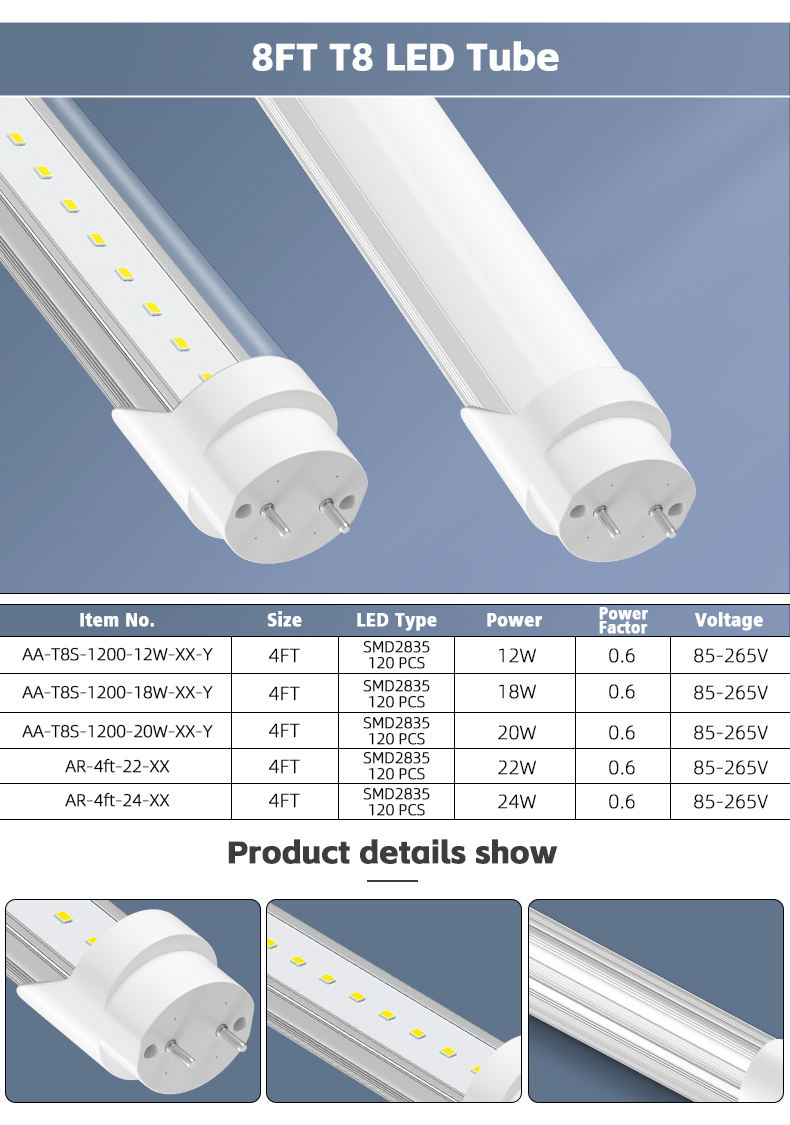
#1 China G13 Base T8 LED Tube Light Manufacturers Suppliers Factory
Domain Est. 2012
Website: benweilighting.com
Key Highlights: *12V-36V T8 LED Tube, the tube can work with power from 12V, 24V and 36V. *Ideal for 12-36V DC Automotive RV Marine lighting system. *DO NOT put into 110V, ……
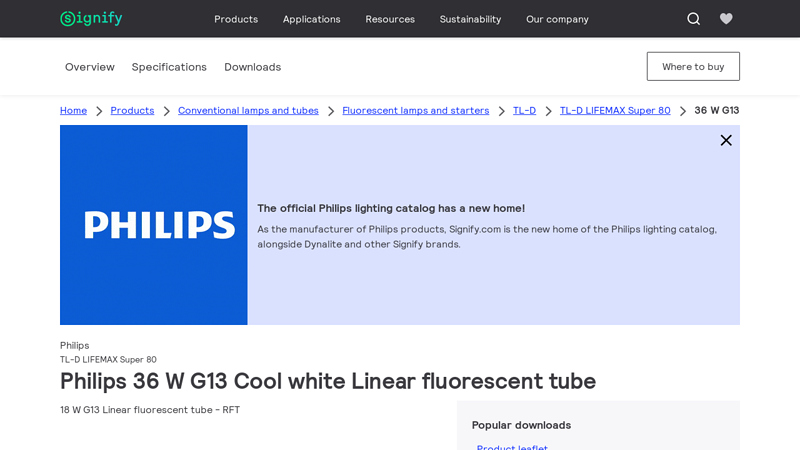
#2 Philips 36 W G13 Cool white Linear fluorescent tube
Domain Est. 1996
Website: signify.com
Key Highlights: Specifications · Cap-Base. G13 [Medium Bi-Pin Fluorescent] · Nominal lifetime. 15,000 hour(s) · Life to 50% Failures (Nom). 15,000 hour(s)….
#3 Renesas Electronics Corporation
Domain Est. 2002
Website: renesas.com
Key Highlights: A global leader in microcontrollers, analog, power and SoC products, Renesas delivers trusted embedded design innovation to shape a limitless future….
#4 Halco, ProLED®, T8 Linear Tube, 2 Foot, 8 Watt, G13 Base, Type A …
Domain Est. 2010
Website: ledlightingwholesaleinc.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free delivery over $999Halco, ProLED®, T8 Linear Tube, 2 Foot, 8 Watt, G13 Base, Type A **25 Pack Only**, Shop here to save on products like the T824FR8-850-DIR3-LED and …
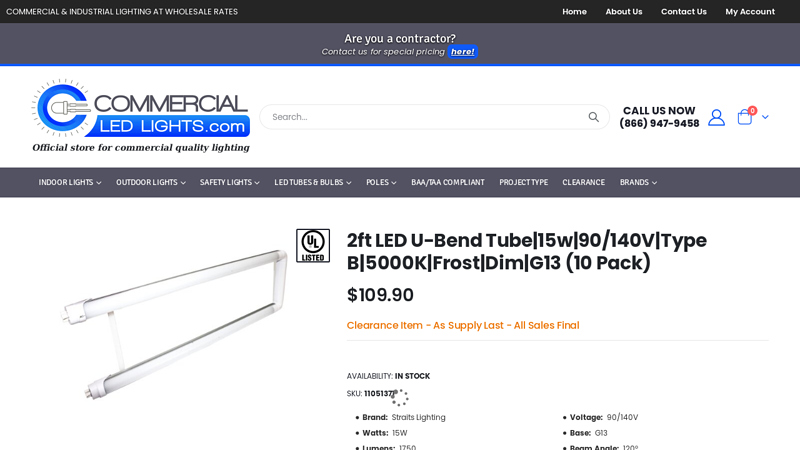
#5 2ft LED U-Bend Tube
Domain Est. 2018
Website: commercialledlights.com
Key Highlights: 6-day delivery 30-day returnsBrand:Straits Lighting · Watts:15W · Lumens:1750 · Kelvin:5000K · Voltage:90/140V · Base:G13 · Beam Angle:120° · Lens:Frosted….
#6 Bank of Lamps
Domain Est. 2020
Website: bankoflamps.com
Key Highlights: Europe-wide B2B wholesale portal for lighting, electrical and automation products. 1.5M items, 12000 SKUs in stock, €15M warehouse and individual B2B ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for G13 Base

H2 2026 Market Trends for G13 Base Lamps
The G13 base, primarily associated with linear fluorescent lamps (especially T8 and T12 tubes), is operating within a market undergoing significant transformation. While still widely present in existing installations, its future trajectory in H2 2026 is defined by continued decline, strategic niche retention, and the dominance of LED alternatives. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends:
-
Accelerated Decline in New Installations:
- Dominance of LED Retrofit & New Builds: By H2 2026, the shift to LED technology will be nearly complete for new commercial, industrial, and institutional lighting projects. LED tubes (with integrated drivers, often bypassing the ballast) and dedicated LED luminaires offer vastly superior energy efficiency (60-80%+ savings), longer lifespans (50,000+ hours vs. 10,000-30,000), lower maintenance costs, and better light quality. Building codes, energy regulations (like the EU’s Ecodesign), and corporate sustainability goals will heavily favor LEDs, leaving minimal room for new G13 fluorescent installations.
- Vanishing Supply Chain: Major lighting manufacturers will have largely ceased production of new fluorescent fixtures and ballasts. Supply of new G13 fluorescent lamps will be significantly constrained, potentially limited to a few niche suppliers or remaining stock, leading to potential price increases and availability issues.
-
Transition Focus on Retrofit & Maintenance:
- Retrofit Kits as Primary Demand Driver: The most significant market activity for G13 bases in H2 2026 will be the retrofit of existing fluorescent fixtures. Demand will center on LED tubes designed to fit G13 sockets. Key types include:
- Ballast-Bypass (Direct-Wire) LED Tubes: Require electrician installation but offer the highest efficiency and reliability (eliminating ballast failure points). This will likely be the dominant retrofit choice.
- Plug-and-Play (Ballast-Compatible) LED Tubes: Easier installation but dependent on the existing ballast’s condition and compatibility. Demand may wane as older ballasts fail and compatibility issues arise.
- Maintenance & Replacement Parts: Demand will persist for G13 base components (sockets, lampholders) and some fluorescent lamps to service the vast existing installed base, particularly in regions or applications where retrofit budgets are tight or delayed. However, this is a shrinking, maintenance-driven market.
- Retrofit Kits as Primary Demand Driver: The most significant market activity for G13 bases in H2 2026 will be the retrofit of existing fluorescent fixtures. Demand will center on LED tubes designed to fit G13 sockets. Key types include:
-
Niche Applications & Geographic Variations:
- Specific Industrial/Commercial Settings: Some specialized applications (e.g., certain horticultural lighting, industrial processes requiring specific spectral output, or very cold environments where early LED performance was questionable) might still see limited use, though LED solutions are rapidly encroaching here too.
- Developing Markets & Legacy Infrastructure: Regions with slower infrastructure upgrade cycles, less stringent energy regulations, or abundant existing stock may see a slower phase-out, maintaining some demand for G13 components and lamps longer than in North America, Europe, or parts of Asia.
- Specialty Fluorescent Lamps: Very specific fluorescent types (e.g., high-output, UV, germicidal) using G13 bases might persist in niche medical, scientific, or industrial applications where LED alternatives are not yet fully viable or cost-effective.
-
Supply Chain & Pricing Dynamics:
- Reduced Competition & Potential Price Volatility: With fewer manufacturers, competition for remaining G13 base components (sockets, new lamps) will decrease. This could lead to higher prices for these parts, especially as manufacturing scales down.
- Focus on Compatibility & Quality: Suppliers of LED retrofit tubes will emphasize certifications (UL, DLC), compatibility lists, lumen output, color rendering (CRI), and warranty length to differentiate in a crowded but mature retrofit market. Reliability and ease of installation (especially for ballast-bypass types) will be key selling points.
-
End-of-Life & Environmental Considerations:
- Increased Disposal Volume: H2 2026 will see a significant volume of fluorescent lamps being removed during retrofits. This will drive demand for proper fluorescent lamp recycling services due to mercury content, creating a parallel market.
- Sustainability Pressure: The environmental burden of mercury disposal will further incentivize the switch to mercury-free LED technology, reinforcing the market trend away from G13 fluorescents.
Conclusion:
By H2 2026, the G13 base market is firmly in a managed decline phase. Its primary relevance lies not in new fluorescent systems, but as a retrofit platform for LED technology. The market will be characterized by:
- Dominance of LED Retrofit Tubes: The vast majority of G13 socket activity will involve installing LED tubes, particularly ballast-bypass types.
- Shrinking Supply: Limited availability of new fluorescent lamps and fixtures, with rising costs for remaining components.
- Niche Survival: Persistence only in specific applications or regions with delayed upgrades.
- Focus on Maintenance & Replacement: Demand driven by servicing the existing, aging fluorescent infrastructure.
The G13 base itself will remain physically relevant as a socket type for years due to the sheer volume of existing fixtures, but its association with fluorescent technology will be increasingly historical. The future belongs entirely to LED solutions utilizing the existing G13 form factor as a bridge to modern lighting.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing G13 Base (Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns)
Sourcing G13 base materials—commonly used in lighting applications such as fluorescent lamps and some LED tubes—can present several challenges, particularly relating to product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply chains and legal compliance.
1. Inconsistent Quality Standards
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing G13 bases is variability in material quality. Suppliers, especially from regions with less stringent manufacturing oversight, may use substandard plastics or metals that degrade quickly under heat or electrical load. Poor-quality G13 bases can lead to flickering, poor electrical contact, or even safety hazards like short circuits. Without rigorous quality control checks or adherence to international standards (e.g., IEC, UL), buyers risk receiving non-compliant components.
2. Lack of Certification and Testing Documentation
Many suppliers fail to provide proper certifications (such as RoHS, REACH, or UL listing) for G13 base components. This absence makes it difficult to verify whether materials meet safety, environmental, and performance requirements. Relying on uncertified parts can expose manufacturers to product recalls, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
3. Counterfeit or Non-OEM Components
The market includes counterfeit or imitation G13 bases falsely labeled as meeting certain specifications or originating from reputable manufacturers. These knock-offs often mimic the appearance of high-quality bases but perform poorly over time. Without thorough vetting, buyers may inadvertently integrate unreliable parts into their products.
4. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
G13 base designs—especially those integrated into proprietary lighting systems—may be protected by patents or design rights. Sourcing generic or cloned versions from third-party manufacturers can lead to IP violations, particularly if the design incorporates patented features beyond the standard G13 specifications. Companies may face legal action if their products use bases that infringe on existing IP, even unintentionally.
5. Ambiguity in Design Specifications
While G13 refers to a standard base type (13mm pin spacing), variations in pin diameter, housing material, and thermal resistance can exist. Suppliers may interpret specifications loosely, leading to compatibility issues. Without clear technical documentation and sample validation, mismatches in fit, form, or function can disrupt production.
6. Unverified Supply Chain Transparency
Many suppliers subcontract production without disclosing the original manufacturer. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to trace the origin of components, assess manufacturing practices, or ensure compliance with ethical and legal standards. It also complicates root-cause analysis in case of quality failures.
7. Insufficient Due Diligence on Suppliers
Relying on low-cost suppliers without verifying their track record, production capabilities, or quality management systems increases the risk of receiving defective or non-compliant G13 bases. Skipping audits or sample testing can result in long-term supply issues and product reliability concerns.
To mitigate these pitfalls, businesses should implement robust supplier qualification processes, demand full compliance documentation, conduct regular quality audits, and consult legal experts when sourcing components with potential IP sensitivities.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for G13 Base
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and compliance requirements for operations at G13 Base. Adherence to these protocols ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and safety across all activities.
Scope and Applicability
This guide applies to all personnel, contractors, vendors, and third parties involved in logistics, transportation, storage, and supply chain operations at G13 Base. It covers inbound and outbound shipments, inventory management, customs documentation, and regulatory adherence.
Logistics Operations
Receiving and Inbound Shipments
All inbound goods must be scheduled in advance via the Base Logistics Portal. Deliveries without prior authorization will be refused. Upon arrival, shipments are inspected for damage and verified against the purchase order and packing list. All discrepancies must be reported within two hours of receipt.
Storage and Inventory Management
Materials must be stored in designated zones according to hazard classification and storage requirements. Temperature-sensitive items require monitoring and logging. Inventory counts are conducted monthly, with cycle counts performed weekly in high-turnover areas. All inventory movements must be recorded in the G13 Inventory Management System (G13-IMS).
Outbound Shipments and Dispatch
Outbound shipments require an approved shipping manifest and load-out authorization. Packaging must meet international shipping standards (e.g., ISTA, UN specifications for hazardous materials). Final verification includes weight checks, documentation review, and seal application for containerized freight.
Regulatory Compliance
Customs and Trade Regulations
All cross-border shipments must comply with local and international trade laws, including export controls (e.g., ITAR, EAR), sanctions screening, and accurate Harmonized System (HS) code classification. Required documentation includes commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and export declarations.
Hazardous Materials Handling
Transport and storage of hazardous materials must follow OSHA HAZCOM, GHS labeling standards, and local environmental regulations. Personnel handling hazardous goods must complete HAZMAT training annually. Spill response kits must be accessible in all storage areas.
Environmental and Safety Standards
Operations must comply with ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and OHSAS 45001 (Occupational Health & Safety). Waste disposal must follow EPA and local jurisdiction guidelines. All spills or safety incidents must be reported immediately through the G13 Incident Reporting System.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
All logistics and compliance documents must be retained for a minimum of seven years. Digital records must be stored in the secure G13 Document Archive with role-based access. Required documents include:
– Bill of Lading (BOL)
– Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS)
– Customs clearance records
– Training certifications
– Audit trails from G13-IMS
Training and Accountability
All personnel must complete G13 Base Logistics and Compliance Training upon onboarding and annually thereafter. Supervisors are responsible for ensuring team compliance. Non-compliance may result in operational suspension, disciplinary action, or termination, depending on severity.
Audits and Continuous Improvement
Internal audits are conducted quarterly to assess compliance with this guide. Findings are reported to the Logistics & Compliance Oversight Committee. Corrective action plans must be implemented within 30 days. Feedback from personnel is encouraged to improve logistics processes and compliance measures.
Contact Information
For logistics support or compliance inquiries, contact:
Logistics Coordinator: [email protected]
Compliance Officer: [email protected]
Emergency After-Hours Line: +1-555-LOG-G131 (564-4131)
Conclusion on Sourcing G13 LED Lamp Bases
Sourcing G13 bases, commonly used in linear fluorescent and LED tube lamps, requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, and supplier reliability. After evaluating multiple sourcing options—such as domestic suppliers, international manufacturers (particularly from Asia), and wholesale distributors—it is evident that each channel presents distinct advantages and challenges. While overseas suppliers often offer competitive pricing and large-scale production capabilities, they may involve longer lead times and quality control risks. Domestic or regional suppliers, though potentially more expensive, provide faster delivery, easier communication, and better compliance with regional safety and regulatory standards (e.g., UL, CE).
To ensure a reliable supply chain, it is recommended to:
- Diversify Suppliers: Mitigate risk by establishing relationships with multiple vendors, combining cost-effective international sources with responsive local partners.
- Conduct Rigorous Quality Audits: Implement strict quality assurance processes, including sample testing and factory audits, especially when sourcing from low-cost regions.
- Verify Compatibility and Certification: Ensure that G13 bases meet required electrical and safety standards for the target market, particularly when used in LED retrofit applications.
- Leverage Long-Term Agreements: Negotiate volume-based pricing and consistent supply terms with trusted manufacturers to enhance cost-efficiency and supply stability.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of G13 bases hinges on a well-balanced strategy that prioritizes quality, compliance, and supply chain resilience, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in end-use lighting applications.